Semantic Part Constraint for Person Re-identification
-
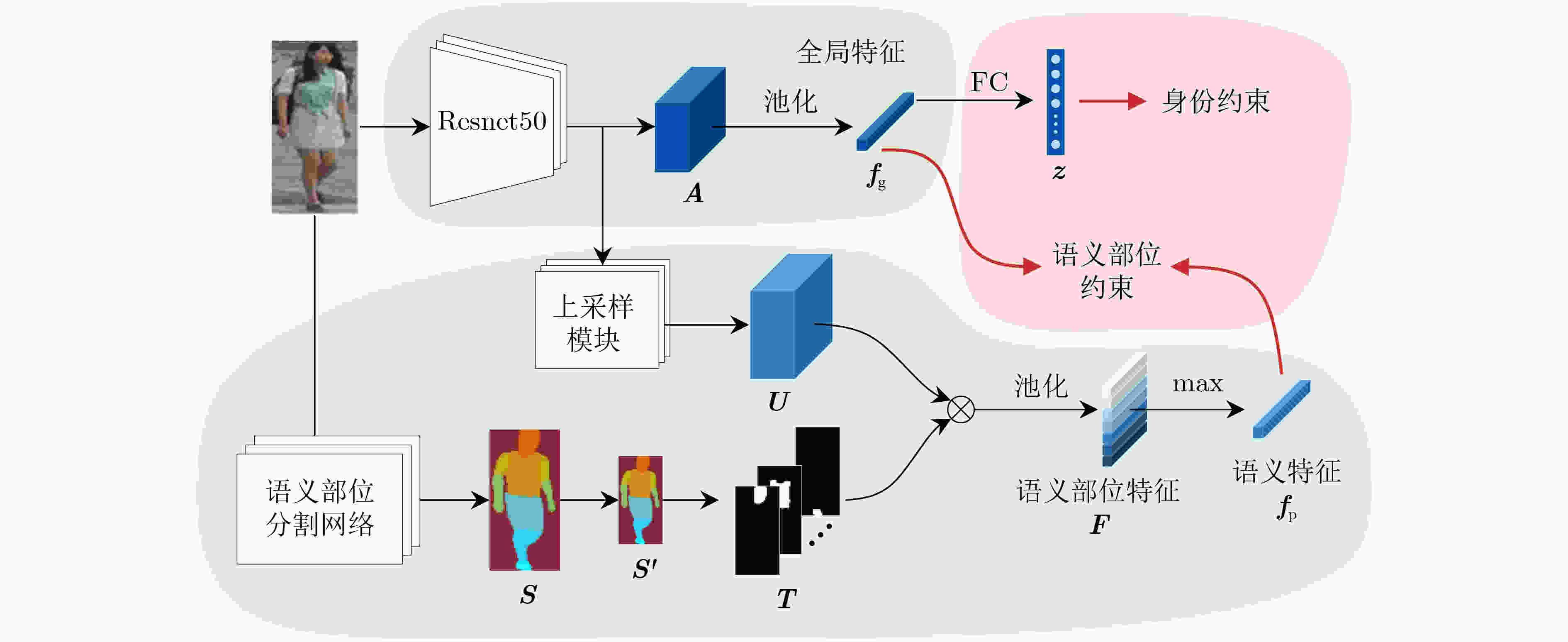
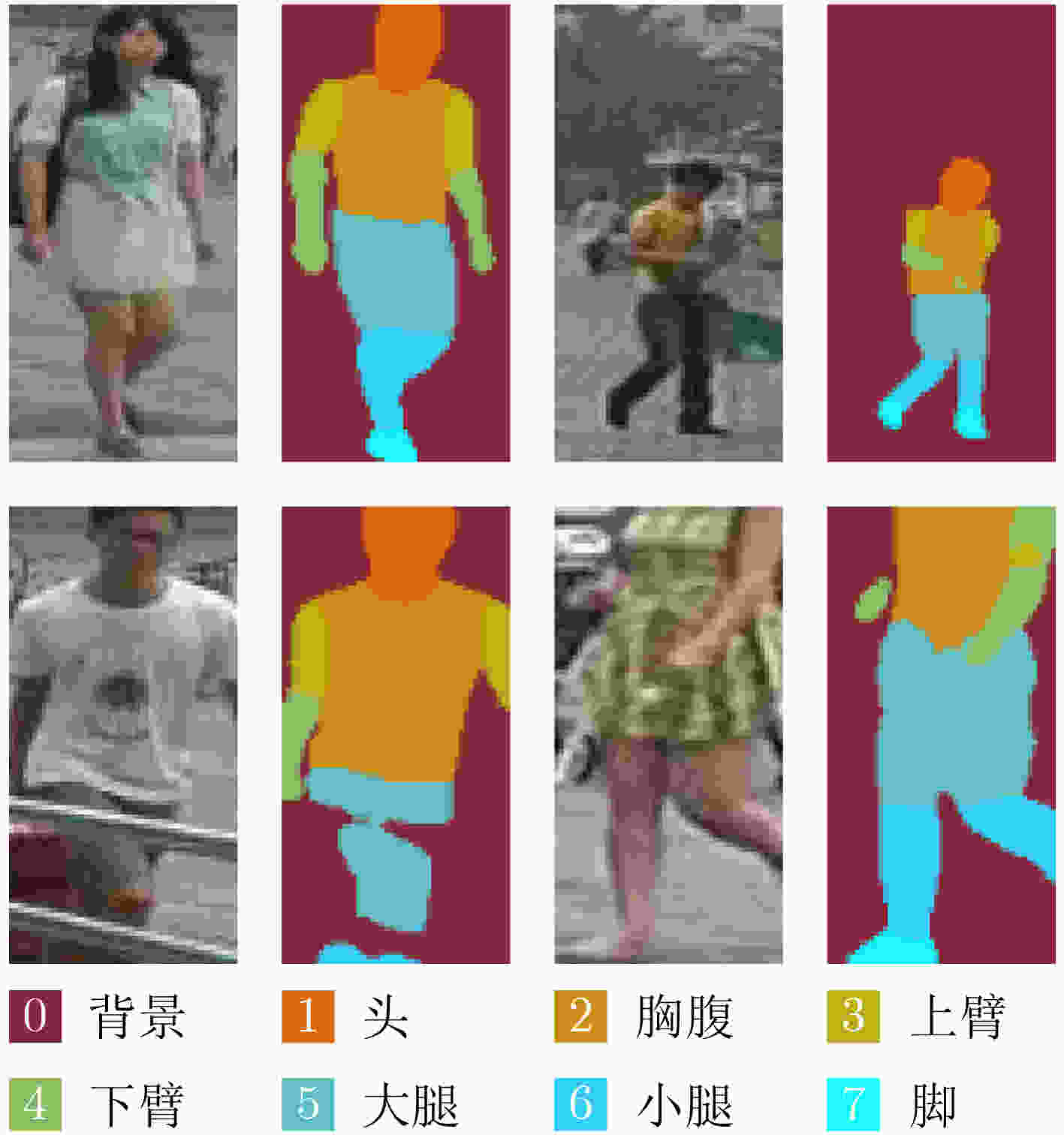
摘要: 为减轻行人图片中的背景干扰,使网络着重于行人前景并且提高前景中人体部位的利用率,该文提出引入语义部位约束(SPC)的行人再识别网络。在训练阶段,首先将行人图片同时输入主干网络和语义部位分割网络,分别得到行人特征图和部位分割图;然后,将部位分割图与行人特征图融合,得到语义部位特征;接着,对行人特征图进行池化得到全局特征;最后,同时使用身份约束和语义部位约束训练网络。在测试阶段,由于语义部位约束使得全局特征拥有部位信息,因此测试时仅使用主干网络提取行人的全局信息即可。在大规模公开数据集上的实验结果表明,语义部位约束能有效使得网络提高辨别行人身份的能力并且缩减推断网络的计算花费。与现有方法比较,该文网络能更好地抵抗背景干扰,提高行人再识别性能。Abstract: In order to alleviate the background clutter in pedestrian images, and make the network focus on pedestrian foreground to improve the utilization of human body parts in the foreground. In this paper, a person re-identification network is proposed that introduces Semantic Part Constraint(SPC). Firstly, the pedestrian image is input into the backbone network and the semantic part segmentation network at the same time, and the pedestrian feature map and the part segmentation label are obtained respectively. Secondly, the part segmentation label and the pedestrian feature maps are merged to obtain the semantic part feature. Thirdly, the pedestrian feature map is obtained and the global average pooling is used to gain global features. Finally, the network is trained using both identity constraint and semantic part constraint. Since the semantic part constraint makes the global features obtain the part information, only the backbone network can be used to extract the features of the pedestrian during the test. Experiments on large-scale datasets show that semantic part constraints can effectively make the network improve the ability to identify pedestrians and reduce the computational cost of inferring networks. Compared with the state of art, the proposed network can better resist background clutter and improve person re-identification performance.
-
表 1 在Market-1501数据集上的对比实验(%)
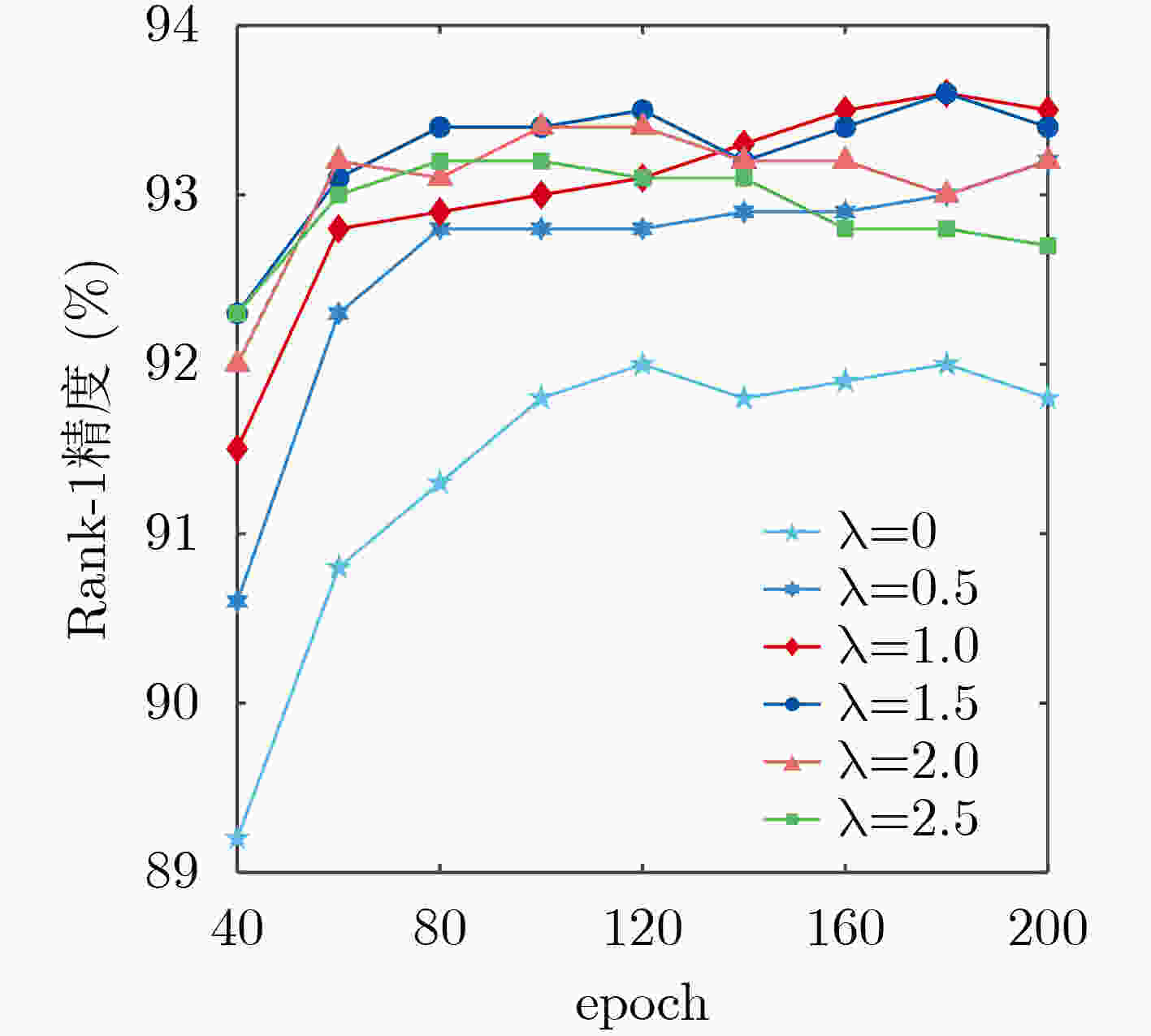
实验编号 行人特征 网络约束 Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 mAP 1 ${{{f}}_{\rm{g}}}$ ${L_{{\rm{id}}}}$ 92.0 96.9 98.2 80.4 2 ${{{C}}_f}$ ${L_{{\rm{id}}}}$ 92.7 97.5 98.6 80.6 3 ${{{f}}_{\rm{g}}}$ ${L_{{\rm{id}}}} + {L_{{\rm{sp}}}}$ 93.6 97.6 98.7 83.6 表 2 不同网络测试时长对比(ms)
方法 批次特征提取耗时 复现SPReID 82.87 本文网络 9.45 表 3 不同方法在两个数据集上的性能比较(%)
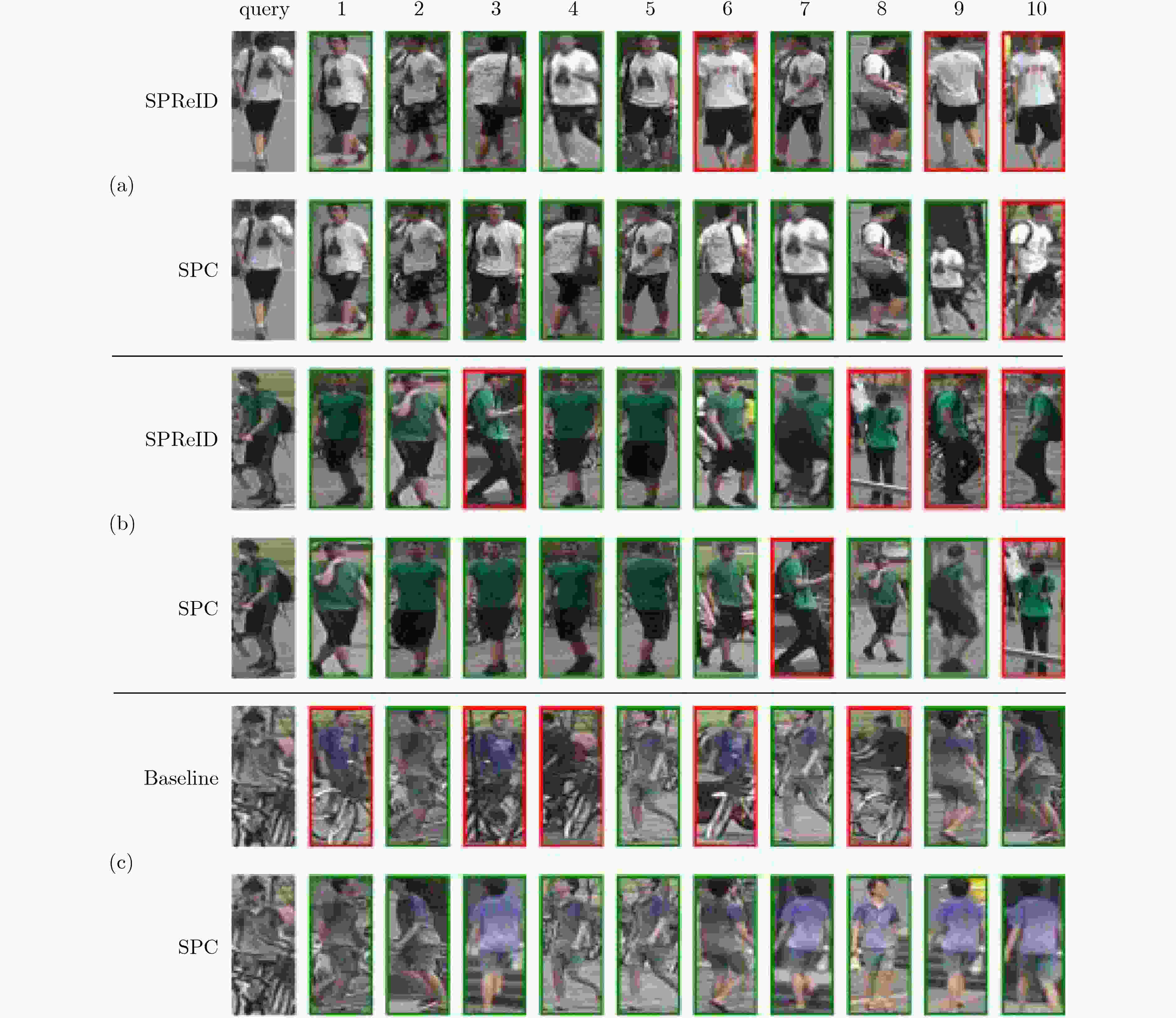
方法 Market-1501 DukeMTMC-reID Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP VIM[11] 79.5 59.9 68.9 49.3 SVDNet[12] 82.3 62.1 76.7 56.8 APR[3] 84.3 64.7 70.7 51.2 FMN[13] 86.0 67.1 74.5 56.9 PSE[14] 87.7 69.0 79.8 62.0 PN-GAN[15] 89.4 72.6 73.6 53.2 CamStyle[16] 89.5 71.6 78.3 57.6 HA-CNN[17] 91.2 75.7 80.5 63.8 Part-Aligned[4] 91.7 79.6 84.4 69.3 SPReID[5] 92.5 81.3 84.4 71.0 AHR[18] 93.1 76.2 81.7 65.9 本文方法 93.6 83.6 85.4 71.3 -
LIAO Shengcai, HU Yang, ZHU Xiangyu, et al. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, America, 2015: 2197–2206. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298832. 陈莹, 许潇月. 基于双向参考集矩阵度量学习的行人再识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 394–402. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190159CHEN Ying and XU Xiaoyue. Matrix metric learning for person re-identification based on bidirectional reference set[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 394–402. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190159 LIN Yutian, ZHENG Liang, ZHENG Zhedong, et al. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity Learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 151–161. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.006 SUH Y, WANG Jingdong, TANG Siyu, et al. Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 402–419. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_25. KALAYEH M M, BASARAN E, GOKMEN M, et al. Human semantic parsing for person re-identification[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, America, 2018: 1062–1071. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00117. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, America, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. FU Jun, LIU Jing, TIAN Haijie, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, America, 2019: 3146–3154. GÜLER R A, NEVEROVA N, and KOKKINOS I. DensePose: Dense human pose estimation in the wild[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, America, 2018: 7297–7306. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00762. ZHENG Liang, SHEN Liyue, TIAN Lu, et al. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1116–1124. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.133. ZHENG Zhedong, ZHENG Liang, and YANG Yi. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3754–3762. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.405. ZHENG Zhedong, ZHENG Liang, and YANG Yi. A discriminatively learned CNN embedding for person reidentification[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2018, 14(1): 13. doi: 10.1145/3159171 SUN Yifan, ZHENG Liang, DENG Weijian, et al. SVDNet for pedestrian retrieval[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3800–3808. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.410. DING Guodong, KHAN S, TANG Zhenmin, et al. Feature mask network for person re-identification[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 137: 91–98. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.02.015 SARFRAZ M S, SCHUMANN A, EBERLE A, et al. A pose-sensitive embedding for person re-identification with expanded cross neighborhood re-ranking[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, America, 2018: 420–429. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00051. QIAN Xuelin, FU Yanwei, XIANG Tao, et al. Pose-normalized image generation for person re-identification[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 650–667. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_40. ZHONG Zhun, ZHENG Liang, ZHENG Zhedong, et al. CamStyle: A novel data augmentation method for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(3): 1176–1190. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2874313 LI Wei, ZHU Xiatian, and GONG Shaogang. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, America, 2018: 2285–2294. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00243. 陈鸿昶, 吴彦丞, 李邵梅, 等. 基于行人属性分级识别的行人再识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2239–2246. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180740CHEN Hongchang, WU Yancheng, LI Shaomei, et al. Person re-identification based on attribute hierarchy recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2239–2246. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180740 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
