Prediction of Passive Intermodulation Level Based on Chaos Method
-
摘要:
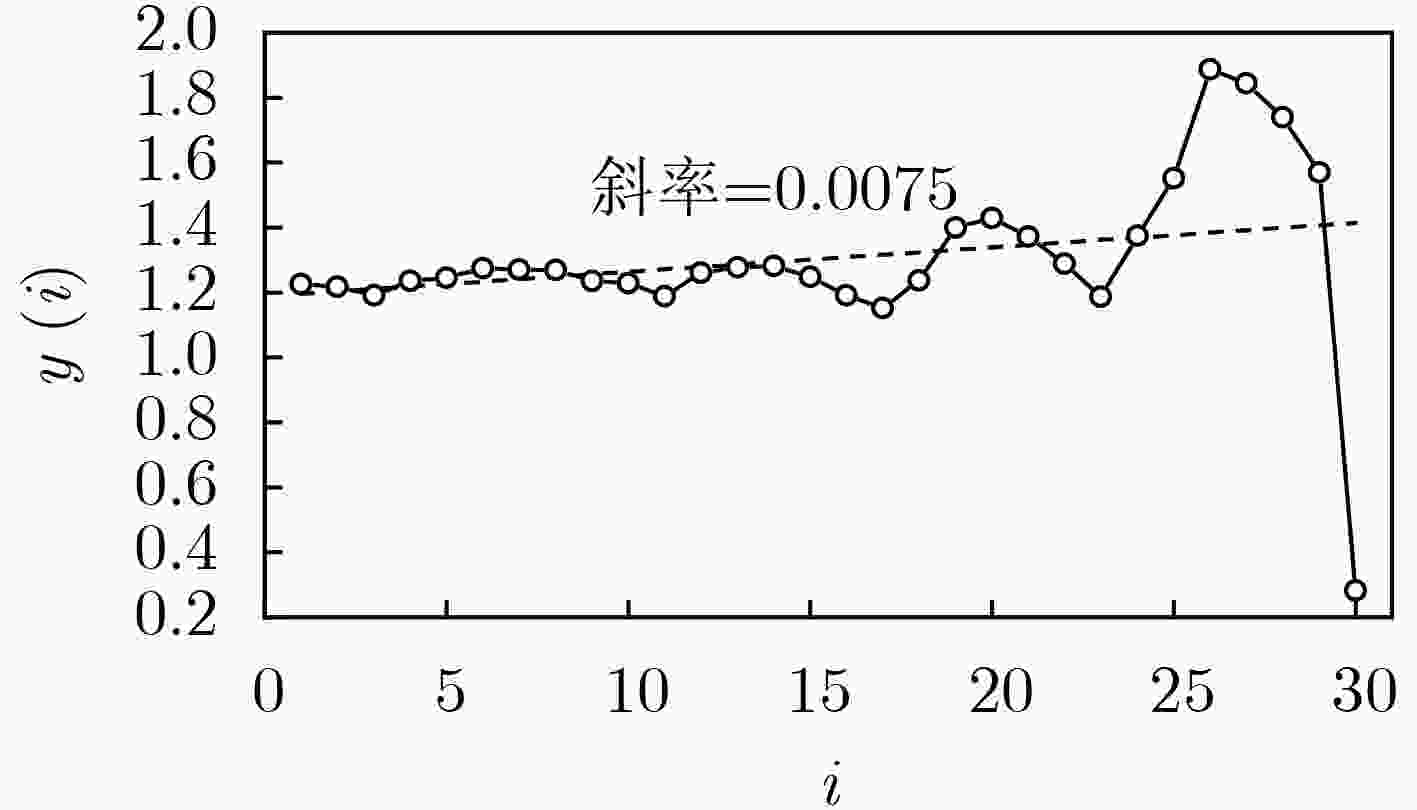
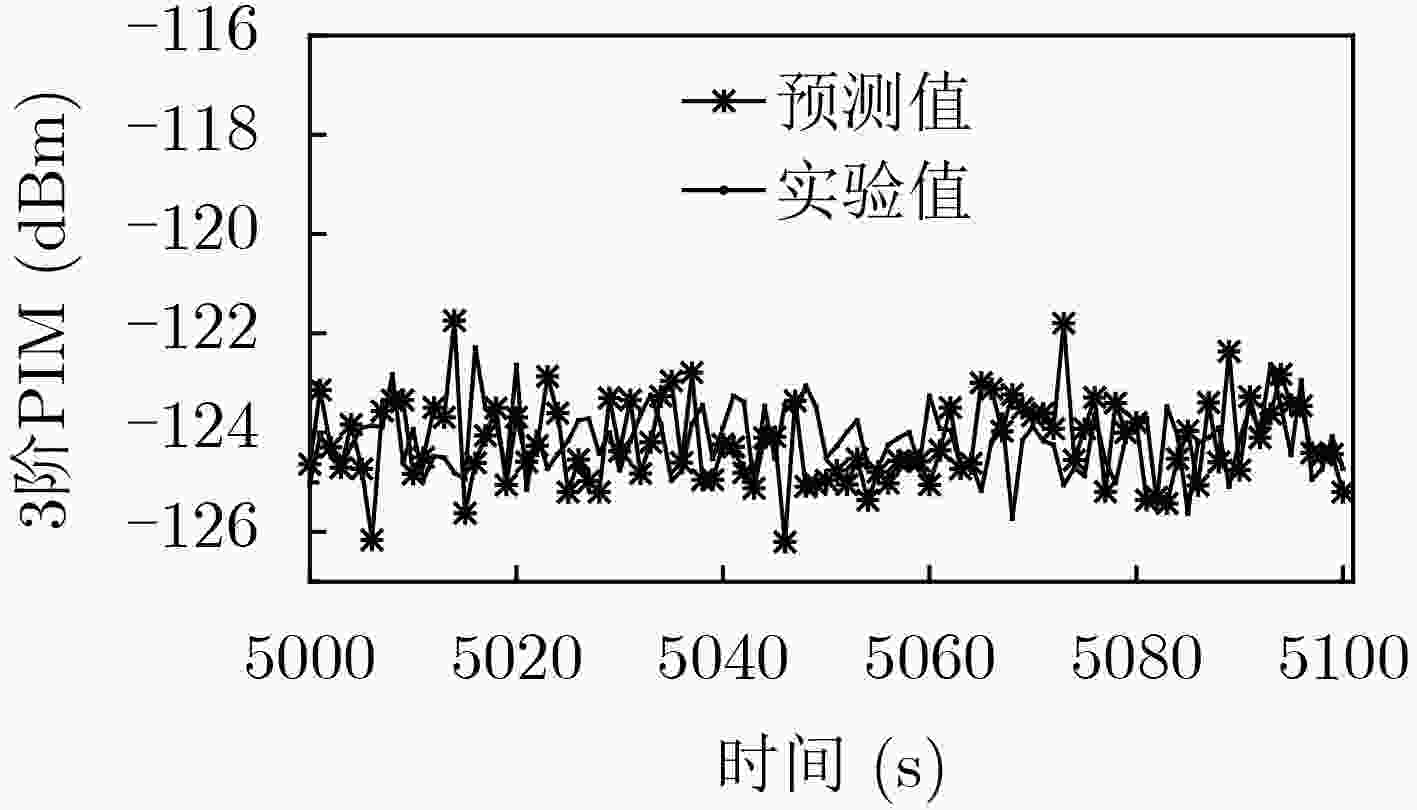
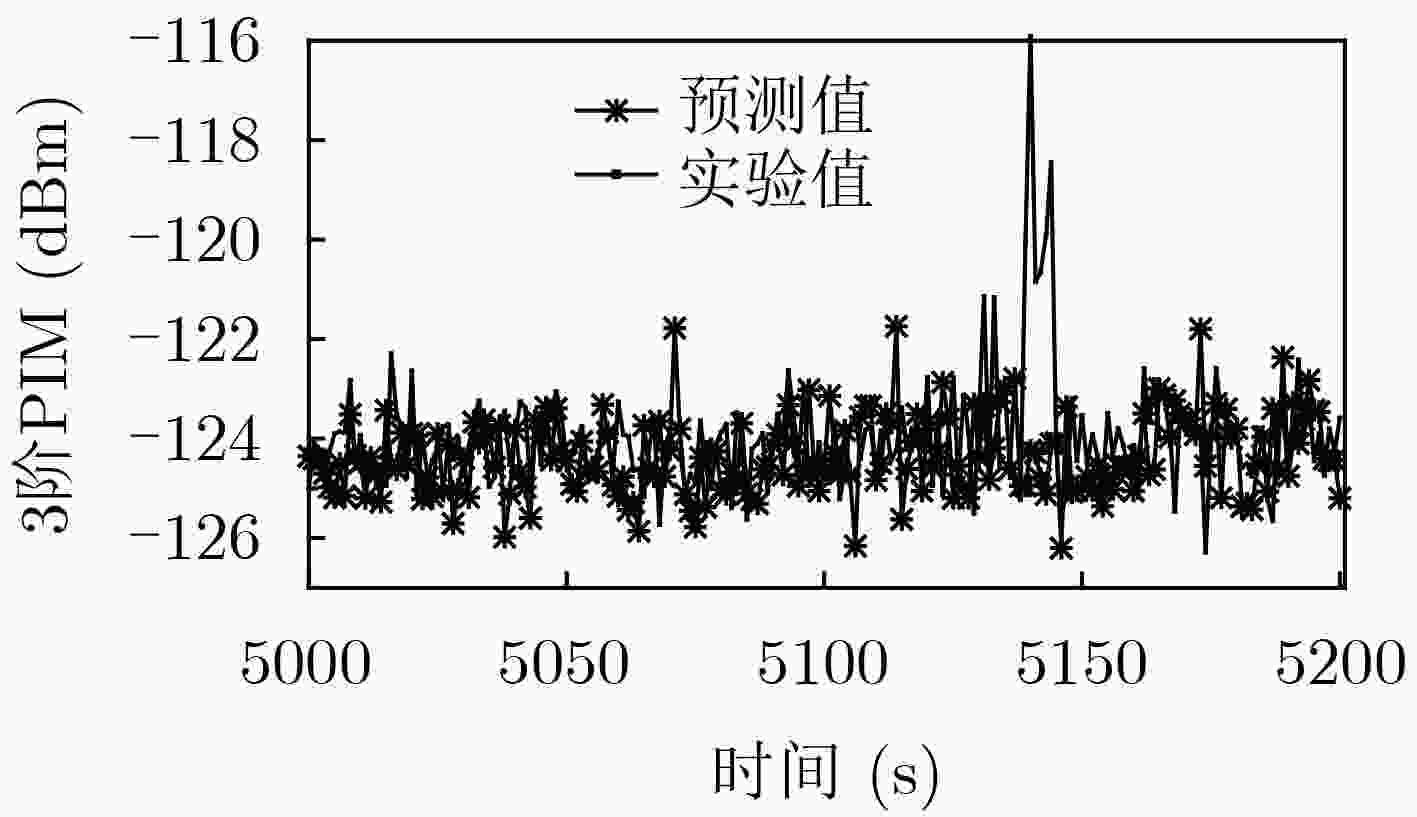
该文以通信系统中常用的典型微波部件——同轴连接器为研究对象,基于混沌理论对获得的同轴连接器的无源互调(PIM)功率时间序列进行分析,验证了使用混沌理论预测无源互调的有效性。首先通过实验系统获得同轴连接器的3阶无源互调功率时间序列,并对得到的实验数据进行相空间重构,确定该时间序列的最佳嵌入维数m和延迟时间τ。然后,结合最佳嵌入维数和延迟时间,分别构建相图和使用小数据量法计算该时间序列的最大Lyapunov指数,从而从定性和定量角度验证了该无源互调功率时间序列具有混沌特性。在此基础上,基于获得的最大Lyapunov指数对该无源互调功率时间序列进行混沌预测,在最大可预测尺度范围内,理论预测值与实验值最大误差为2.61%,表明采用混沌方法预测无源互调功率效果较好。该文提出的使用混沌理论预测通信系统中微波部件无源互调功率的方法,为开展无源互调抑制技术研究,提高通信系统的性能提供了新思路。
-
关键词:
- 无线通信 /
- 无源互调 /
- 混沌 /
- Lyapunov指数 /
- 相空间
Abstract:Passive InterModulation (PIM) products are spurious frequency signals which occur in microwave and radio frequency communication system. And it is noticed that PIM levels have the characteristic of changing with time. In order to find out the relationship between PIM level and time, as the typical microwave component which more often causes PIM in communication system, coaxial connector is chosen and analyzed using chaotic method. Firstly, the third order PIM level time series of coaxial connector is obtained by PIM measurement system. Based on the experimental data, the phase space is reconstructed and the optimal embedding dimension m and delay time τ are confirmed. Secondly, the largest Lyapunov exponent is calculated by the method named the small data sets with embedding dimension m and delay time τ. And from the qualitative and quantitative perspective, it is verified that the passive intermodulation level time series have the characteristic of chaos. Lastly, the prediction of PIM level with chaotic method is performed on the basis of the largest Lyapunov exponent. And the maximum error between the theoretical prediction value and the experimental value is 2.61% within the maximum predictable scale, indicating that the chaotic prediction is an effective way. The method that predicts the PIM level of microwave components in the communication system discussed in this paper provides a new way of studying the PIM mitigation technique for communication system and provides a new idea for improving the performance of the communication system.
-
Key words:
- Wireless communication /
- Passive InterModulation (PIM) /
- Chaos /
- Lyapunov exponent /
- Phase space
-
LUI P L. Passive intermodulation interference in communication systems[J]. Electronics & Communication Engineering Journal, 1990, 2(3): 109–118. 张世全, 傅德民, 葛德彪. 无源互调干扰对通信系统抗噪性能的影响[J]. 电波科学学报, 2002, 17(2): 138–142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2002.02.009ZHANG Shiquan, FU Demin, and GE Debiao. The effects of passive intermodulation interference on the anti-noise property of communications systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2002, 17(2): 138–142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2002.02.009 BOYHAN J W, HENZING H F, and KODURU C. Satellite passive intermodulation: Systems considerations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1996, 32(3): 1058–1064. doi: 10.1109/7.532264 ZHAO Xiaolong, HE Yongning, YE Ming, et al. Analytic passive intermodulation model for flange connection based on metallic contact nonlinearity approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(7): 2279–2287. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2668402 VICENTE C and HARTNAGEL H L. Passive-intermodulation analysis between rough rectangular waveguide flanges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(8): 2515–2525. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.852771 CHEN Xiong, HE Yongning, YANG Sen, et al. Analytic passive intermodulation behavior on the coaxial connector using monte carlo approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2018, 60(5): 1207–1214. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2018.2809449 ZHANG Kai, LI Tuanjie, and JIANG Jie. Passive intermodulation of contact nonlinearity on microwave connectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2018, 60(2): 513–519. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2017.2725278 张世全, 葛德彪. 通信系统无源非线性引起的互调干扰[J]. 陕西师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 32(1): 58–62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-4291.2004.01.016ZHANG Shiquan and GE Debiao. Intermodulation interference due to passive nonlinearity in communication systems[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2004, 32(1): 58–62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-4291.2004.01.016 王海宁, 梁建刚, 王积勤, 等. 高功率微波条件下的无源互调问题综述[J]. 微波学报, 2005, 21(S1): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6122.2005.z1.001WANG Haining, LIANG Jiangang, WANG Jiqin, et al. Review of passive intermodulation in HPM condition[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2005, 21(S1): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6122.2005.z1.001 田露. 星上无源互调干扰数字抑制技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京理工大学, 2017.TIAN Lu. Digital suppression technique of passive intermodulation interference for satellite systems[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Beijing Institute of Technology, 2017. 李玲玲, 马东娟, 李志刚. 触点动态接触电阻时间序列混沌预测[J]. 电工技术学报, 2014, 29(9): 187–193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.09.027LI Lingling, MA Dongjuan, and LI Zhigang. Chaotic predication of dynamic contact resistance times series on contacts[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(9): 187–193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.09.027 曾以成, 成德武, 谭其威. 简洁无电感忆阻混沌电路及其特性[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 862–869. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190859ZENG Yicheng, CHENG Dewu, and TAN Qiwei. A simple inductor-free memristive chaotic circuit and its characteristics[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 862–869. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190859 眭萍, 郭英, 李红光, 等. 基于混沌吸引子重构和Low-rank聚类的跳频信号电台分选[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2965–2971. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180947SUI Ping, GUO Ying, LI Hongguang, et al. Frequency-hopping transmitter classification based on chaotic attractor reconstruction and low-rank clustering[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2965–2971. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180947 MAZZINI G, SETTI G, and ROVATTI R. Chaotic complex spreading sequences for asynchronous DS-CDMA. I. System modeling and results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 1997, 44(10): 937–947. doi: 10.1109/81.633883 SCHIMMING T and HASLER M. Chaos communication in the presence of channel noise[J]. Journal of Signal Process, 2000, 4(1): 21–28. ROSENSTEIN M T, COLLINS J J, and DE LUCA C J. A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets[J]. Physica D, 1993, 65(1/2): 117–134. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(93)90009-P WOLF A, SWIFT J B, SWINNEY H L, et al. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1985, 16(3): 285–317. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(85)90011-9 SATO S, SANO M, and SAWADA Y. Practical methods of measuring the generalized dimension and the largest Lyapunov exponent in high dimensional chaotic systems[J]. Progress of Theoretical Physics, 1987, 77(1): 1–5. doi: 10.1143/ptp.77.1 ZHANG Jun, LAM K C, YAN W J, et al. Time series prediction using Lyapunov exponents in embedding phase space[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2004, 30(1): 1–15. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7906(03)00015-6 CAO Liangyue. Practical method for determining the minimum embedding dimension of a scalar time series[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1997, 110(1/2): 43–50. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2789(97)00118-8 KIM H S, EYKHOLT R, and SALAS J D. Nonlinear dynamics, delay times, and embedding windows[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1999, 127(1/2): 48–60. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2789(98)00240-1 龚祝平. 混沌时间序列的平均周期计算方法[J]. 系统工程, 2010, 28(12): 111–113.GONG Zhuping. The calculating method of the average period of chaotic time series[J]. Systems Engineering, 2010, 28(12): 111–113. 张春涛, 刘学飞, 向瑞银, 等. 基于最大互信息的混沌时间序列多步预测[J]. 控制与决策, 2012, 27(6): 941–944.ZHANG Chuntao, LIU Xuefei, XIANG Ruiyin, et al. Multi-step-prediction of chaotic time series based on maximized mutual information[J]. Control and Decision, 2012, 27(6): 941–944. -





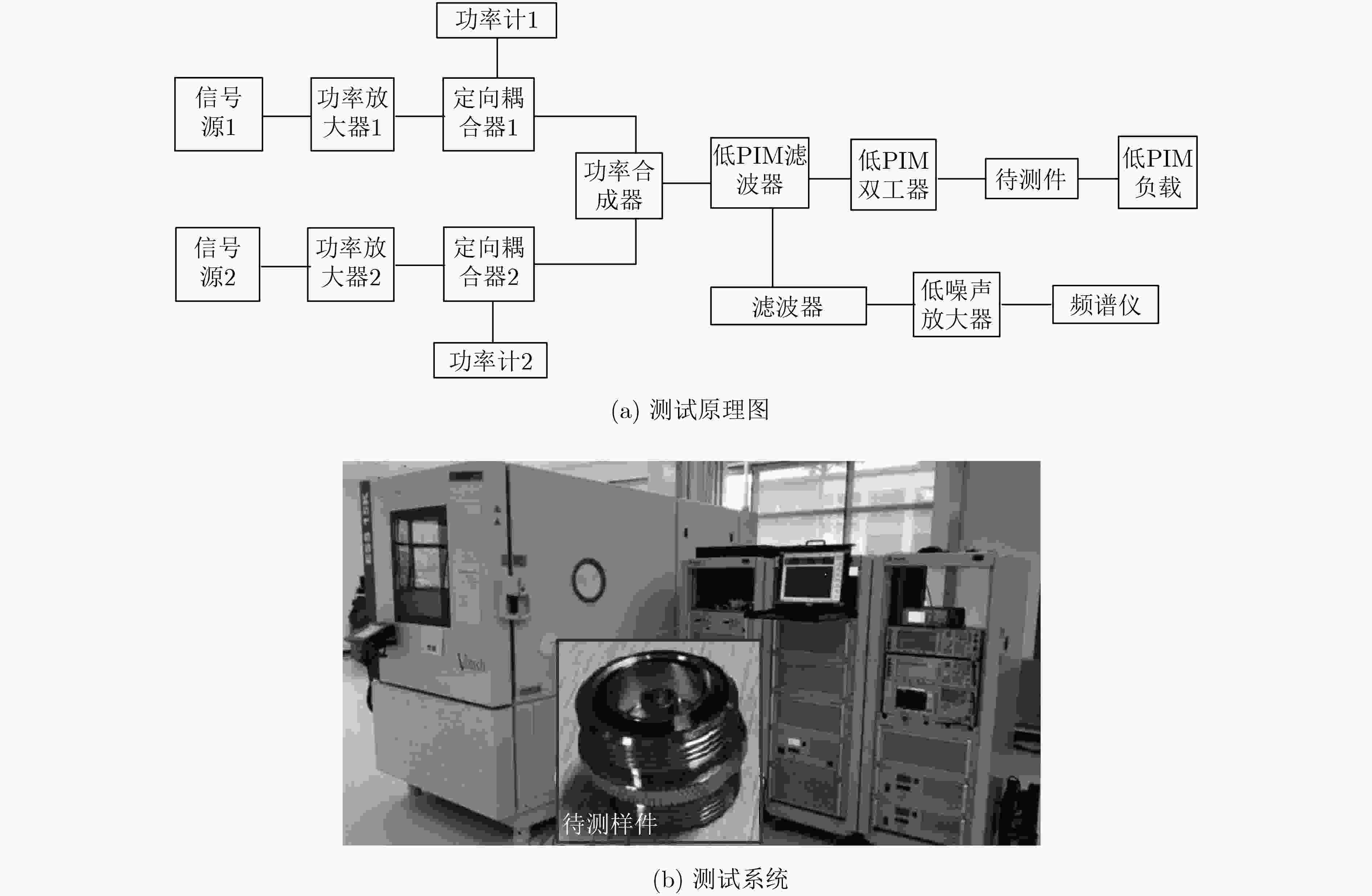
 下载:
下载:
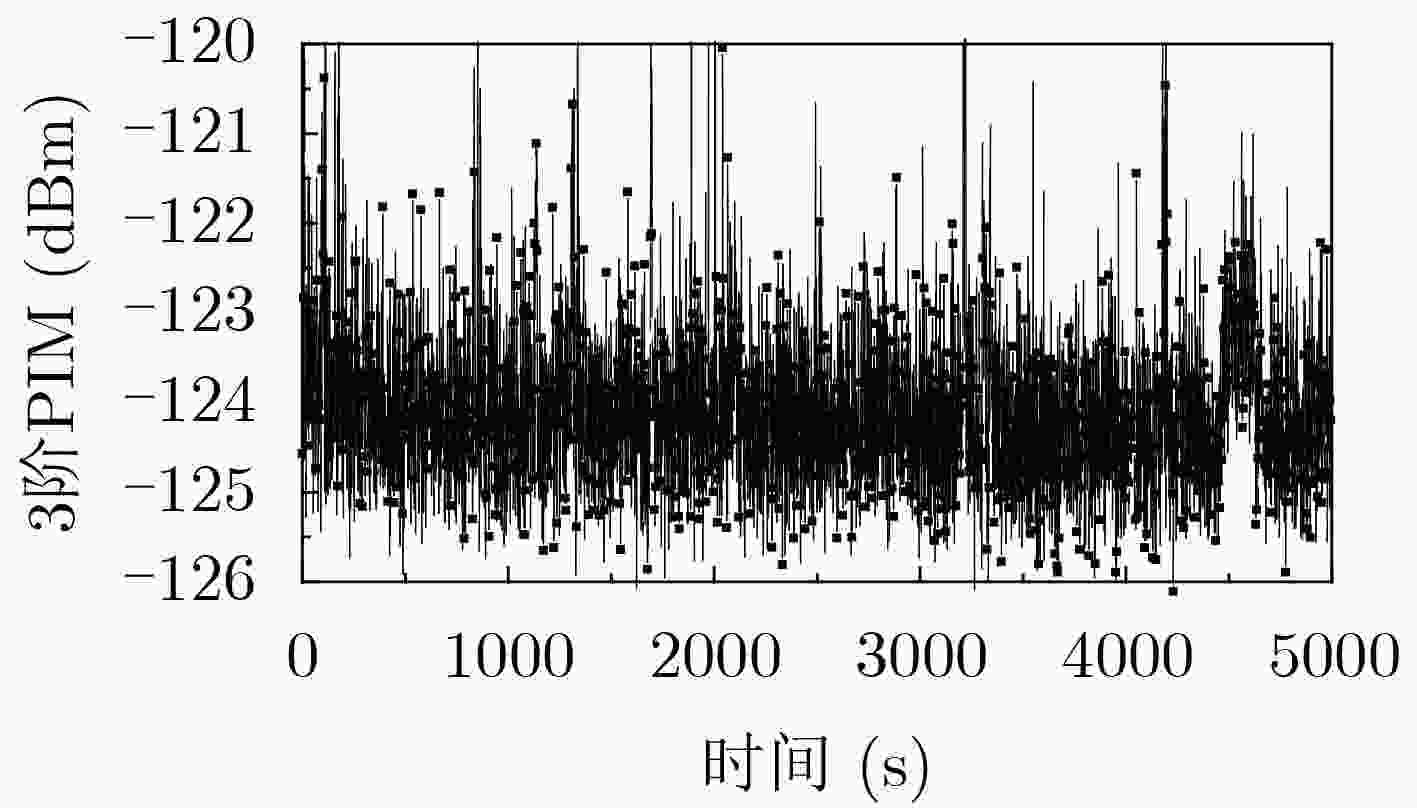
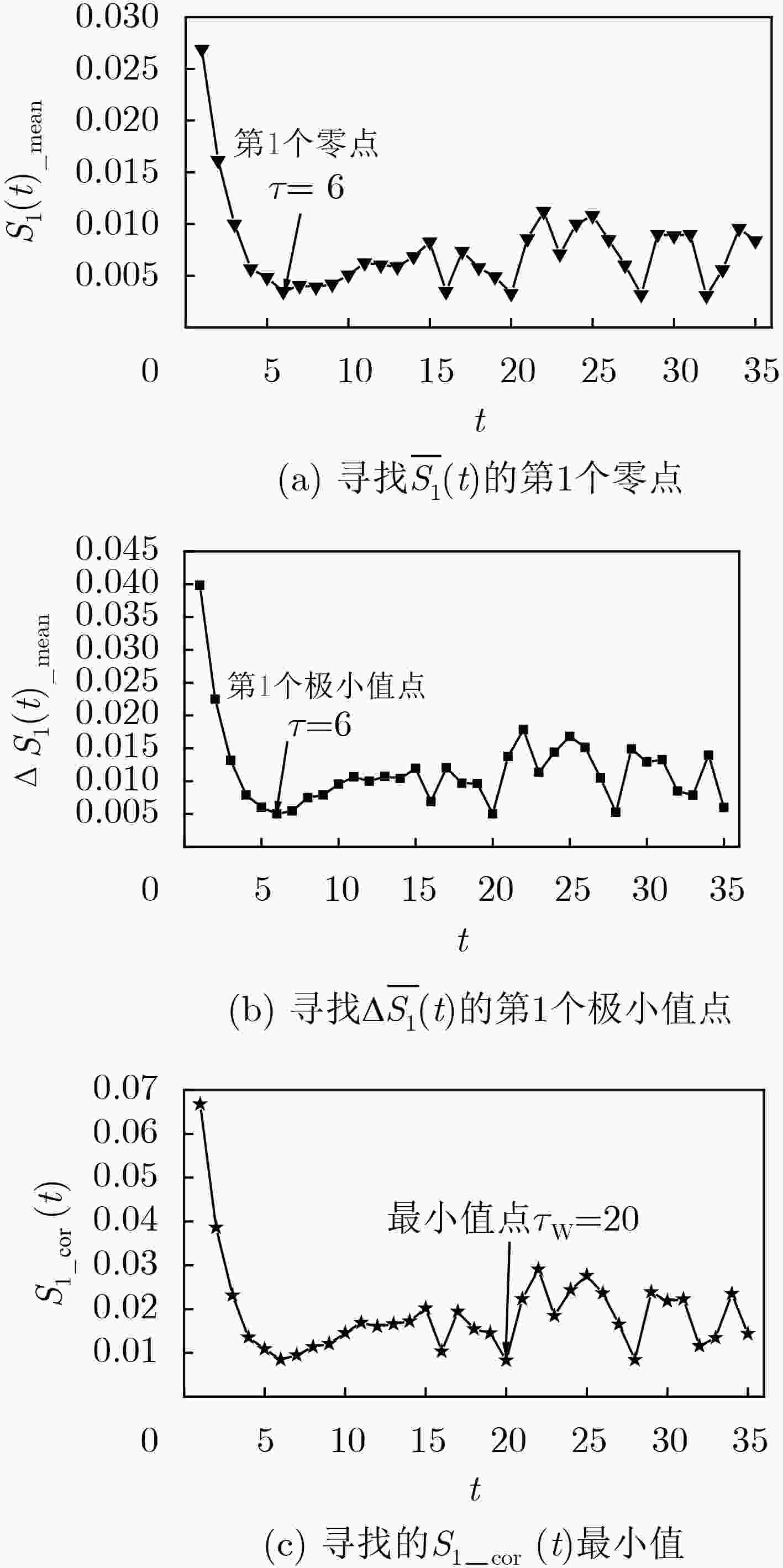
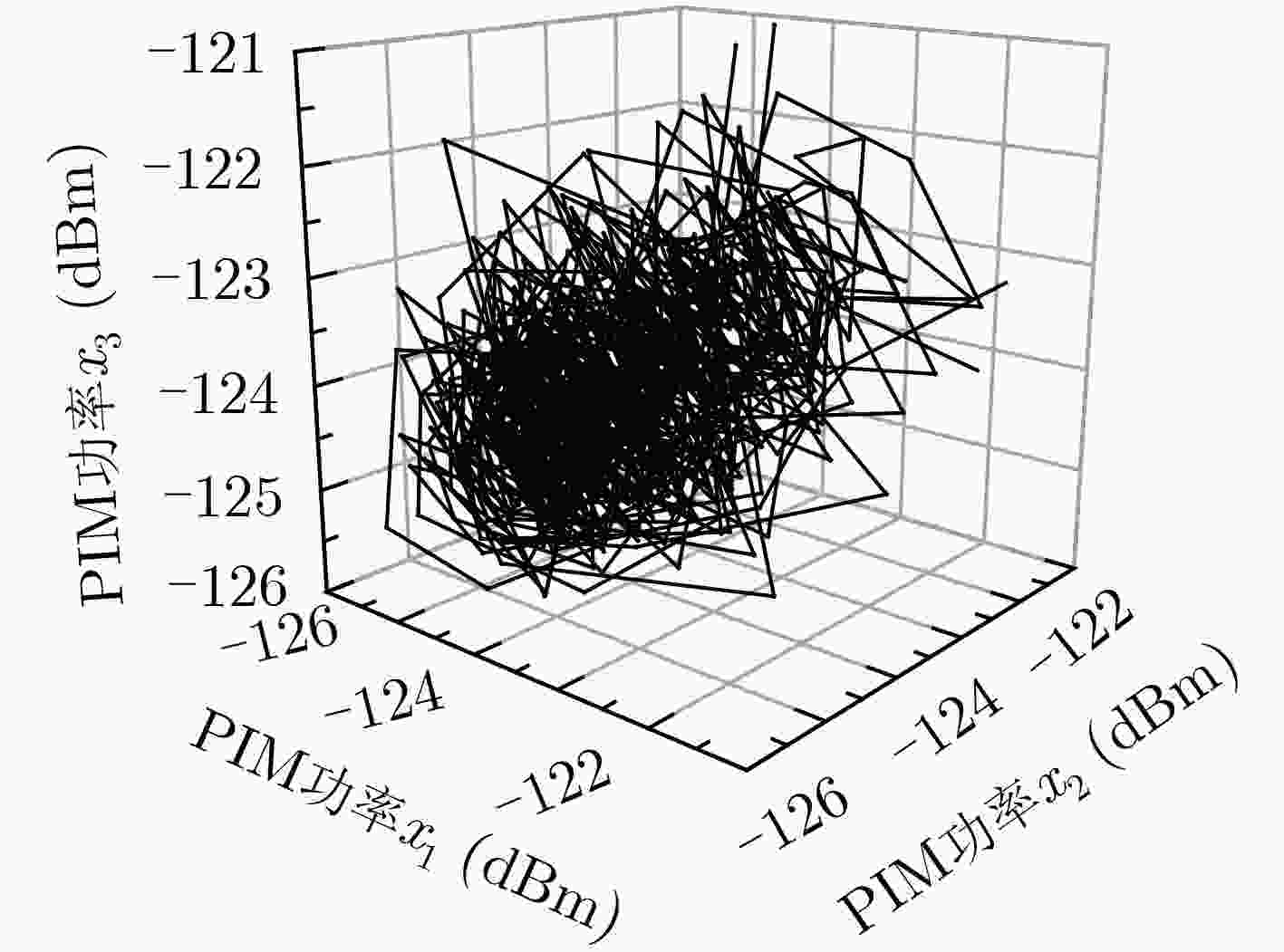


 下载:
下载:
