Energy Efficiency Model and Mapping Algorithm of Block Cipher for Cipher Specific Programmable Logic Array
-
摘要: 密码专用可编程逻辑阵列(CSPLA)是一种数据流驱动的密码处理结构,该文针对不同规模的阵列结构和密码算法映射实现能效关系的问题,首先以CSPLA的特定硬件结构为基础,以分组密码的高能效实现为切入点,建立基于该结构的分组密码算法映射能效模型并分析影响能效的相关因素,然后进一步根据阵列结构上算法映射的基本过程提出映射算法,最后选取几种典型的分组密码算法分别在不同规模的阵列进行映射实验。结果表明越大的规模并不一定能够带来越高的能效,为取得映射的最佳能效,阵列的规模参数应当与具体的硬件资源限制和密码算法运算需求相匹配,CSPLA规模为4×4~4×6时映射取得最优能效,AES算法最优能效为33.68 Mbps/mW,对比其它密码处理结构,CSPLA具有较优的能效特性。
-
关键词:
- 密码专用可编程逻辑阵列 /
- 分组密码 /
- 能效 /
- 映射
Abstract: Cipher Specific Programmable Logic Array (CSPLA) is a data stream-driven cryptographic processing structure. The relations between cryptographic mapping energy efficiency and array structures of different scales is considered in this paper. First, based on the specific hardware structure of CSPLA and block ciphers, an energy efficiency model of block cipher algorithm mapping based on this structure is established and related factors affecting energy efficiency are analyzed. Then the basic process of algorithm mapping on the array structure is discussed and a mapping algorithm is proposed. Finally, several typical block cipher algorithms are selected to perform mapping experiments on arrays of different scales. The results show that larger scale CSPLA does not necessarily bring higher energy efficiency. When the CSPLA scale is about 4×4~4×6 which achieves the best energy efficiency. In order to obtain the best energy efficiency, the scale parameter of the array should match the specific hardware resource constraints and cryptographic algorithm parameters. The optimal energy efficiency of AES algorithm is 33.68 Mbps/mW. CSPLA has better energy efficiency characteristics compared with other cryptographic processing structures. -
表 1 分组密码的自循环单分组并行映射算法
输入:$A = \{ {\rm{FUN}},{\rm{CON}},{\rm{CTR}},{\rm{MEM}},{\rm{IO}}\} $, ${\rm{Block}} = \{ I,R,L\} $ 输出:${\rm{Map} } = \{ {\rm{Tex} }{ {\rm{t} }_{ {\rm{FUN} } } },{\rm{Tex} }{ {\rm{t} }_{ {\rm{CON} } } },{\rm{Tex} }{ {\rm{t} }_{ {\rm{CTR} } } },{\rm{Tex} }{ {\rm{t} }_{ {\rm{MEM} } } },{\rm{Tex} }{ {\rm{t} }_{ {\rm{IO} } } }\}$ (1) ${\rm{Block}} = \{ C,M\} \leftarrow {\rm{Block}} = \{ I,R,L\} $ (2) generate $C = (V,E)$ and $M = (V,E)$
(3) initial $a = \left\lfloor {\dfrac{{m \times n}}{{{N_{\max }}}}} \right\rfloor $(4) while $E(a \cdot C) \not\subset {\rm{IO}}$ and $E(a \cdot C) \not\subset {\rm{con\_ex}}$ do (5) $a = a - 1$ (6) end while (7) for each ${\rm{o}}{{\rm{p}}_i} \in {\rm{Block}}$ do (8) $Q = a$ (9) $\{ {({\rm{AG}},{\rm{LG}},{\rm{NF}},{\rm{BP}})_{i,j}}|i = 1,2, ··· ,m;j = 1,2, ··· ,n\} \leftarrow {\rm{o}}{{\rm{p}}_k}$, (10) update ${\rm{FUN}}$ and ${\rm{MEM}}$ (11) $\{ {({\rm{Con\_in}},{\rm{Con\_ex}})_{i,j}}|i = 1,2, ··· ,m;j = 1,2, ··· ,n\} \leftarrow $
$< {\rm{o}}{{\rm{p}}_{i - 1}},{\rm{o}}{{\rm{p}}_i} > $(12) update ${\rm{IO}}$ and ${\rm{CON}}$ (13) end for (14) ${\rm{FU}}{{\rm{N}}_C} \leftarrow {V_n}(C)$,${\rm{Con\_e}}{{\rm{x}}_C} \leftarrow {E_n}(C)$ (15) ${\rm{FU}}{{\rm{N}}_M} \leftarrow V(M)$,${\rm{Con\_e}}{{\rm{x}}_M} \leftarrow E(M)$ (16) generate ${\rm{CTR}}$ (17) return ${\rm{Map}}$ 表 2 典型分组密码算法映射参数
参数 映射分组数量 运算周期 时钟频率(MHz) 功耗(mW) 吞吐率(Mbps) 规模 4×2 4×4 4×6 4×8 4×2 4×4 4×6 4×8 4×2 4×4 4×6 4×8 4×2 4×4 4×6 4×8 4×2 4×4 4×6 4×8 AES 1 2 3 4 24 24 24 28 120 120 110 110 19 38 59 82 640 1280 1760 2011 SM4 1 3 5 7 72 78 86 96 110 110 110 100 19 36 57 78 207 515 819 933 DES 1 2 3 4 46 42 48 54 130 130 130 130 18 35 56 78 181 396 520 616 参数 映射分组数量 运算周期 时钟频率(MHz) 功耗(mW) 吞吐率(Mbps) 规模 8×2 8×4 8×6 8×8 8×2 8×4 8×6 8×8 8×2 8×4 8×6 8×8 8×2 8×4 8×6 8×8 8×2 8×4 8×6 8×8 AES 2 4 6 8 28 30 32 36 120 110 110 110 40 82 121 168 1097 1877 2640 3129 SM4 2 6 10 14 76 84 92 102 110 100 100 100 39 80 123 166 371 914 1391 1756 DES 2 4 6 8 60 46 54 58 130 1300 120 120 35 79 117 155 277 724 853 1059 表 3 AES算法相关参数对比
处理结构 工艺(nm) 换算工艺(nm) 性能(Mbps) 功耗(mW) 能效(Mbps/mW) 等价能效(Mbps/mW) CryptoManiac[11] 250 55 64 606 0.11 0.50 SophSEC[12] 130 55 654 325 2.01 4.76 文献[13] 180 55 1190 285 4.18 13.67 Cryptoraptor[14] 45 55 128000 6130 20.88 17.08 REMUS_LPP[15] 65 55 2840 103 27.57 32.59 本文(4×4) 55 55 1280 38 33.68 33.68 本文(4×8) 55 55 2011 82 24.52 24.52 本文(8×8) 55 55 3129 168 19.80 19.80 -
[1] LIU Leibo, WANG Bo, and WEI Shaojun. Reconfigurable Computing Cryptographic Processors[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Science, 2018: 5–8. [2] WANG Bo and LIU Leibo. Dynamically reconfigurable architecture for symmetric ciphers[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(4): 042403. doi: 10.1007/s11432-015-5381-z [3] ANSALONI G, TANIMURA K, POZZI L, et al. Integrated kernel partitioning and scheduling for coarse-grained reconfigurable arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2012, 31(12): 1803–1816. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2012.2209886 [4] 杨子煜, 严明, 王大伟, 等. 面向CGRA循环流水映射的数据并行优化[J]. 计算机学报, 2013, 36(6): 1280–1289. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2013.01280YANG Ziyu, YAN Ming, WANG Dawei, et al. Data parallelism optimization for the CGRA loop pipelining mapping[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2013, 36(6): 1280–1289. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2013.01280 [5] SHAO Shengjia, YIN Shouyi, LIU Leibo, et al. Map-reduce inspired loop parallelization on CGRA[C]. 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Melbourne, Australia, 2014: 1231–1234. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2014.6865364. [6] 戴紫彬, 曲彤洲. 基于预配置和配置重用的粗粒度动态可重构系统任务调度技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1458–1465. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180831DAI Zibin and QU Tongzhou. Task scheduling technology for coarse-grained dynamic reconfigurable system based on configuration prefetching and reuse[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1458–1465. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180831 [7] YIN Shouyi, LIU Dajiang, PENG Yu, et al. Improving nested loop pipelining on coarse-grained reconfigurable architectures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2016, 24(2): 507–520. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2015.2400219 [8] 孙康. 可重构计算相关技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 浙江大学, 2007.SUN Kang, Research on reconfigurable computing technologies[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2007. [9] WANG Yansheng, LIU Leibo, YIN Shouyi, et al. On-chip memory hierarchy in one coarse-grained reconfigurable architecture to compress memory space and to reduce reconfiguration time and data-reference time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2014, 22(5): 983–994. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2013.2263155 [10] 高嘉浩, 李伟, 陈韬. 基于密码逻辑阵列的分组密码高能效映射方法[J]. 电子技术应用, 2019, 45(11): 21–26, 31.GAO Jiahao, LI Wei, and CHEN Tao. Block cipher energy efficient mapping method based on cipher logic array[J]. Application of Electronic Technique, 2019, 45(11): 21–26, 31. [11] WU L, WEAVER C, and AUSTIN T. CryptoManiac: A fast flexible architecture for secure communication[C]. The 28th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Goteborg, Sweden, 2001: 110–119. doi: 10.1109/ISCA.2001.937439. [12] HUANG Wei, HAN Jun, WANG Shuai, et al. A low-complexity heterogeneous multi-core platform for security soc[C]. 2010 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, Beijing, China, 2010: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ASSCC.2010.5716621. [13] WEI Li, ZENG Xiaoyang, DAI Zibin, et al. A high energy-efficient reconfigurable VLIW symmetric cryptographic processor with loop buffer structure and chain processing mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2017, 26(6): 1161–1167. doi: 10.1049/cje.2017.06.010 [14] SAYILAR G and CHIOU D. Cryptoraptor: High throughput reconfigurable cryptographic processor[C]. 2014 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Jose, USA, 2014: 155–161. doi: 10.1109/ICCAD.2014.7001346. [15] LIU Leibo, WANG Dong, ZHU Min, et al. An energy-efficient coarse-grained reconfigurable processing unit for multiple-standard video decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(10): 1706–1720. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2015.2463735 [16] LIU Bin and BAAS B M. Parallel AES encryption engines for many-core processor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2013, 62(3): 536–547. doi: 10.1109/TC.2011.251 -





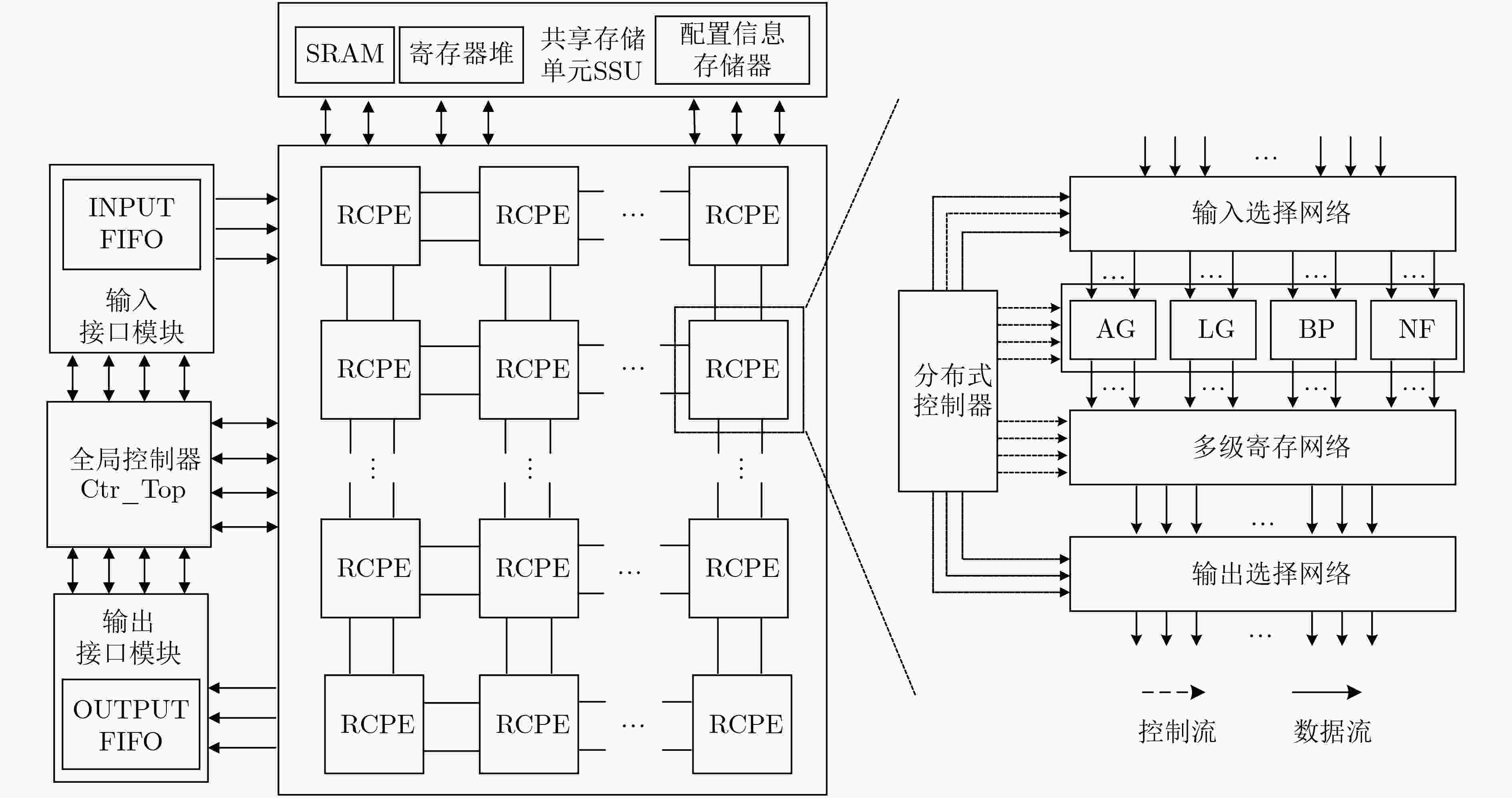
 下载:
下载:
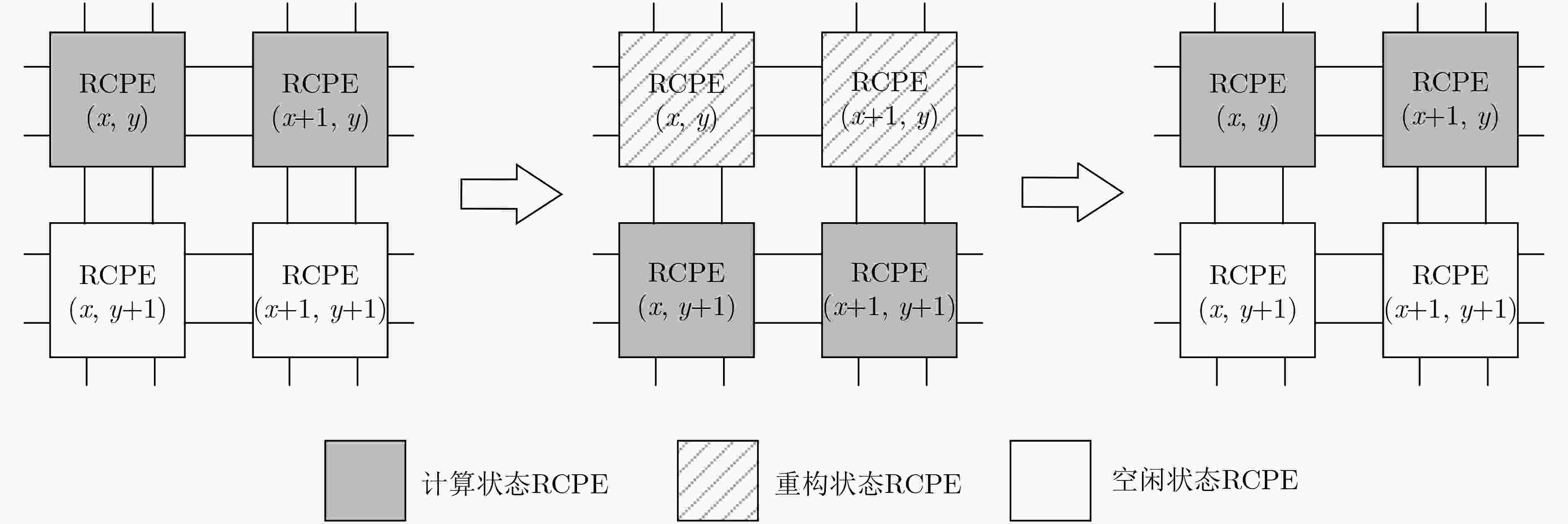
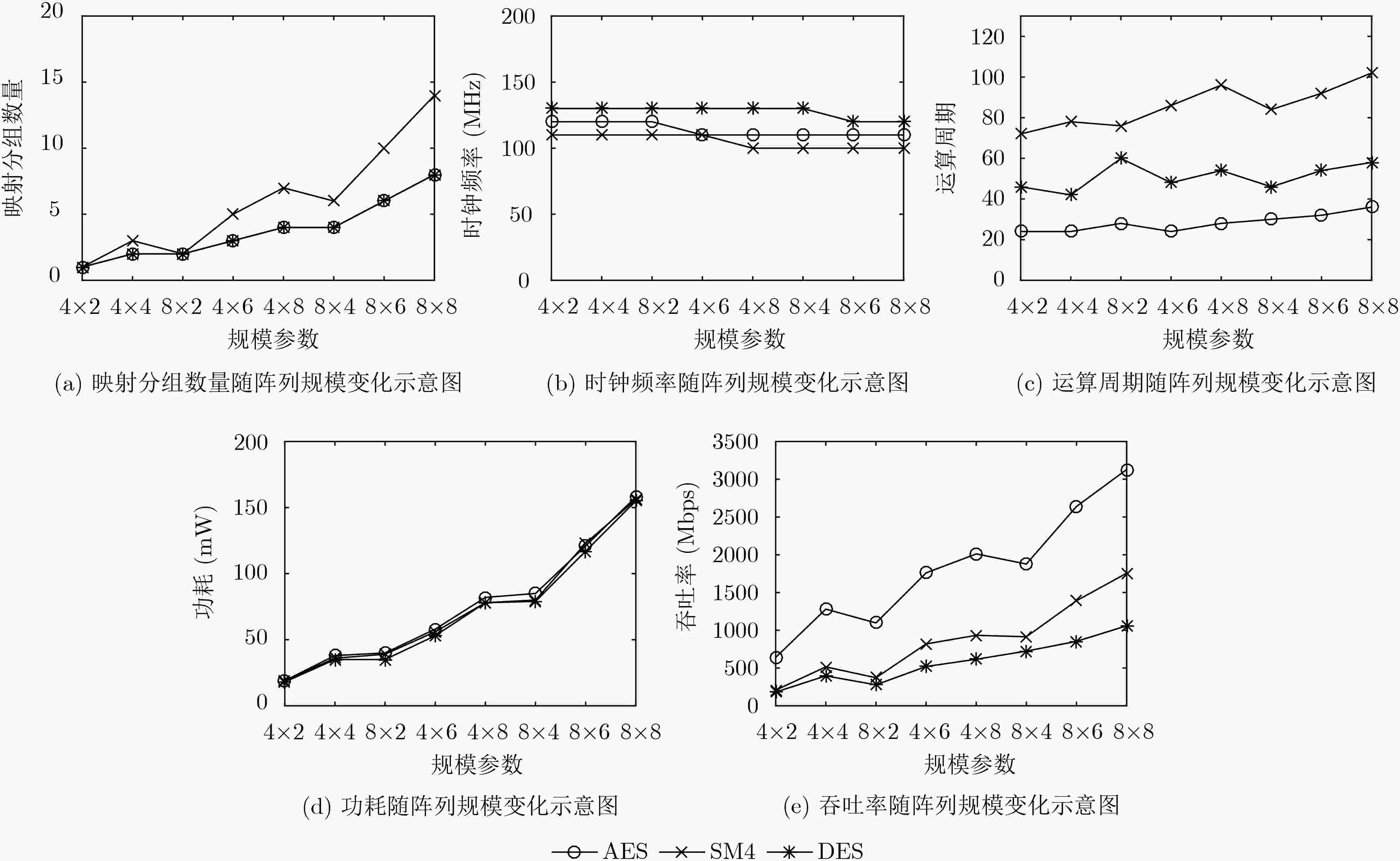
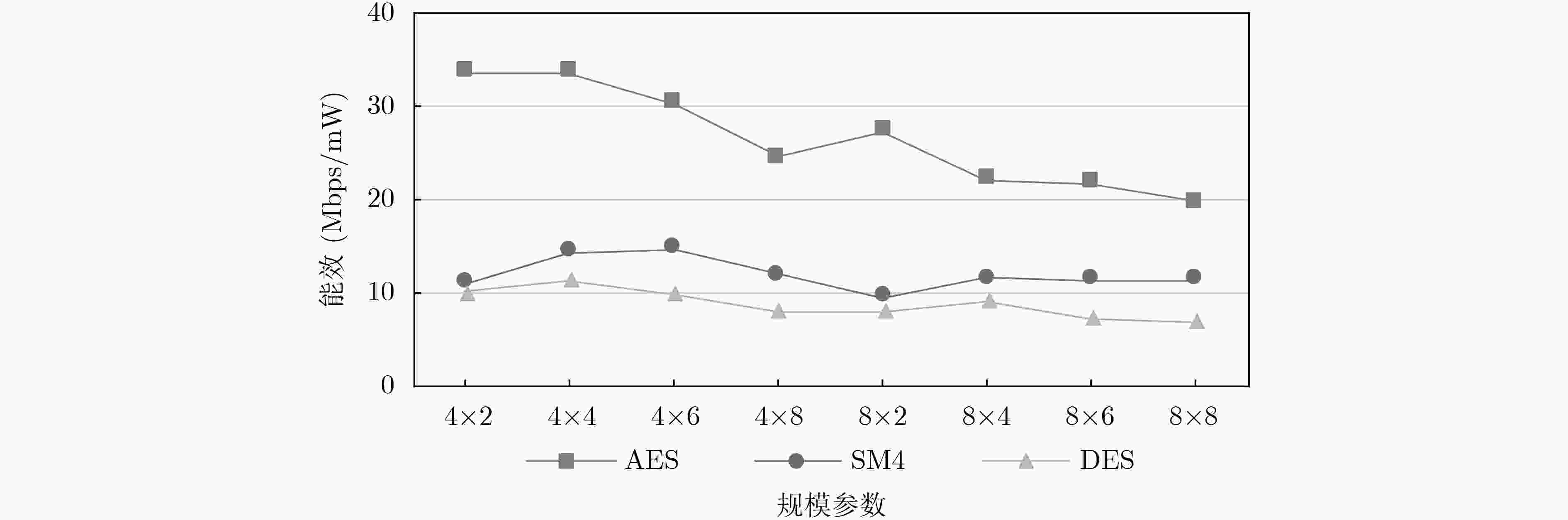


 下载:
下载:
