Fault Diagnosis Algorithm of Service Function Chain Based on Deep Dynamic Bayesian Network
-
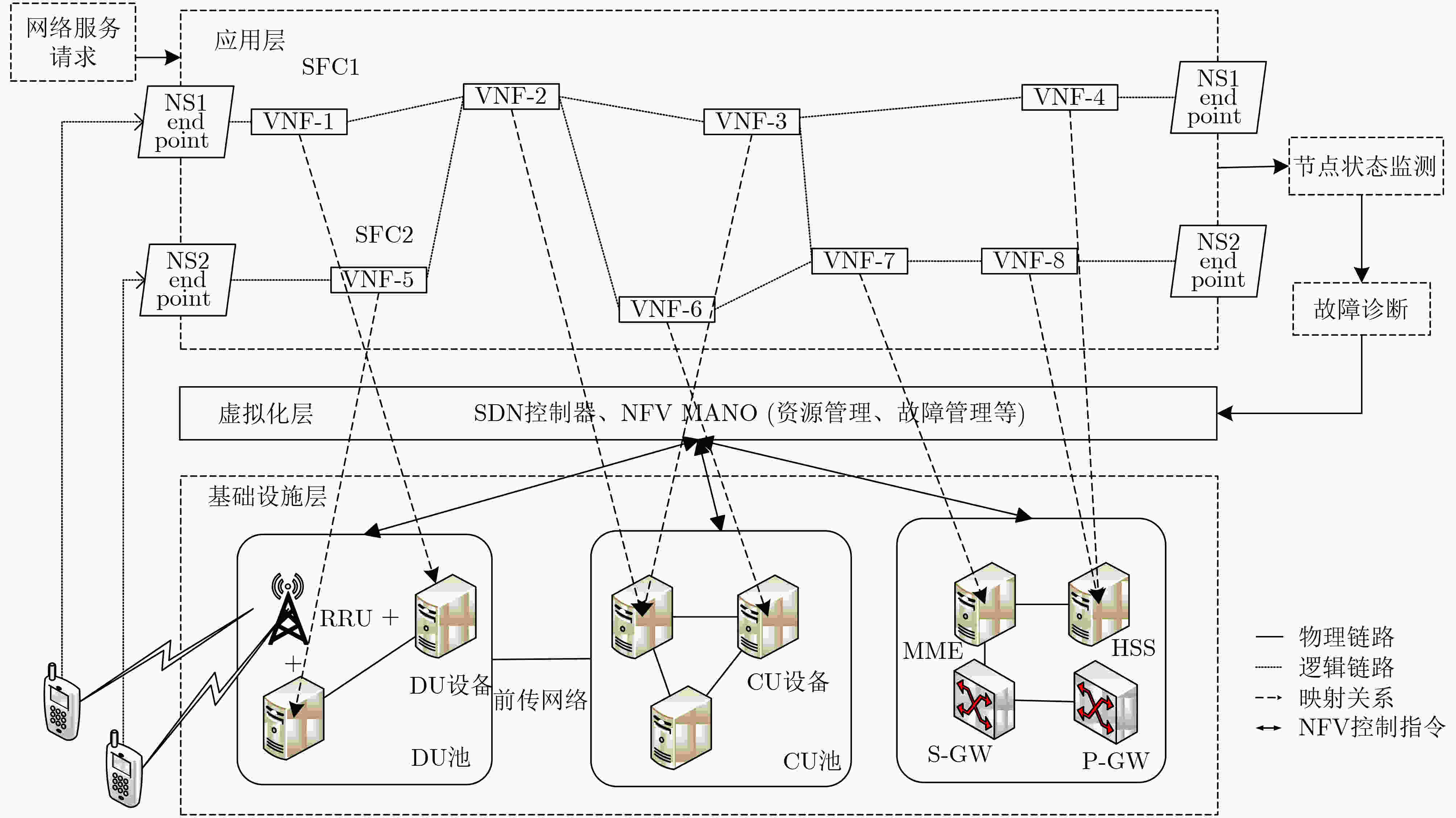
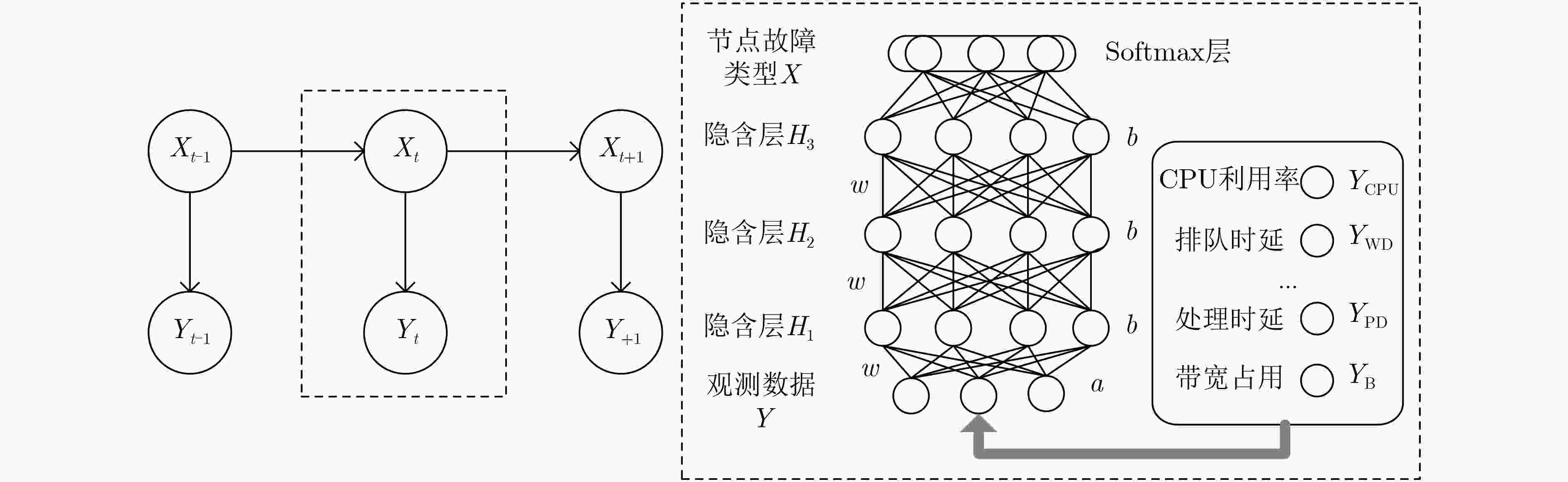
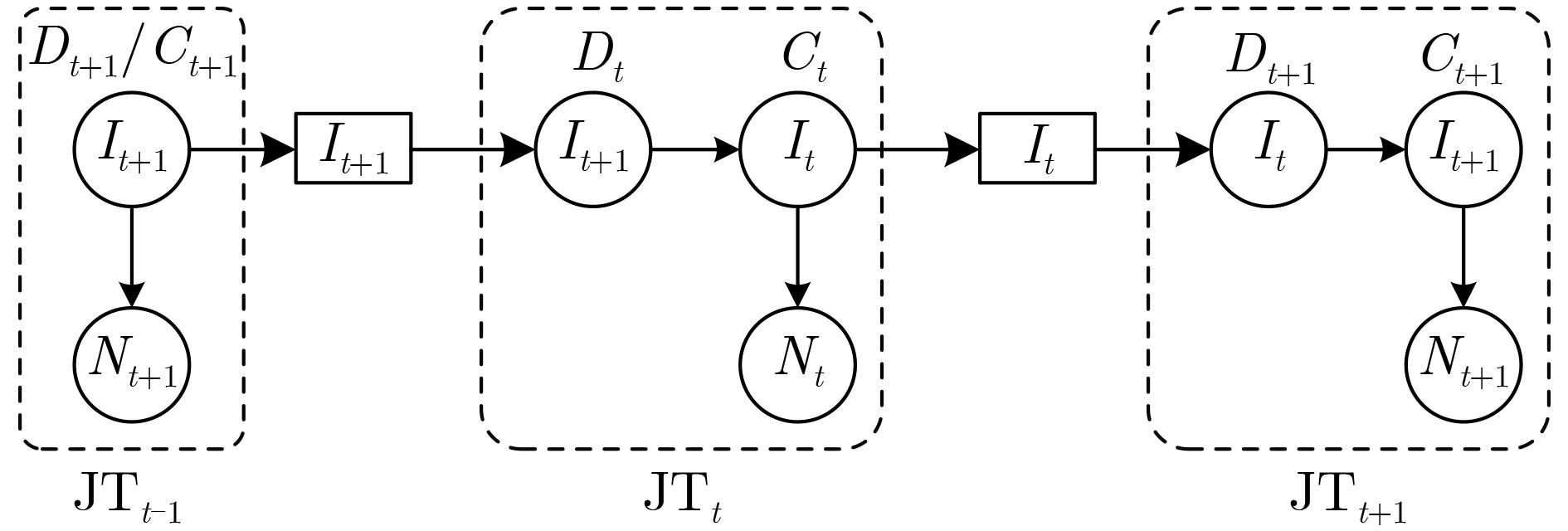
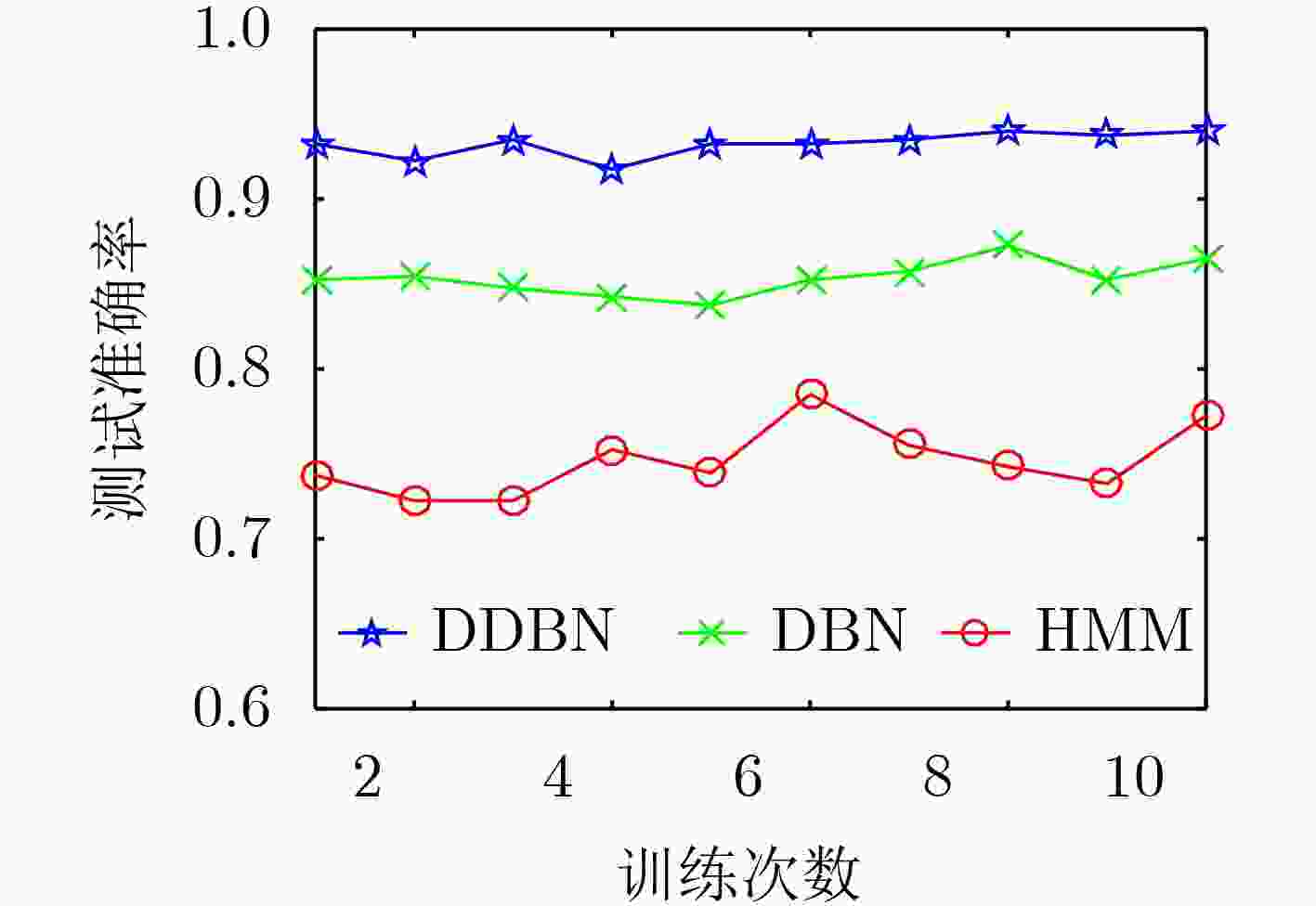
摘要: 针对5G端到端网络切片场景下底层物理节点出现故障会导致运行在其上的多条服务功能链出现性能异常的问题,该文提出一种基于深度动态贝叶斯网络(DDBN)的服务功能链故障诊断算法。首先根据网络虚拟化环境下故障的多层传播关系,构建故障与症状的依赖图模型,并采用在物理节点监测其上多个虚拟网络功能相关性能数据的方式收集症状。其次,考虑到基于软件定义网络(SDN)和网络功能虚拟化(NFV)的架构下网络症状观测数据的多样性以及物理节点和虚拟网络功能的空间相关性,引入深度信念网络对观测数据特征进行提取,使用加入动量项的自适应学习率算法对模型进行微调以加快收敛速度。最后,利用故障传播的时间相关性,引入动态贝叶斯网络对故障根源进行实时诊断。仿真结果表明,该算法能够有效地诊断故障根源且具有良好的诊断准确度。Abstract: To solve the problem of the abnormal performance of multiple service function chains caused by the failure of the underlying physical node under the 5G end-to-end network slicing scenario, a service function chain fault diagnosis algorithm based on Deep Dynamic Bayesian Network (DDBN) is proposed in this paper. This algorithm builds a dependency relationship between faults and symptoms based on a multi-layer propagation model of faults in a network virtualization environment. This algorithm first builds a dependency graph model of faults and symptoms based on the multi-layer propagation relationship of faults in a network virtualization environment, and collects symptoms by monitoring performance data of multiple virtual network functions on physical nodes. Then, considering the diversity of network symptom observation data based on Software Defined Network (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) architecture and the spatial correlation between physical nodes and virtual network functions, a deep belief network is introduced to extract the characteristics of the observation data, and the adaptive learning rate algorithm with momentum is used to fine-tune the model to accelerate the convergence speed. Finally, dynamic Bayesian network is introduced to diagnose the root cause of faults in real time by using the temporal correlation between faults. The simulation results show that the algorithm can effectively diagnose the root cause of faults and has good diagnostic accuracy.
-
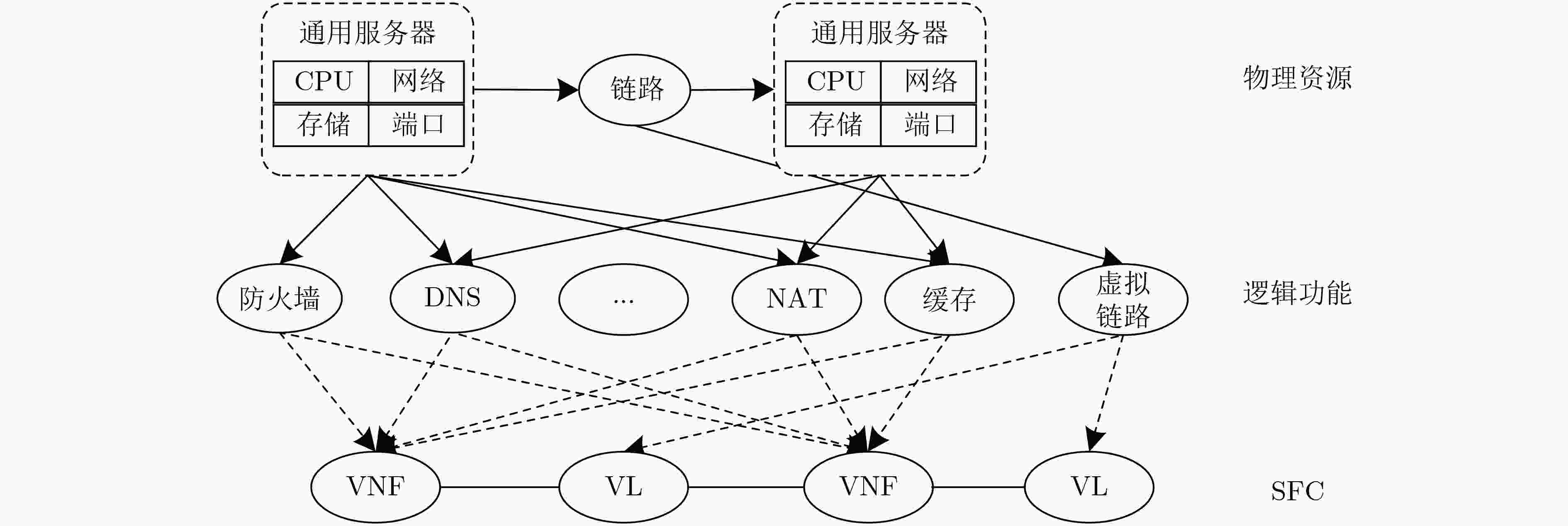
表 1 各层包含的资源类型
子层 对应资源、功能及服务 基础设施层 物理层 CPU、内存、网络、存储、带宽、端口、链路 逻辑层 Web代理、防火墙、负载平衡器、虚拟移动核心网络功能、DNS、缓存、虚拟链路 应用层 VNF、虚拟链路 表 2 故障类型和样本长度
故障类型 单组样本长度 样本组数 类别标记 类别编号 正常 60 400 [10000] 1 应用程序异常 60 400 [01000] 2 路由错误 60 400 [00100] 3 CPU故障 60 400 [00010] 4 端口节点故障 60 400 [00001] 5 样本总数 - 2000 - - 表 3 网络参数设置
仿真参数 参数设置 仿真参数 参数设置 物理节点数 10个 物理链路带宽资源 U[80, 100] Mbps SFC条数 6条 通用服务器处理速度 100 MB/s 每条SFC包含的VNF数 4~6个 VNF占用计算资源 U[10, 20] units 通用服务器计算资源 U[80, 100] units 虚拟链路带宽资源 U[10, 20] units -
[1] AHMAD I, KUMAR T, LIYANAGE M, et al. Overview of 5G security challenges and solutions[J]. IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, 2018, 2(1): 36–43. doi: 10.1109/MCOMSTD.2018.1700063 [2] AFOLABI I, TALEB T, FRANGOUDIS P A, et al. Network slicing-based customization of 5G mobile services[J]. IEEE Network, 2019, 33(5): 134–141. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1800072 [3] TALEB T, AFOLABI I, SAMDANIS K, et al. On multi-domain network slicing orchestration architecture and federated resource control[J]. IEEE Network, 2019, 33(5): 242–252. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1800267 [4] 陈前斌, 杨友超, 周钰, 等. 基于随机学习的接入网服务功能链部署算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 417–423. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180310CHEN Qianbin, YANG Youchao, ZHOU Yu, et al. Deployment algorithm of service function chain of access network based on stochastic learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 417–423. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180310 [5] WEN Ruihan, FENG Gang, TANG Jianhua, et al. On robustness of network slicing for next-generation mobile networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(1): 430–444. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2868652 [6] OI A, ENDOU D, MORIYA T, et al. Method for estimating locations of service problem causes in service function chaining[C]. 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2015.7416993. [7] ZHANG Shilei, WANG Ying, LI Wenjing, et al. Service failure diagnosis in service function chain[C]. The 19th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Seoul, Korea (South), 2017: 70–75. doi: 10.1109/APNOMS.2017.8094181. [8] SÁNCHEZ J M, YAHIA I G B, and CRESPI N. Self-modeling based diagnosis of services over programmable networks[C]. 2016 IEEE NetSoft Conference and Workshops (NetSoft), Seoul, Korea (South), 2016: 277–285. doi: 10.1109/NETSOFT.2016.7502423. [9] CHENG Lu, QIU Xuesong, MENG Luoming, et al. Probabilistic fault diagnosis for IT services in noisy and dynamic environments[C]. 2009 IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management, New York, USA, 2009: 149–156. doi: 10.1109/INM.2009.5188804. [10] SRINIVASAN S M, TRUONG-HUU T, and GURUSAMY M. TE-Based machine learning techniques for link fault localization in complex networks[C]. The IEEE 6th International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud (FiCloud), Barcelona, Spain, 2018: 25–32. doi: 10.1109/FiCloud.2018.00012. [11] ZHANG Lei, ZHU Xiaorong, ZHAO Su, et al. A novel virtual network fault diagnosis method based on long short-term memory neural networks[C]. The IEEE 86th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Toronto, Canada, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTCFall.2017.8288236. [12] ORDONEZ-LUCENA J, AMEIGEIRAS P, LOPEZ D, et al. Network slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, architectures, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(5): 80–87. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600935 [13] ZHANG Haibing, ZHANG Qian, LIU Jiajia, et al. Fault detection and repairing for intelligent connected vehicles based on dynamic Bayesian network model[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(4): 2431–2440. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2844287 [14] ZHANG Nan, LIU Yafeng, FARMANBAR H, et al. Network slicing for service-oriented networks under resource constraints[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(11): 2512–2521. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2760147 [15] 文成林, 吕菲亚. 基于深度学习的故障诊断方法综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 234–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190715WEN Chenglin and LÜ Feiya. Review on deep learning based fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 234–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190715 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
