Deepfake Videos Detection Based on Image Segmentation with Deep Neural Networks
-
摘要:
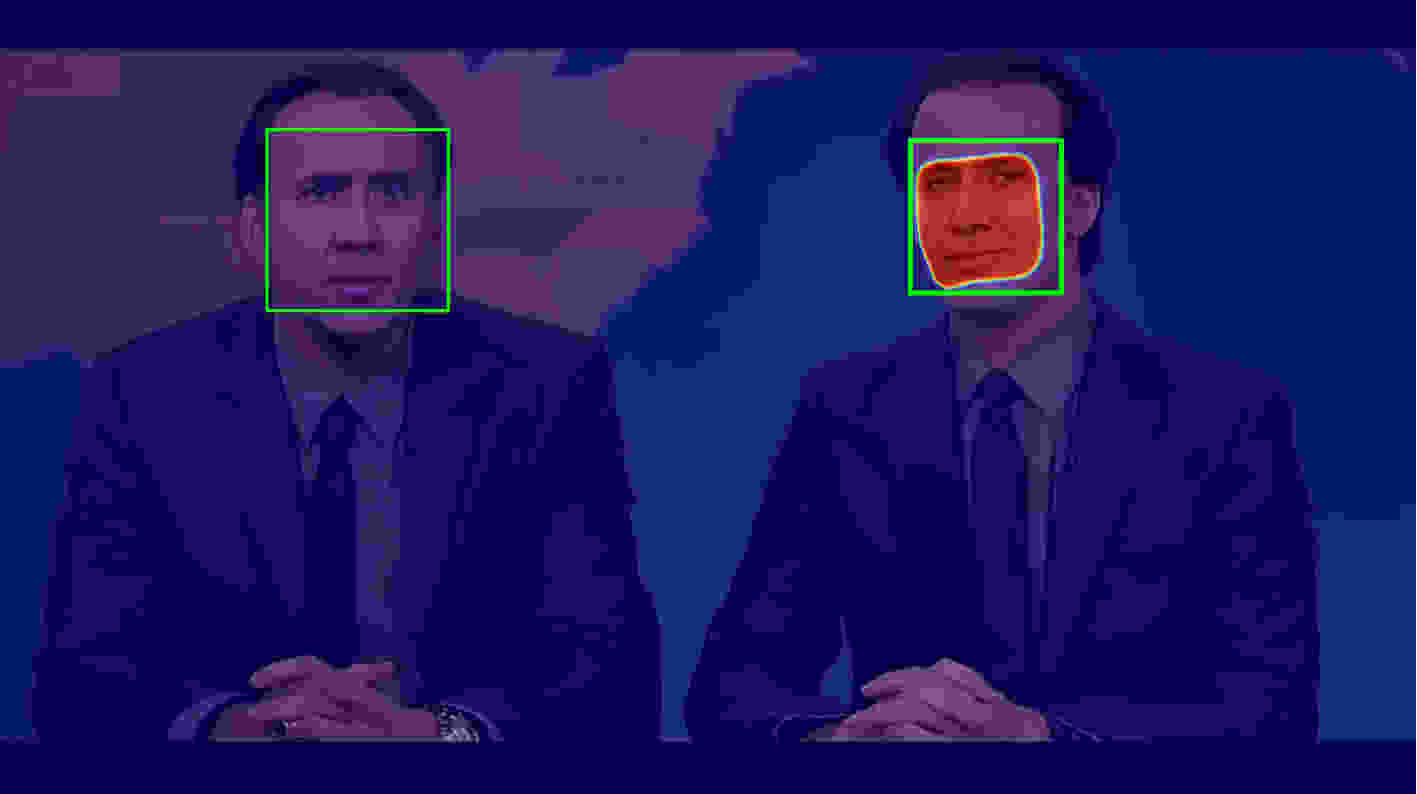
随着深度学习技术的快速发展,利用深度神经网络模型伪造出的深度假脸(deepfake)视频越来越逼真,假脸视频造成的威胁也越来越大。文献中已出现一些基于卷积神经网络的换脸视频检测算法,他们在库内获得较好的检测效果,但跨库检测性能急剧下降,存在泛化能力不足的问题。该文从假脸篡改的机制出发,将视频换脸视为特殊的拼接篡改问题,利用流行的神经分割网络首先预测篡改区域,得到预测掩膜概率图,去噪并二值化,然后根据换脸主要发生在人脸区域的前提,提出一种计算人脸交并比的新方法,并进一步根据换脸处理的先验知识改进人脸交并比的计算,将其作为篡改检测的分类准则。所提出方法分别在3个不同的基础分割网络上实现,并在TIMIT, FaceForensics++, FFW数据库上进行了实验,与文献中流行的同类方法相比,在保持库内检测的高准确率同时,跨库检测的平均错误率显著下降。在近期发布的合成质量较高的DFD数据库上也获得了很好的检测性能,充分证明了所提出方法的有效性和通用性。
Abstract:With the rapid development of deep learning technology, videos with changed faces generated by deep neural networks (i.e., Deepfake videos) become more and more indistinguishable. As a result, the threat raised by Deepfake videos becomes greater and greater. In literature, there are some convolutional neural networks-based detection algorithms for fake face videos. Although those algorithms perform well when the training set and the testing set are from the same dataset, their performance could deteriorate dramatically in cross-dataset scenario where the training and the testing sets are from different sources. Motivated by the fabrication course of fake face videos, this article attempts to solve the problem of fake faces detection with the way of image splicing detection. A neural network borrowed from image segmentation is adopted for predicting the tampered face area from which a tampering mask is obtained through denoising and thresholding the probability map. Using the prior knowledge of face tampering that the changing of face mainly happens in face region, a new way is proposed to determine the Face-Intersection over Union (Face-IoU) and to further improve the ratio calculation method. The Face-Intersection over Union with Penalty (Face-IoUP) is used as the classification criterion for deepfake video detection. The proposed method is impletmented using three basic image segmentation neural networks separately and is tested them on datasets of TIMIT, FaceForensics++, Fake Face in the Wild(FFW). Compared with current methods in literature, the HTER (Half Total Error Rate) in cross-dataset test decreases significantly while the detection accuracy in intra-dataset test keeps high. For the Deep Fake Detection(DFD) dataset with higher synthesis quality, the proposed method still performs very well. Experimental results validate the proposed method and demonstrate its good generality.
