CFAR for Passive Radar Based on Dynamic Ordered Matrix
-
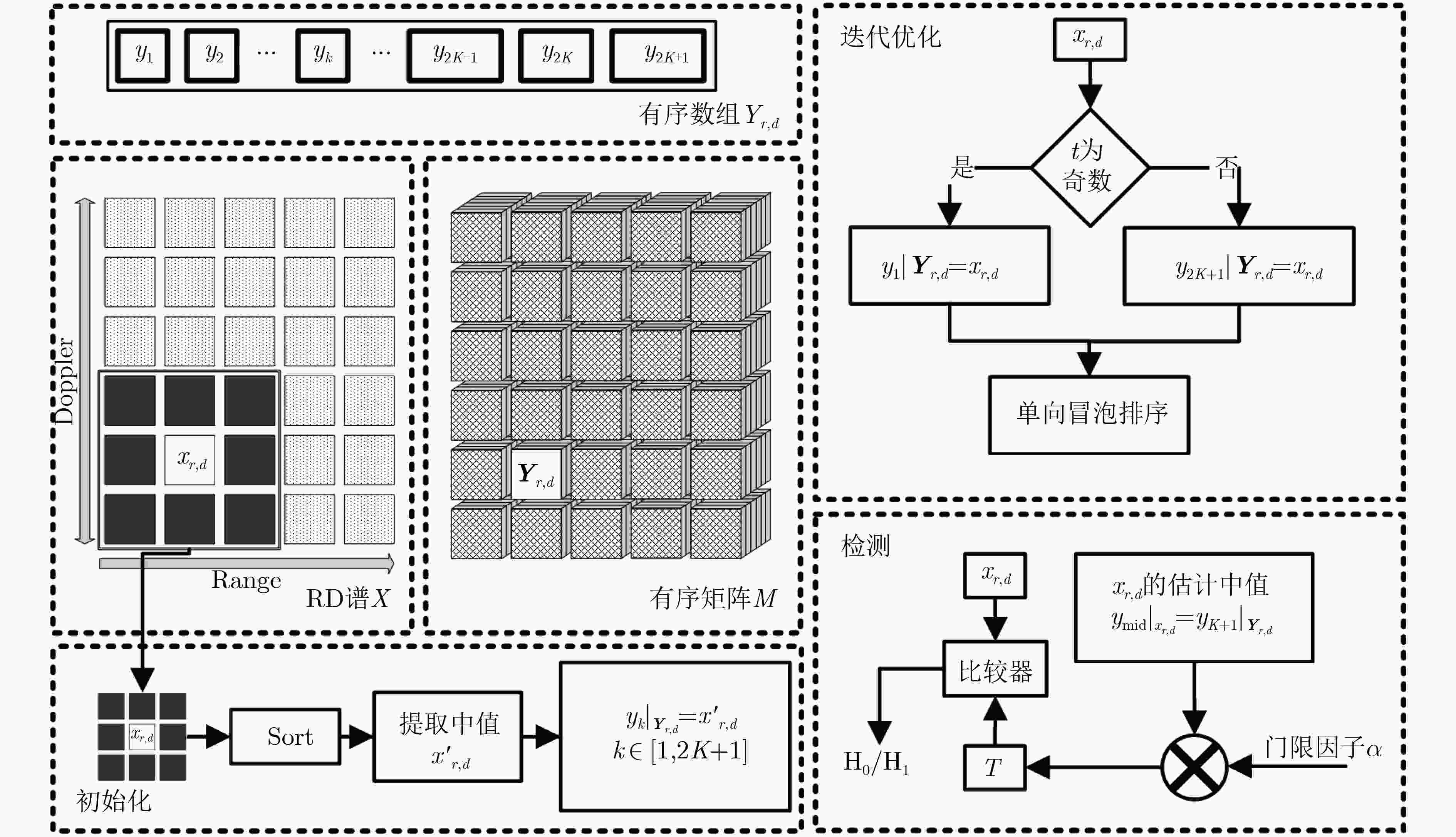
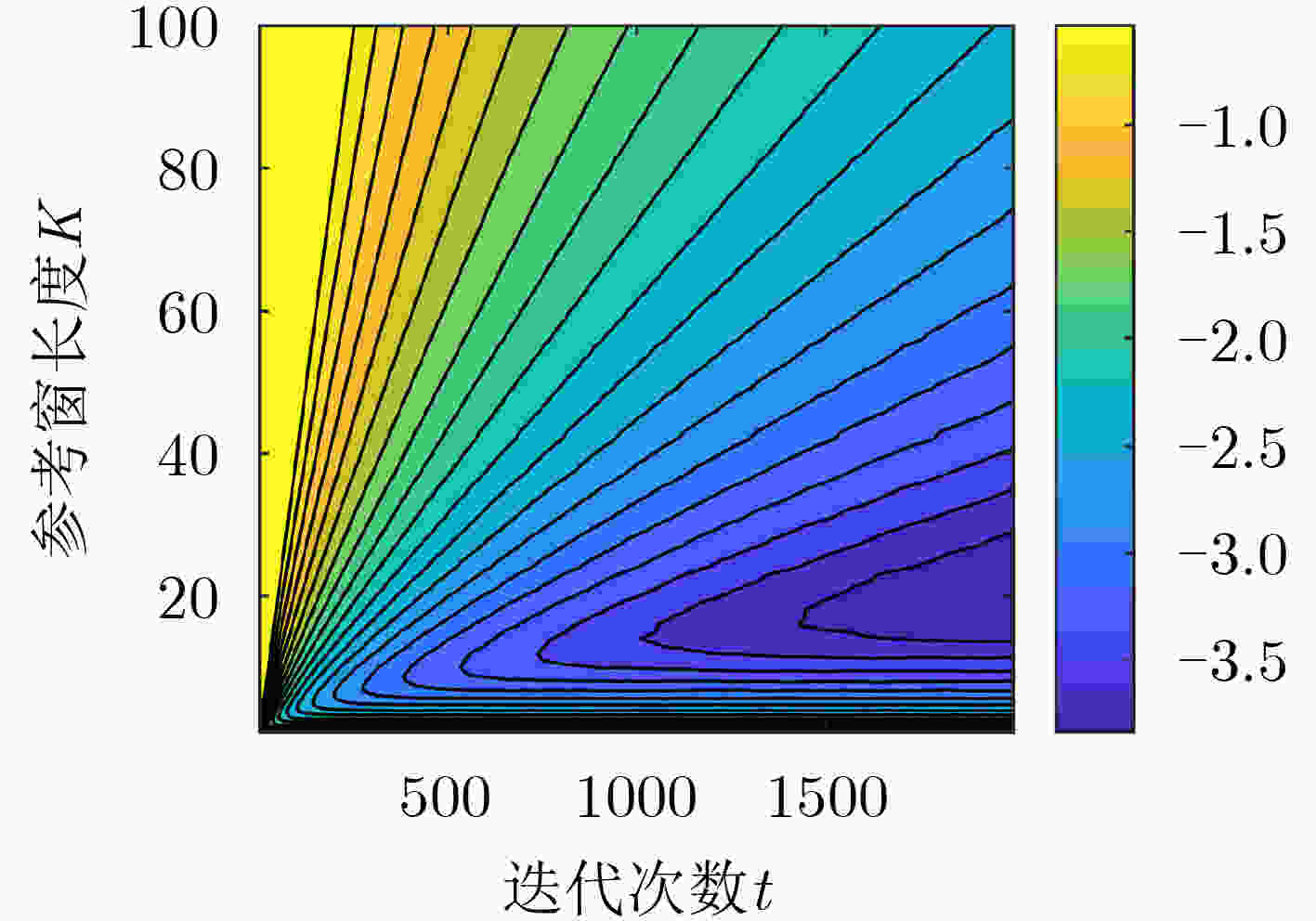
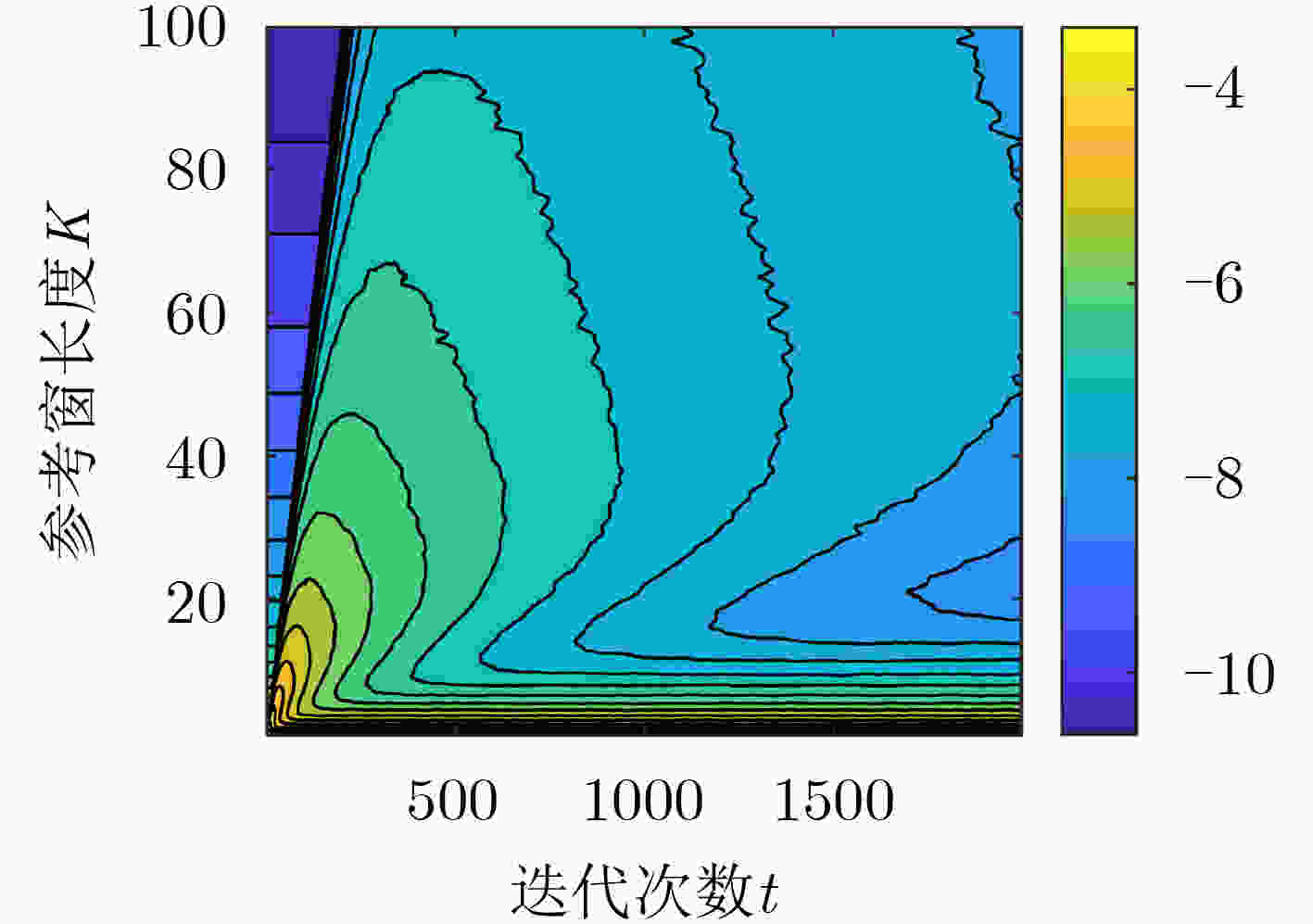
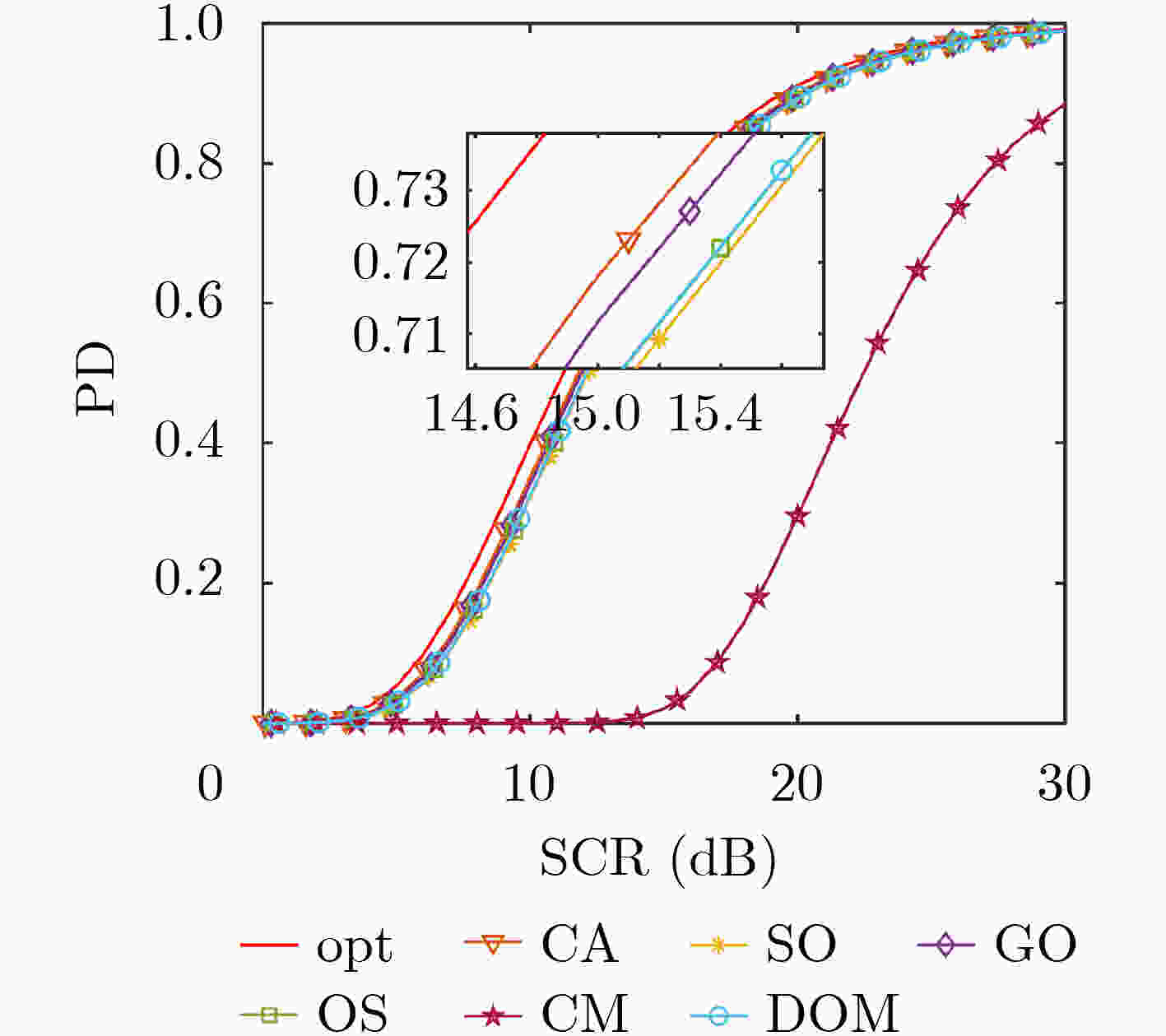
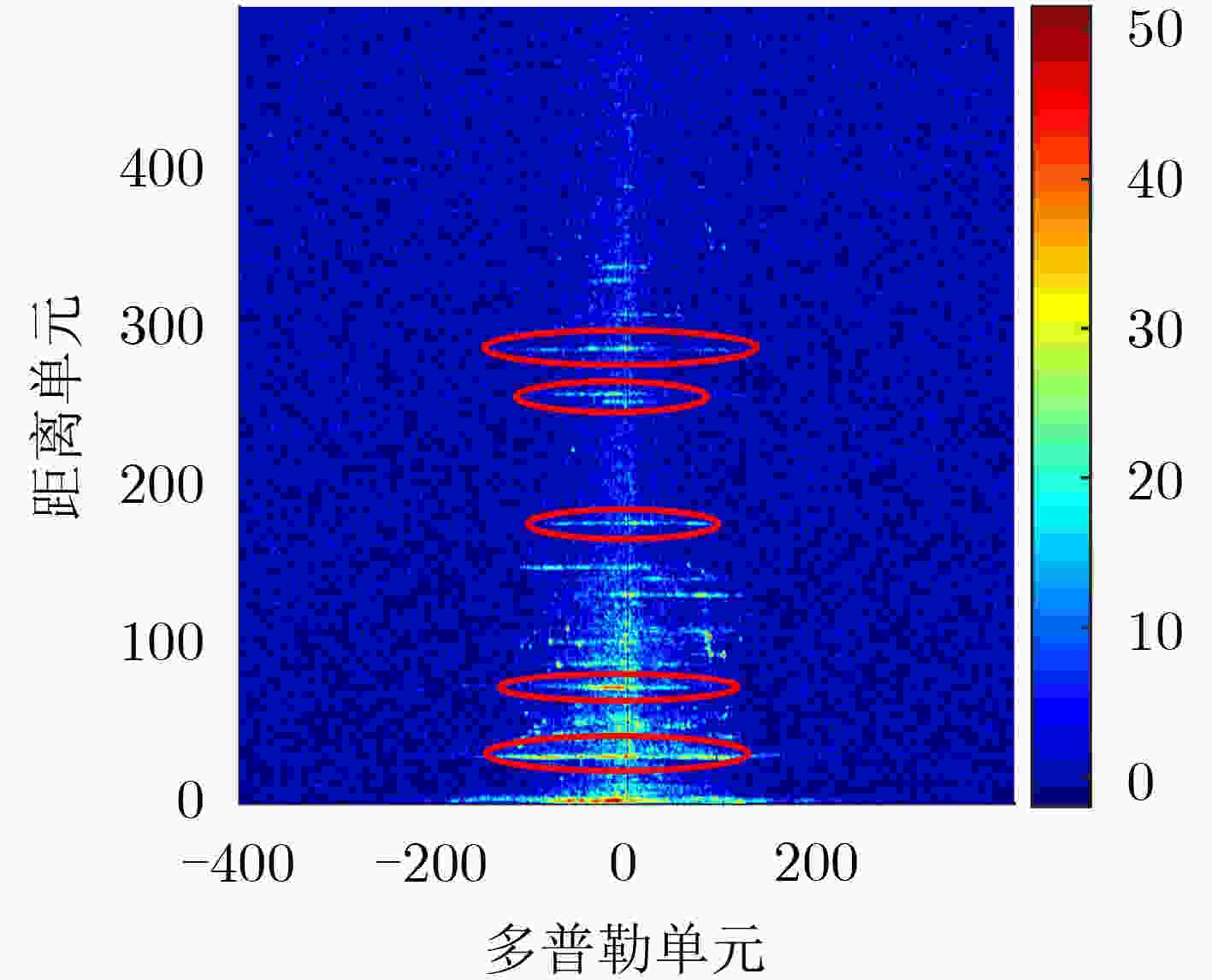
摘要: 外辐射源雷达采用不可控的第三方辐射源,其电磁传播条件复杂,尤其是在低空目标探测中,检测性能极大地受到杂波特性的影响,使得传统恒虚警算法性能明显下降。为了改善检测性能,该文提出一种基于雷达杂波空间划分的动态有序矩阵恒虚警检测算法(DOM-CFAR)。该算法将杂波空间从距离和多普勒维进行划分,构造为有序矩阵,再根据背景杂波变化进行动态极值替换、提取杂波估计中值用以计算检测阈值,从而使得检测算法阈值可动态适应杂波功率变化。仿真和实测结果表明,该算法可以在均匀杂波、多目标和杂波边缘等复杂情况下保持稳定的检测性能。Abstract: Passive radar uses third party radiation source, which is uncontrollable. Due to the complicated electromagnetic propagation conditions, especially in a low altitude target detection, the detection performance of the radar is greatly affected by clutters, leading to significant degradation of the performance of traditional constant false alarm algorithm. In order to improve the detection performance, a Dynamic Ordered Matrix Constant False Alarm Rate (DOM-CFAR) algorithm based on radar clutter space partition is proposed. In this algorithm, an ordered matrix is constructed after dividing the clutter space from distance and Doppler dimension. Then the dynamic extreme value is replaced according to the background clutter change and the estimated median value of clutter is extracted so as to calculate the detection threshold. This algorithm makes the threshold value of detection can dynamically adapt to the clutter power change. The simulation and measurement results show that the algorithm can maintain excellent detection performance under the complex environment with uniform clutter, multi-target and clutter edge.
