Robust Nonnegative Least Mean Square Algorithm Based on Sigmoid Framework
-
摘要:
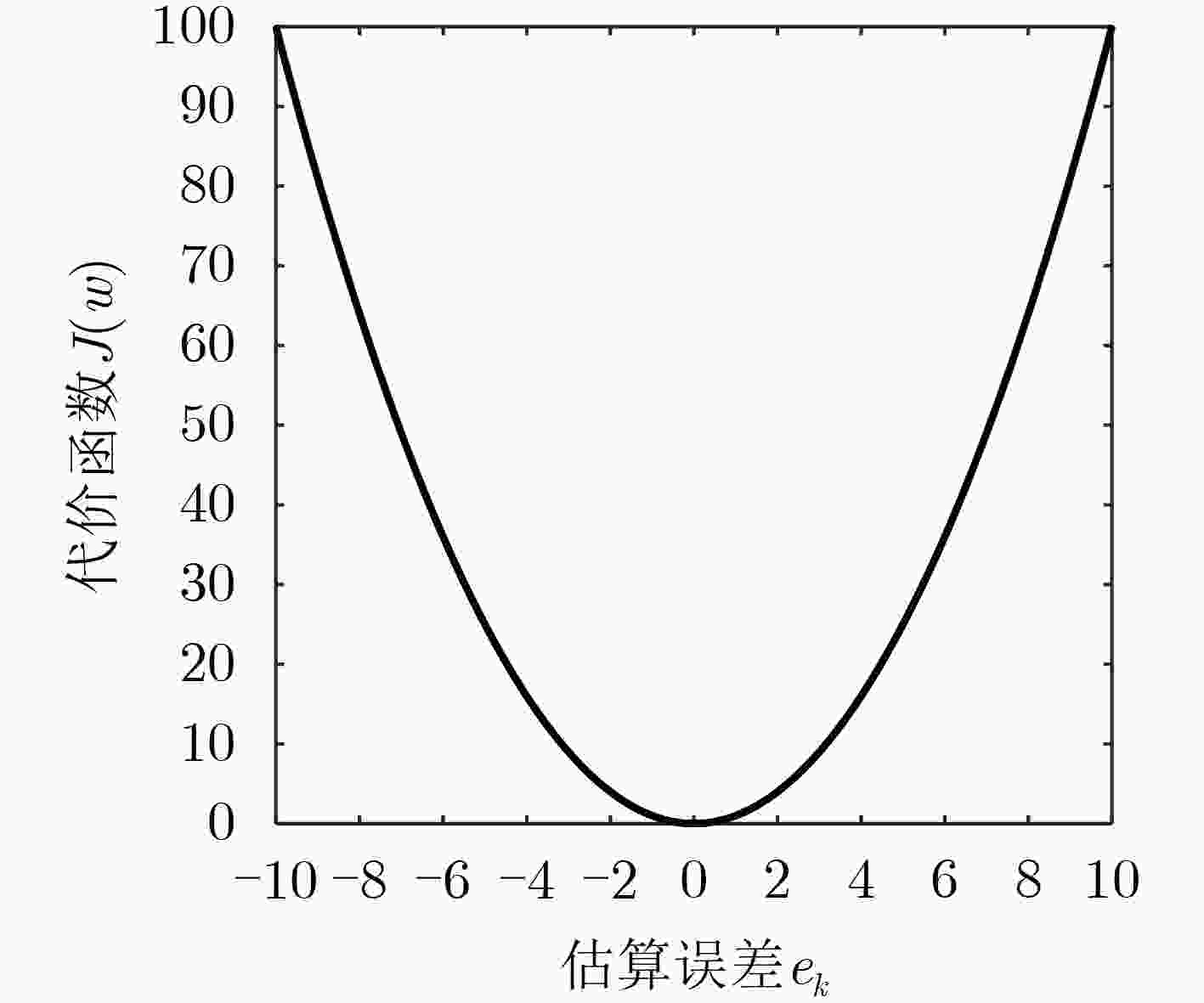
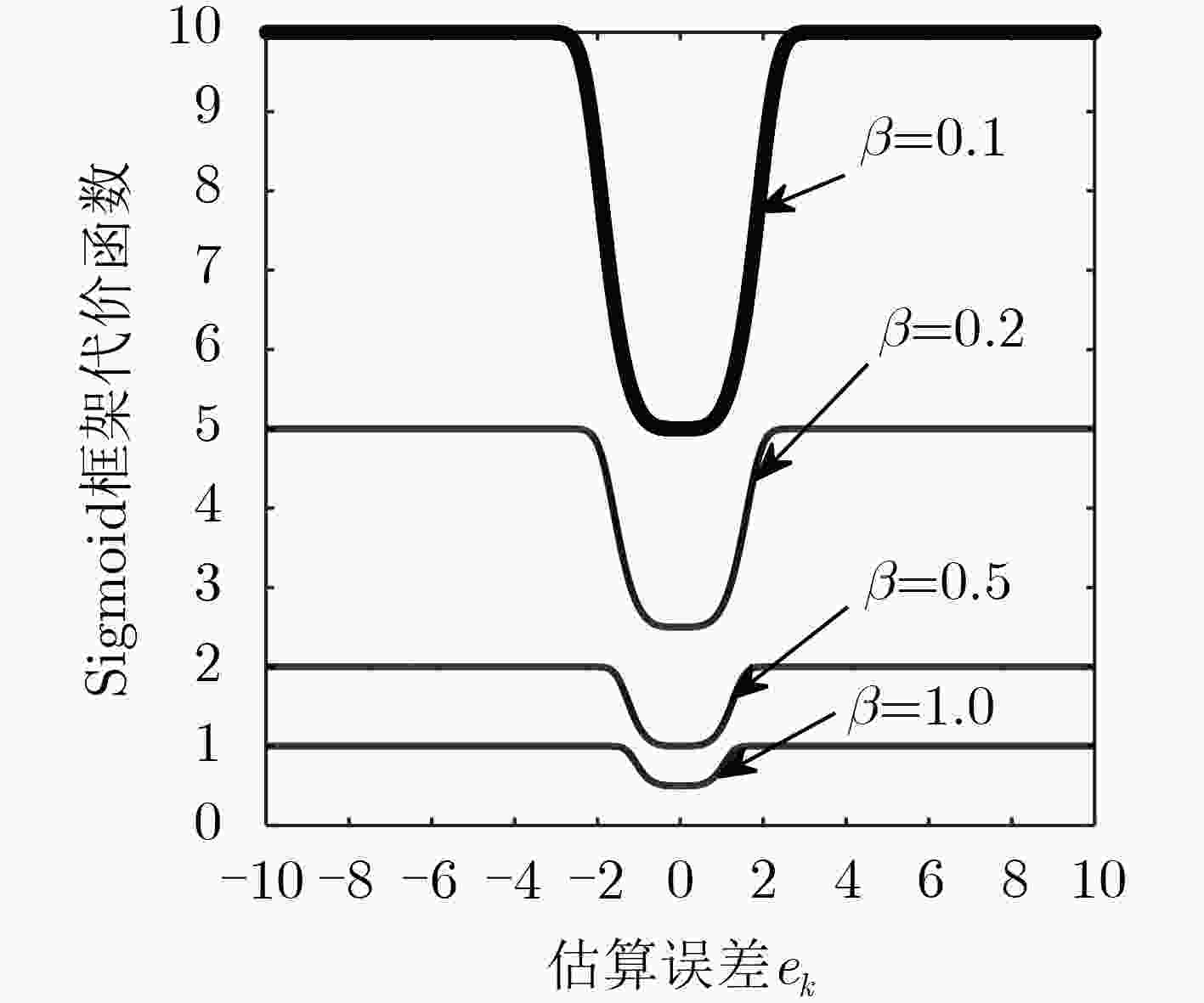
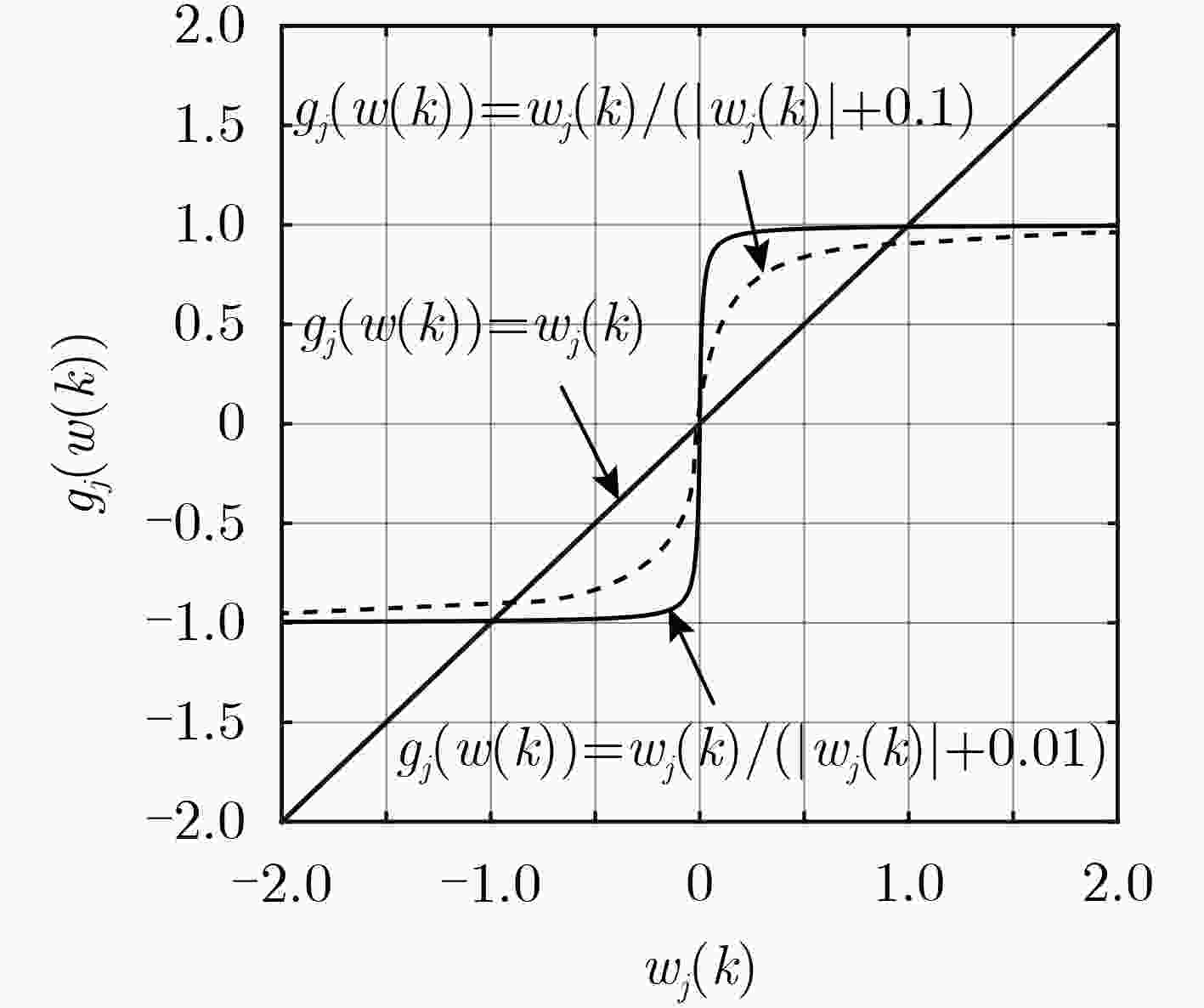
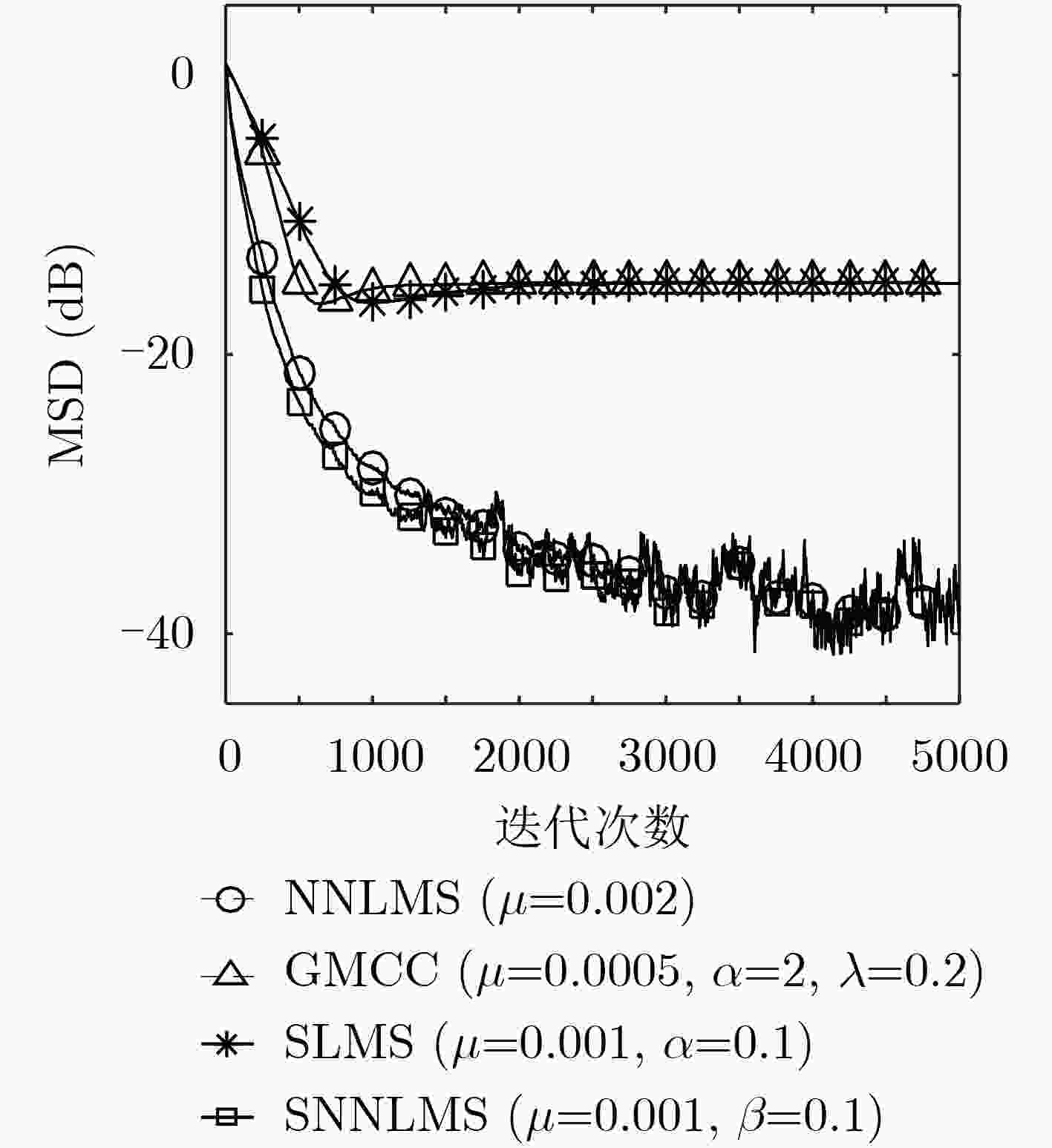
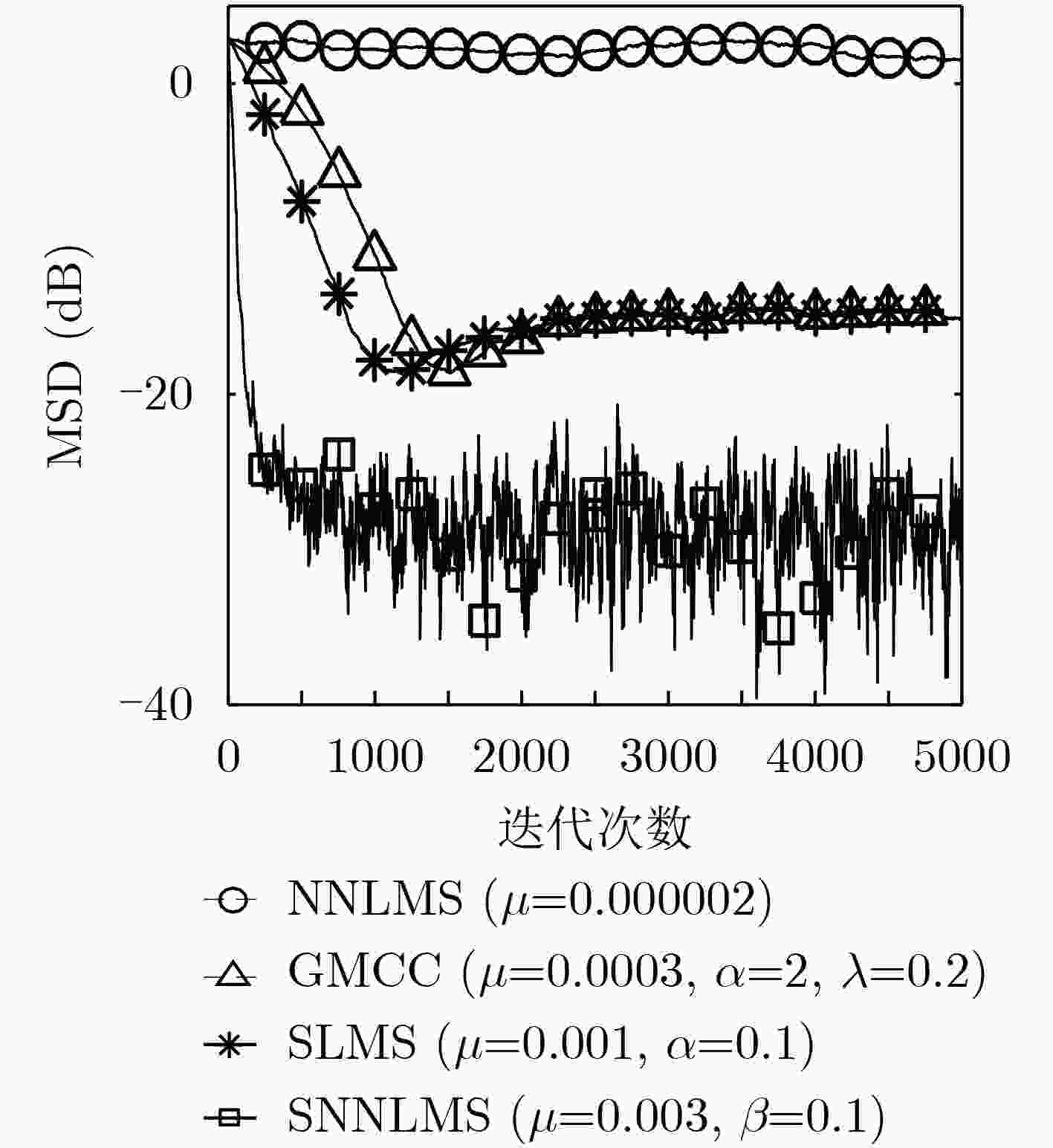
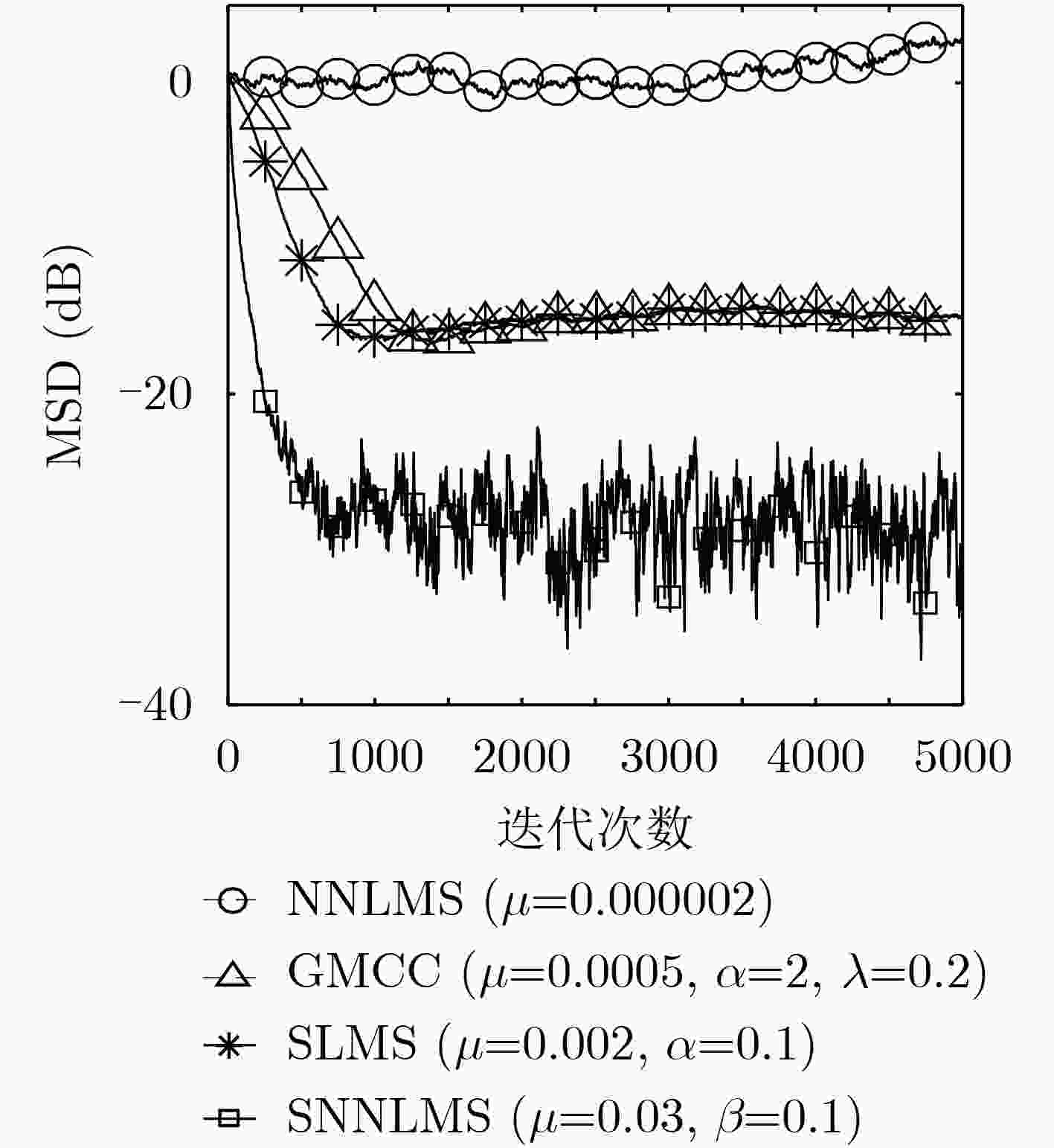
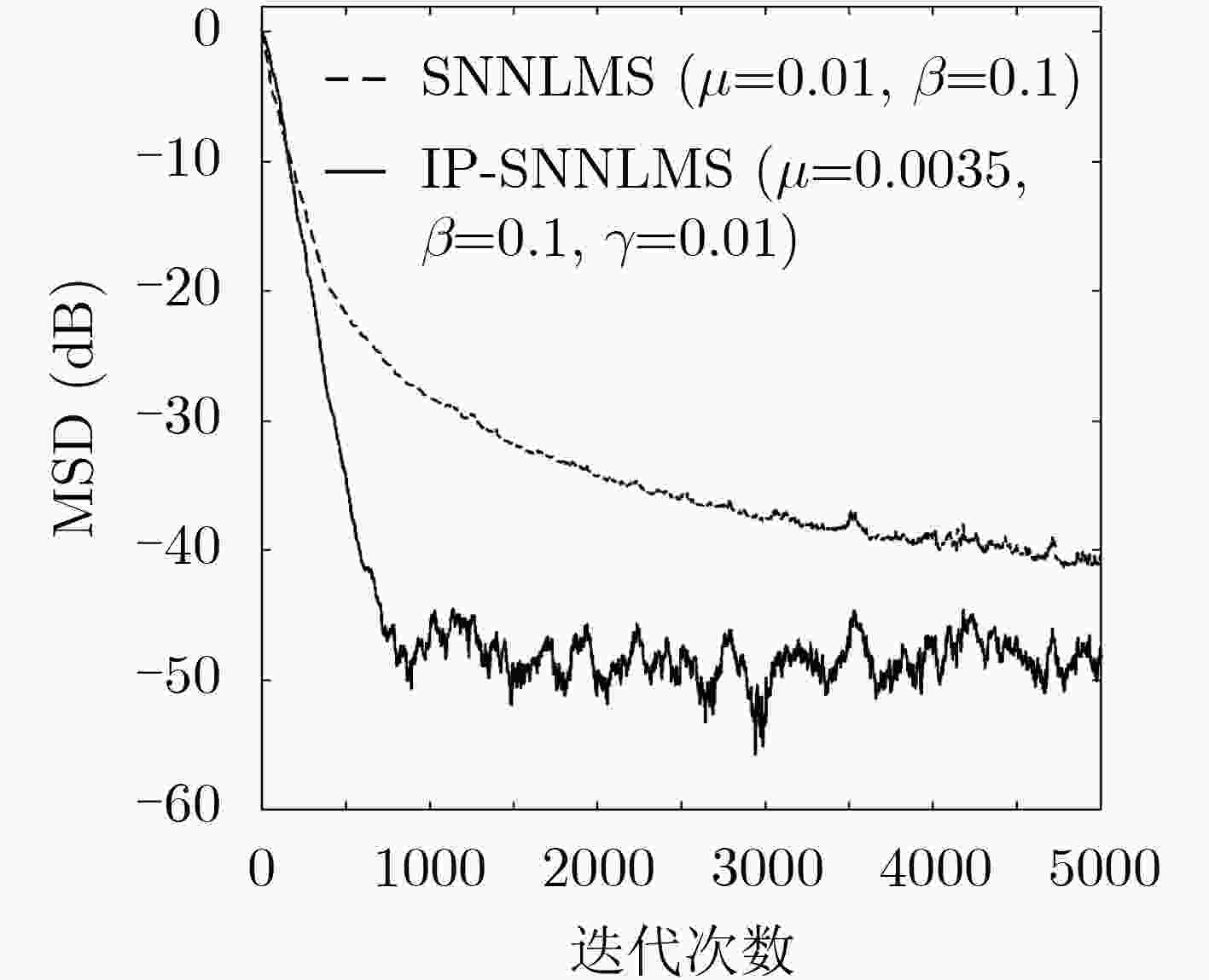
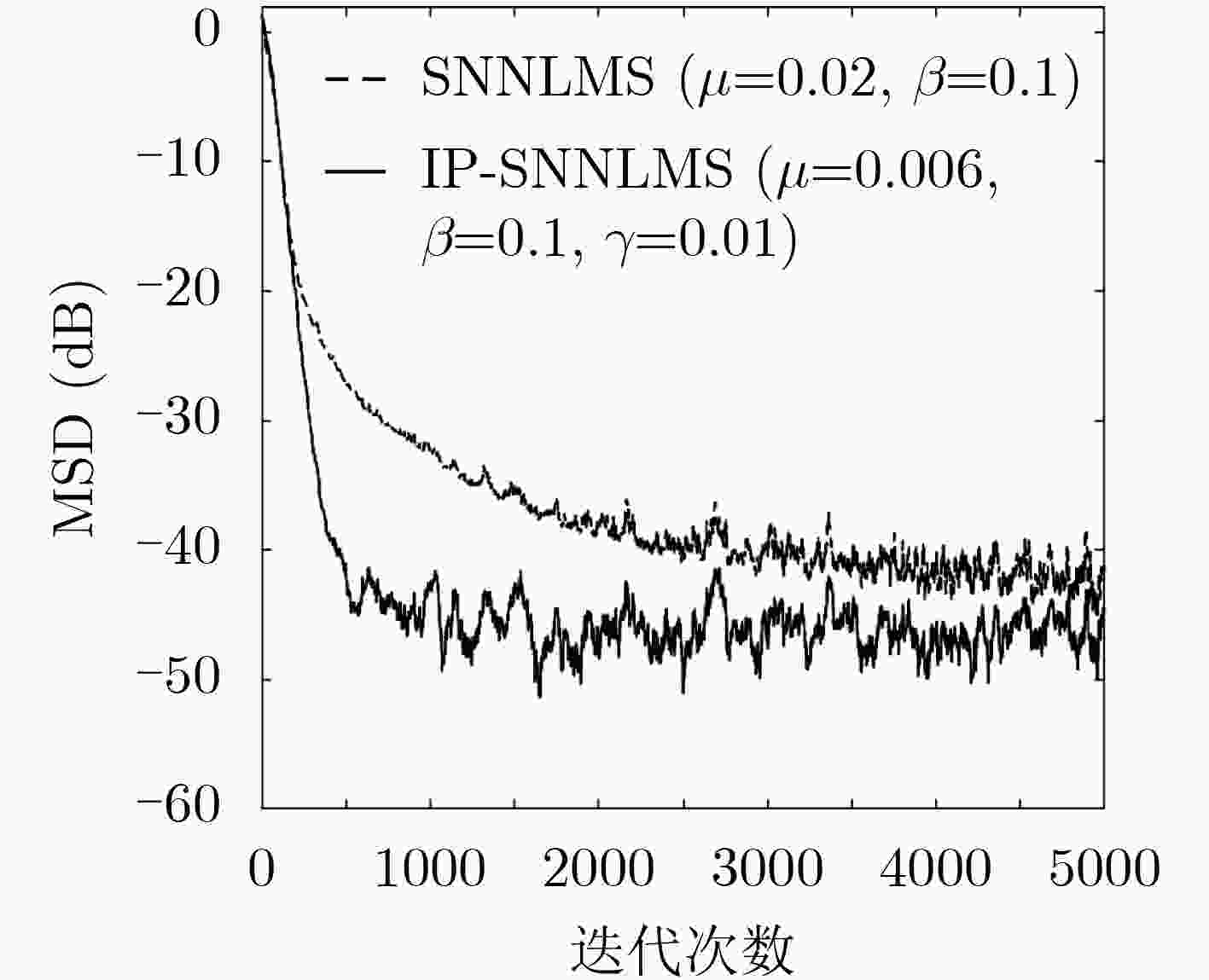
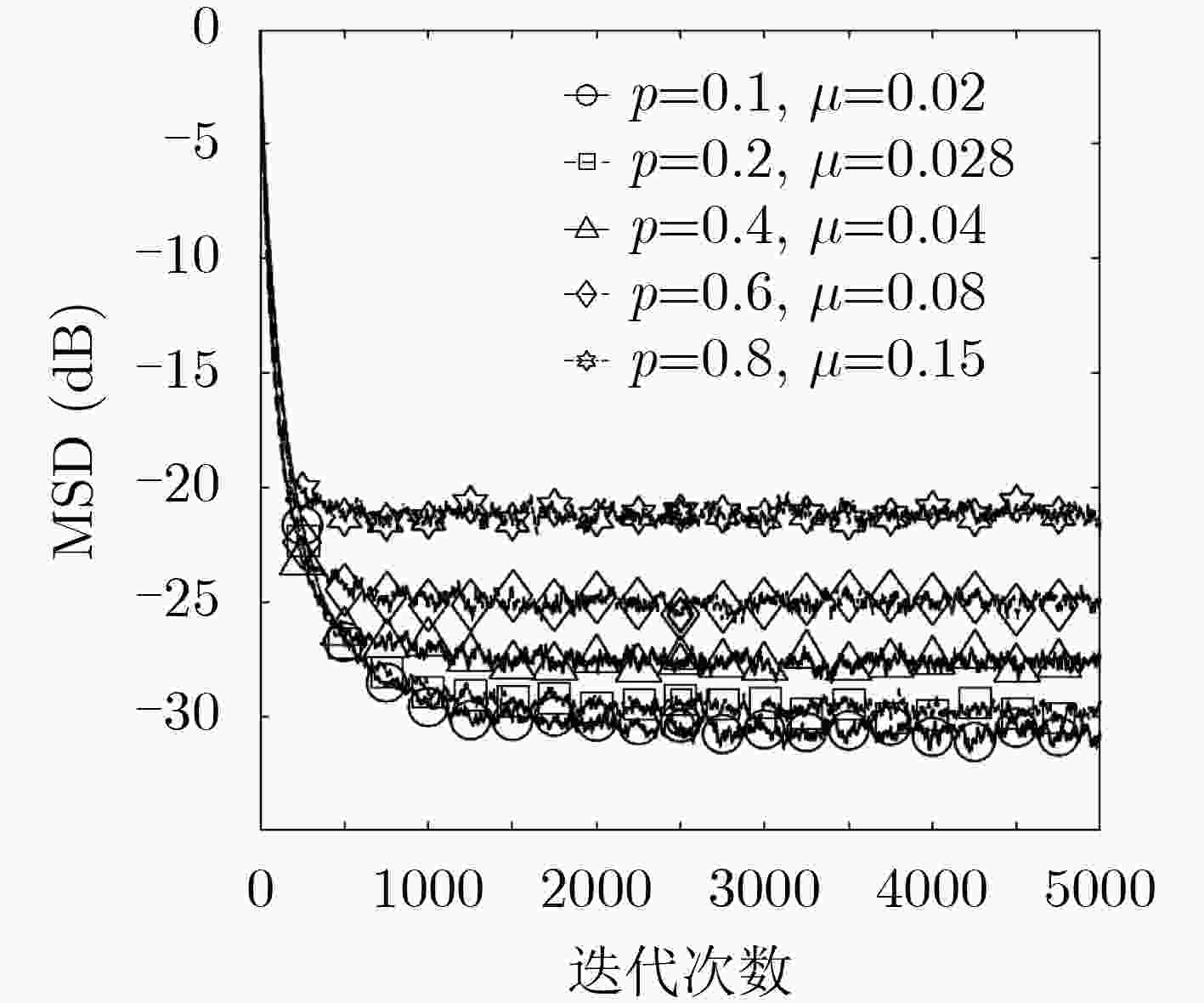
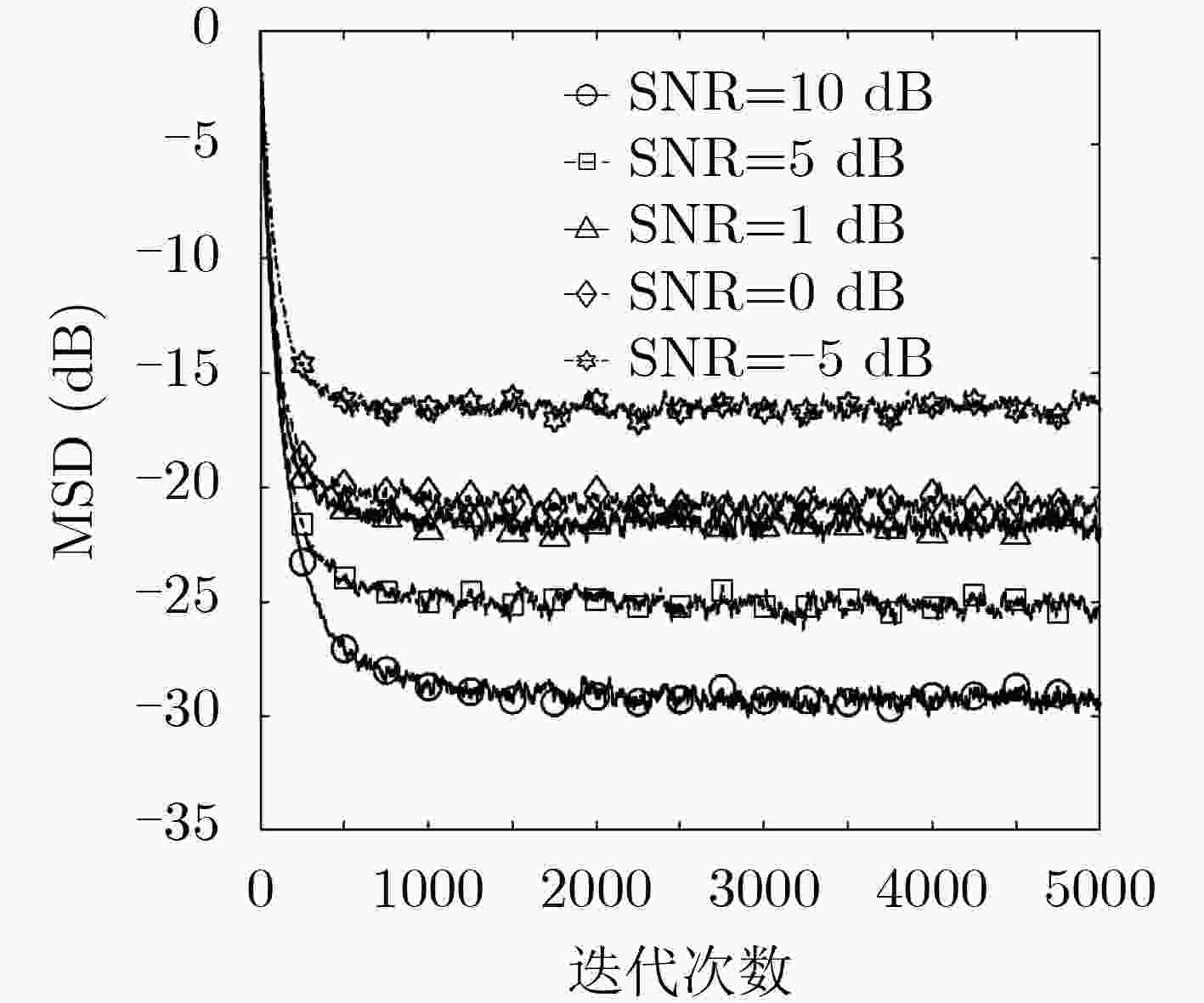
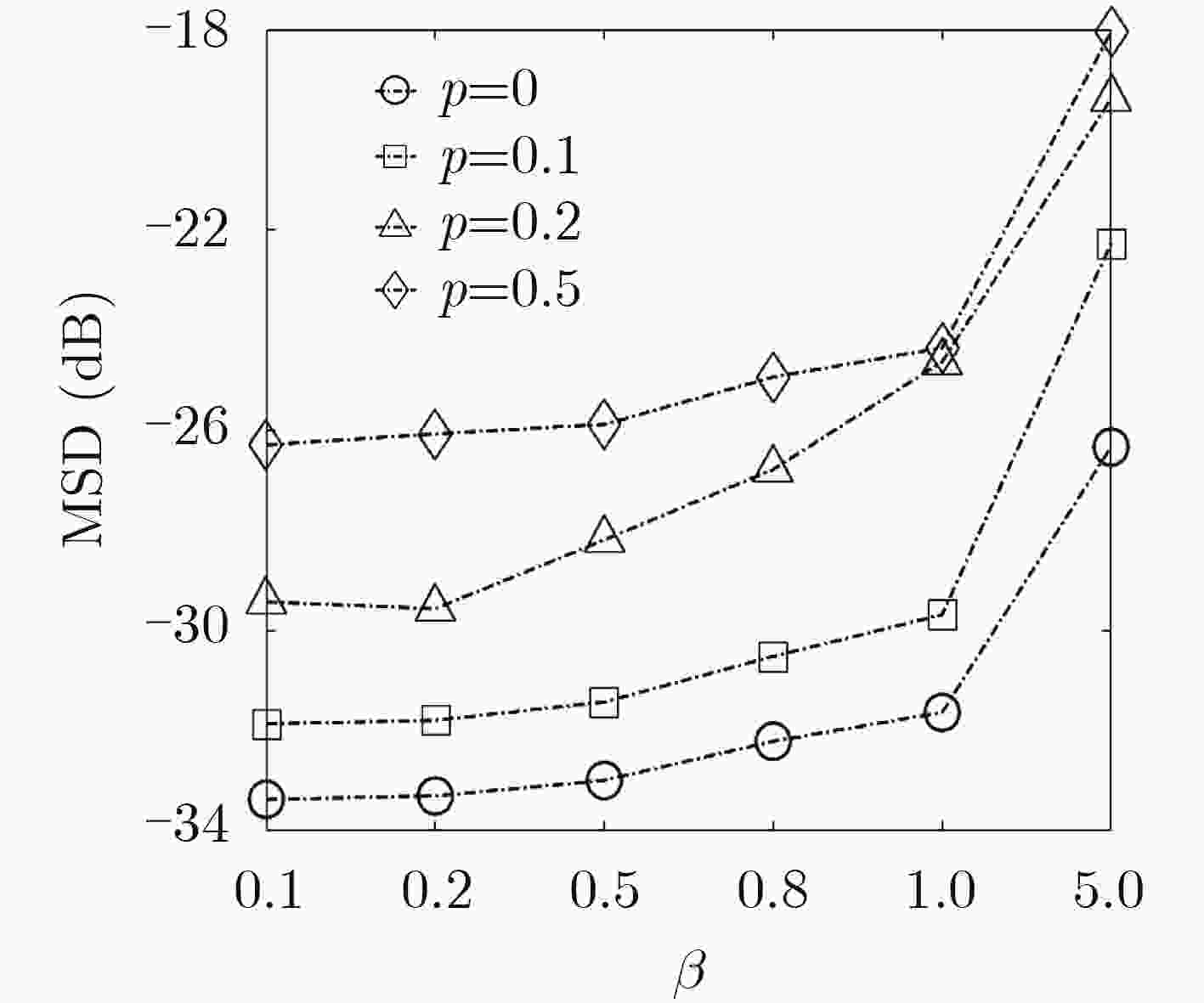
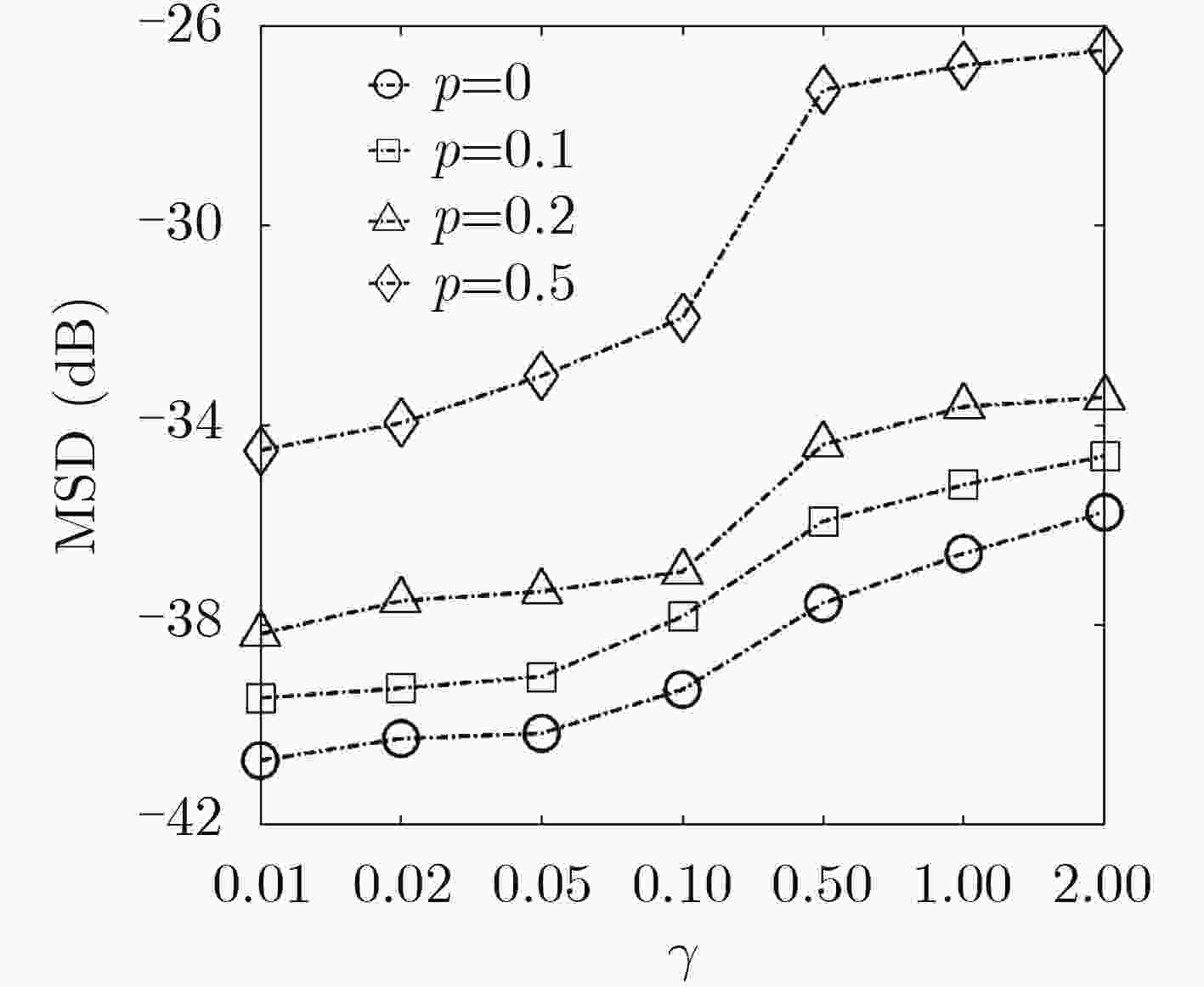
脉冲噪声会导致非负算法在迭代过程中存在过大的误差值,进而破坏算法的稳定性使其性能严重下降,对此该文提出一种基于Sigmoid框架的非负最小均方算法(SNNLMS)。该算法将传统的非负代价函数嵌入Sigmoid框架中得到新的代价函数,新的代价函数具有抑制脉冲噪声影响的特性。此外,为了增强SNNLMS算法在稀疏系统识别问题上的鲁棒性,该文还提出基于反比例函数的反比例Sigmoid非负最小均方算法(IP-SNNLMS)。仿真结果表明SNNLMS算法有效地解决了脉冲噪声造成的失调问题;IP-SNNLMS增强了算法鲁棒性,改进了算法在稀疏系统识别问题中收敛速率上的缺陷。
