|
CHUA L O. Memristor—the missing circuit element[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5): 507–519. doi: 10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337
|
|
CHUA L O and KANG S M. Memristive devices and systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1976, 64(2): 209–223. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1976.10092
|
|
STRUKOV D B, SNIDER G S, STEWART D R, et al. The missing memristor found[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 80–83. doi: 10.1038/nature06932
|
|
TOUR J M and HE Tao. Electronics: The fourth element[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 42–43. doi: 10.1038/453042a
|
|
YANG J J, PICKETT M D, LI Xuema, et al. Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2008, 3(7): 429–433. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.160
|
|
VONGEHR S and MENG Xiangkang. The missing memristor has not been found[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 11657. doi: 10.1038/srep11657
|
|
ASCOLI A, TETZLAFF R, CHUA L O, et al. History erase effect in a non-volatile Memristor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2016, 63(3): 389–400. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2525043
|
|
ASCOLI A, TETZLAFF R, CHUA L O, et al. Fading memory effects in a memristor for cellular nanoscale network applications[C]. The 2016 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Dresden, Germany, 2016: 421–425.
|
|
MENZEL S, WASER R, SIEMON A, et al. On the origin of the fading memory effect in ReRAMs[C]. The 27th IEEE 2017 International Symposium on Power and Timing Modeling, Optimization and Simulation, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2017: 1–5.
|
|
ASCOLI A, TETZLAFF R, and CHUA L O. The first ever real Bistable Memristors—Part I: Theoretical insights on local fading memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2016, 63(12): 1091–1095. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2016.2604567
|
|
ASCOLI A, TETZLAFF R, and CHUA L O. The first ever real bistable memristors -- Part Ⅱ: Design and analysis of a local fading memory system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2016, 63(12): 1096–1100. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2016.2613560
|
|
ASCOLI A, TETZLAFF R, and MENZEL S. Exploring the dynamics of real-world Memristors on the basis of circuit theoretic model predictions[J]. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 2018, 18(2): 48–76. doi: 10.1109/MCAS.2018.2821760
|
|
CHUA L. Five non-volatile memristor enigmas solved[J]. Applied Physics A, 2018, 124(8): Artical No. 563. doi: 10.1007/s00339-018-1971-0
|
|
BOYD S and CHUA L. Fading memory and the problem of approximating nonlinear operators with Volterra series[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 1985, 32(11): 1150–1161. doi: 10.1109/TCS.1985.1085649
|
|
CHUA L. Everything you wish to know about memristors but are afraid to ask[J]. Radioengineering, 2015, 24(2): 319–368. doi: 10.13164/re.2015.0319
|
|
ASCOLI A, SLESAZECK S, MAHNE H, et al. Nonlinear dynamics of a locally-active memristor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2015, 62(4): 1165–1174. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2015.2413152
|
|
CHUA L O. 3 new theorems on memristors[C]. The 7th Workshop and MC Meeting Memristors-Devices, Models, Circuits, Systems and Applications, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2018.
|
|
CORINTO F, ASCOLI A, and GILLI M. Analysis of current-voltage characteristics for memristive elements in pattern recognition systems[J]. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 2012, 40(12): 1277–1320. doi: 10.1002/cta.1804
|





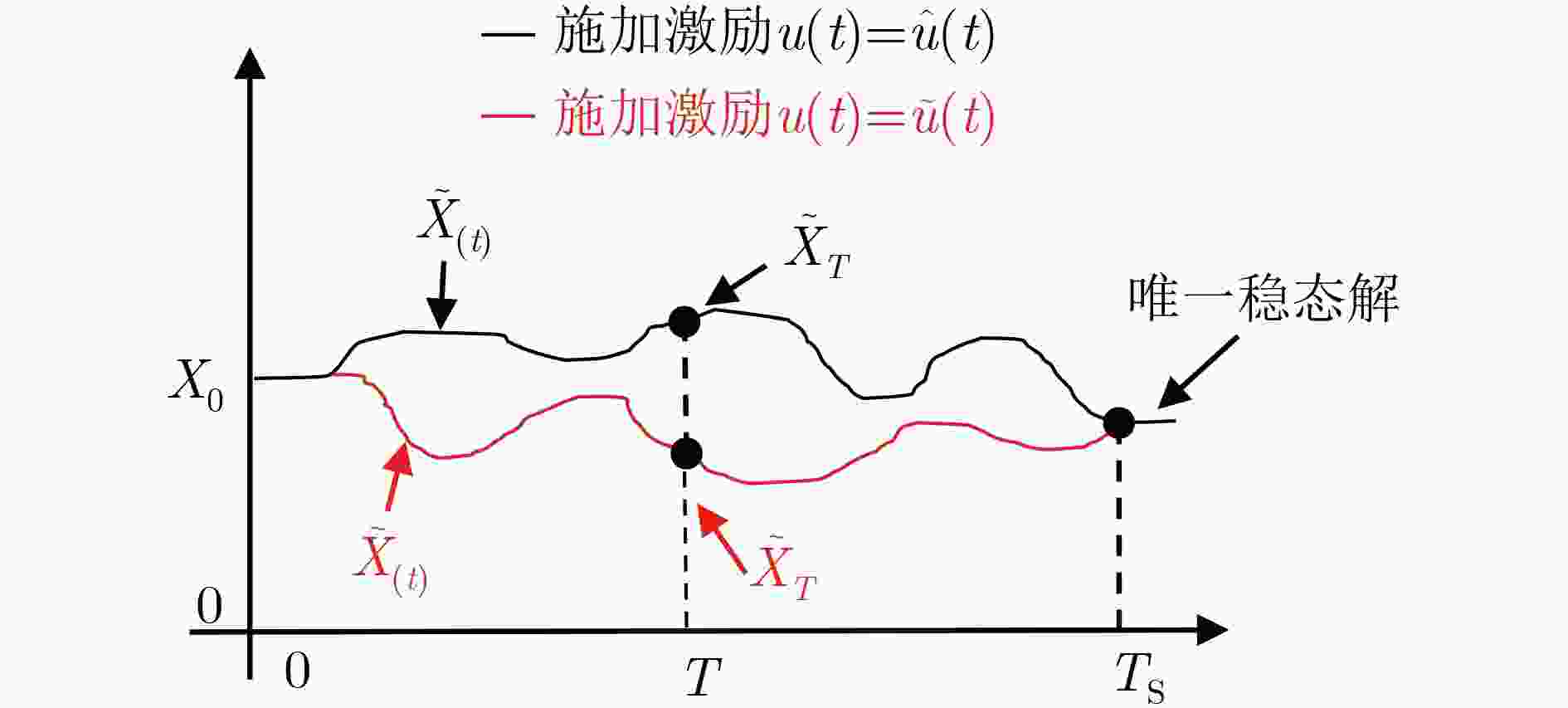
 下载:
下载:
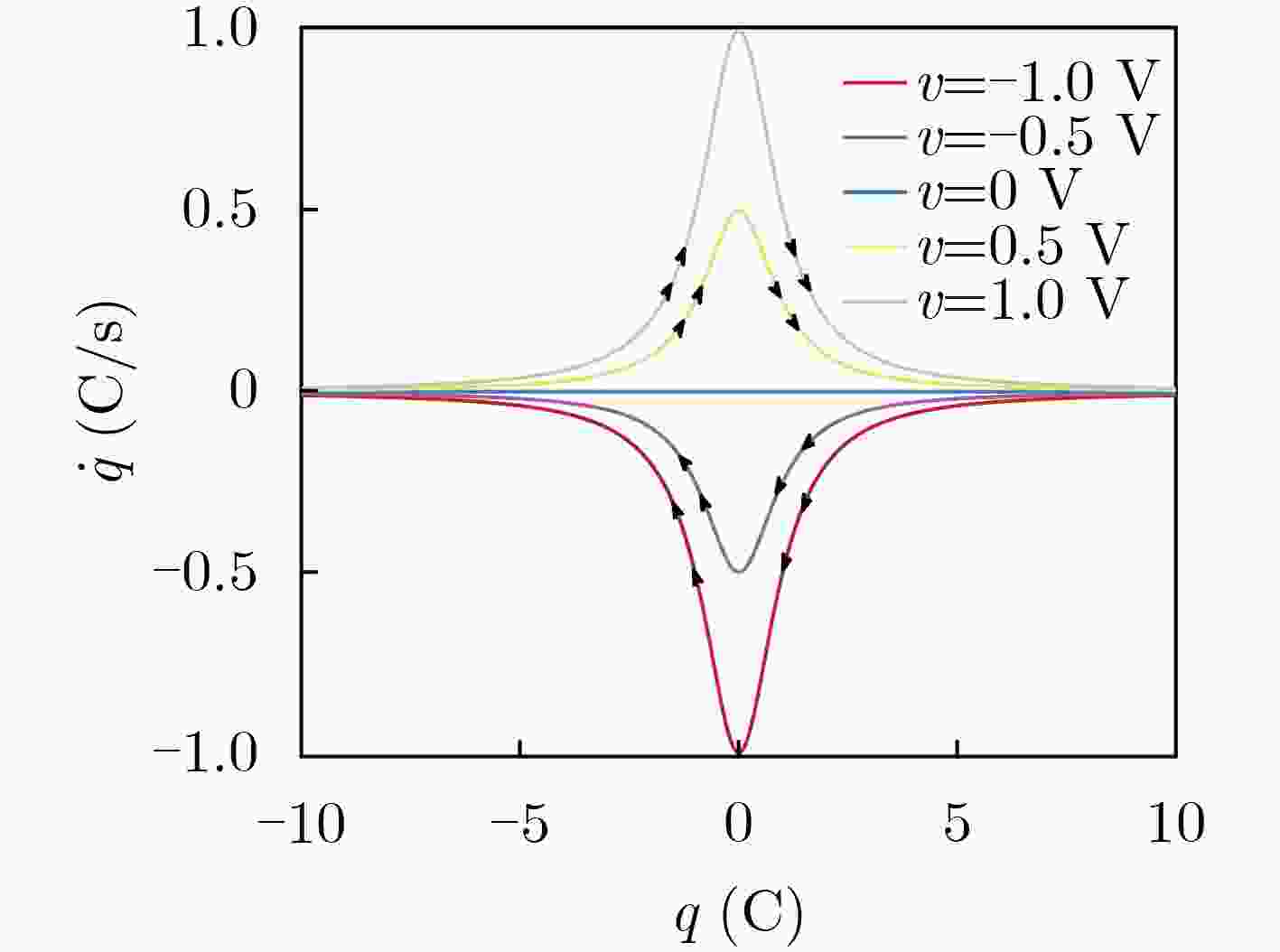
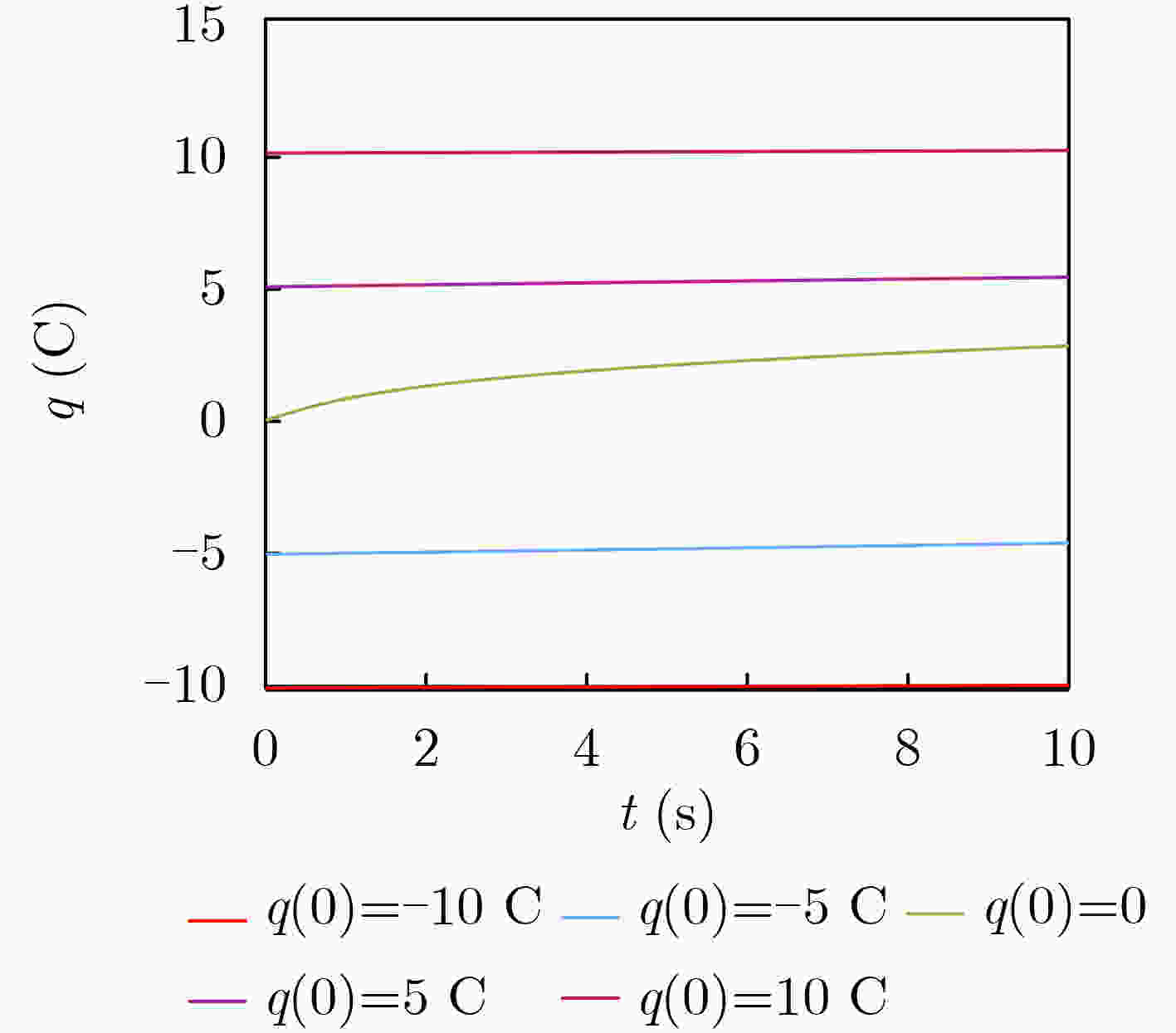

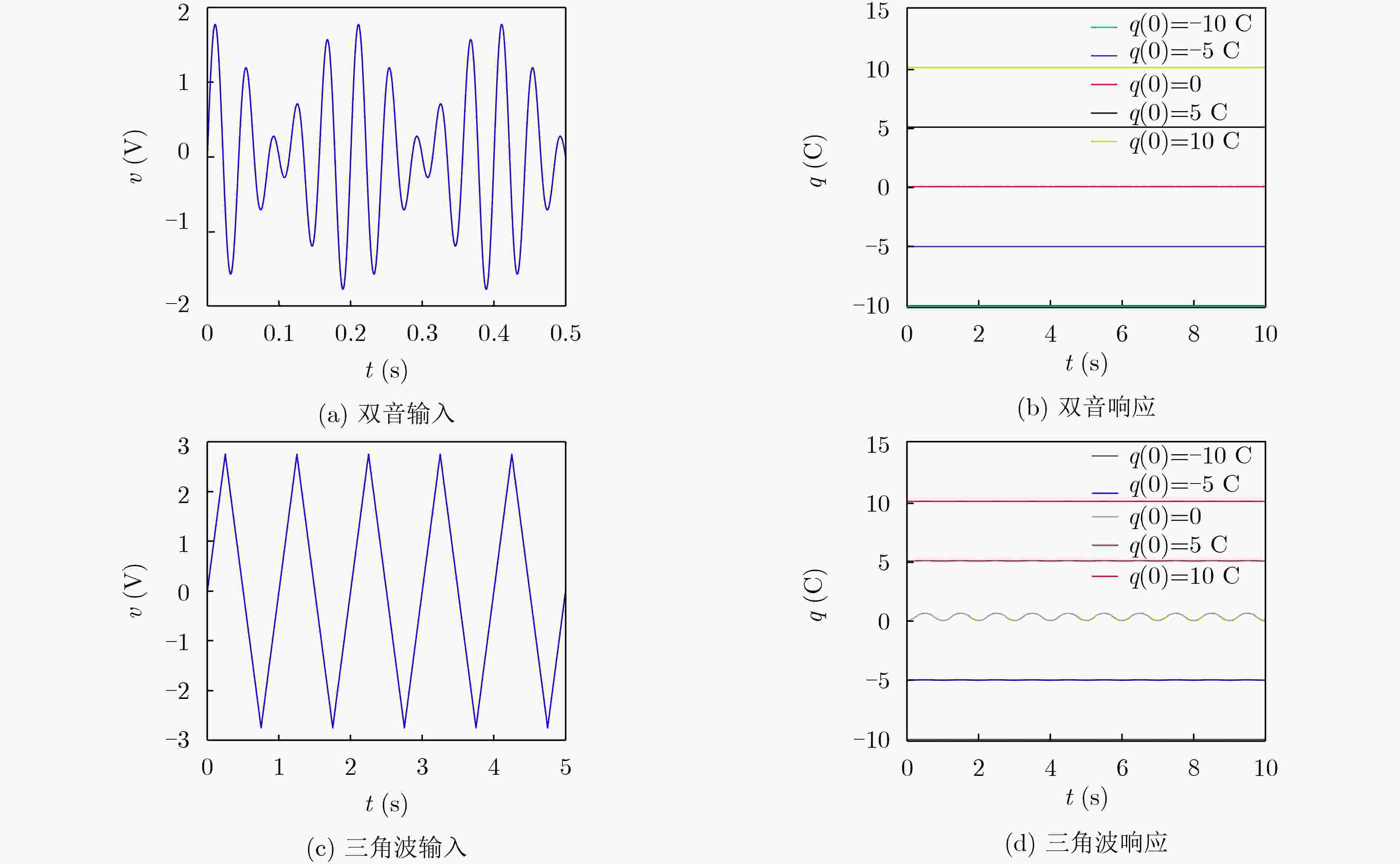
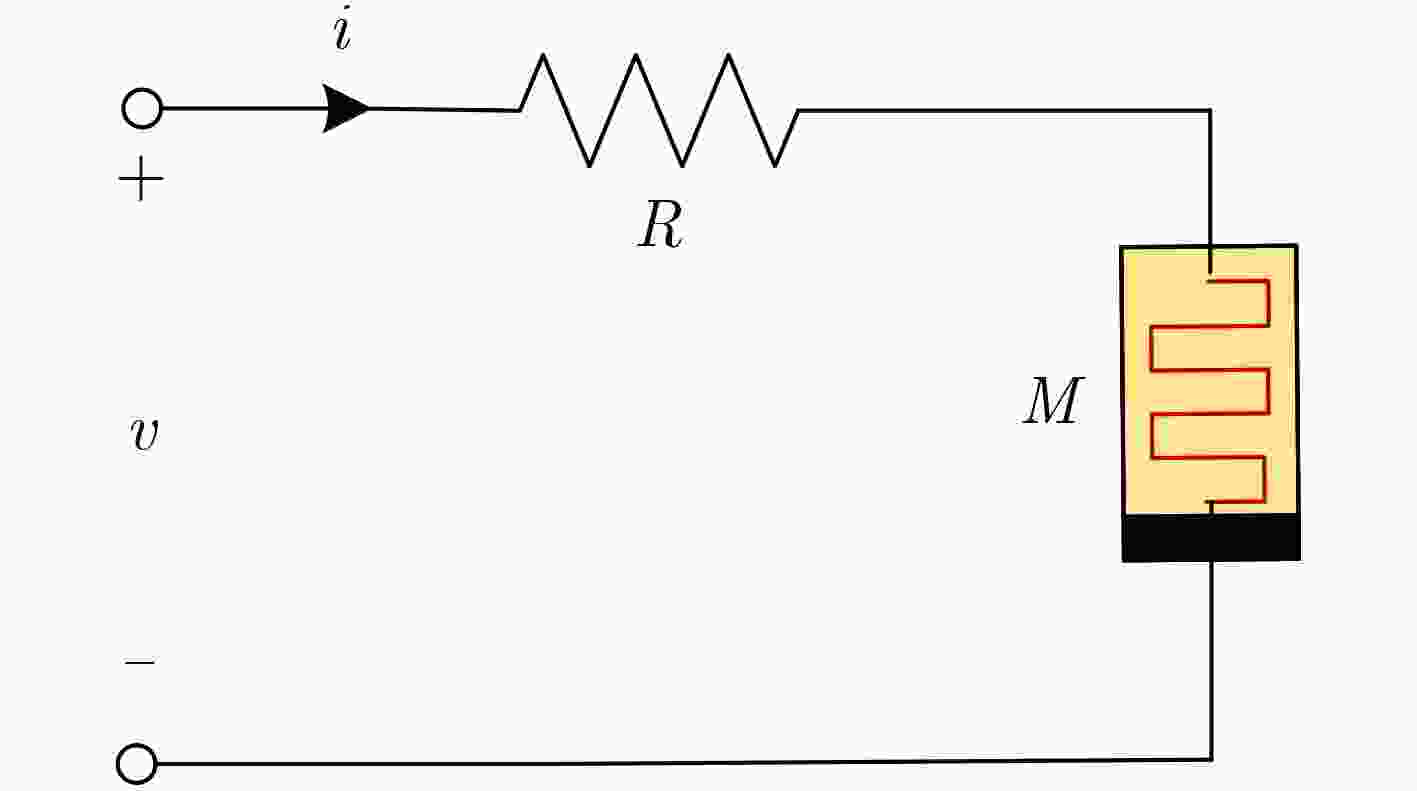
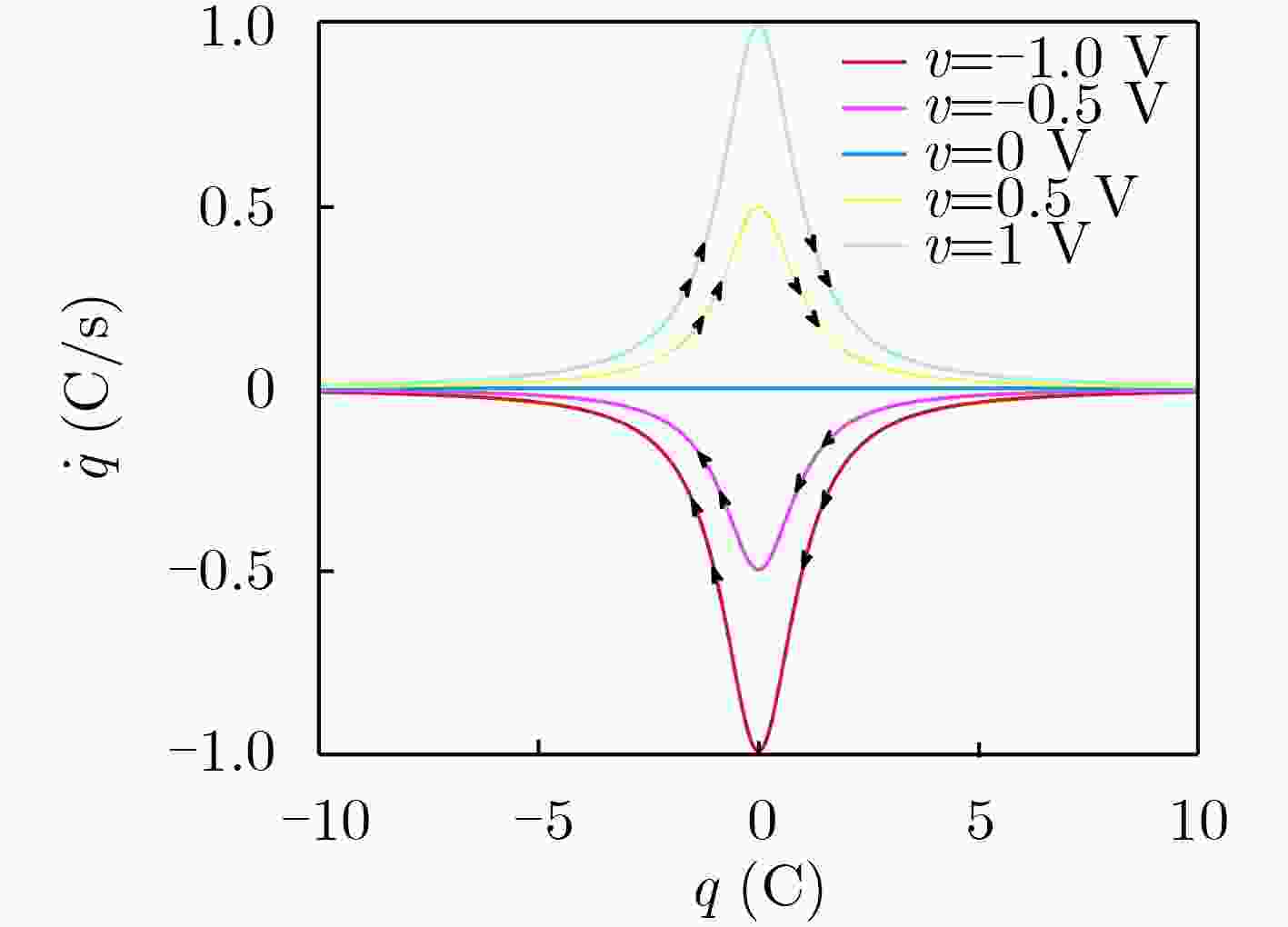
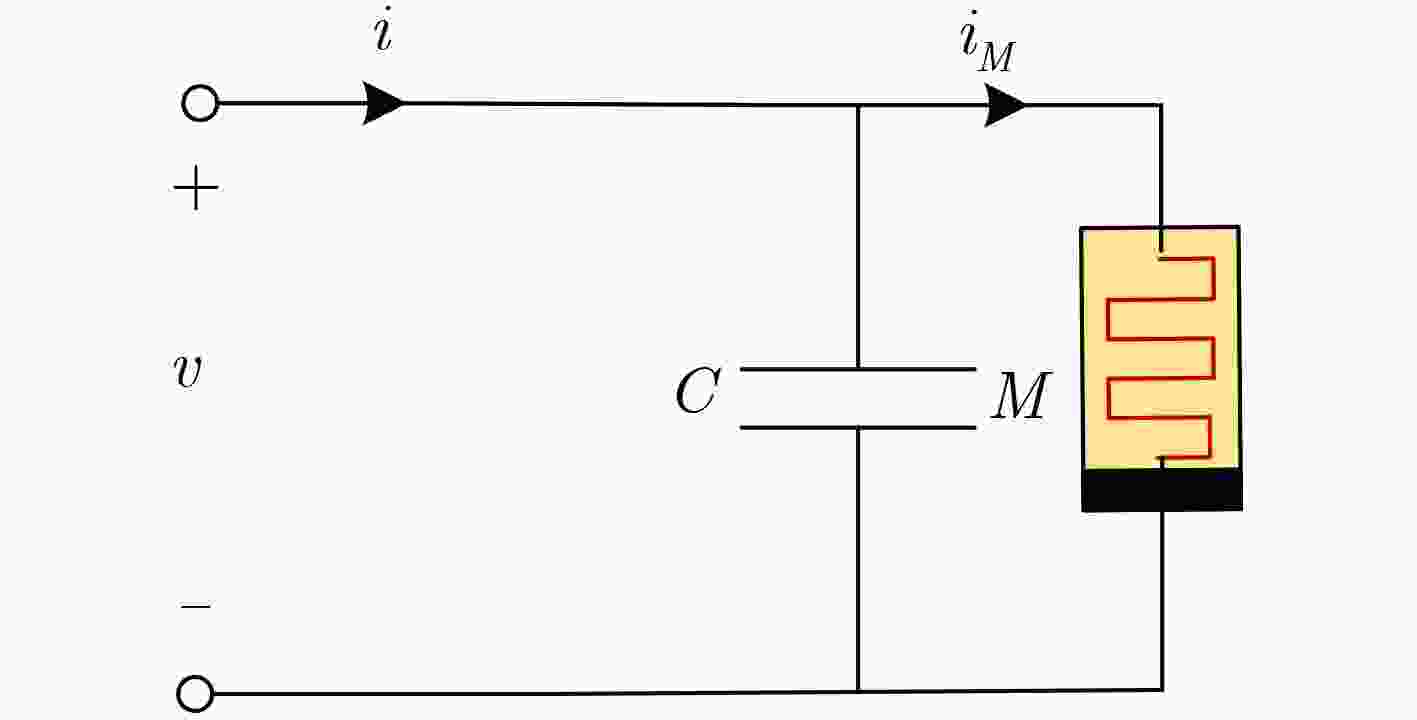
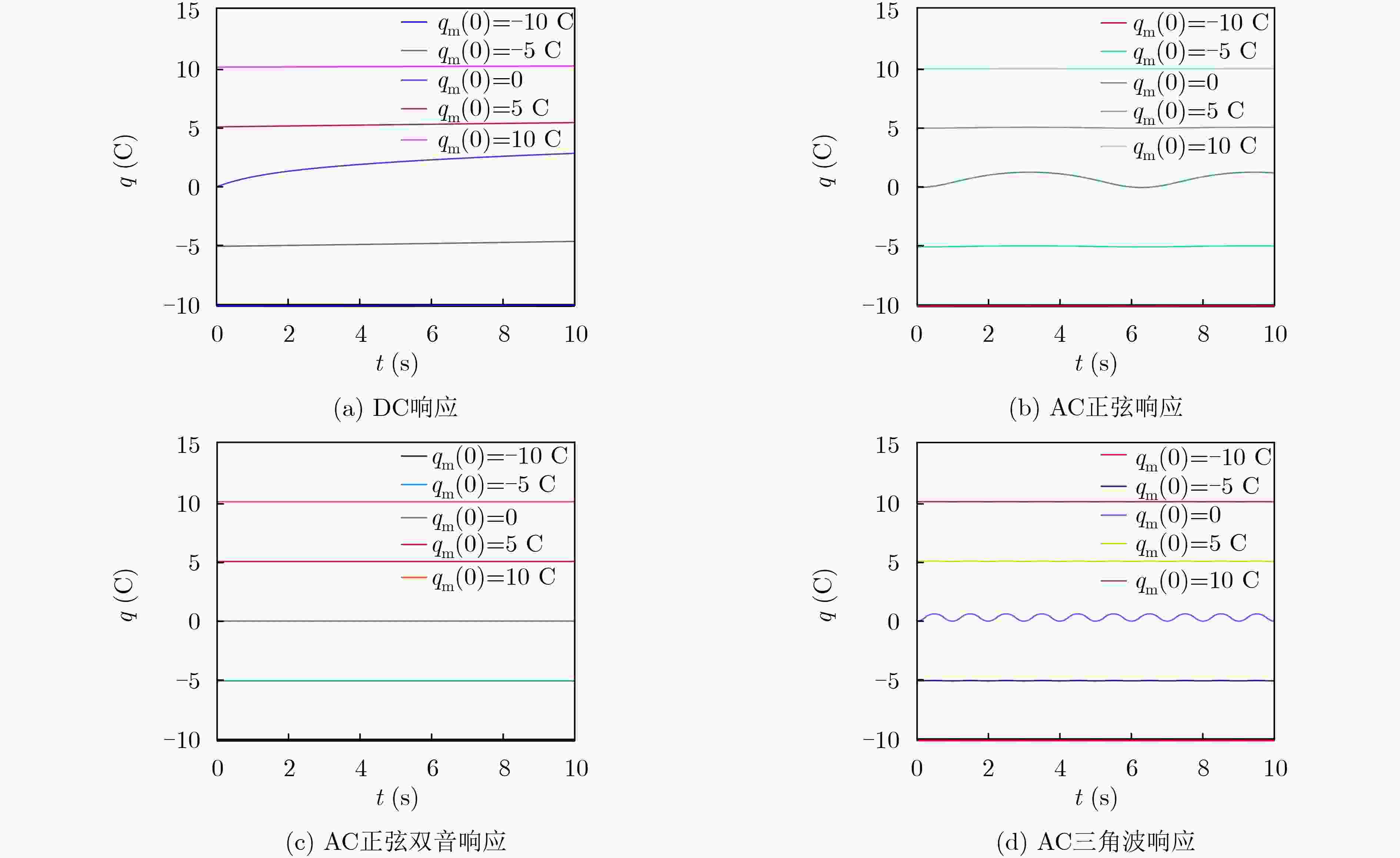
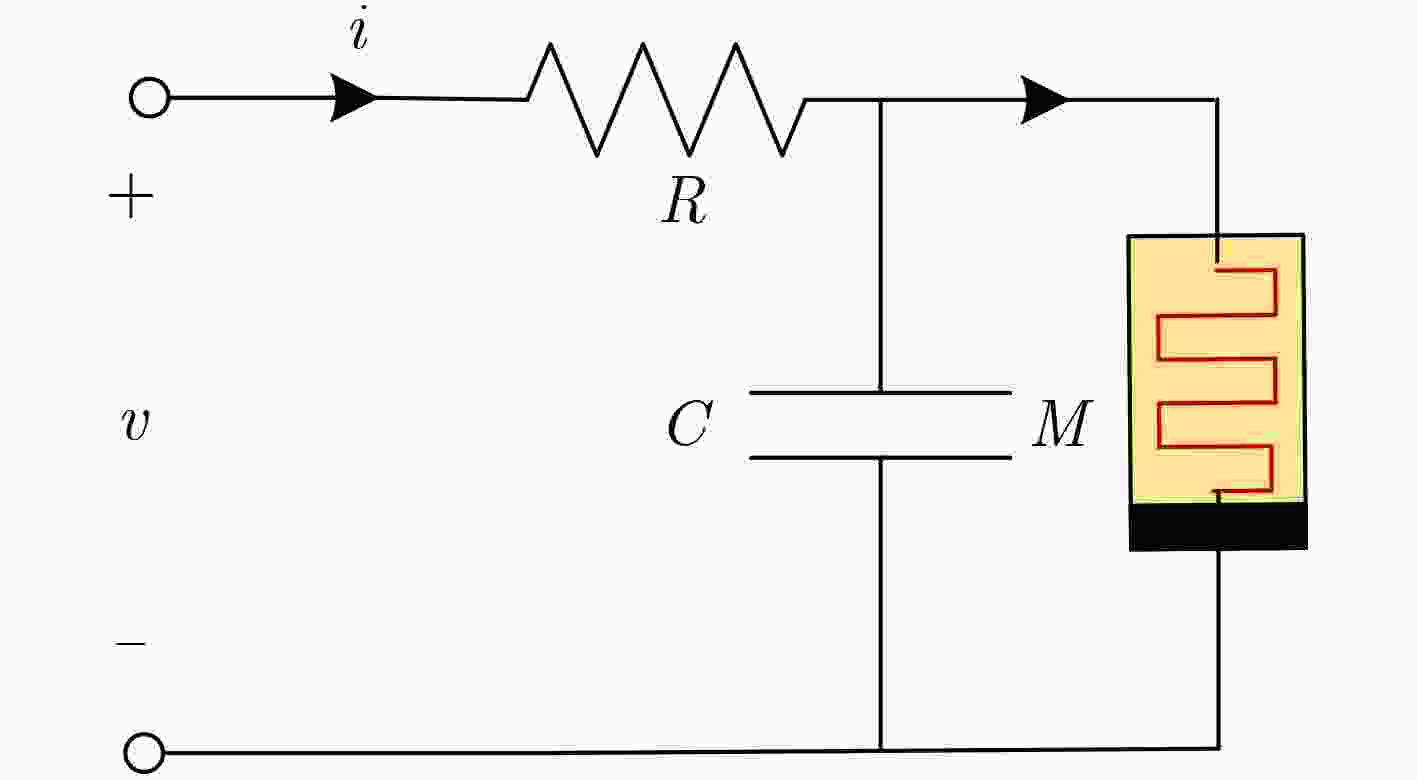
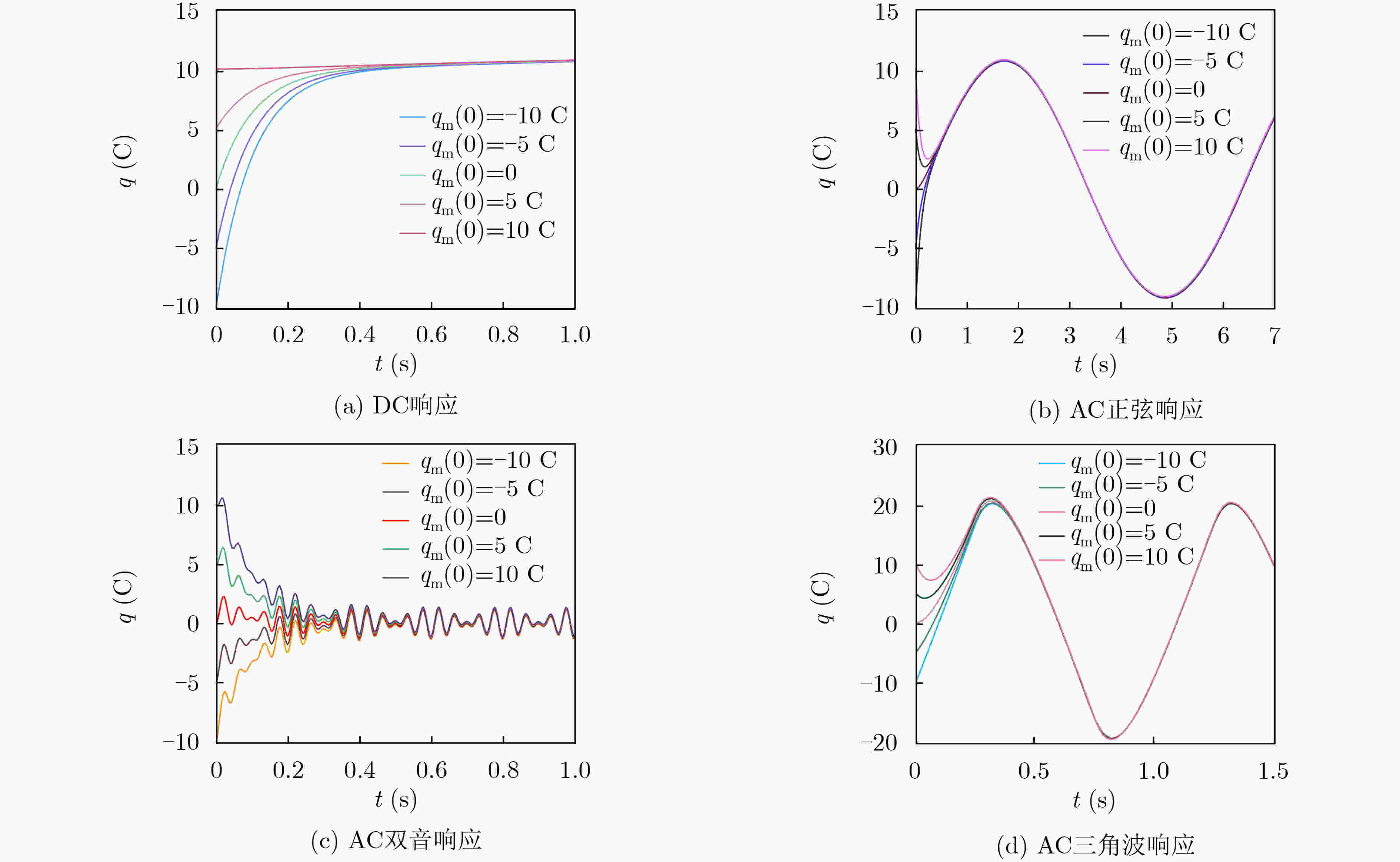


 下载:
下载:
