The Status and Trends of Silicon-based Millimeter-wave Radar SoCs
-
摘要:
毫米波雷达具备全天候复杂环境下的工作能力,在汽车雷达、智能机器人等方面有广泛的应用。同时,随着半导体技术的快速发展,硅基工艺晶体管的截止频率提升,硅基毫米波雷达成为研究热点,大量的工作从系统设计、电路设计等方面提高毫米波雷达的性能。该文从系统和核心电路等方面对硅基毫米波雷达芯片的研究现状和发展趋势进行综述。
Abstract:The millimeter wave radar is robust against various environments such as rain, fog, snow. It has huge potentials in applications such as automotive radars, intelligent robots. At the same time, the rapid development of silicon technology improves the cut off frequency of the transistor, which make it possible to implement low cost millimeter wave radar SoCs in silicon. Recently a lot of research is dedicated to improve the performance of the silicon based millimeter wave SoCs from both system level and key building blocks level. The current research status and future trends of the silicon based millimeter wave radar SoCs are reviewed in this paper.
-
Key words:
- Millimeter-Wave Radar /
- Silicon /
- SoCs
-
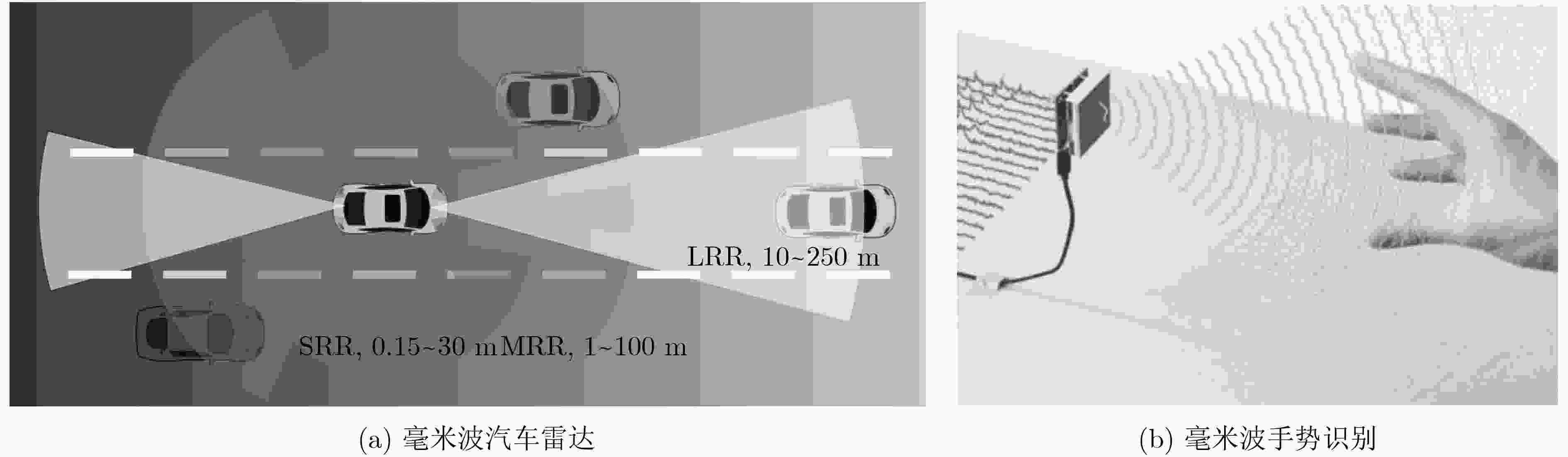
图 1 毫米波汽车雷达和谷歌Soli项目[14]
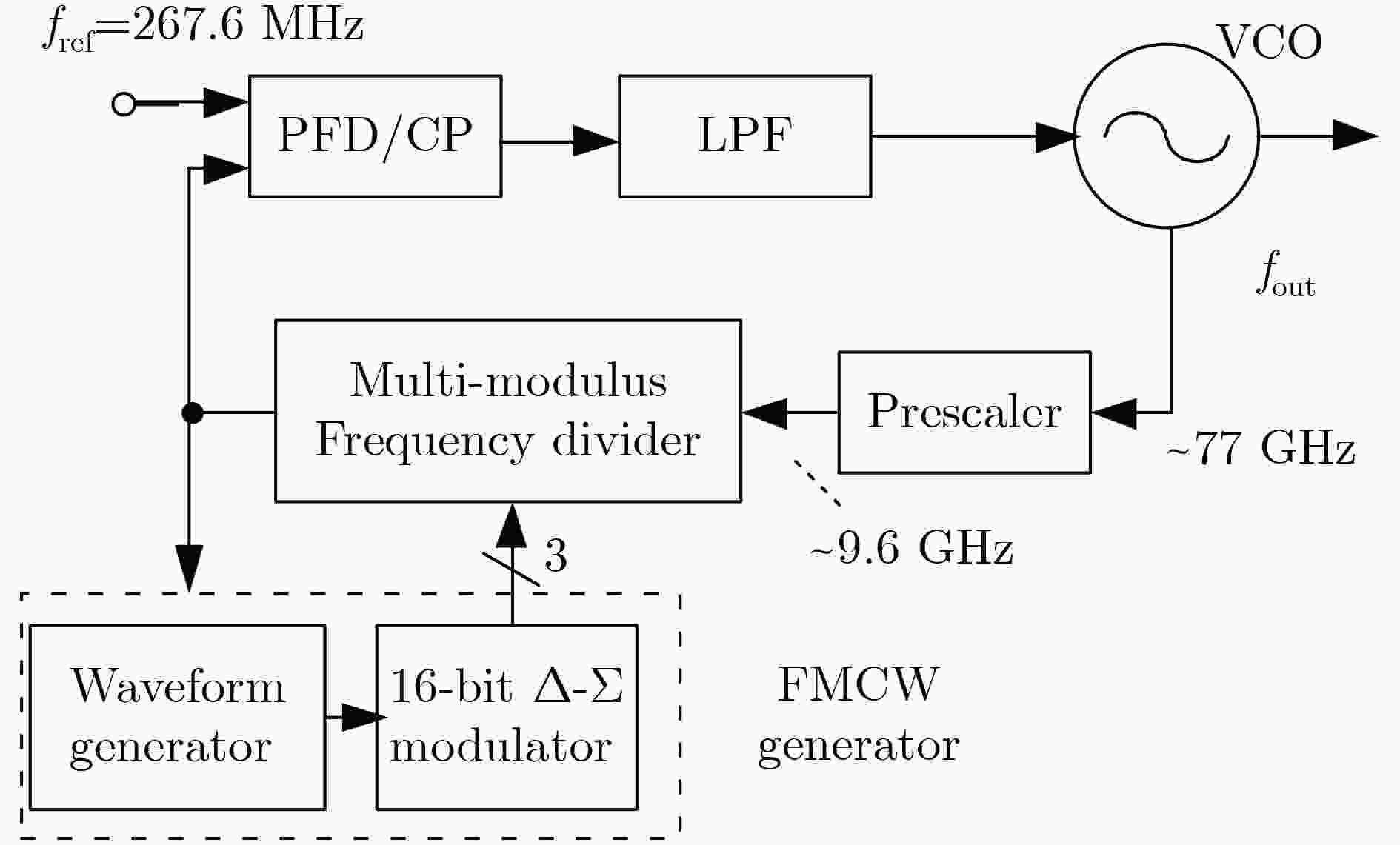
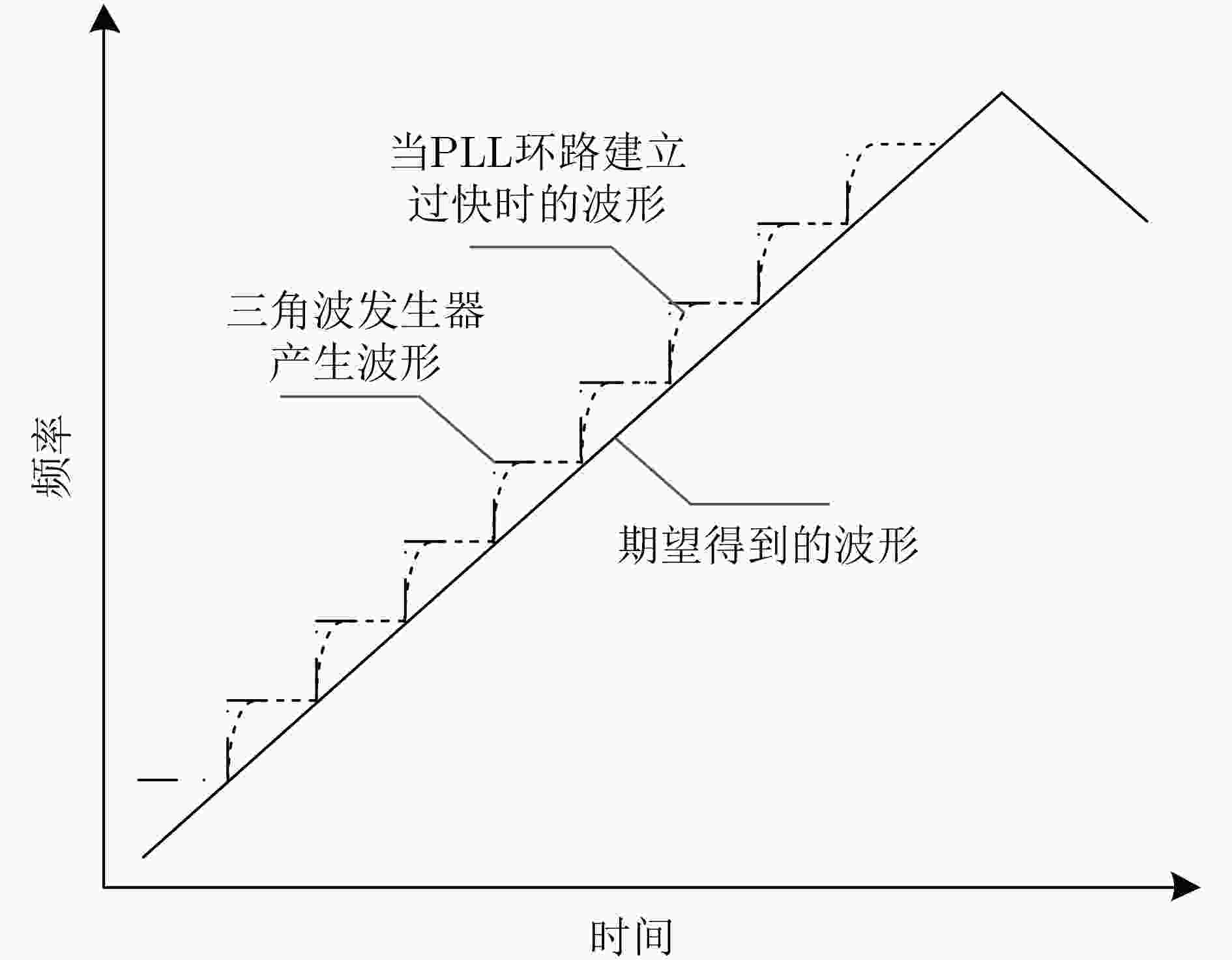
图 5 文献[34]中基于DSM小数型锁相环的FMCW信号发生器
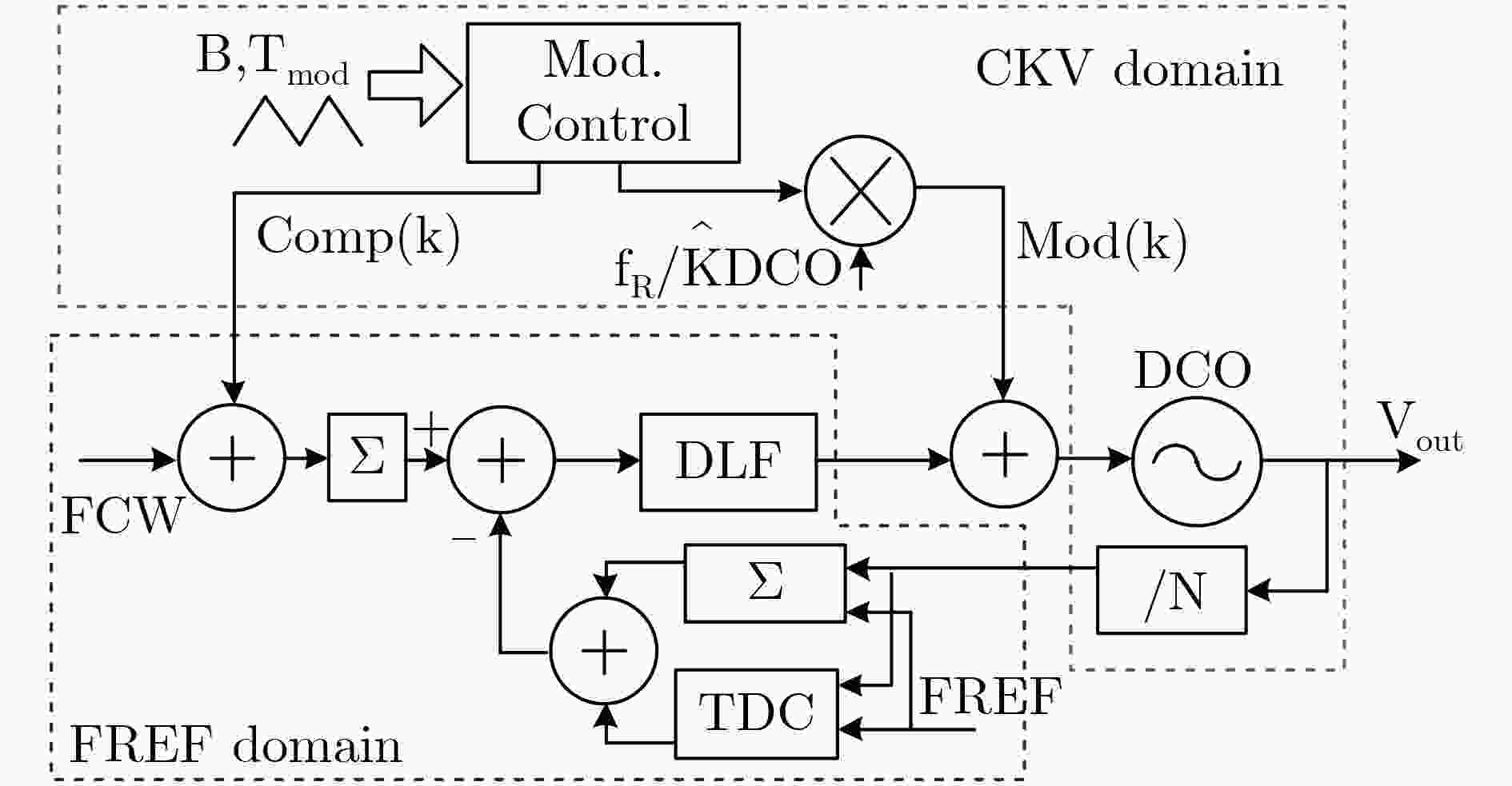
图 7 全数字锁相环用于毫米波FMCW信号产生[37]
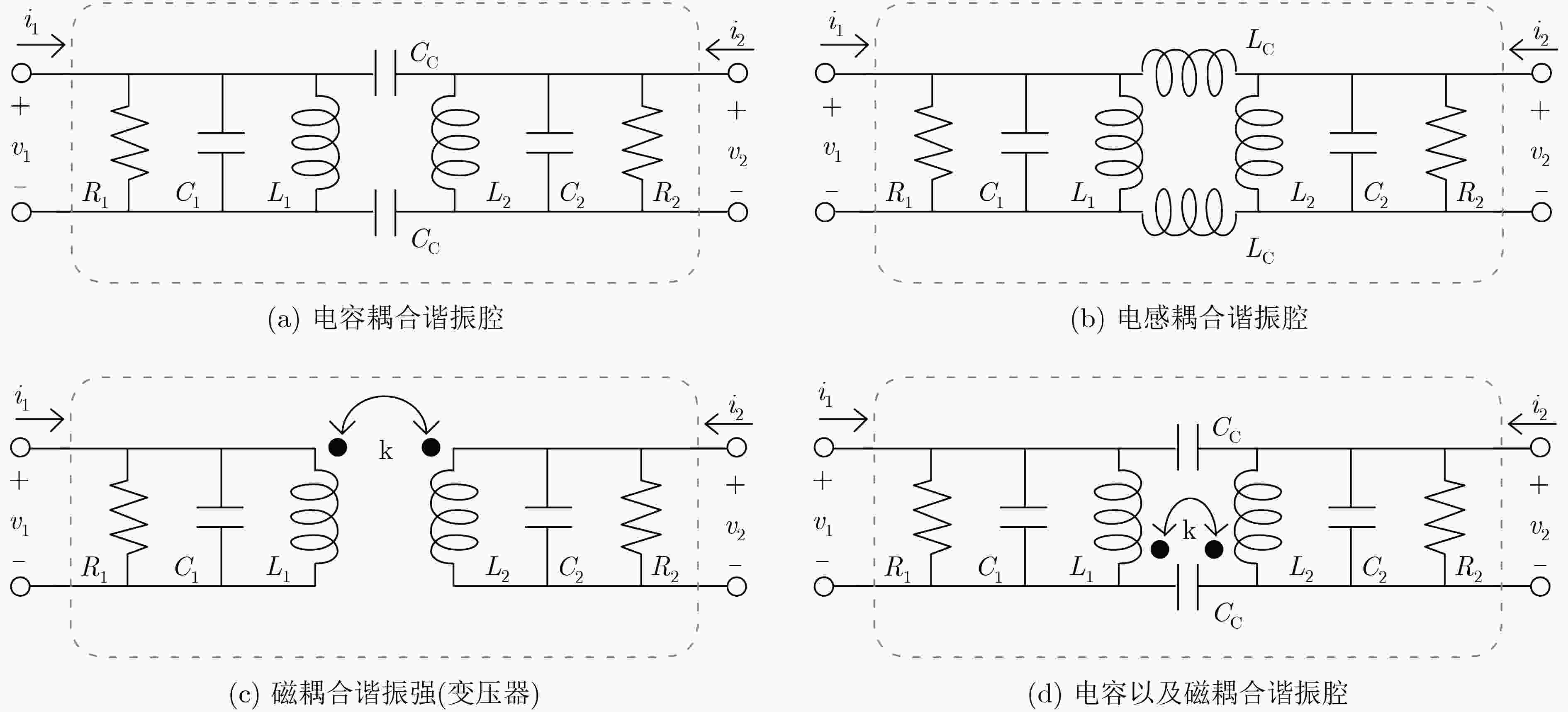
图 9 4种4阶匹配网络[66]
图 10 4种4阶匹配网络的频率响应对比[66]
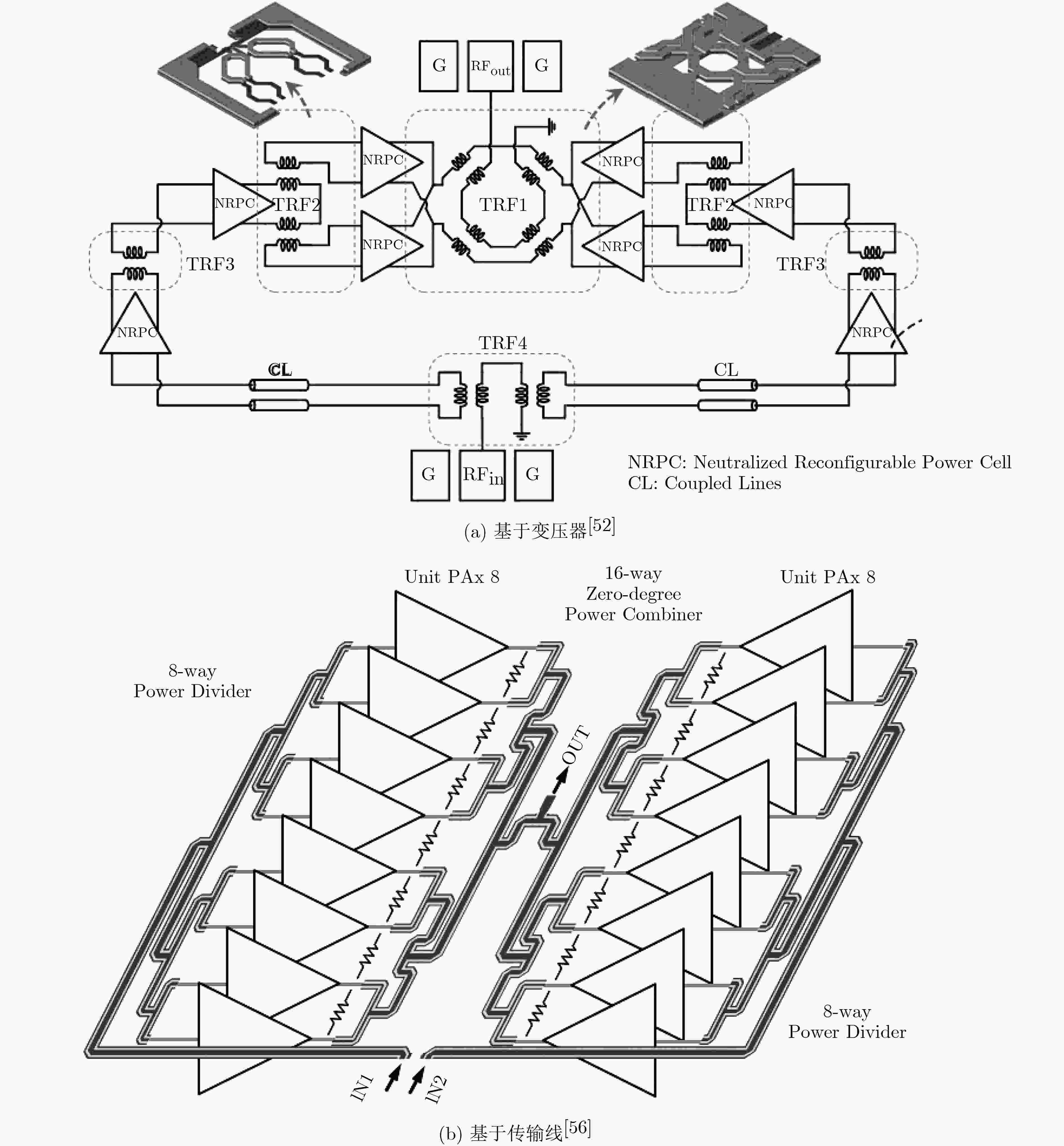
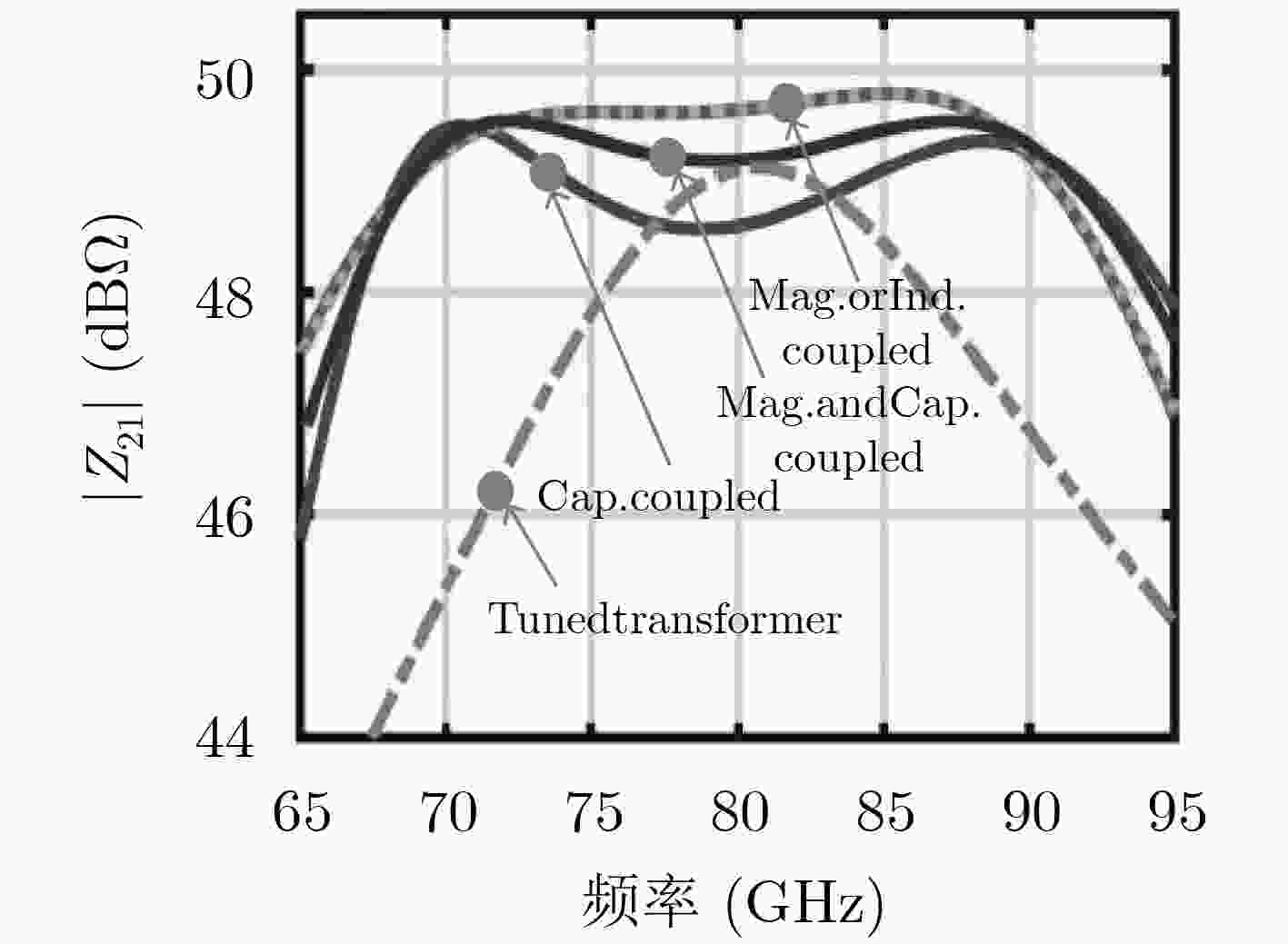
图 11 基于变压器耦合谐振腔的特性[67]
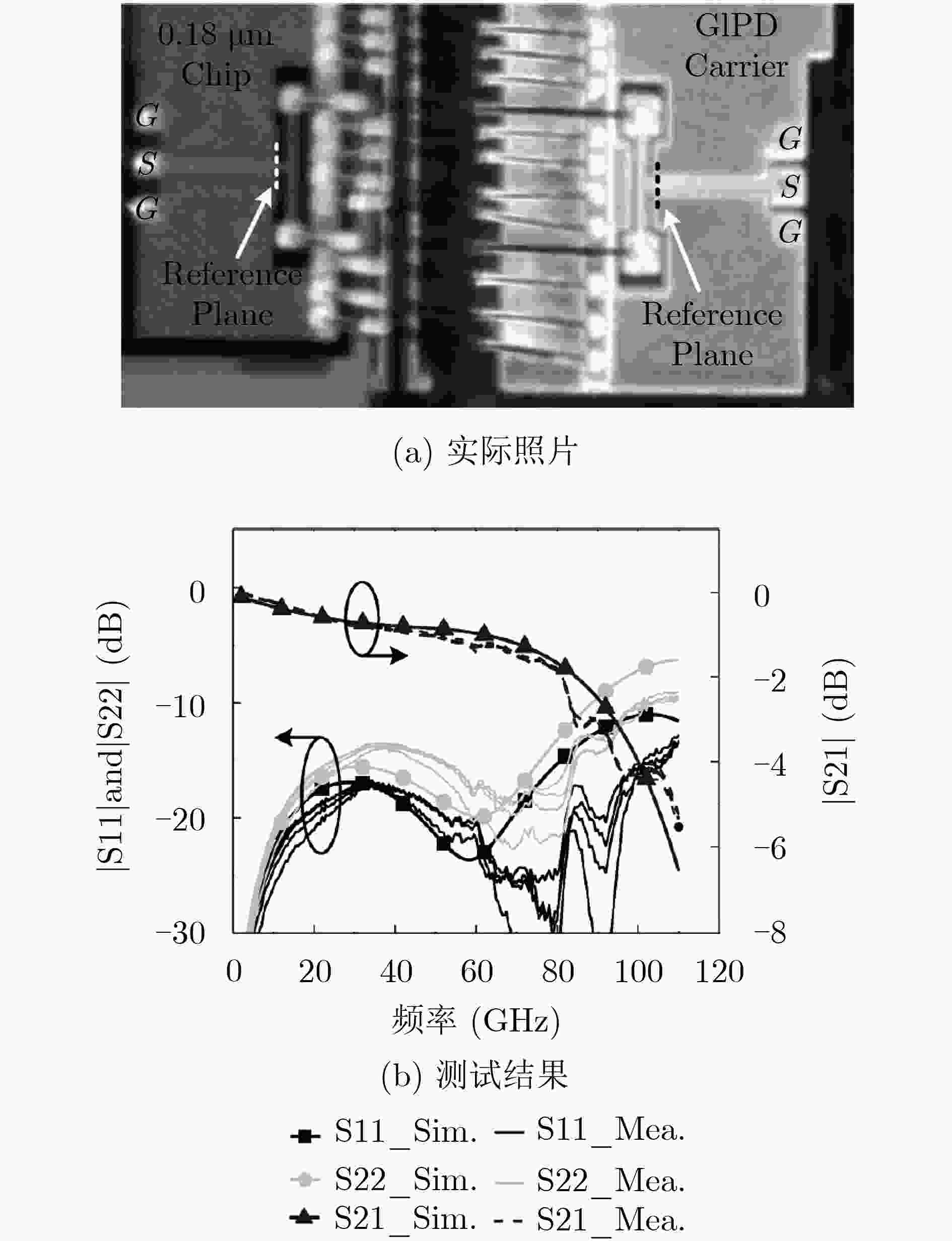
图 13 片上传输线与键合线协同设计以提高其带宽[81]
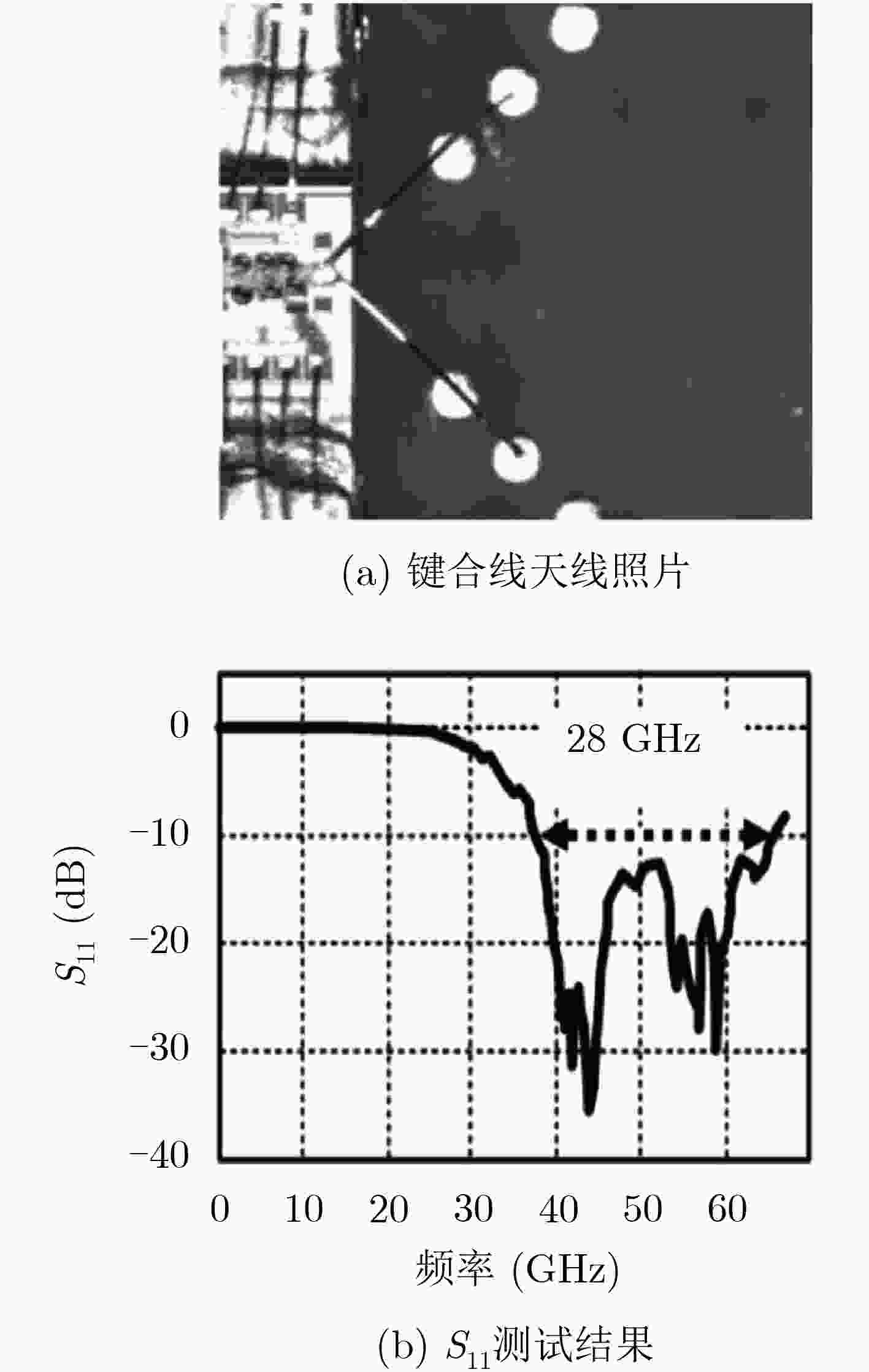
图 14 工作在60 GHz的键合线天线,增益为4 dBi[80]
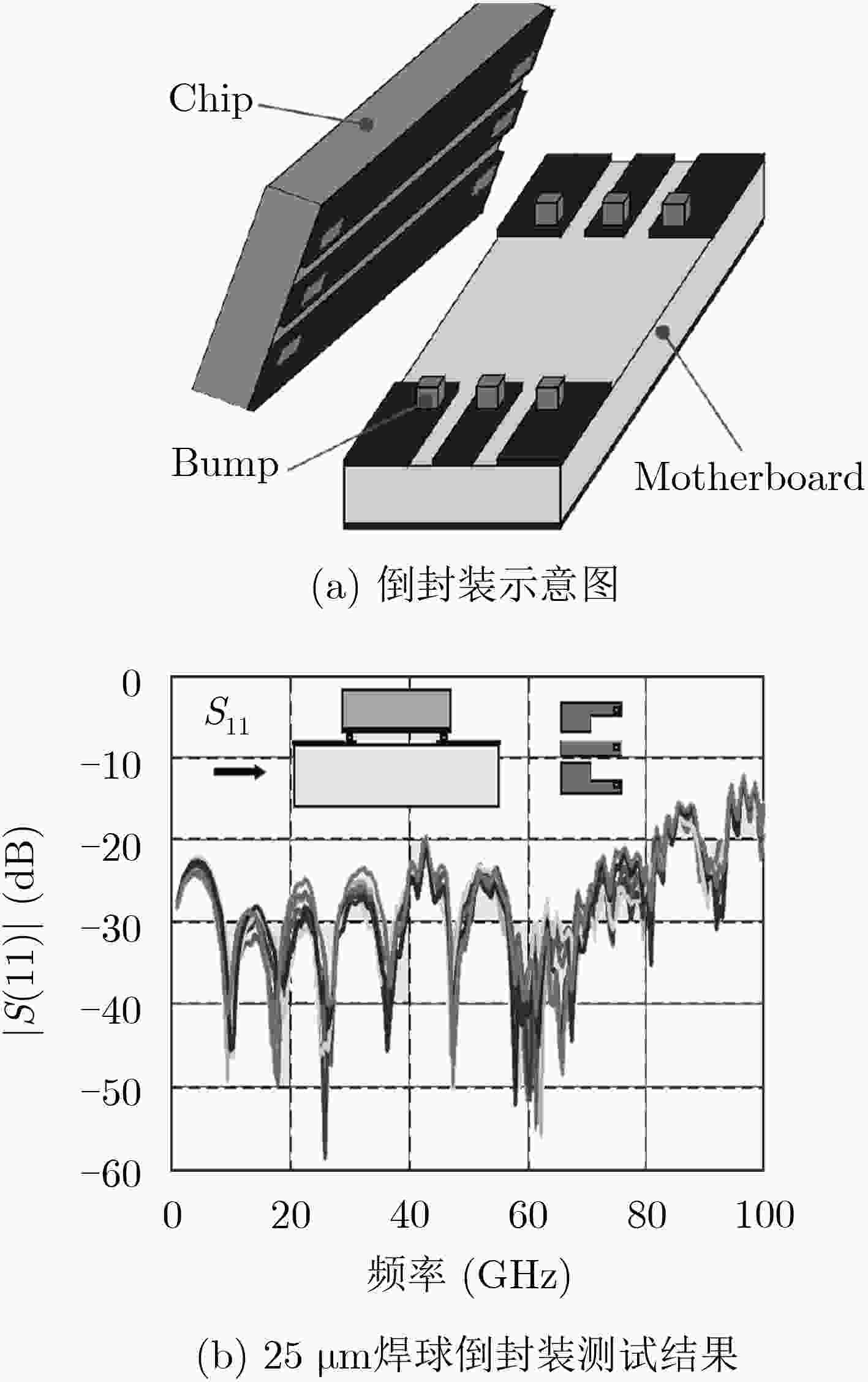
图 15 文献[82]倒封装
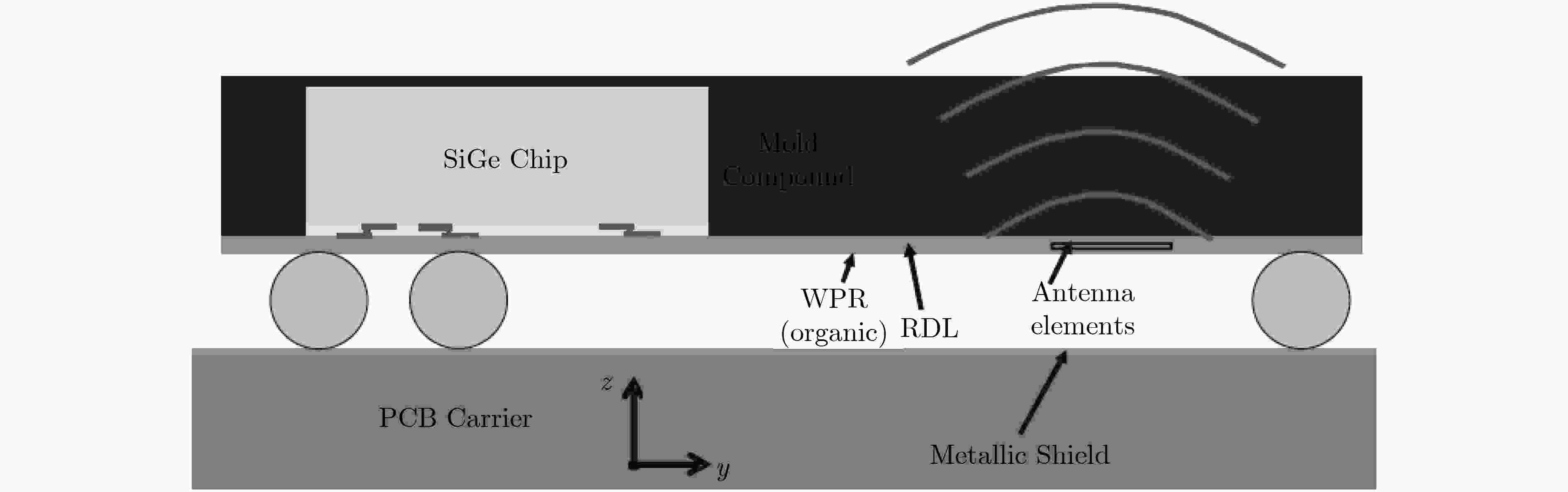
图 16 封装天线示意图[84]
图 17 在封装中集成了2×2的接收天线阵列以及1×2的发射天线阵列[13]
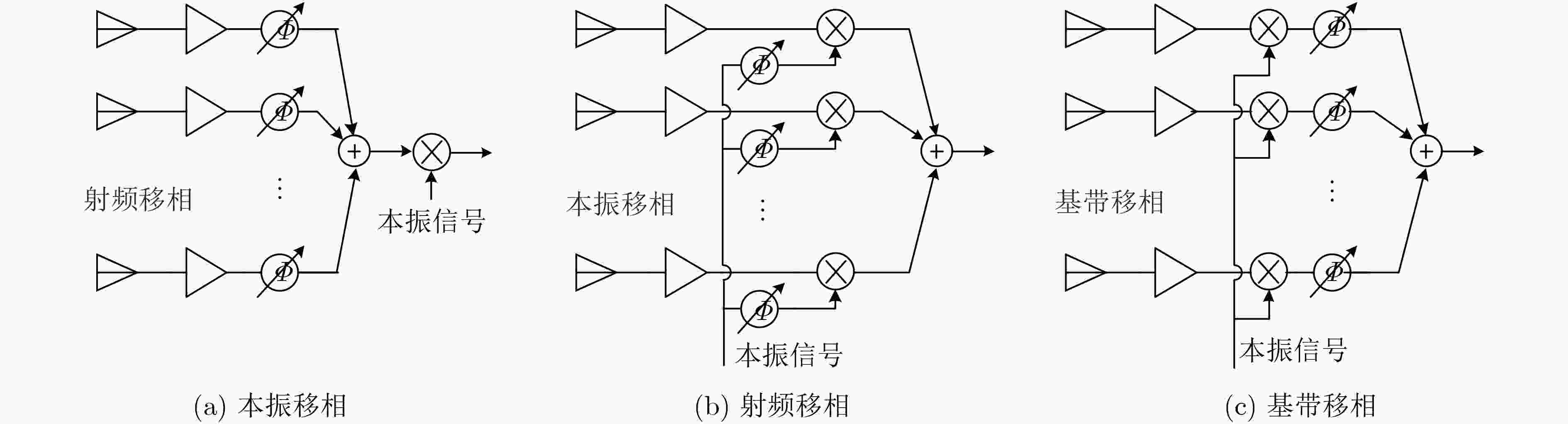
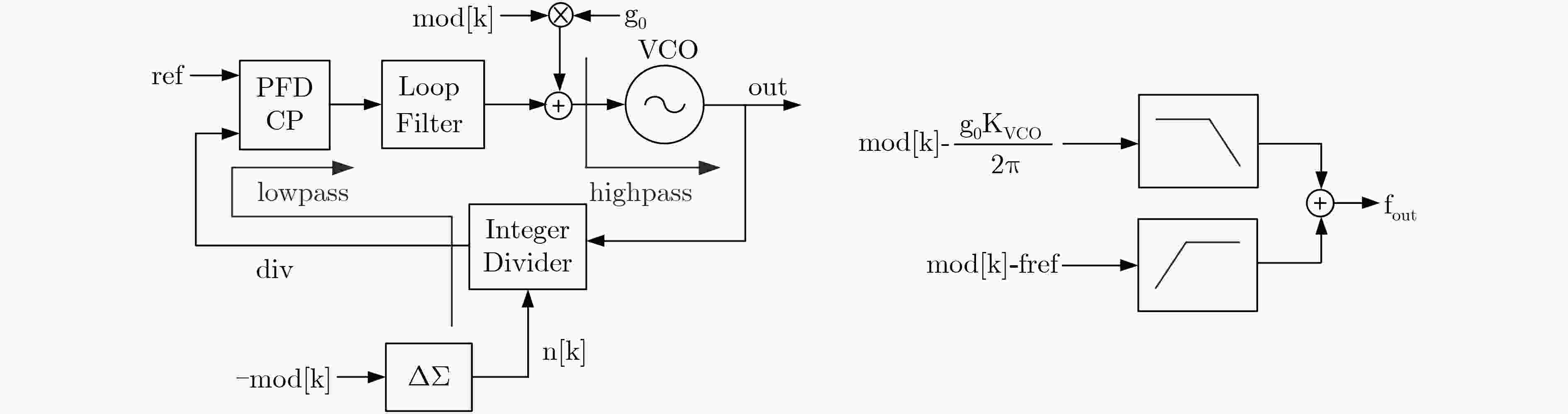
图 20 两点调制基本原理[39]
图 21 采用LMS相关算法校准高通支路与低通支路的匹配[39]
表 1 FMCW信号发生器性能汇总
文献编号 [5] [27] [28] [33] [34] [37] [42] [43] 工艺 65 nm CMOS, 65 nm CMOS, 65 nm CMOS, 90 nm CMOS, 65 nm CMOS, 65 nm CMOS, 65 nm CMOS, 40 nm CMOS, 结构 DSM小数环 DSM小数环 DSM小数环 DDFS整数环 DSM小数环 全数字小数环 混合信号小数环 CTDSM小数环 频率(GHz) 76.0 76~81 77 77 76 60 83 37 扫频带宽(GHz) 0.700 0.500 1.930 0.614 0.700 1.220 1.500 0.500 RMS频差(kHz) 64 ±961 674 >1000 <73 117 <180 820 功耗(mW) 73.0 320.0 N/A 101.0 51.4 48.0 152.0 68.0 面积(mm2) N/A 2.74 0.44 ~0.50 0.29 0.72 1.70 0.18 表 2 硅基毫米波功率放大器性能汇总
文献编号 [49] [50] [51] [52] [53] [54] [55] [56] [57] 工艺 45 nm
CMOS SOI45 nm
CMOS SOI65 nm
CMOS28 nm
UTBB
FD-SOI40 nm
CMOS65 nm
CMOS40 nm
CMOS0.13 μm
SiGe
BiCMOS45 nm
CMOS
SOI结构 堆叠 堆叠 堆叠 功率合成 功率合成 功率合成 功率合成 功率合成 功率合成 频率(GHz) 41.0 45.0 60.0 60.0 60.0 60.0 70.3~85.5 42.0 60.0 电源电压(V) 5.0 2.7 2.5 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.9 4.0/2.4 2.2 PSAT(dBm) 21.6 18.6~19.4 17.6 18.9 17.4 17.7 20.9 28.4 30.1 PAEMAX(%) 25.1 32.0~33.9 20.4 17.7 28.5 11.1 22.3 10.0 20.8 增益(dB) 8.9 9.5 23.5 35.0 21.2 19.2 18.1 18.5 24.7 面积(mm2) 0.300 0.300 0.240 0.162 0.074 0.830 0.190 5.550 6.600 -
YUJIRI L, SHOUCRI M, and MOFFA P. Passive millimeter wave imaging[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2003, 4(3): 39–50. doi: 10.1109/MMW.2003.1237476 HASCH J, TOPAK E, SCHNABEL R, et al. Millimeter-wave technology for automotive radar sensors in the 77 GHz frequency band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2012, 60(3): 845–860. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2178427 CAMIADE M, DOMNESQUE D, OUARCH Z, et al. Fully MMIC-based front end for FMCW automotive radar at 77 GHz[C]. The 2000 30th European Microwave Conference, Paris, France, 2000: 1–4. FOLSTER F, ROHLING H, and LUBBERT U. An automotive radar network based on 77 GHz FMCW sensors[C]. IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2005: 871–876. LEE J, LI Yian, HUNG M H, et al. A fully-integrated 77-GHz FMCW radar transceiver in 65-nm CMOS technology[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(12): 2746–2756. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2075250 LI Yian, HUNG M H, HUANG S J, et al. A fully integrated 77GHz FMCW radar system in 65nm CMOS[C]. 2010 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 216–217. KU B H, SCHMALENBERG P, INAC O, et al. A 77-81-GHz 16-element phased-array receiver with ±50° beam scanning for advanced automotive radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2014, 62(11): 2823–2832. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2014.2354134 WANG Li, GLISIC S, BORNGRAEBER J, et al. A single-ended fully integrated SiGe 77/79 GHz receiver for automotive radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(9): 1897–1908. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2003994 PETKIE D T, BENTON C, and BRYAN E. Millimeter wave radar for remote measurement of vital signs[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–3. CHUANG H R, KUO H C, LIN Fuling, et al. 60-GHz millimeter-wave life detection system (MLDS) for noncontact human vital-signal monitoring[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2012, 12(3): 602–609. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2011.2118198 YANG Zhicheng, PATHAK P H, ZENG Yunze, et al. Monitoring vital signs using millimeter wave[C]. The 17th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing, Paderborn, Germany, 2016: 211–220. YANG Zhicheng, PATHAK P H, ZENG Yunze, et al. Vital sign and sleep monitoring using millimeter wave[J]. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN) , 2017, 13(2): 14. NASR I, JUNGMAIER R, BAHETI A, et al. A highly integrated 60 GHz 6-channel transceiver with antenna in package for smart sensing and short-range communications[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(9): 2066–2076. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2585621 WANG Saiwen, SONG Jie, LIEN J, et al. Interacting with soli: Exploring fine-grained dynamic gesture recognition in the radio-frequency spectrum[C]. The 29th Annual Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 2016: 851–860. HUNG C M, LIN A T C, PENG B C, et al. 9.1 Toward automotive surround-view radars[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 162–164. SKOLNIK W I. Introduction to Radar Systems[M]. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1980: 4. GINSBURG B P, RAMASWAMY S M, RENTALA V, et al. A 160 GHz pulsed radar transceiver in 65 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49(4): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2298033 OH J, JANG J, KIM C Y, et al. A W-band 4-GHz bandwidth phase-modulated pulse compression radar transmitter in 65-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2015, 63(8): 2609–2618. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2442992 ARBABIAN A, CALLENDER S, KANG S, et al. A 90 GHz hybrid switching pulsed-transmitter for medical imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(12): 2667–2681. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2077150 ARBABIAN A, CALLENDER S, KANG S, et al. A 94 GHz mm-wave-to-baseband pulsed-radar transceiver with applications in imaging and gesture recognition[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(4): 1055–1071. GIANNINI V, GUERMANDI D, SHI Qixian, et al. A 79 GHz phase-modulated 4 GHz-BW CW radar transmitter in 28 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49(12): 2925–2937. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2355819 GUERMANDI D, SHI Qixian, DEWILDE A, et al. A 79-GHz 2×2 MIMO PMCW radar SoC in 28-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2017, 52(10): 2613–2626. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2723499 BOURDOUX A, AHMAD U, GUERMANDI D, et al. PMCW waveform and MIMO technique for a 79 GHz CMOS automotive radar[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–5. GIANNINI V, GOLDENBERG M, ESHRAGHI A, et al. 9.2 A 192-virtual-receiver 77/79GHz GMSK code-domain MIMO radar system-on-chip[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 164–166. SOWLATI T, SARKAR S, PERUMANA B, et al. A 60GHz 144-element phased-array transceiver with 51dBm maximum EIRP and ±60° beam steering for backhaul application[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 66–68. JIA Haikun, KUANG Lixue, ZHU Wei, et al. A 77 GHz frequency doubling two-path phased-array FMCW transceiver for automotive radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(10): 2299–2311. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2580599 LIN Jianfu, SONG Zheng, QI Nan, et al. A 77-GHz mixed-mode FMCW signal generator based on bang-bang phase detector[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(10): 2850–2863. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2856248 PARK J, RYU H, HA K W, et al. 76-81-GHz CMOS transmitter with a phase-locked-loop-based multichirp modulator for automotive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2015, 63(4): 1399–1408. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2406071 TOWNLEY A, SWIRHUN P, TITZ D, et al. A 94GHz 4TX-4RX phased-array for FMCW radar with integrated LO and flip-chip antenna package[C]. 