Abstract:Impulsive noise causes nonnegative algorithms to yield excessive error during iterations, which will damage the stability of the algorithm and causes performance degradation. In the paper, a NonNegative Least Mean Square algorithm based on the Sigmoid framework (SNNLMS) is proposed. The algorithm embeds the conventional nonnegative cost function into the Sigmoid framework to receive a new cost function. The new cost function has the characteristics of suppressing the impact of impulse noise. In addition, in order to enhance the robustness of the SNNLMS algorithm under sparse system identification, the Inversely-Proportional Sigmoid NonNegative Least Mean Square (IP-SNNLMS) is proposed based on the inversely-proportional function. Simulation results demonstrate that the SNNLMS algorithm effectively solves the problem of misadjustment caused by impulsive noise. IP-SNNLMS enhances the robustness of the algorithm and improves the defect of the convergence rate of the SNNLMS algorithm under the sparse system identification.
-
SLOCK D T M. On the convergence behavior of the LMS and the normalized LMS algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(9): 2811–2825. doi: 10.1109/78.236504 KANG B, YOO J, and PARK P. Bias-compensated normalised LMS algorithm with noisy input[J]. Electronics Letters, 2013, 49(8): 538–539. doi: 10.1049/el.2013.0246 JUNG S M and PARK P G. Normalised least-mean-square algorithm for adaptive filtering of impulsive measurement noises and noisy inputs[J]. Electronics Letters, 2013, 49(20): 1270–1272. doi: 10.1049/el.2013.2482 WANG Wenyuan, ZHAO Haiquan, LU Lu, et al. Bias-compensated constrained least mean square adaptive filter algorithm for noisy input and its performance analysis[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 84: 26–37. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2018.07.021 LIU Weifeng, POKHAREL P P, and PRINCIPE J C. The kernel least-mean-square algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(2): 543–554. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.907881 LIU Yuqi, SUN Chao, and JIANG Shouda. A reduced Gaussian kernel Least-Mean-Square algorithm for nonlinear adaptive signal processing[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2019, 38(1): 371–394. doi: 10.1007/s00034-018-0862-0 邱天爽, 杨志春, 李小兵, 等. α稳定分布下的加权平均最小p-范数算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(2): 410–413.QIU Tianshuang, YANG Zhichun, LI Xiaobing, et al. A weighted average least p-norm algorithm under alpha stable noise conditions[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(2): 410–413. 李群生, 赵剡, 寇磊, 等. 一种基于多尺度核学习的仿射投影滤波算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 924–931. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190023LI Qunsheng, ZHAO Yan, KOU Lei, et al. An affine projection algorithm with multi-scale kernels learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 924–931. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190023 LIN C J. On the convergence of multiplicative update algorithms for nonnegative matrix factorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2007, 18(6): 1589–1596. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2007.895831 BRO R and DE JONG S. A fast non-negativity-constrained least squares algorithm[J]. Journal of Chemometrics, 1997, 11(5): 393–401. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-128X(199709/10)11:5<393::AID-CEM483>3.0.CO;2-L CHEN Jie, RICHARD C, BERMUDEZ J C M, et al. Nonnegative least-mean-square algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(11): 5225–5235. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2162508 CHEN Jie, RICHARD C, BERMUDEZ J C M, et al. Variants of non-negative least-mean-square algorithm and convergence analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(15): 3990–4005. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2332440 CHEN Jie, BERMUDEZ J C M, and RICHARD C. Steady-state performance of non-negative least-mean-square algorithm and its variants[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(8): 928–932. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2320944 CHEN Jie, RICHARD C, and BERMUDEZ J C M. Reweighted nonnegative least-mean-square algorithm[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 128: 131–141. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.03.017 SHOKROLAHI S M and JAHROMI M N. Logarithmic reweighting nonnegative least mean square algorithm[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2018, 12(1): 51–57. doi: 10.1007/s11760-017-1129-0 CHEN Badong, XING Lei, ZHAO Haiquan, et al. Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(13): 3376–3387. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2539127 SONG Insun, PARK P, and NEWCOMB R W. A normalized least mean squares algorithm with a step-size scaler against impulsive measurement noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2013, 60(7): 442–445. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2013.2258266 FAN Kuan’gang, QIU Haiyun, PEI Chunyang, et al. Robust non-negative least mean square algorithm based on step-size scaler against impulsive noise[J]. Advances in Difference Equations, 2020(1): 199. doi: 10.1186/s13662-020-02654-5 HUANG Fuyi, ZHANG Jiashu, and ZHANG Sheng. A family of robust adaptive filtering algorithms based on sigmoid cost[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 149: 179–192. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.03.013 XIONG Kui and WANG Shiyuan. Robust least mean logarithmic square adaptive filtering algorithms[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(1): 654–674. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.10.019 代振, 王平波, 卫红凯. 非高斯背景下基于Sigmoid函数的信号检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2945–2950. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190012DAI Zhen, WANG Pingbo, and WEI Hongkai. Signal detection based on Sigmoid function in non-Gaussian noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2945–2950. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190012 -






 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载:
