A Resilient Recovery Method on ADS-B Attack Data
-
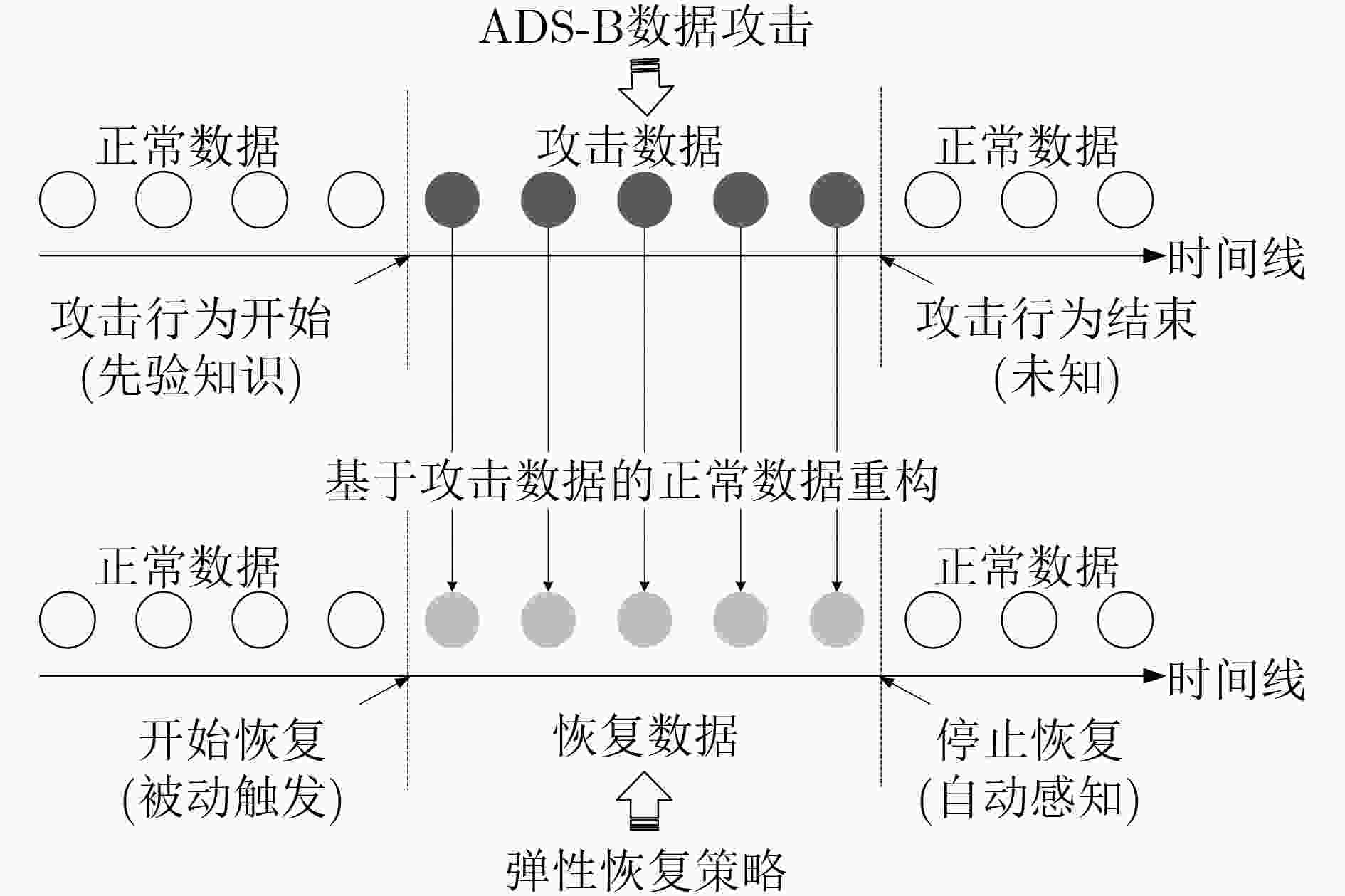
摘要: 为了对自动广播相关监视(ADS-B)攻击数据进行弹性恢复,确保空情态势感知信息的持续可用性,该文提出针对ADS-B攻击数据的弹性恢复方法。基于前置的攻击检测机制,获取当前ADS-B量测数据序列和预测数据序列,并在此基础上构建偏差数据序列、差分数据序列和邻近密度数据序列。依托偏差数据构建恢复向量,依托差分数据挖掘攻击数据的时序特性,依托邻近密度数据挖掘攻击数据的空间特性。通过整合3种数据序列构建弹性恢复策略并确定恢复终止点,实现对攻击影响的弱化,将ADS-B攻击数据向正常数据方向进行定向恢复。通过对6种典型攻击样式的实验分析,证明该弹性恢复方法能够有效恢复ADS-B攻击数据,削弱数据攻击对监视系统的影响。Abstract: In order to conduct effective resilient recovery on Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) attack data and ensure the continuous availability of air traffic situation awareness, a resilient recovery method on ADS-B attack data is proposed. Based on attack detection strategies, the measurement and prediction sequences of ADS-B data are obtained to set up deviation data, differential data and neighbor density data sequences, which are designed to construct recovery vectors, mine the temporal correlations and the spatial correlations respectively. The selected data sequences are integrated to accomplish the whole recovery method and decide the end point of recovery. The method is applied to elinimating attack effects and recovering the attack data towards normal data. According to the results of experiments on six classical attack patterns, the proposed method is effective on recovering attack data and eliminating the attack impacts.
-
表 1 构造的典型攻击样式
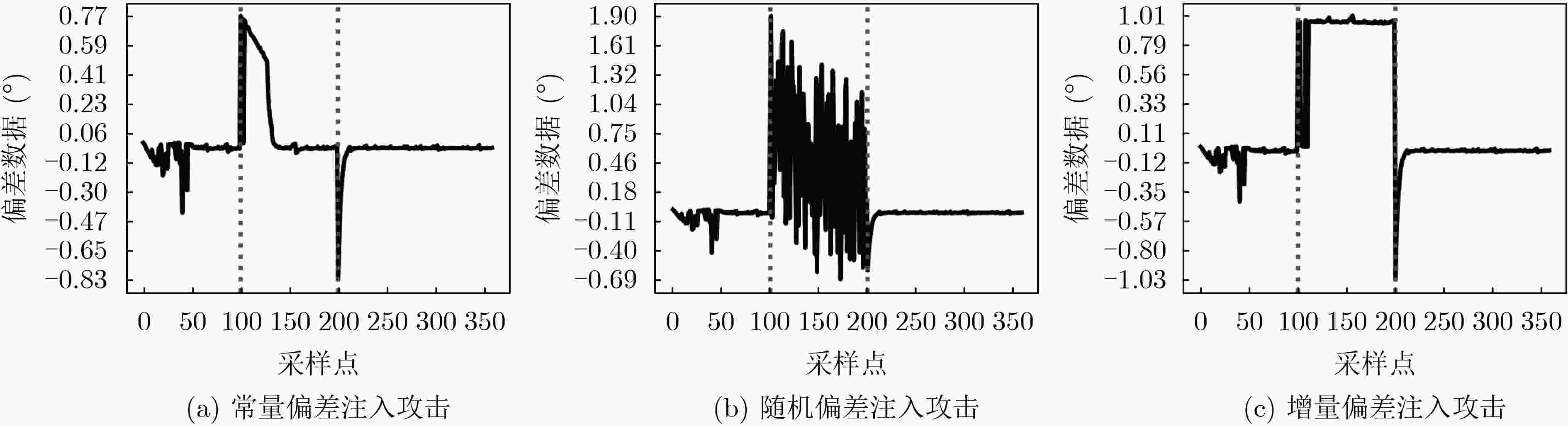
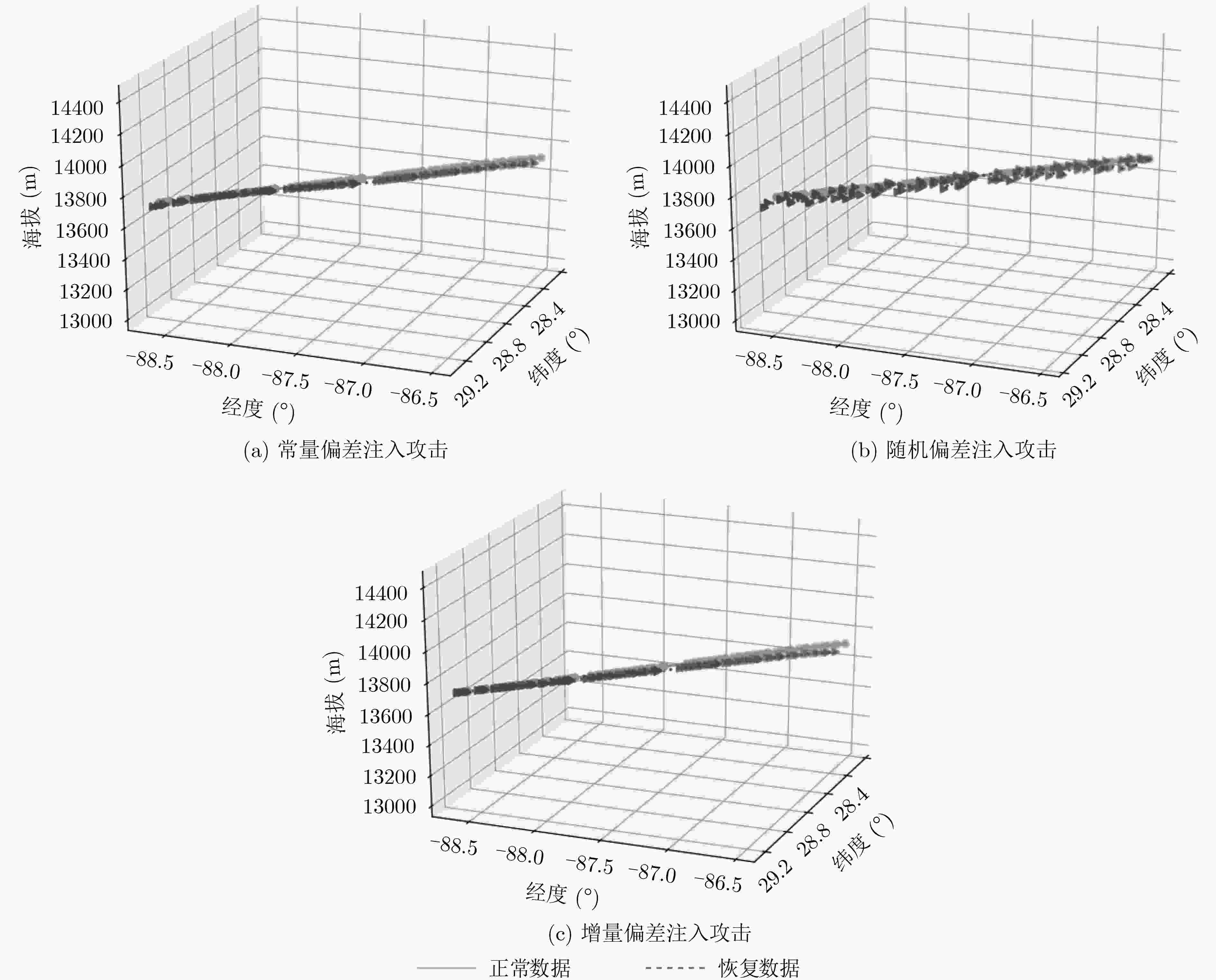
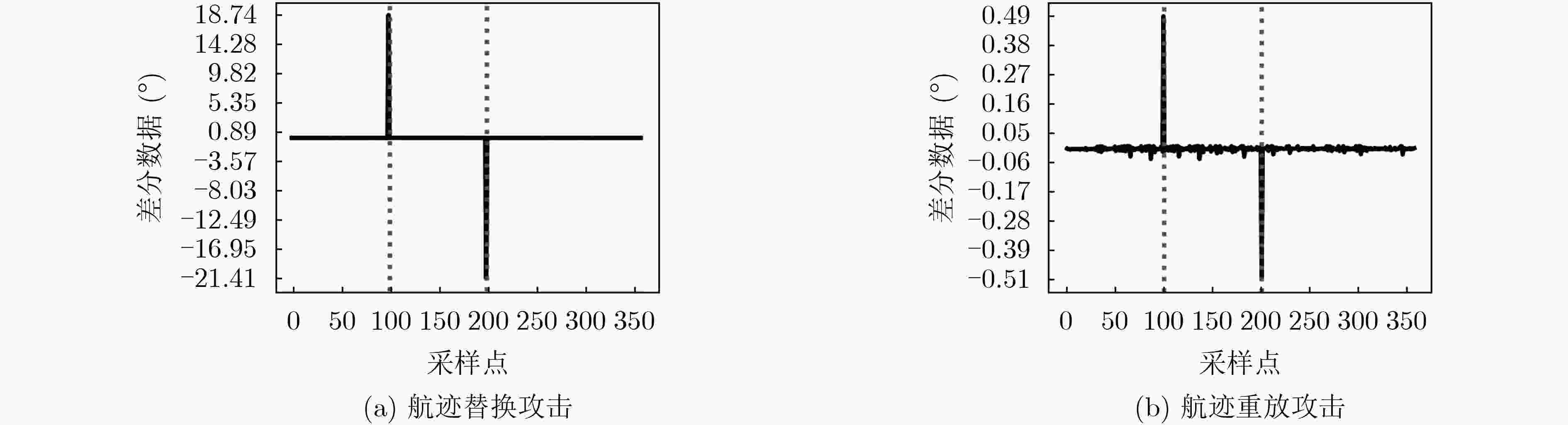
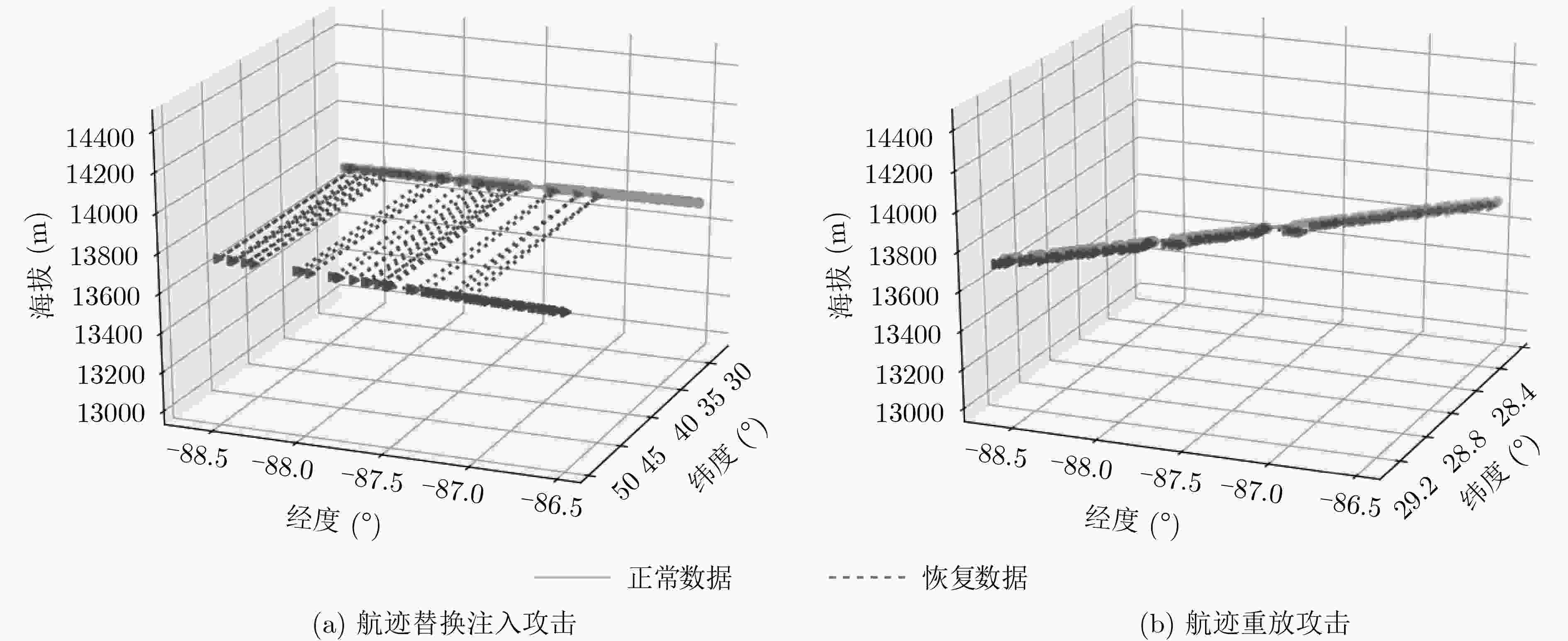
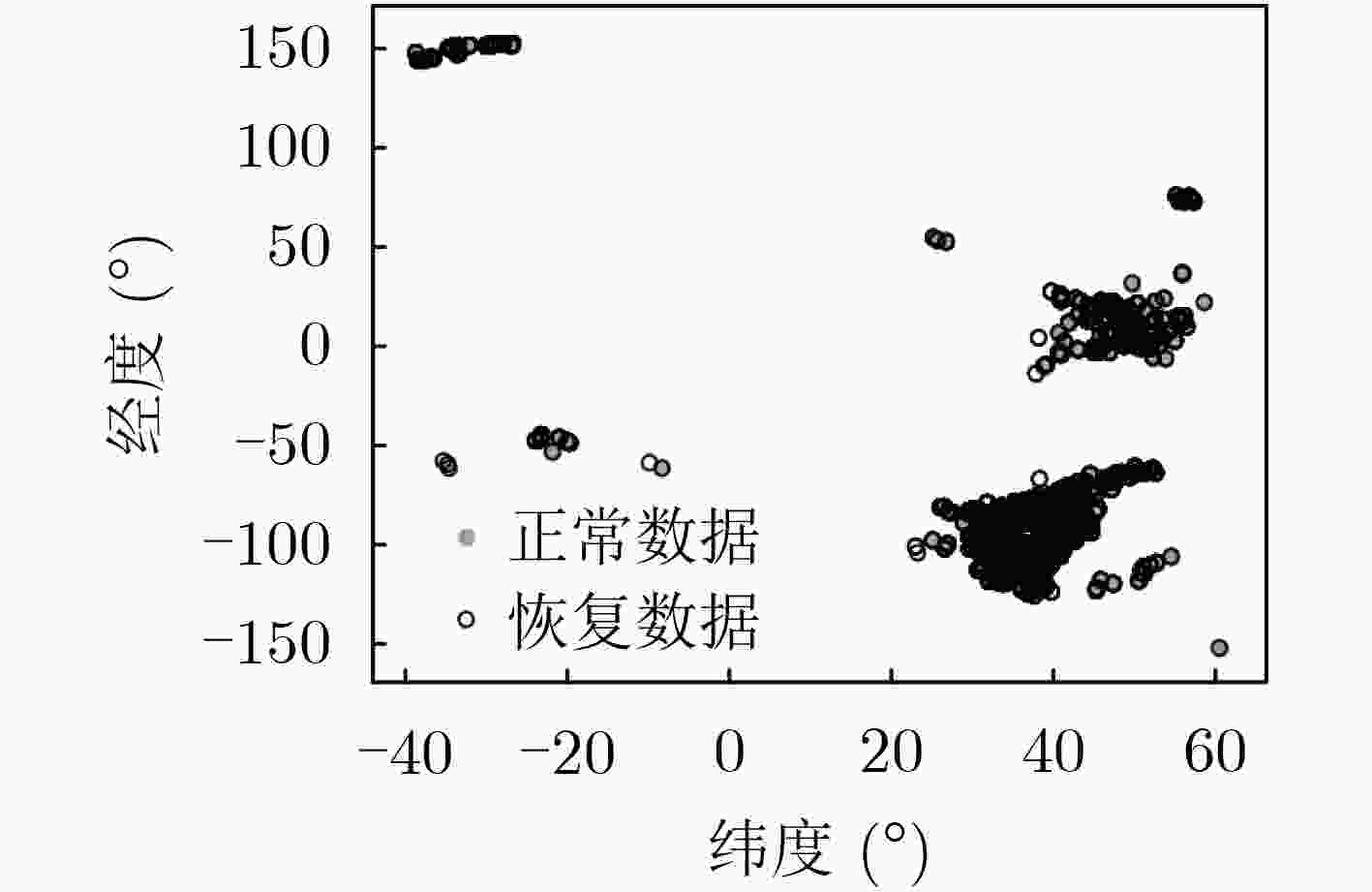
编号 攻击模式 攻击影响 ATK-1 常量偏差注入攻击 针对ADS-B多属性数据注入常量偏差 ATK-2 随机偏差注入攻击 针对ADS-B多属性数据注入随机偏差 ATK-3 增量偏差注入攻击 针对ADS-B多属性数据注入增量偏差 ATK-4 航迹替换攻击 针对特定时间窗口内的航迹进行替换 ATK-5 航迹重放攻击 在特定时间长度下实现航迹重放 ATK-6 飞行器泛洪攻击 向当前空域态势中注入大量幽灵飞行器目标 -
STROHMEIER M, SCHÄFER M, PINHEIRO R, et al. On perception and reality in wireless air traffic communication security[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(6): 1338–1357. doi: 10.1109/tits.2016.2612584 WANG Wenyi, WU Renbiao, and LIANG Junli. ADS-B signal separation based on blind adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(7): 6547–6556. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2914233 SUN Junzi, VÛ H, ELLERBROEK J, et al. pyModeS: Decoding mode-S surveillance data for open air transportation research[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(7): 2777–2786. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2914770 STROHMEIER M, SCHÄFER M, LENDERS V, et al. Realities and challenges of NextGen air traffic management: The case of ADS-B[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(5): 111–118. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6815901 STROHMEIER M, LENDERS V, and MARTINOVIC I. On the security of the automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast protocol[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(2): 1066–1087. doi: 10.1109/comst.2014.2365951 MANESH M R and KAABOUCH N. Analysis of vulnerabilities, attacks, countermeasures and overall risk of the automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) system[J]. International Journal of Critical Infrastructure Protection, 2017, 19: 16–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcip.2017.10.002 钱亚冠, 卢红波, 纪守领, 等. 基于粒子群优化的对抗样本生成算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1658–1665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180777QIAN Yaguan, LU Hongbo, JI Shouling, et al. Adversarial example generation based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1658–1665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180777 SCHÄFER M, LENDERS V, and MARTINOVIC I. Experimental analysis of attacks on next generation air traffic communication[C]. The 11th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, Berlin, Germany, 2013: 253–271. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-38980-1_16. COSTIN A and FRANCILLON A. Ghost in the air (traffic): On insecurity of ADS-B protocol and practical attacks on ADS-B devices[C]. Black Hat, Las Vegas, USA, 2012: 1–10. 陈红松, 陈京九. 基于循环神经网络的无线网络入侵检测分类模型构建与优化研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1427–1433. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180691CHEN Hongsong and CHEN Jingjiu. Recurrent neural networks based wireless network intrusion detection and classification model construction and optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1427–1433. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180691 YING Xuhang, MAZER J, BERNIERI G, et al. Detecting ADS-B spoofing attacks using deep neural networks[C]. 2019 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security, Washington, USA, 2019: 187–195. doi: 10.1109/CNS.2019.8802732. HABLER E and SHABTAI A. Using LSTM encoder-decoder algorithm for detecting anomalous ADS-B messages[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 78: 155–173. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2018.07.004 丁建立, 邹云开, 王静, 等. 基于深度学习的ADS-B异常数据检测模型[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(12): 323220. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23220DING Jianli, ZOU Yunkai, WANG Jing, et al. ADS-B anomaly data detection model based on deep learning[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 323220. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23220 LI Tengyao, WANG Buhong, SHANG Fute, et al. Online sequential attack detection for ADS-B data based on hierarchical temporal memory[J]. Computers & Security, 2019, 87: 101599. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2019.101599 ZHANG Tao, WU Renbiao, LAI Ran, et al. Probability hypothesis density filter for radar systematic bias estimation aided by ADS-B[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 120: 280–287. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.09.012 SMITH M, STROHMEIER M, HARMAN J, et al. Safety vs. security: Attacking avionic systems with humans in the loop[J]. arXiv, 2019, 1905.08039. STROHMEIER M, MARTINOVIC I, FUCHS M, et al. Opensky: A swiss army knife for air traffic security research[C]. The 34th IEEE/AIAA Digital Avionics Systems Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 2015: 1–14. doi: 10.1109/DASC.2015.7311411. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