-
表 1 网络训练
输入:训练集数据$X$,验证集数据$Z$ 输出:训练好的分割网络模型${\rm{Model}}$、二值化阈值$T_1^*$和判决阈值
${\kern 1pt} T_2^*$(1) Begin(算法开始) (2) 初始化${\rm{Model}}$的权重 (3) 将$X$输入${\rm{Model}}$中进行训练,更新得到训练好的权重模型 (4) 将$Z$输入${\rm{Model}}$中,计算最小等错误率下的$T_1^*$和${\kern 1pt} T_2^*$ (5) End(算法结束) 表 2 样本测试
输入:测试样本视频$V$,训练好的分割网络模型${\rm{Model}}$、二值化
阈值$T_1^*$和判决阈值${\kern 1pt} T_2^*$输出:检测结果$Y$ (1) Begin(算法开始) (2) 对$V$分帧并定位裁剪出人脸区域,得到$I = \left\{ { {I_1},{I_2},···,{I_Q} } \right\}$。 (3) For q=1 to Q do: (4) 将${I_q}$输入${\rm{Model}}$,得到预测篡改区域掩膜${M_q}$ (5) 对${M_q}$滤波得到${\rm{M} }{ {\rm{F} }_{{q} } }$ (6) 根据$T_1^*$对${\rm{M}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{q}}}$二值化,得到${\rm{M} }{ {\rm{B} }_{{q} } }$ (7) 对${\rm{M} }{ {\rm{B} }_{{q} } }$计算${\rm{Face - IoU} }{ {\rm{P} }_{{q} } }$ (8) 根据${\kern 1pt} T_2^*$对${\rm{Face - IoU} }{ {\rm{P} }_{{q} } }$进行二分类判决,得到${y_q}$ (9) end For (10) End(算法结束) 表 3 检测模型在不同滤波器下的平均错误率(%)
$p$ =1网络 训练数据库
测试数据库
滤波器类型核大小 TIMIT FaceForensics++ TIMIT(库内) FaceForensics++(跨库) FFW(跨库) FaceForensics++(库内) TIMIT(跨库) FCN-8s 无 无 2.5 23.2 24.4 2.2 24.1 均值 3×3 2.6 23.4 23.0 2.1 24.8 5×5 2.5 23.2 22.9 2.3 25.2 中值 3×3 2.6 23.1 22.9 2.1 25.3 5×5 2.6 22.9 23.4 2.2 24.0 高斯 3×3 2.4 22.7 22.9 1.8 22.6 5×5 2.5 23.2 22.9 1.9 24.8 FCN-32s 无 无 5.8 27.2 20.8 1.9 29.2 均值 3×3 5.8 26.0 20.1 1.9 29.6 5×5 5.2 26.3 20.4 1.9 29.7 中值 3×3 5.9 27.4 20.7 1.9 30.4 5×5 5.6 27.0 20.3 1.8 29.7 高斯 3×3 5.7 26.8 20.5 1.8 27.5 5×5 6.0 27.0 20.7 1.7 30.4 表 4 检测模型在不同惩罚因子下的平均错误率(%)
训练数据库 TIMIT FaceForensics++ 测试数据库 TIMIT(库内) FaceForensics++(跨库) FFW(跨库) FaceForensics++(库内) TIMIT(跨库) 网络 惩罚因子 FCN-8s 0 2.5 23.6 23.3 1.9 24.3 0.5 2.5 23.1 23.5 1.8 24.5 1.0 2.4 22.7 22.9 1.8 22.6 1.5 2.5 22.7 23.1 1.9 23.7 FCN-32s 0 6.0 27.2 20.5 2.2 29.8 0.5 5.8 27.0 20.8 1.9 30.6 1.0 5.7 26.8 20.5 1.8 27.5 1.5 5.9 27.2 20.6 1.8 29.6 表 5 以TIMIT数据库训练模型所得到的测试结果(%)
测试数据库 TIMIT(库内) FaceForensics++(跨库) FFW(跨库) 网络 等错误率 平均错误率 准确率 平均错误率 平均错误率 MesoInception-4[10] 11.2 14.4 86.1 37.7 40.1 ShallowNetV1[11] 1.4 4.3 95.8 38.2 42.3 MISLnet[12] 5.4 5.2 94.8 30.3 41.0 ResNet-50[8,14] 0.8 2.5 97.6 44.9 45.7 Xception[9] 1.6 2.4 97.8 35.4 35.7 FCN-8s(本文算法) 4.0 2.4 97.7 22.7 22.9 FCN-32s(本文算法) 6.2 5.7 94.4 26.8 20.5 DeepLabv3(本文算法) 1.1 3.7 96.4 30.0 25.0 表 6 以FaceForensics++数据库训练模型所得到的测试结果(%)
表 7 通过DFD的C23数据库训练模型所得到的平均错误率(%)
测试数据库 DFD(C23)(库内) TIMIT(跨库) FaceForensics++(C0)(跨库) FaceForensics++(C23)(跨库) FFW(跨库) FCN-8s(本文算法) 1.7 15.9 14.2 16.9 21.5 FCN-32s(本文算法) 1.9 17.9 7.9 11.4 20.2 -
RÖSSLER A, COZZOLINO D, VERDOLIVA L, et al. FaceForensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2019.00009. KORSHUNOV P and MARCEL S. DeepFakes: A new threat to face recognition? Assessment and detection[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.08685, 2018. KHODABAKHSH A, RAMACHANDRA R, RAJA K, et al. Fake face detection methods: Can they be generalized?[C]. 2018 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group, Darmstadt, Germany, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.23919/BIOSIG.2018.8553251. YANG Xin, LI Yuezun, and LÜ Siwei. Exposing deep fakes using inconsistent head poses[C]. ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, England, 2019: 8261–8265. doi: 10.1109/icassp.2019.8683164. MATERN F, RIESS C, and STAMMINGER M. Exploiting visual artifacts to expose deepfakes and face manipulations[C]. 2019 IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Waikoloa Village, USA, 2019: 83–92. doi: 10.1109/WACVW.2019.00020. KORSHUNOV P and MARCEL S. Speaker inconsistency detection in tampered video[C]. The 26th European Signal Processing Conference, Rome, Italy, 2018: 2375–2379. doi: 10.23919/eusipco.2018.8553270. AGARWAL S, FARID H, GU Yuming, et al. Protecting world leaders against deep fakes[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, California, USA, 2019: 38–45. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1251–1258. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.195. AFCHAR D, NOZICK V, YAMAGISHI J, et al. MesoNet: A compact facial video forgery detection network[C]. 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Hong Kong, China, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/WIFS.2018.8630761. TARIQ S, LEE S, KIM H, et al. Detecting both machine and human created fake face images in the wild[C]. The 2nd International Workshop on Multimedia Privacy and Security, Toronto, Canada, 2018: 81–87. doi: 10.1145/3267357.3267367. BAYAR B and STAMM M C. Constrained convolutional neural networks: A new approach towards general purpose image manipulation detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(11): 2691–2706. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2825953 GÜERA D and DELP E J. Deepfake video detection using recurrent neural networks[C]. The 15th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, Auckland, New Zealand, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2018.8639163. WANG Shengyu, WANG O, ZHANG R, et al. CNN-generated images are surprisingly easy to spot... for now[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.11035, 2019. SHELHAMER E, LONG J, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640–651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05587, 2017. 毕秀丽, 魏杨, 肖斌, 等. 基于级联卷积神经网络的图像篡改检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2987–2994. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190043BI Xiuli, WEI Yang, XIAO Bin, et al. Image forgery detection algorithm based on cascaded convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2987–2994. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190043 LI Haodong, LI Bin, TAN Shunquan, et al. Detection of deep network generated images using disparities in color components[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.07276, 2018. NATARAJ L, MOHAMMED T M, MANJUNATH B S, et al. Detecting GAN generated fake images using co-occurrence matrices[J]. Electronic Imaging, 2019(5): 532-1–532-7. doi: 10.2352/ISSN.2470-1173.2019.5.MWSF-532 杨宏宇, 王峰岩. 基于深度卷积神经网络的气象雷达噪声图像语义分割方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2373–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190098YANG Hongyu and WANG Fengyan. Meteorological radar noise image semantic segmentation method based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2373–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190098 高逸飞, 胡永健, 余泽琼, 等. 5种流行假脸视频检测网络性能分析和比较[J]. 应用科学学报, 2019, 37(5): 590–608. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0255-8297.2019.05.002GAO Yifei, HU Yongjian, YU Zeqiong, et al. Evaluation and comparison of five popular fake face detection networks[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2019, 37(5): 590–608. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0255-8297.2019.05.002 -





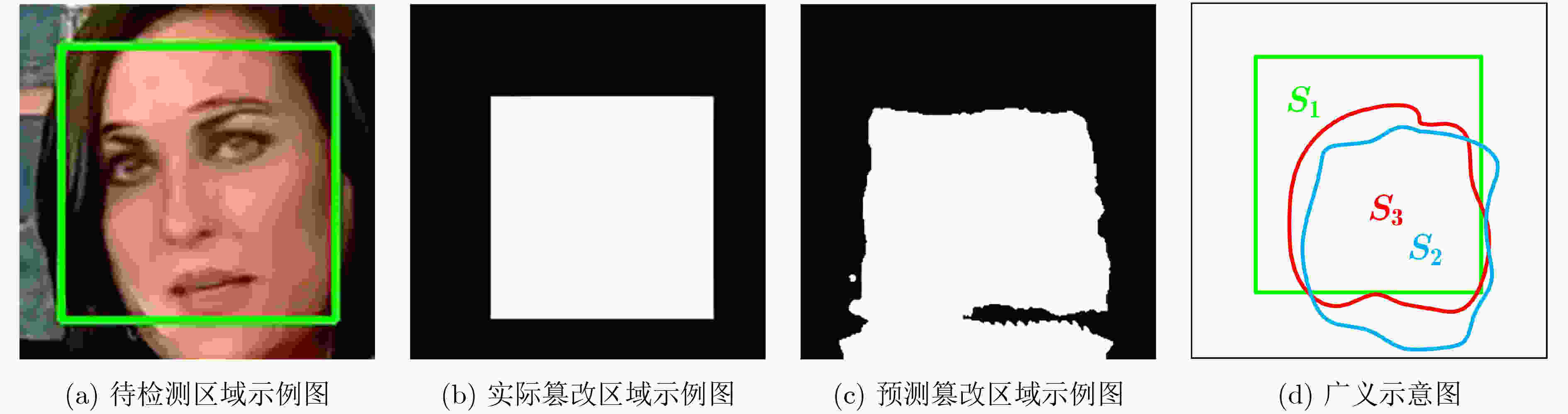
 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