-
Key words:
- Target detection /
- Clutter matrix /
- Clutter map /
- Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR)
-
表 1 算法复杂度及耗时比较
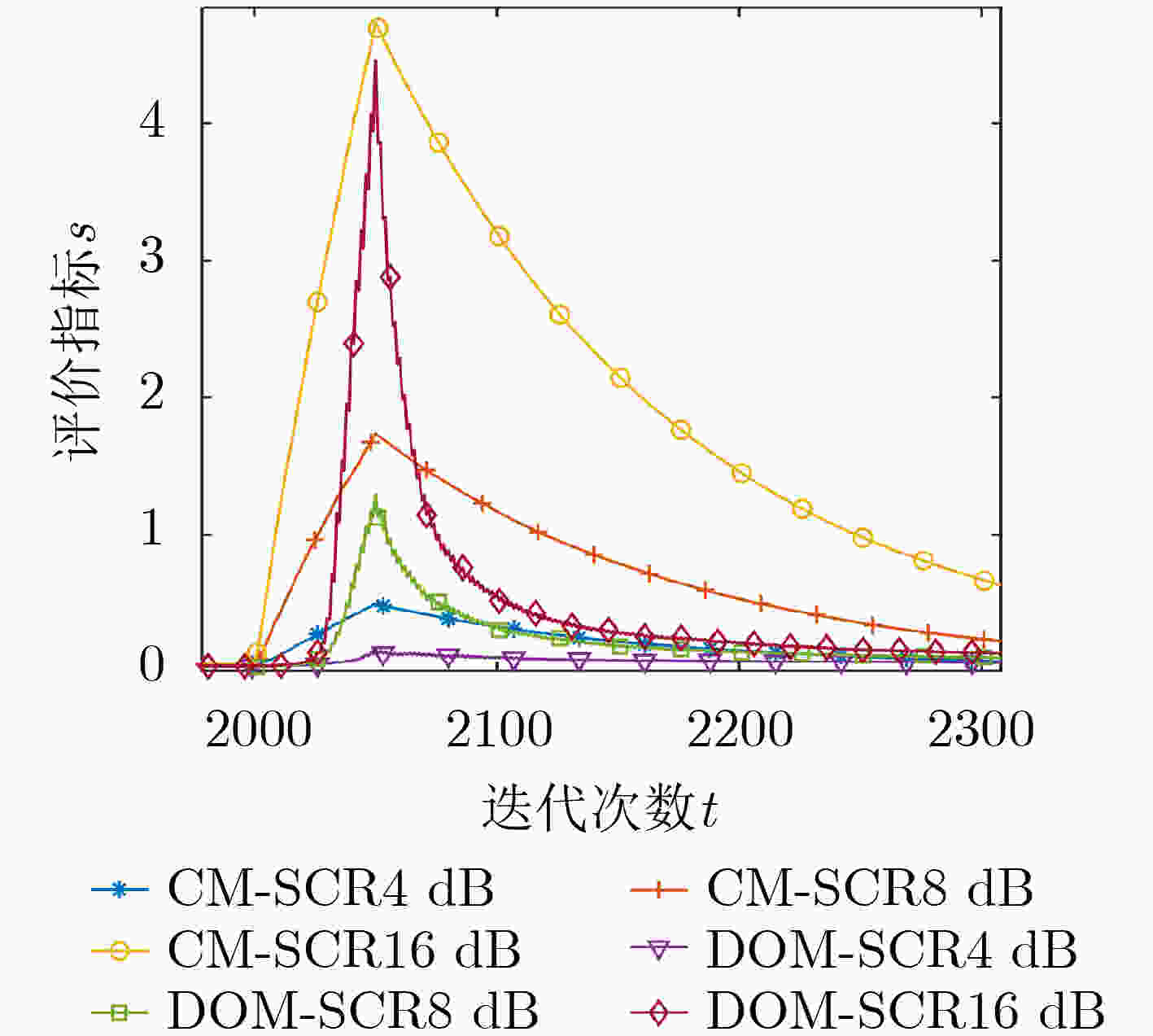
算法名称 空间复杂度 运算复杂度 串行耗时(s) 并行耗时(s) CA 1 MN 51.337 2.776 SO 1 MN 73.588 3.260 GO 1 MN 75.176 3.289 OS 1 MNlgN 449.651 7.632 CM M M 0.087 0.073 DOM MK MK 88.490 5.560 表 2 实测的检测概率与虚警概率
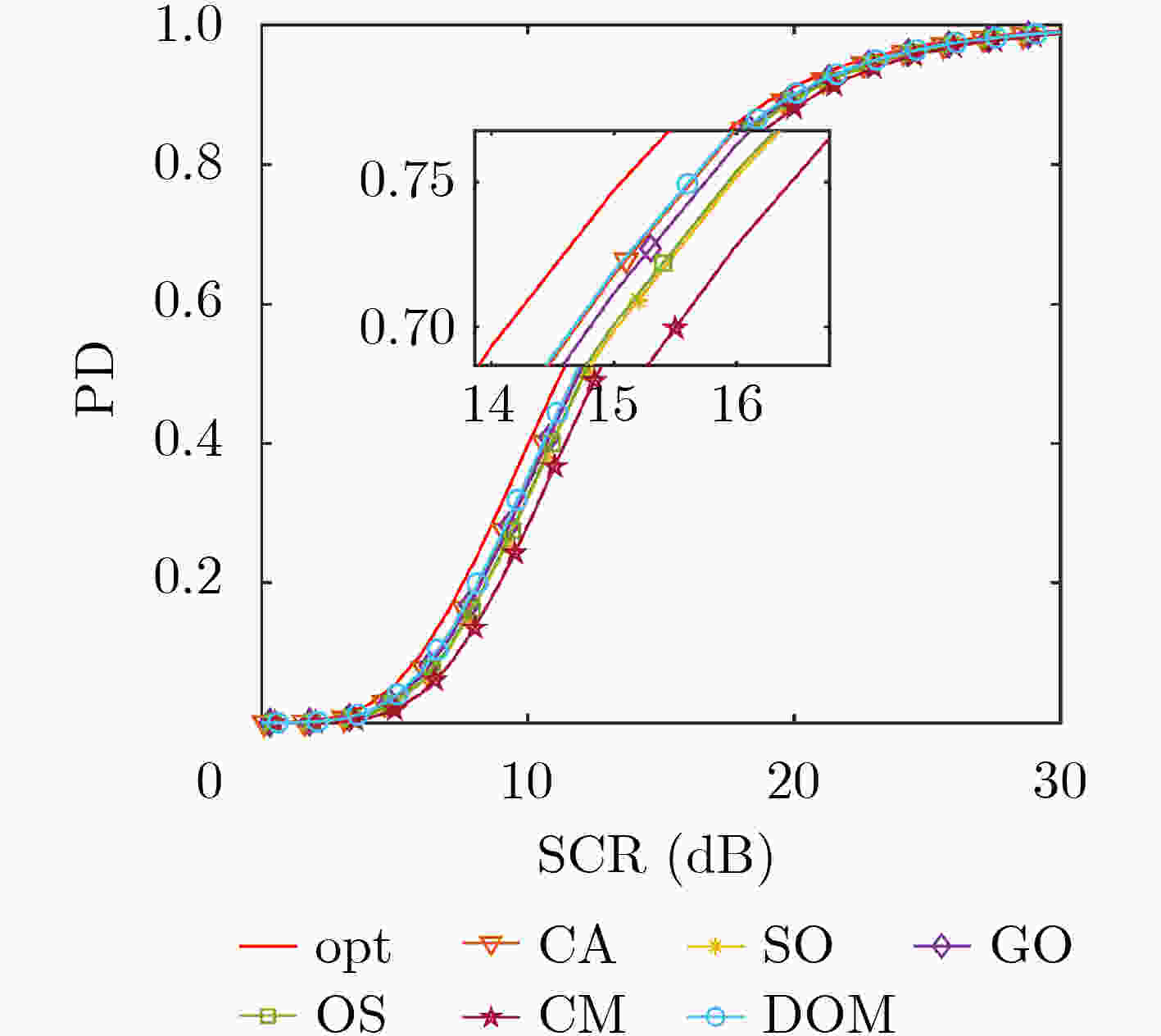
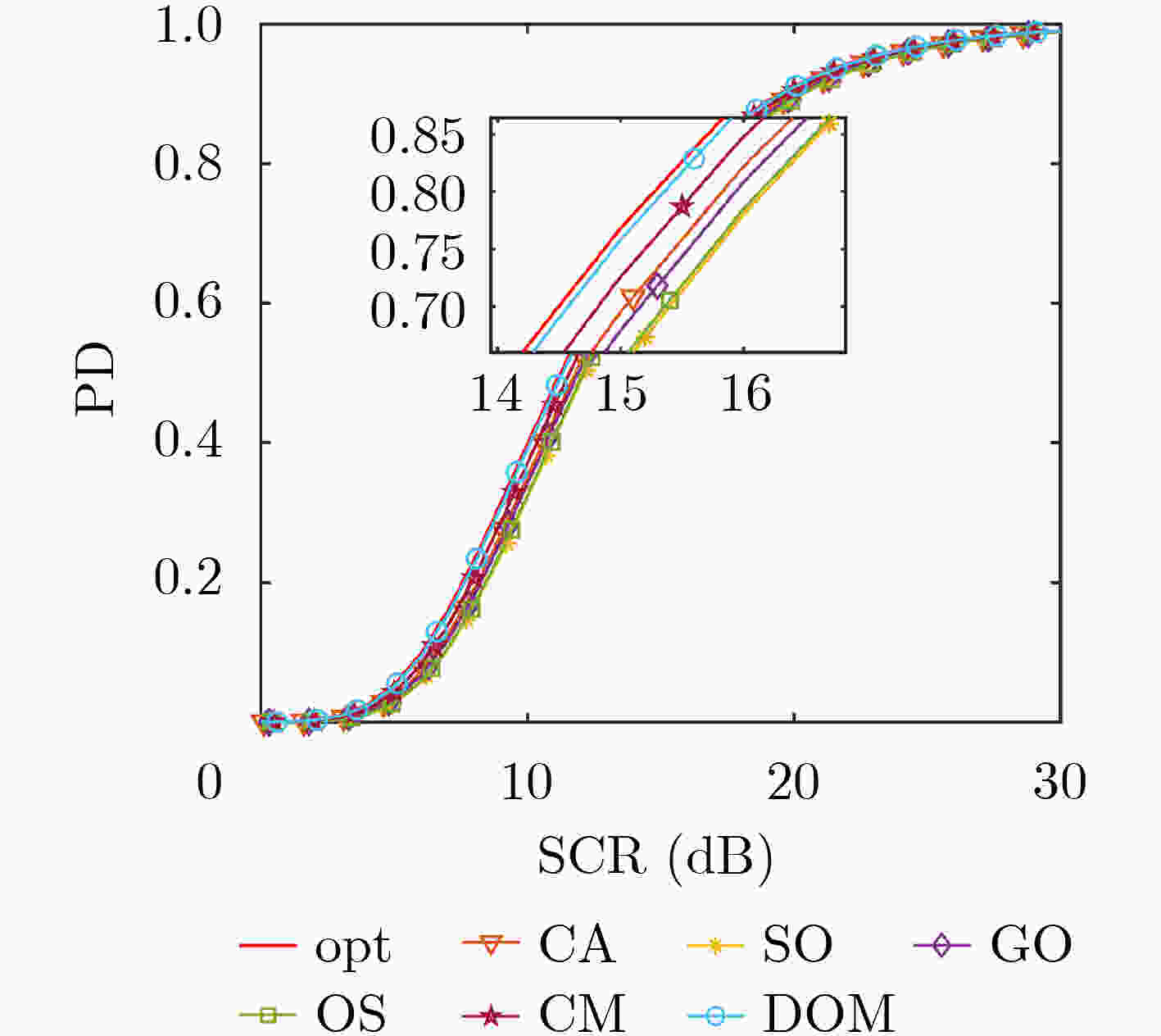
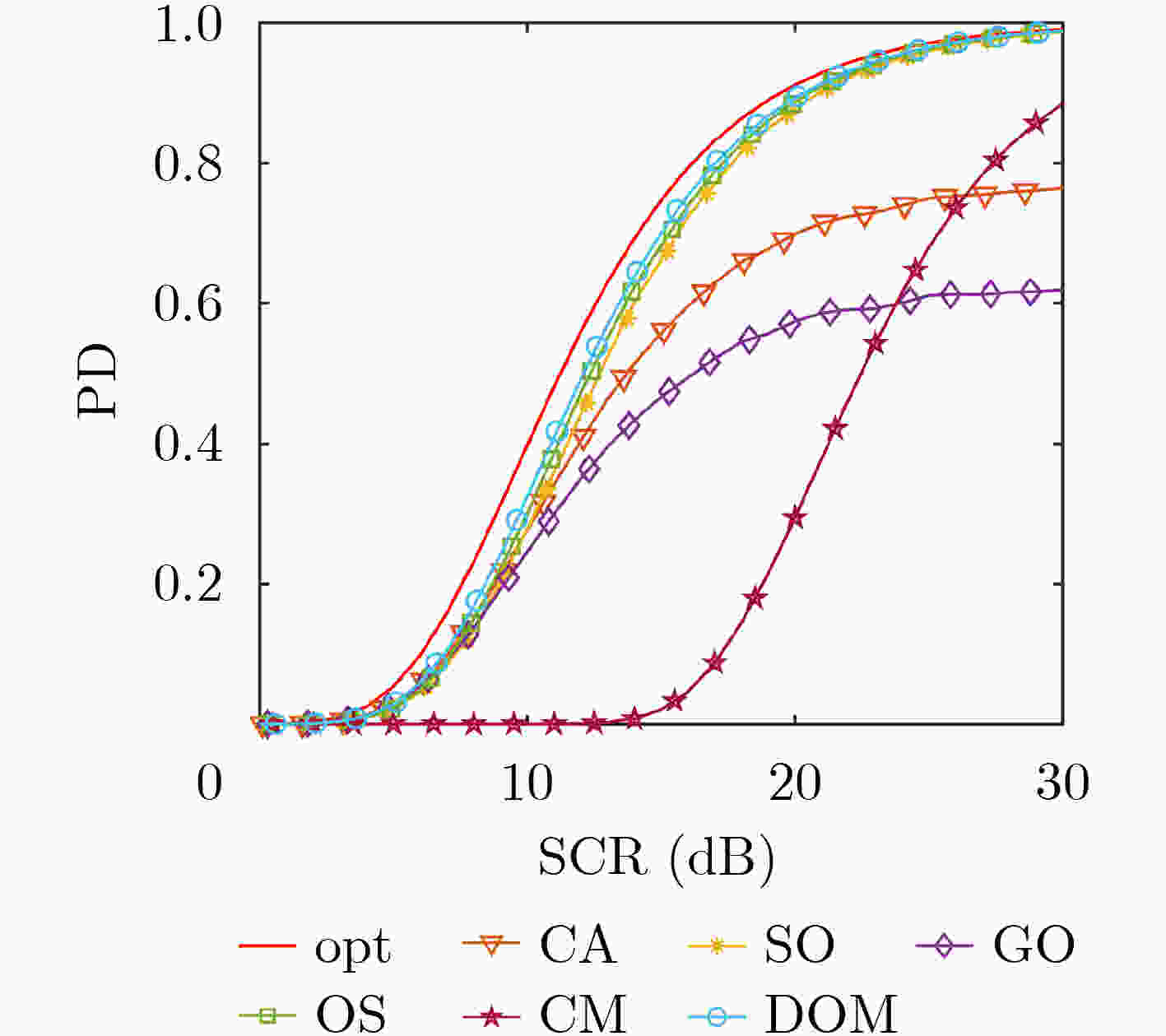
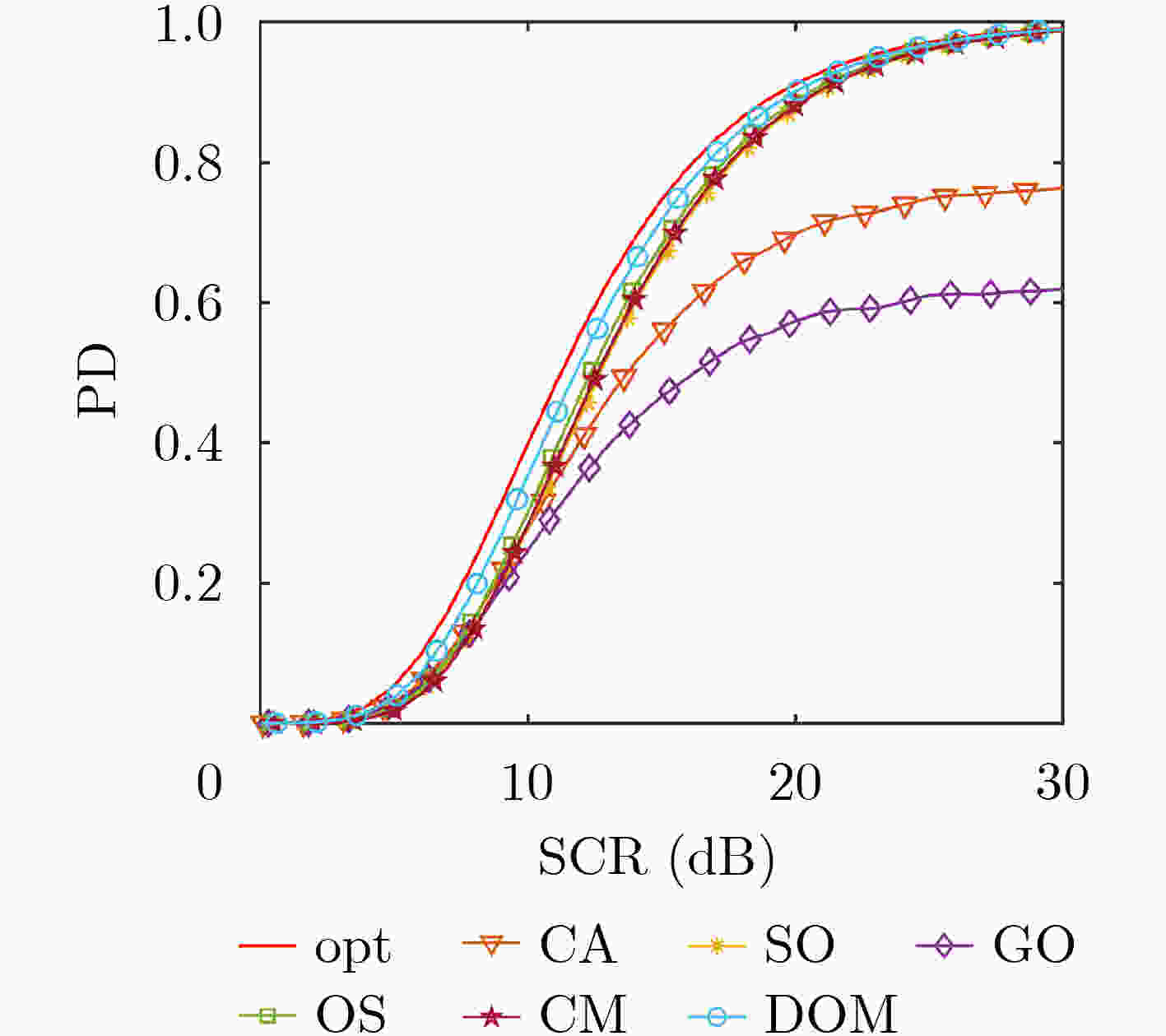
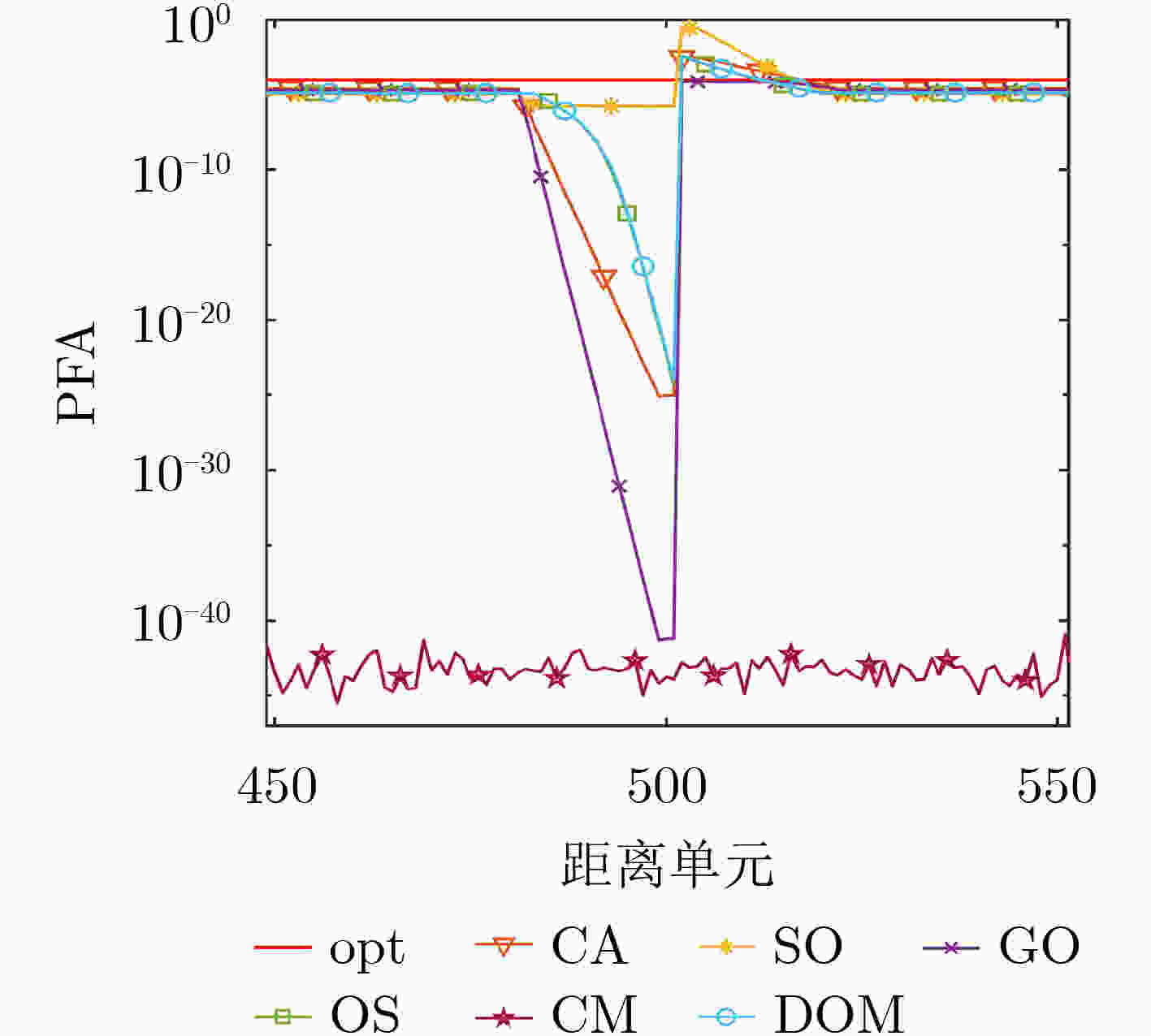
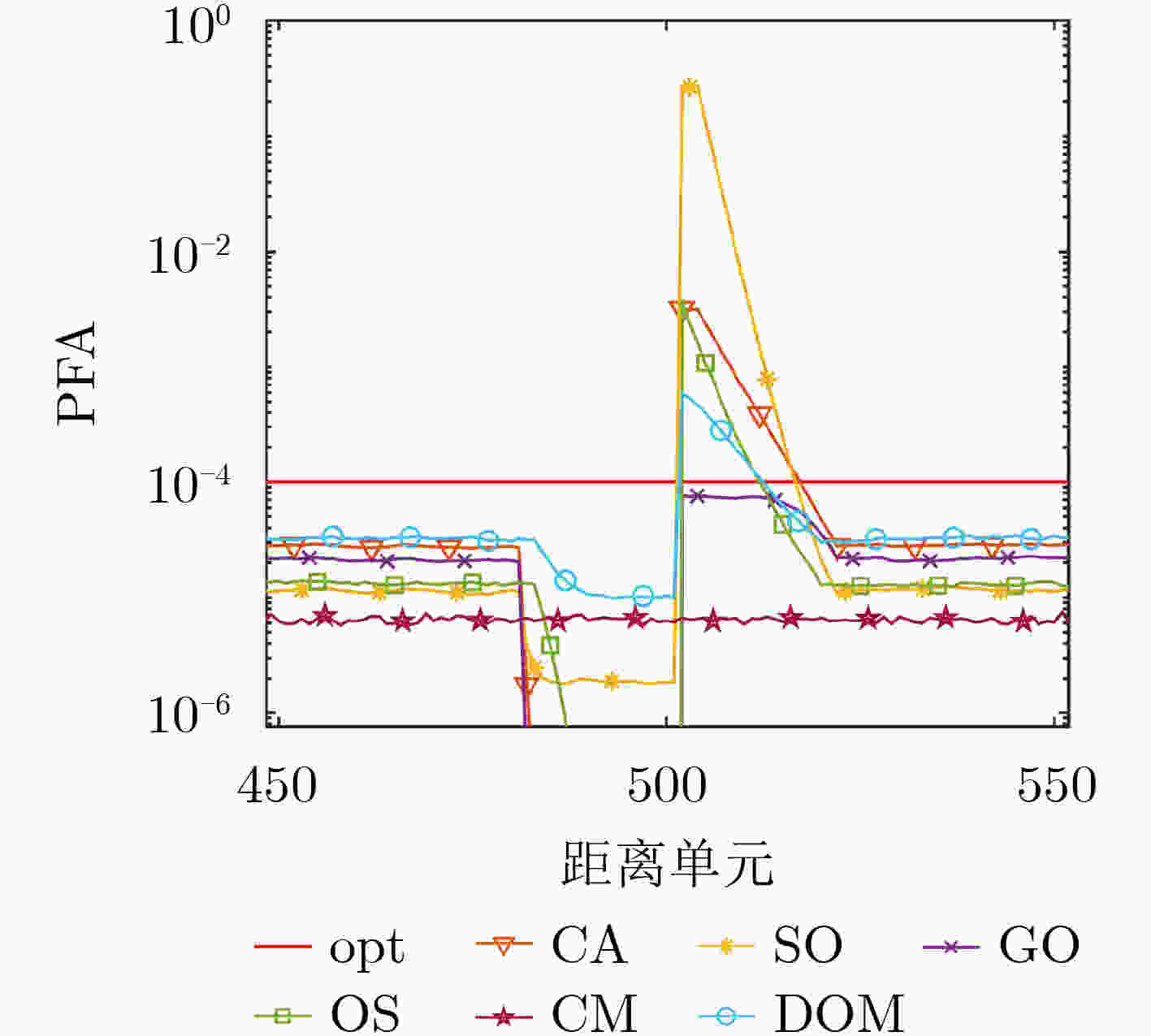
CFAR CA SO GO OS CM迭代次数 DOM迭代次数 10 100 200 400 10 100 200 400 检测概率(%) 72.4 51.3 78.8 86.8 1.3 62.1 76.4 93.0 88.0 98.3 98.1 98.2 虚警概率(10–5) 2.68 9.58 1.93 22.06 0.13 2.93 4.25 4.45 20.93 5.08 2.85 1.28 -
FINN H M. Adaptive detection in clutter[C]. The 5th Symposium on Adaptive Processes, New Jersey, USA, 1966: 562–567. doi: 10.1109/SAP.1966.271149. WANG Weijiang, WANG Runyi, JIANG Rongkun, et al. Modified reference window for two-dimensional CFAR in radar target detection[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7924–7927. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0687 TRUNK G V. Range resolution of targets using automatic detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1978, AES-14(5): 750–755. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1978.308625 HANSEN V G and SAWYERS J H. Detectability loss due to "greatest of" selection in a cell-averaging CFAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, 16(1): 115–118. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308885 SMITH M E and VARSHNEY P K. Intelligent CFAR processor based on data variability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(3): 837–847. doi: 10.1109/7.869503 WANG Leiou, WANG Donghui, and HAO Chengpeng. Intelligent CFAR detector based on support vector machine[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 26965–26972. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2774262 CARRETERO M V I, HARMANNY R I A, and TROMMEL R P. Smart-CFAR, A machine learning approach to floating level detection in radar[C]. The 16th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Paris, France, 2019: 161–164. ROHLING H. Radar CFAR thresholding in clutter and multiple target situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1983, AES-19(4): 608–621. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1983.309350 VILLAR S A, DE PAULA M, SOLARI F J, et al. A framework for acoustic segmentation using order statistic-constant false alarm rate in two dimensions from sidescan sonar data[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2018, 43(3): 735–748. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2017.2721058 柳向, 李东生, 胡瑞. 基于有序统计类恒虚警检测的脉冲压缩雷达移频特征消隐多载波干扰研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(11): 2134–2142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.008LIU Xiang, LI Dongsheng, and HU Rui. Research on blanking shift-frequency-multi-carrier jamming against pulse-compression radar based on OS-CFAR[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(11): 2134–2142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.008 LIN C H, LIN Y C, BAI Yue, et al. DL-CFAR: A Novel CFAR target detection method based on deep learning[C]. The 90th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/VTCFall.2019.8891420. JIN Erwen, YAN Danqing, ZHANG Zhongjin, et al. FOD Detection on Airport Runway with Clutter Map CFAR Plane Technique[M]. LIANG Qilian, WANG Wei, MU Jiasong, et al. Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems. New York: Springer, 2012: 335–342. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5803-6_34. AKÇAPINAR K and BAYKUT S. CM-CFAR parameter learning based square-law detector for foreign object debris radar[C]. The 48th European Microwave Conference, Madrid, Spain, 2018: 421–424. doi: 10.23919/EuMC.2018.8541714. TAO Ding, ANFINSEN S N, and BREKKE C. Robust CFAR detector based on truncated statistics in multiple-target situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 117–134. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2451311 WU Fengtao, WU Nan, and WU Maosong. A fast and slow time combined CFAR detection algorithm used in through-the-wall radar[C]. 2017 IEEE Electrical Design of Advanced Packaging and Systems Symposium, Haining, China, 2017: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/EDAPS.2017.8276955. LAYEGHY S, ODABAEE M, KHLIF M S, et al. A time frequency approach to CFAR detection[C]. 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Bilbao, Spain, 2011: 230–234. doi: 10.1109/ISSPIT.2011.6151565. 代振, 王平波, 卫红凯. 非高斯背景下基于Sigmoid函数的信号检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2945–2950. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190012DAI Zhen, WANG Pingbo, and WEI Hongkai. Signal detection based on sigmoid function in Non-Gaussian noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2945–2950. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190012 NARASIMHAN R S, RAMAKRISHNAN K R, and VENGADARAJAN A. Robust variability index CFAR for non-homogeneous background[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(10): 1775–1786. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5435 ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Renli, SHENG Weixing, et al. Intelligent CFAR detector for non-homogeneous weibull clutter environment based on skewness[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma, USA, 2018: 322–326. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378578. 赵文静, 刘畅, 刘文龙, 等. K分布海杂波背景下基于最大特征值的雷达信号检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2235–2241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171092ZHAO Wenjing, LIU Chang, LIU Wenlong, et al. Maximum eigenvalue based radar signal detection method for K distribution sea clutter environment[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2235–2241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171092 万显荣. 基于低频段数字广播电视信号的外辐射源雷达发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 109–123. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20027WAN Xianrong. An overview on development of passive radar based on the low frequency band digital broadcasting and TV signals[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 109–123. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20027 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
