EEG Feature Extraction Based on Brain Function Network and Sample Entropy
-
摘要:
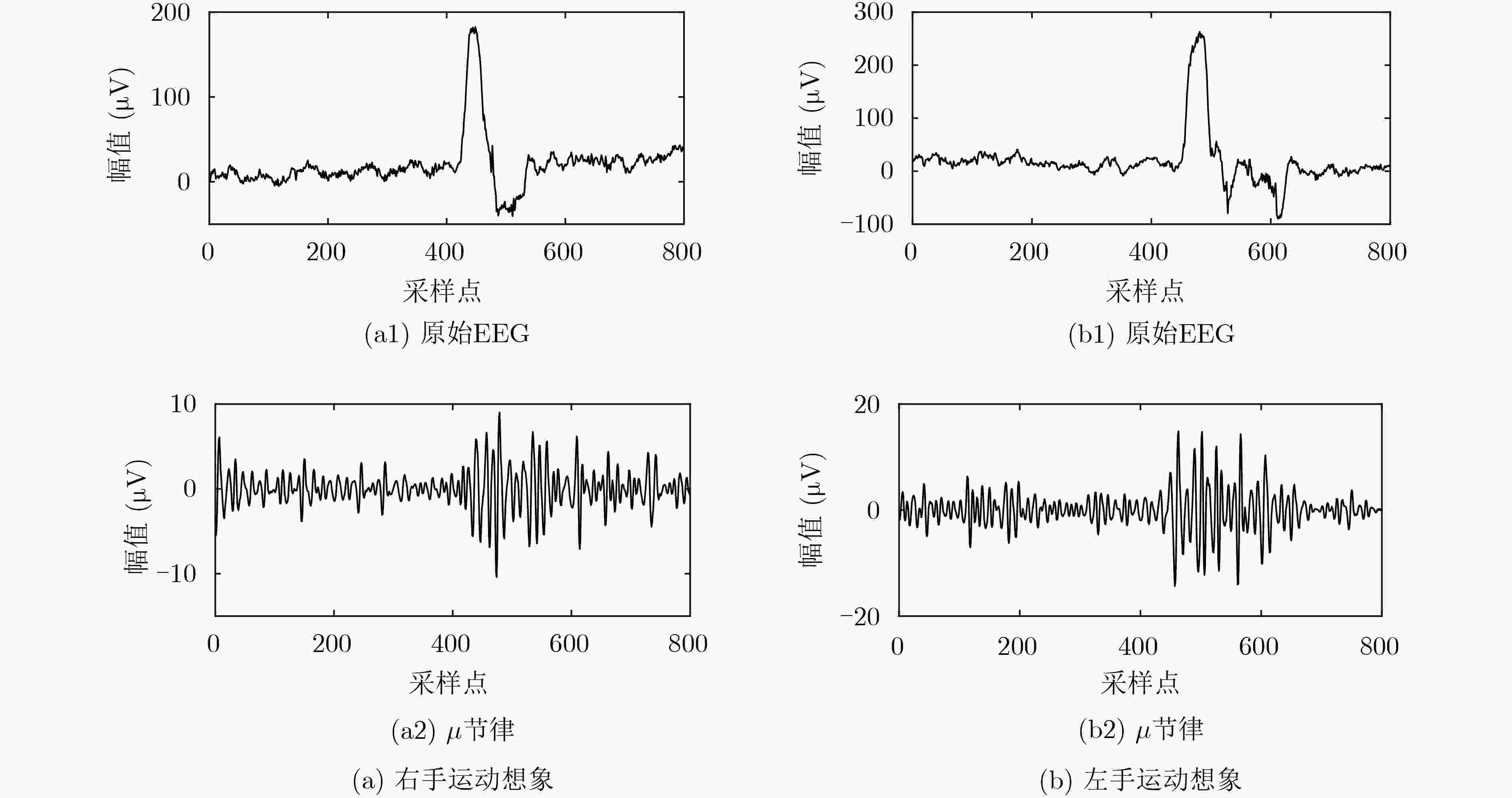
针对脑-机接口(BCI)研究中采用单一特征对运动想象脑电信号(EEG)识别率不高的问题,该文提出一种结合脑功能网络和样本熵的特征提取方法。根据事件相关同步/去同步(ERS/ERD)现象以及皮层与肢体运动想象间的对侧映射机制,选取小波包变换消噪重构后的
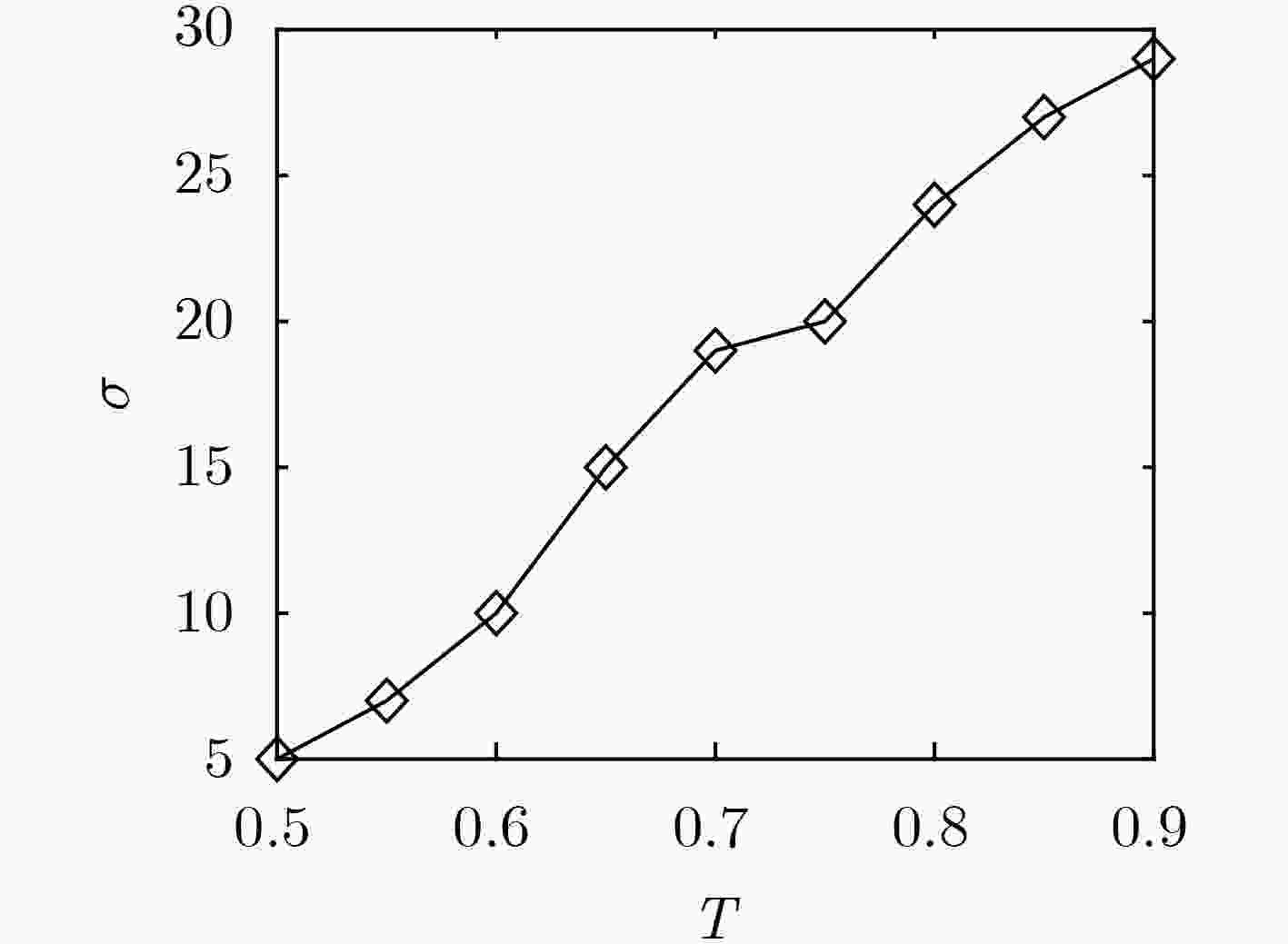
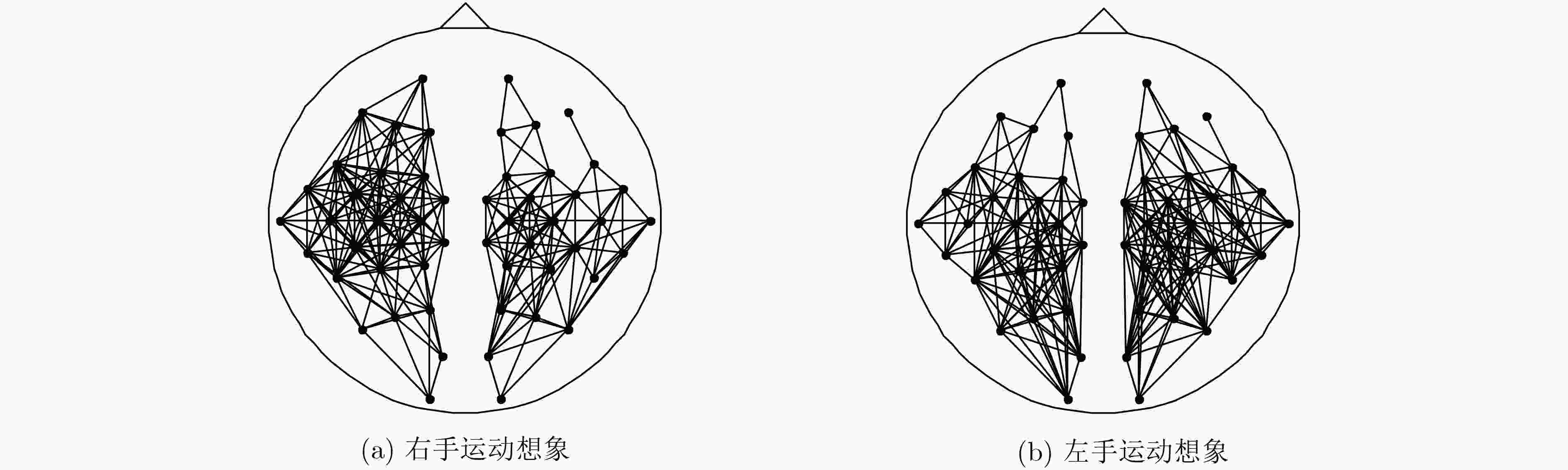
\begin{document}$ \mu$\end{document} 节律脑电信号,用左侧27个通道、右侧27个通道分别对左半球脑区和右半球脑区构建脑功能网络,计算网络的平均节点度和平均聚集系数作为运动想象的脑功能网络特征,并结合C3, C4通道
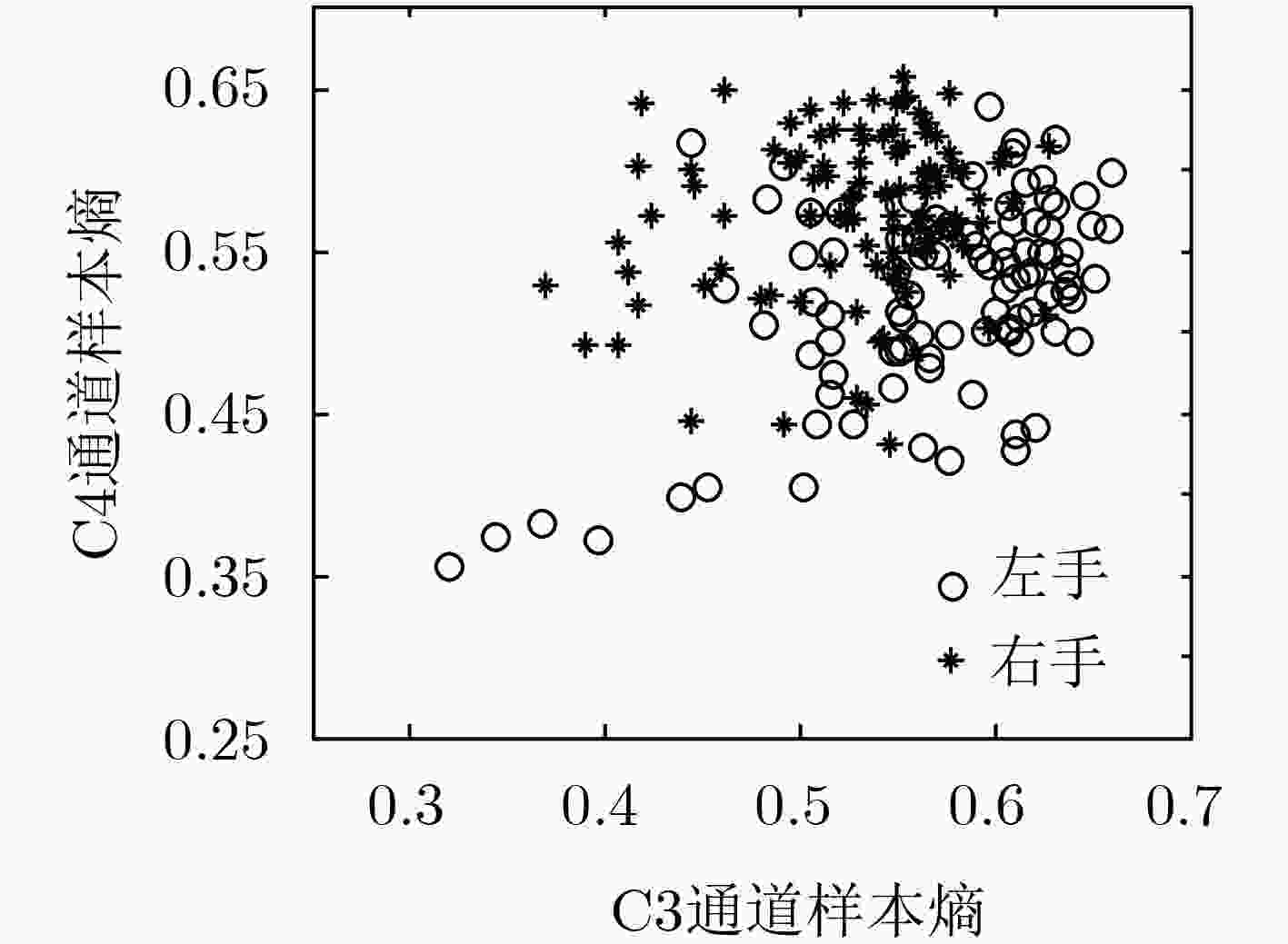
节律的样本熵构筑分布性和指向性相结合的特征向量。选用支持向量机(SVM)对左右手运动想象脑电信号进行分类,结果表明基于脑功能网络和样本熵的特征提取方法能够实现更优的分类效果,分类准确率最高可达90.27%。
-
关键词:
- 脑电信号 /
- 脑功能网络 /
- 样本熵 /
- 特征提取 /
- 事件相关同步/去同步
Abstract:For the low recognition rate of motor imagery ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) signals using single feature in Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) research, a feature extraction method combining brain function network and sample entropy is proposed. According to the neural mechanism appearing in Event Related Synchronization/Event Related Desynchronization (ERS/ERD) phenomenon and the contralateral mapping mechanism between cortex and limb motor imagery, the μ rhythm is denoised by wavelet packet transform. The brain function network is constructed for left hemispherical brain region and right hemispherical brain region by μ rhythm of 27 left channels and 27 right channels respectively. The mean node degree and the mean clustering coefficient are calculated as the brain function network characteristics, and the feature vectors combining the distribution and directivity are constructed by the sample entropy of C3 and C4 channels with the μ rhythm. The Support Vector Machine (SVM) is used to classify the left hand and right hand motor imagery EEG signals. The results show that the feature extraction method based on brain function network and sample entropy achieves better classification result, and the highest classification rate reached 90.27%.
-
表 1 不同特征向量平均正确识别率与方差(%)
特征向量 受试B 受试C 受试D 受试E 受试G 平均正确识别率 脑功能网络 75.37±1.02 79.58±1.54 80.71±1.90 74.42±1.39 82.32±0.58 78.48±7.89 样本熵 70.28±1.93 76.70±2.25 74.59±3.96 69.43±1.87 77.36±1.58 73.67±11.20 脑功能网络+样本熵 85.28±0.85 89.59±0.94 87.11±1.69 83.88±0.75 90.27±0.34 87.23±5.94 表 2 各受试不同特征t检验的p值
受试 (脑网络+样本熵,脑网络) (脑网络+样本熵,样本熵) B <0.01 <0.01 C <0.01 <0.01 D <0.01 <0.01 E <0.01 <0.01 G <0.01 <0.01 -
LUO Zhizeng, LU Xianju, and XI Xugang. EEG feature extraction based on a bilevel network: Minimum spanning tree and regional network[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(2): 203. doi: 10.3390/electronics9020203 谭平, 刘利枚, 郭璠, 等. Chernoff加权分类器框架在运动想象脑-机接口中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 488–494. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181132TAN Ping, LIU Limei, GUO Fan, et al. Applying Chernoff weighted classification frame method to motorimagery brain computer interface[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 488–494. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181132 唐贤伦, 李伟, 马伟昌, 等. 基于条件经验模式分解和串并行CNN的脑电信号识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1041–1048. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190124TANG Xianlun, LI Wei, MA Weichang, et al. Conditional empirical mode decomposition and serial parallel CNN for electroencephalogram signal recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1041–1048. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190124 MOURA A, LOPEZ S, OBEID I, et al. A comparison of feature extraction methods for EEG signals[C]. 2015 IEEE Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium, Philadelphia, USA, 2015: 1–2. doi: 10.1109/SPMB.2015.7405430. BANITALEBI A, SETAREHDAN S K, HOSSEIN-ZADEH G A. A technique based on chaos for brain computer interfacing[C]. The 2009 14th International CSI Computer Conference, Tehran, Iran, 2009: 464–469. doi: 10.1109/CSICC.2009.5349623. ABÁSOLO D, HORNERO R, GÓMEZ G, et al. Analysis of EEG background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients with Lempel–Ziv complexity and central tendency measure[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2006, 28(4): 315–322. 周静, 吴效明. 基于样本熵的睡眠呼吸暂停综合征脑电研究[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2016, 33(7): 722–725. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2016.07.017ZHOU Jing and WU Xiaoming. Electroencephalogram of sleep apnea syndrome based on sample entropy[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Physics, 2016, 33(7): 722–725. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2016.07.017 BIRBAUMER N. Breaking the silence: Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) for communication and motor control[J]. Psychophysiology, 2006, 43(6): 517–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2006.00456.x SPORNS O. Structure and function of complex brain networks[J]. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 2013, 15(3): 247–262. CHAOVALITWONGSE W A, POTTENGER R S, WANG Shouyi, et al. Pattern- and network-based classification techniques for multichannel medical data signals to improve brain diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics- Part A: Systems and Humans, 2011, 41(5): 977–988. doi: 10.1109/tsmca.2011.2106118 STANLEY M L, SIMPSON S L, DALE D, et al. Changes in brain network efficiency and working memory performance in aging[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0123950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123950 杨硕, 艾娜, 王磊, 等. 脑疲劳状态的脑功能网络特征分类研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2018, 35(2): 171–175.YANG Shuo, AI Na, WANG Lei, et al. Research on classification of brain functional network features during mental fatigue[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 35(2): 171–175. 周鹏, 葛家怡, 曹红宝, 等. 基于样本熵的运动想象分类研究[J]. 信息与控制, 2008, 37(2): 191–196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2008.02.013ZHOU Peng, GE Jiayi, CAO Hongbao, et al. Classification of motor imagery based on sample entropy[J]. Information and Control, 2008, 37(2): 191–196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2008.02.013 PINCUS S. Approximate entropy (ApEn) as a complexity measure[J]. Chaos, 1995, 5(1): 110–117. BLANKERTZ B, DORNHEGE G, KRAULEDAT M, et al. The non-invasive Berlin Brain–Computer Interface: Fast acquisition of effective performance in untrained subjects[J]. NeuroImage, 2007, 37(2): 539–550. JOCHUMSEN M, ROVSING C, ROVSING H, et al. Classification of hand grasp kinetics and types using movement-related cortical potentials and EEG rhythms[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2017, 2017: 7470864. doi: 10.1155/2017/7470864 NAGAMORI S and TANAKA H. Analysis method for ERD in mu-rhythm detection in motor imagery brain-computer interface[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Budapest, Hungary, 2017: 867–870. doi: 10.1109/SMC.2016.7844349. ZHANG Haihong, CHIN Z Y, ANG K K, et al. Optimum spatio-spectral filtering network for brain-computer interface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(1): 52–63. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2084099 李静, 王金甲, 李慧. 融合脑电特征的弹性网特征选择和分类[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016, 33(3): 413–419. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160070LI Jing, WANG Jinjia, and LI Hui. Selection and classification of elastic net feature with fused electroencephalogram features[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(3): 413–419. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160070 袁玲, 杨帮华, 马世伟. 基于HHT和SVM的运动想象脑电识别[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2010, 31(3): 649–654. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2010.03.029YUAN Ling, YANG Banghua, and MA Shiwei. Discrimination of movement imagery EEG based on HHT and SVM[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2010, 31(3): 649–654. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2010.03.029 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
