Micro-motion Gesture Recognition Based on Multi-channel Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave Millimeter Wave Radar
-
摘要:
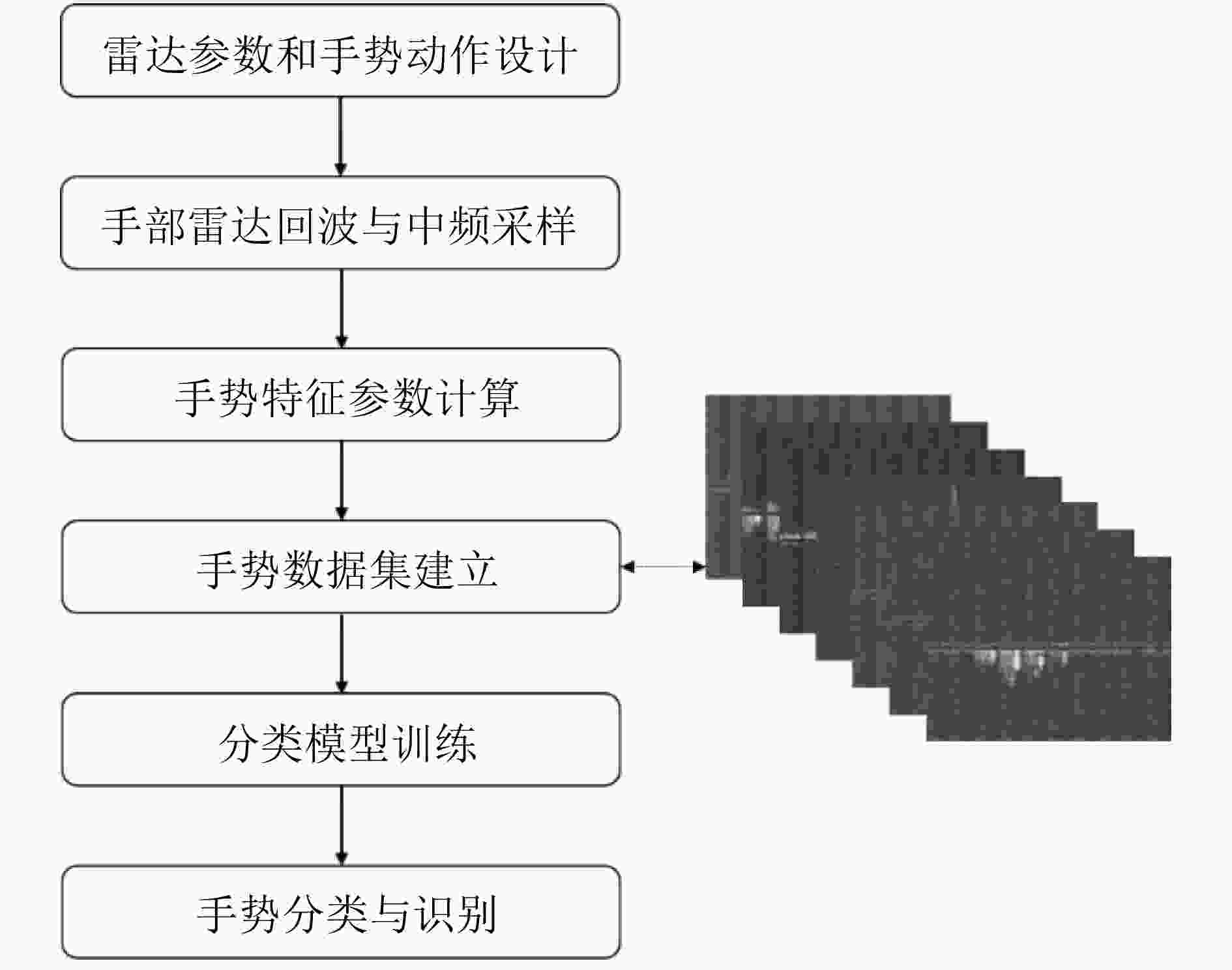
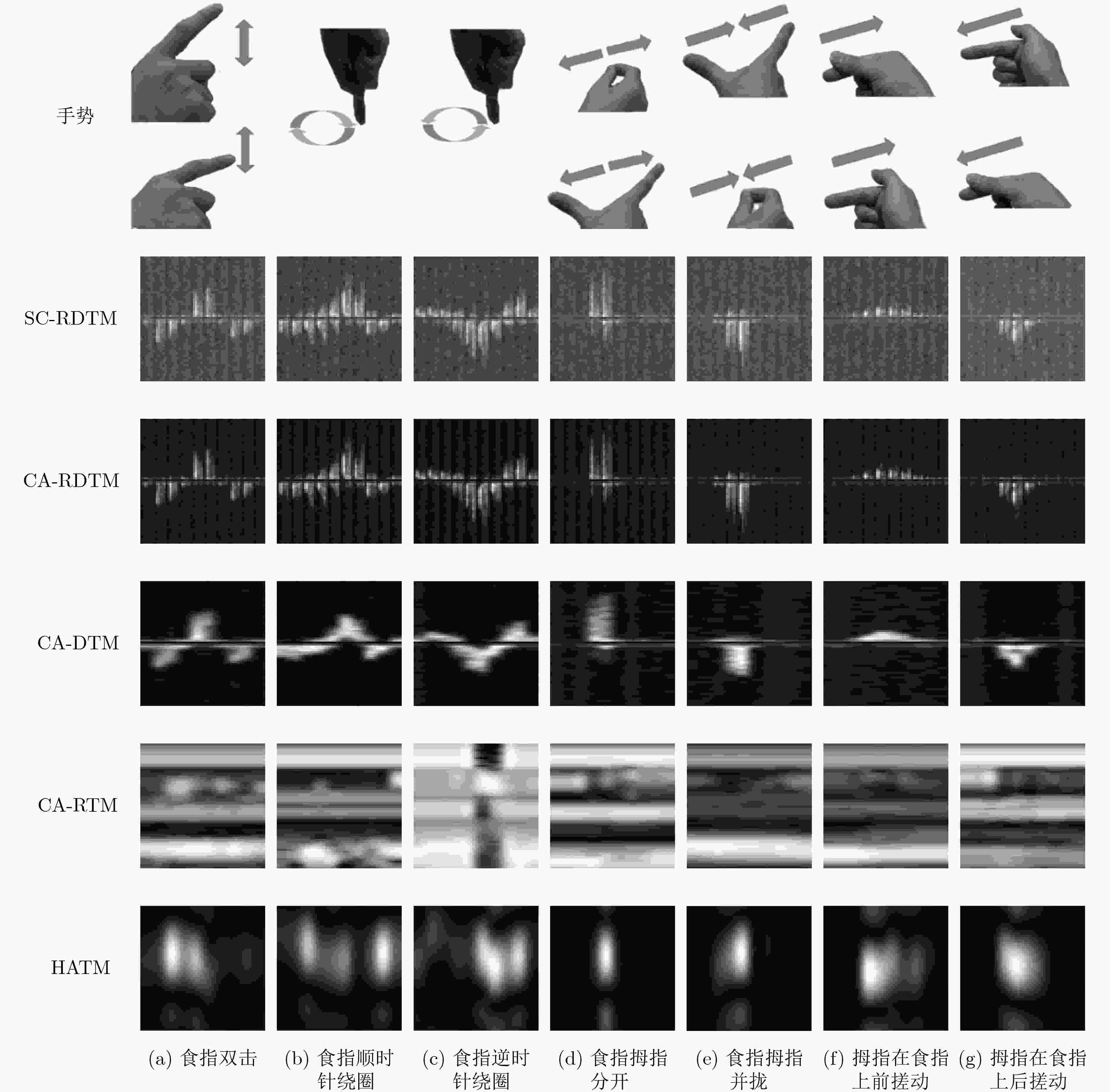
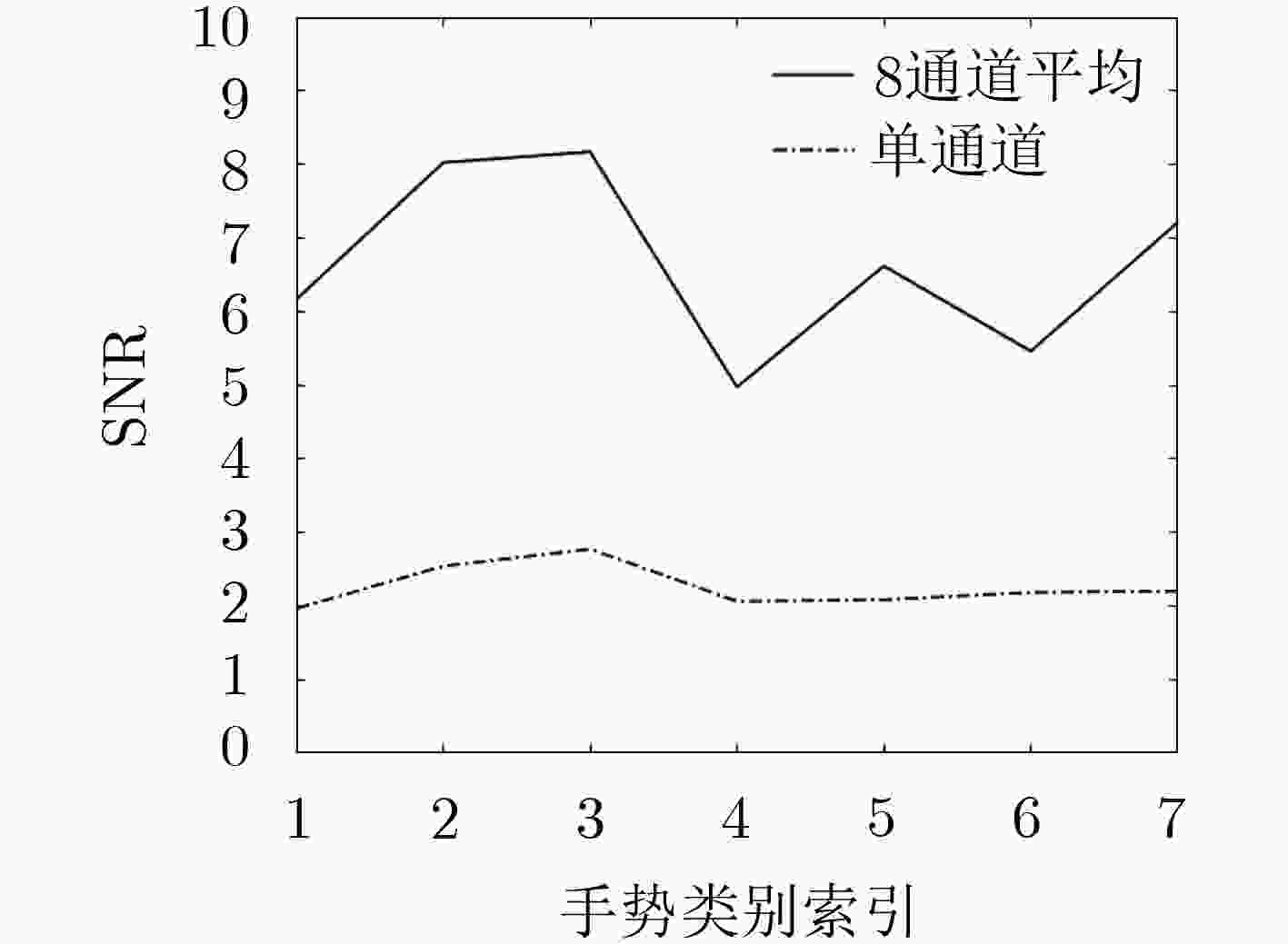
该文提出一种基于多通道调频连续波(FMCW)毫米波雷达的微动手势识别方法,并给出一种微动手势特征提取的最优雷达参数设计准则。通过对手部反射的雷达回波进行时频分析处理,估计目标的距离多普勒谱、距离谱、多普勒谱和水平方向角度谱。设计固定帧时间长度拼接的距离-多普勒-时间图特征,与距离-时间特征、多普勒-时间特征、水平方向角度-时间图特征和三者联合特征等,分别对7类微动手势进行表征。根据手势运动过程振幅和速度差异,进行手势特征捕获和对齐。利用仅有5层的轻量化卷积神经网络对微动手势特征进行分类。实验结果表明,相较其他特征,设计的距离-多普勒-时间图特征能够更为准确地表征微动手势,且对未经训练的测试对象具有更好的泛化能力。
Abstract:A micro-motion gesture recognition method based on multi-channel Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) millimeter wave radar is proposed, and an optimal radar parameter design criterion for feature extraction of micro-motion gestures is presented. The time-frequency analysis process is performed on the radar echo reflected by the hand, and the range Doppler spectrum, the range spectrum, the Doppler spectrum and the horizontal direction angle spectrum of the target are estimated. Then the range-Doppler-time-map feature is designed, range-time-map feature, Doppler-time-map feature, horizontal-angle-time-map feature, and three-joint feature with fixed frame time length are used to characterize the 7 classes micro-motion gestures, respectively. And these gesture features are captured and aligned according to the difference in amplitude and speed of the gesture motion process. Then a five-layer lightweight convolutional neural network is designed to classify the gesture features. The experimental results show that, the range-Doppler-time-map feature designed in this paper characterizes the micro-motion gesture more accurately and has a better generalization ability for untrained test objects compared with other features.
-
表 1 不同时间长度特征的分类准确率对比(%)
数据集长度 6帧 8帧 10帧 15帧 平均分类准确率 76.86 91.86 99.14 99.29 表 2 多种手势表征方法的对比
特征类型 分类方法 5名训练对象平均
分类准确率(%)SC-RDTM 单通道CNN 98.28 CA-RDTM 单通道CNN 99.14 CA-DTM 单通道CNN 97.14 CA-RTM 单通道CNN 88.00 HATM 单通道CNN 71.71 CA-RTM, CA-DTM
与HATM联合3通道CNN 93.57 表 3 多种手势表征方法的对比
特征类型 分类方法 测试对象A平均分类准确率(%) 测试对象B平均分类准确率(%) SC-RDTM 单通道CNN 86.00 84.29 CA-RDTM 单通道CNN 87.71 85.43 CA-DTM 单通道CNN 84.57 83.43 CA-RTM 单通道CNN 27.14 25.42 HATM 单通道CNN 34.28 30.57 CA-RTM, CA-DTM与HATM联合 3通道CNN 65.14 55.71 表 4 7种微动手势分类的混淆矩阵
预测类别 食指双击 食指顺时
针绕圈食指逆时
针绕圈食指拇
指分开食指拇
指并拢拇指在食指
上前搓动拇指在食指
上后搓动准确度(%) 真实类别 食指双击 100 0 0 0 0 0 0 100 食指顺时针绕圈 0 100 0 0 0 0 0 100 食指逆时针绕圈 0 0 100 0 0 0 0 100 食指拇指分开 0 0 0 100 0 0 0 100 食指拇指并拢 0 0 0 0 98 0 2 98 拇指在食指上前搓动 0 0 0 0 0 100 0 100 拇指在食指上后搓动 0 0 0 0 4 0 96 96 准确度(%) 100 100 100 100 96.08 100 97.96 99.14 表 5 测试对象A 7类微动手势分类的混淆矩阵
预测类别 食指双击 食指顺时
针绕圈食指逆时
针绕圈食指拇
指分开食指拇
指并拢拇指在食指
上前搓动拇指在食指
上后搓动准确度(%) 真实类别 食指双击 46 3 1 0 0 0 0 92 食指顺时针绕圈 0 35 15 0 0 0 0 70 食指逆时针绕圈 3 13 34 0 0 0 0 68 食指拇指分开 0 0 0 49 0 1 0 98 食指拇指并拢 0 0 0 0 46 0 4 92 拇指在食指上前搓动 0 0 0 1 0 49 0 98 拇指在食指上后搓动 0 0 0 0 2 0 48 96 准确度(%) 93.88 68.63 68 98 95.83 98 92.31 87.71 表 6 测试对象B 7类微动手势分类的混淆矩阵
预测类别 食指双击 食指顺
时针绕圈食指逆时
针绕圈食指拇
指分开食指拇
指并拢拇指在食指
上前搓动拇指在食指
上后搓动准确度(%) 真实类别 食指双击 45 2 3 0 0 0 0 90 食指顺时针绕圈 0 32 18 0 0 0 0 64 食指逆时针绕圈 1 16 33 0 0 0 0 66 食指拇指分开 0 0 0 46 0 4 0 92 食指拇指并拢 0 0 0 0 48 0 2 96 拇指在食指上前搓动 0 0 0 2 0 48 0 96 拇指在食指上后搓动 0 0 0 0 3 0 47 94 准确度(%) 97.83 64 61.11 95.83 94.12 92.31 95.92 85.43 -
WAN Qian, LI Yiran, LI Changzhi, et al. Gesture recognition for smart home applications using portable radar sensors[C]. The 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, USA, 2014: 6414–6417. KHAN F, LEEM S K, and CHO S H. Hand-based gesture recognition for vehicular applications using IR-UWB radar[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(4): 833. doi: 10.3390/s17040833 XIA Zia, SANG Xinzhu, CHEN Duo, et al. An interactive VR system based on full-body tracking and gesture recognition[C]. The SPIE 10021, Optical Design and Testing VⅡ, Beijing, China 2016: 1002129. LEE B G and LEE S M. Smart wearable hand device for sign language interpretation system with sensors fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(3): 1224–1232. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2779466 TARANTA Ⅱ E M, SIMONS T K, SUKTHANKAR R, et al. Exploring the benefits of context in 3D gesture recognition for game-based virtual environments[J]. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems, 2015, 5(1): Article No.1. BONATO V, FERNANDES M M, and MARQUES E. A smart camera with gesture recognition and SLAM capabilities for mobile robots[J]. International Journal of Electronics, 2006, 93(6): 385–401. doi: 10.1080/00207210600565465 孟春宁, 吕建平, 陈萱华. 基于普通红外摄像机的手势识别[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2015, 51(16): 17–22. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1504-0303MENG Chunning, LÜ Jianping, and CHEN Xuanhua. Gesture recognition based on universal infrared camera[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2015, 51(16): 17–22. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1504-0303 PLOUFFE G and CRETU A M. Static and dynamic hand gesture recognition in depth data using dynamic time warping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(2): 305–316. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2015.2498560 YANG Qifan, TANG Hao, ZHAO Xuebing, et al. Dolphin: Ultrasonic-based gesture recognition on smartphone platform[C]. The 2014 IEEE 17th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, Chengdu, China, 2014: 1461–1468. KELLOGG B, TALLA V, and GOLLAKOTA S. Bringing gesture recognition to all devices[C]. The 11th Usenix Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Seattle, USA, 2014: 303–316. ZOU Yongpan, XIAO Jiang, HAN Jinsong, et al. GRfid: A device-free RFID-based gesture recognition system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(2): 381–393. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2549518 ABDELNASSER H, YOUSSEF M, and HARRAS K A. WiGest: A ubiquitous WiFi-based gesture recognition system[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Hongkong, China, 2015: 1472–1480. ZHANG Jiajun, TAO Jinkun, and SHI Zhiguo. Doppler-radar based hand gesture recognition system using convolutional neural networks[C]. The 2017 International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems, Singapore, 2019: 1096–1113. LIEN J, GILLIAN N, KARAGOZLER M, et al. Soli: Ubiquitous gesture sensing with millimeter wave radar[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2016, 35(4): Article No.142. WANG Saiwen, SONG Jie, LIEN J, et al. Interacting with Soli: Exploring fine-grained dynamic gesture recognition in the radio-frequency spectrum[C]. The 29th Annual Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 2016: 851–860. HAZRA S and SANTRA A. Robust gesture recognition using Millimetric-wave radar system[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2018, 2(4): 7001804. MALYSA G, WANG Dan, NETSCH L, et al. Hidden Markov model-based gesture recognition with FMCW radar[C]. 2016 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Washington, USA, 2016: 1017–1021. 王勇, 吴金君, 田增山, 等. 基于FMCW雷达的多维参数手势识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485WANG YONG, WU Jinjun, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Gesture recognition with multi-dimensional parameter using FMCW radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485 刘熠辰, 徐丰. 基于雷达技术的手势识别[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2016, 11(6): 609–613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2016.06.009LIU Yichen and XU Feng. Gesture recognition based on radar technology[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2016, 11(6): 609–613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2016.06.009 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