2016 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 294–297. GINSBURG B P, SUBBURAJ K, SAMALA S, et al. A multimode 76-to-81GHz automotive radar transceiver with autonomous monitoring[C]. 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 158–160. KU B H, INAC O, CHANG M, et al. 75–85 GHz flip-chip phased array RFIC with simultaneous 8-transmit and 8-receive paths for automotive radar applications[C]. 2013 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Seattle, USA, 2013: 371–374. KIM S Y and REBEIZ G M. A low-power BiCMOS 4-element phased array receiver for 76-84 GHz radars and communication systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 47(2): 359–367. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2170769 MITOMO T, ONO N, HOSHINO H, et al. A 77 GHz 90 nm CMOS transceiver for FMCW radar applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(4): 928–937. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2040234 LUO Tangnian, WU C H E, and CHEN Y J E. A 77-GHz CMOS FMCW frequency synthesizer with reconfigurable chirps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(7): 2641–2647. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2264685 STASZEWSKI R B, WALLBERG J L, REZEQ S, et al. All-digital PLL and transmitter for mobile phones[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(12): 2469–2482. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.857417 WU Wanghua, STASZEWSKI R B, and LONG J R. A 56.4-to-63.4 GHz multi-rate all-digital fractional-N PLL for FMCW radar applications in 65 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49(5): 1081–1096. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2301764 WU Wanghua, BAI Xuefei, STASZEWSKI R B, et al. A mm-wave FMCW radar transmitter based on a multirate ADPLL[C]. 2013 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Seattle, USA, 2013: 107–110. SHI Qixian, BUNSEN K, MARKULIC N, et al. 26.1 A self-calibrated 16 GHz subsampling-PLL-based 30 s fast chirp FMCW modulator with 1.5GHz bandwidth and 100 kHz rms error[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 408–410. CHERNIAK D, GRIMALDI L, BERTULESSI L, et al. A 23-GHz low-phase-noise digital bang-bang PLL for fast triangular and sawtooth chirp modulation[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(12): 3565–3575. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2869097 YEO H, RYU S, LEE Y, et al. 13.1 A 940 MHz-bandwidth 28.8 µs-period 8.9 GHz chirp frequency synthesizer PLL in 65nm CMOS for X-band FMCW radar applications[C]. 2016 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 238–239. HUANG Zhiqiang and LUONG H C. A dithering-less 54.79-to-63.16 GHz DCO with 4-Hz frequency resolution using an exponentially-scaling C-2C switched-capacitor ladder[C]. 2015 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 2015: C234–C235. SAKURAI H, KOBAYASHI Y, MITOMO T, et al. A 1.5 GHz-modulation-range 10 ms-modulation-period 180 kHzrms-frequency-error 26 MHz-reference mixed-mode FMCW synthesizer for mm-wave radar application[C]. 2011 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2011: 292–294. WEYER D, DAYANIK M B, JANG S, et al. A 36.3-to-38.2 GHz− 216 dBc/Hz2 40 nm CMOS fractional-N FMCW chirp synthesizer PLL with a continuous-time bandpass delta-sigma time-to-digital converter[C]. 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 250–252. XU Zule, MIYAHARA M, OKADA K, et al. A 3.6 GHz low-noise fractional-N digital PLL using SAR-ADC-based TDC[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(10): 2345–2356. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2582854 NGUYEN H T, LI Sensen, and WANG Hua. 4.6 A mm-wave 3-way linear Doherty radiator with multi antenna coupling and on-antenna current-scaling series combiner for deep power back-off efficiency enhancement[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 84–86. WANG Fei, LI T W, and WANG Hua. 4.8 A highly linear super-resolution mixed-signal Doherty power amplifier for high-efficiency mm-wave 5G multi-GB/s communications[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 88–90. XIONG Liang, LI Tong, YIN Yun, et al. A broadband switched-transformer digital power amplifier for deep back-off efficiency enhancement[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 76–78. PAEK J S, KIM D, BANG J S, et al. 15.1 An 88%-efficiency supply modulator achieving 1.08 μs/V fast transition and 100 mhz envelope-tracking bandwidth for 5G new radio RF power amplifier[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 238–240. DABAG H T, HANAFI B, GOLCUK F, et al. Analysis and design of stacked-FET millimeter-wave power amplifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(4): 1543–1556. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2247698 AGAH A, DABAG H, HANAFI B, et al. A 34% PAE, 18.6dBm 42-45 GHz stacked power amplifier in 45 nm SOI CMOS[C]. 2012 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Montreal, Canada, 2012: 57–60. KUANG Lixue, CHI Baoyong, JIA Haikun, et al. A 60-GHz CMOS dual-mode power amplifier with efficiency enhancement at low output power[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2015, 62(4): 352–356. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2014.2387675 LARIE A, KERHERVÉ E, MARTINEAU B, et al. 2.10 A 60 GHz 28 nm UTBB FD-SOI CMOS reconfigurable power amplifier with 21% PAE, 18.2 dBm P1 dB and 74 mW PDC[C]. 2015 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, USA, 2015: 1–3. ZHAO Dixian and REYNAERT P. A 60-GHz dual-mode class AB power amplifier in 40-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(10): 2323–2337. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2275662 LAI Jiewei and VALDES-GARCIA A. A 1V 17.9 dBm 60 GHz power amplifier in standard 65 nm CMOS[C]. 2010 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 424–425. ZHAO Dixian and REYNAERT P. 14.1 A 0.9V 20.9 dBm 22.3%-PAE E-band power amplifier with broadband parallel-series power combiner in 40 nm CMOS[C]. 2014 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, USA, 2014: 248–249. TAI Wei, CARLEY L R, and RICKETTS D S. A 0.7W fully integrated 42 GHz power amplifier with 10% PAE in 0.13 µm SiGe BiCMOS[C]. 2013 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, USA, 2013: 142–143. NGUYEN H T, JUNG D, and WANG Hua. 4.9 A 60GHz CMOS power amplifier with cascaded asymmetric distributed-active-transformer achieving watt-level peak output power with 20.8% PAE and supporting 2Gsym/s 64-QAM modulation[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 90–92. CHEN Ying, VAN DER HEIJDEN M P, and LEENAERTS D M W. A 1-Watt Ku-band power amplifier in SiGe with 37.5% PAE[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 324-325. JIA Haikun, CHI Baoyong, KUANG Lixue, et al. A 77 GHz FMCW radar transmitter with reconfigurable power amplifier in 65 nm CMOS[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2014, 45(7): 898–903. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2014.03.004 HADIPOUR K, GHILIONI A, MAZZANTI A, et al. A 40 GHz to 67 GHz bandwidth 23 dB gain 5.8 dB maximum NF mm-Wave LNA in 28 nm CMOS[C]. 2015 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Phoenix, USA, 2015: 327–330. YE Wanxin, MA Kaixue, YEO K S, et al. A 65 nm CMOS Power Amplifier With Peak PAE above 18.9% from 57 to 66 GHz using synthesized transformer-based matching network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2015, 62(10): 2533–2543. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2015.2476315 BHAGAVATULA V, ZHANG Tong, SUVARNA A R, et al. An ultra-wideband IF millimeter-wave receiver with a 20 GHz channel bandwidth using gain-equalized transformers[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(2): 323–331. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2504411 LI C H, KUO C N, and KUO M C. A 1.2-V 5.2-mW 20-30-GHz wideband receiver front-end in 0.18-μm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2012, 60(11): 3502–3512. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2216285 JIA Haikun, KUANG Lixue, WANG Zhihua, et al. A W-band injection-locked frequency doubler based on top-injected coupled resonator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2016, 64(1): 210–218. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2498600 BASSI M, ZHAO Junlei, BEVILACQUA A, et al. A 40-67 GHz Power Amplifier With 13 dBm PSAT and 16% PAE in 28 nm CMOS LP[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50(7): 1618–1628. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2409295 VIGILANTE M and REYNAERT P. On the design of wideband transformer-based fourth order matching networks for E-band receivers in 28-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2017, 52(8): 2071–2082. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2690864 JIA Haikun, PRAWOTO C C, CHI Baoyong, et al. A full Ka-band power amplifier with 32.9% PAE and 15.3-dBm power in 65-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2018, 65(9): 2657–2668. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2799983 HASHEMI H, GUAN Xiang, KOMIJANI A, et al. A 24-GHz SiGe phased-array receiver-LO phase-shifting approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(2): 614–626. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2004.841218 SOWLATI T, SARKAR S, PERUMANA G B, et al. A 60-GHz 144-Element Phased-Array Transceiver for Backhaul Application[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(12): 3640–3659. HUANG Dong, ZHANG Li, ZHU Huabing, et al., A 94 GHz 2x2 Phased-Array FMCW Imaging Radar Transceiver with 11dBm Output Power and 10.5 dB NF in 65nm CMOS[C]. 2019 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), 2019, 47–50. JANG S, LU Rundao, JEONG J, et al. A 1-GHz 16-element four-beam true-time-delay digital beamformer[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(5): 1304–1314. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2894357 TABESH M, CHEN Jiashu, MARCU C, et al. A 65 nm CMOS 4-element sub-34 mW/element 60 GHz phased-array transceiver[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(12): 3018–3032. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2166030 PELLERANO S, CALLENDER S, SHIN W, et al. 9.7 a scalable 71-to-76 GHz 64-element phased-array transceiver module with 2× 2 direct-conversion IC in 22 nm FinFET CMOS technology[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 174–176. SHAHRAMIAN S, HOLYOAK M, SINGH A, et al. A fully integrated scalable W-band phased-array module with integrated antennas, self-alignment and self-test[C]. 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 74–76. DUNWORTH J D, HOMAYOUN A, KU B H, et al. A 28 GHz Bulk-CMOS dual-polarization phased-array transceiver with 24 channels for 5G user and basestation equipment[C]. 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 70–72. 张光义, 赵玉洁. 相控阵雷达技术. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2006: 15. WU H T, TEKLE M, NALLANI C S, et al. Bond wire antenna/feed for operation near 60 GHz[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2009, 57(12): 2966–2972. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2009.2033836 JOHANNSEN U and SMOLDERS A B. On the yield of millimeter-wave bond-wire-antennas in high volume production[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(8): 4363–4366. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2259456 JAMESON S and SOCHER E. A wide-band CMOS to waveguide transition at mm-wave frequencies with wire-bonds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2015, 63(9): 2741–2750. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2461160 KAWASAKI K, AKIYAMA Y, KOMORI K, et al. A millimeter-wave intra-connect solution[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(12): 2655–2666. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2077130 LI C H, KO C L, KUO C N, et al. A low-cost DC-to-84-GHz broadband bondwire interconnect for SoP heterogeneous system integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(12): 4345–4352. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2281966 HEINRICH W. The flip-chip approach for millimeter wave packaging[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2005, 6(3): 36–45. doi: 10.1109/MMW.2005.1511912 JENTZSCH A and HEINRICH W. Theory and measurements of flip-chip interconnects for frequencies up to 100 GHz[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2001, 49(5): 871–878. doi: 10.1109/22.920143 AL HENAWY M and SCHNEIDER M. Integrated antennas in eWLB packages for 77 GHz and 79 GHz automotive radar sensors[C]. The 8th European Radar Conference, Manchester, UK, 2011: 424–427. HASCH J, WOSTRADOWSKI U, GAIER S, et al. 77 GHz radar transceiver with dual integrated antenna elements[C]. 2010 German Microwave Conference Digest of Papers, Berlin, Germany, 2010: 280–283. YANG Yang and BLUM R S. Minimax robust MIMO radar waveform design[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1(1): 147–155. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2007.897056 DE MAIO A and LOPS M. Design principles of MIMO radar detectors[J]. IEEE transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(3): 886–898. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4383581 FUHRMANN D R and ANTONIO G A. Transmit beamforming for MIMO radar systems using signal cross-correlation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(1): 171–186. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4516997 STOICA P, LI Jian, and XIE Yao. On probing signal design for MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(8): 4151–4161. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894398 BLEH D, RÖSCH M, KURI M, et al. W-band time-domain multiplexing FMCW MIMO radar for far-field 3-D imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(9): 3474–3484. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2661742 GANIS A, NAVARRO E M, SCHOENLINNER B, et al. A portable 3-D imaging FMCW MIMO radar demonstrator with a 24×24 antenna array for medium-range applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 298–312. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2746739 DÜRDODT C, FRIEDRICH M, GREWING C, et al. A low-if RX two-point SΔ-modulation TX CMOS single-chip Bluetooth solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2001, 49(9): 1531–1537. doi: 10.1109/22.942563 XU Ni, RHEE W, and WANG Zhihua. A hybrid loop two-point modulator without DCO nonlinearity calibration by utilizing 1 bit high-pass modulation[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49(10): 2172–2186. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2345021 MARKULIC N, RACZKOWSKI K, MARTENS E, et al. A DTC-based subsampling PLL capable of self-calibrated fractional synthesis and two-point modulation[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(12): 3078–3092. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2596766 -





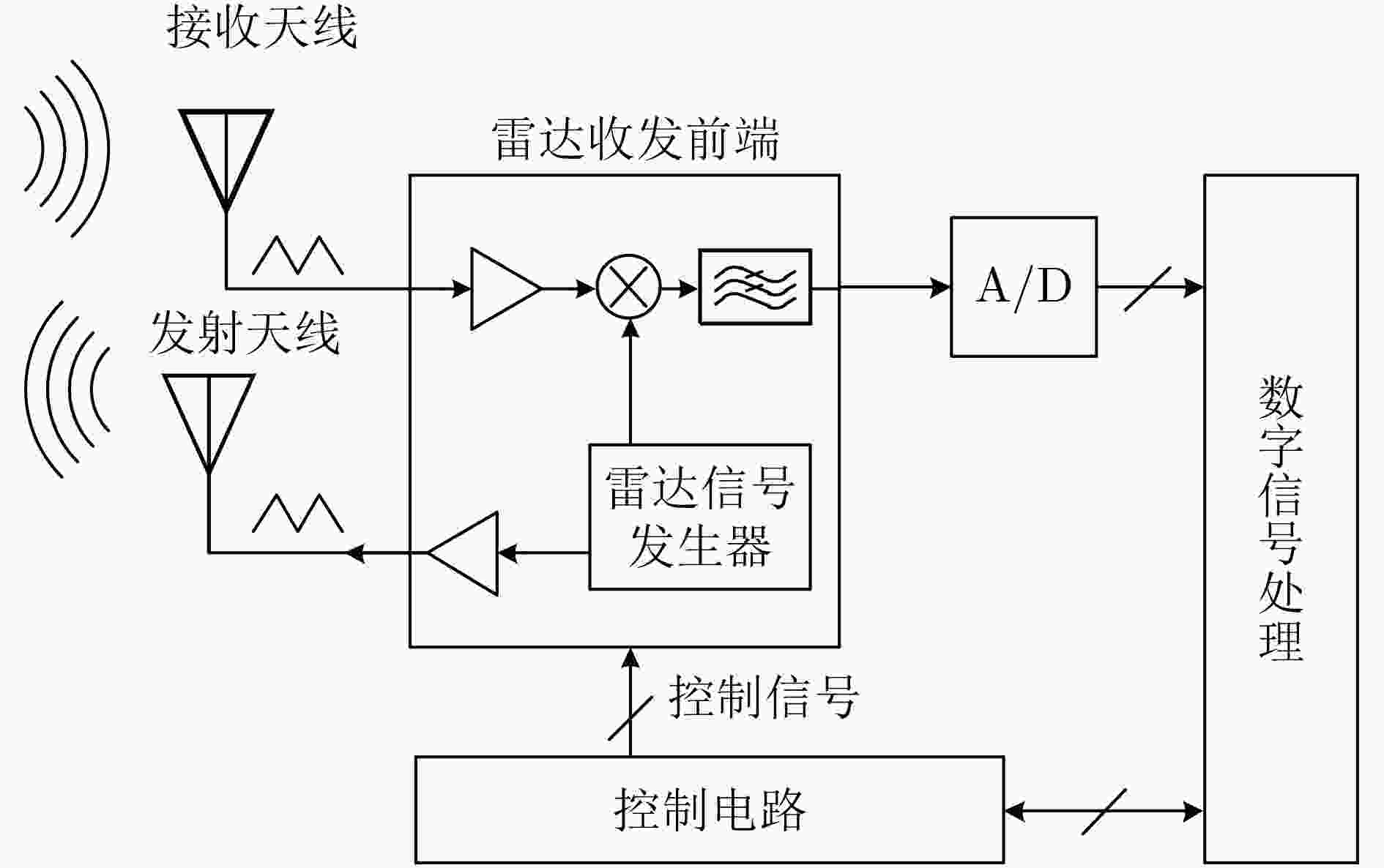
 下载:
下载:
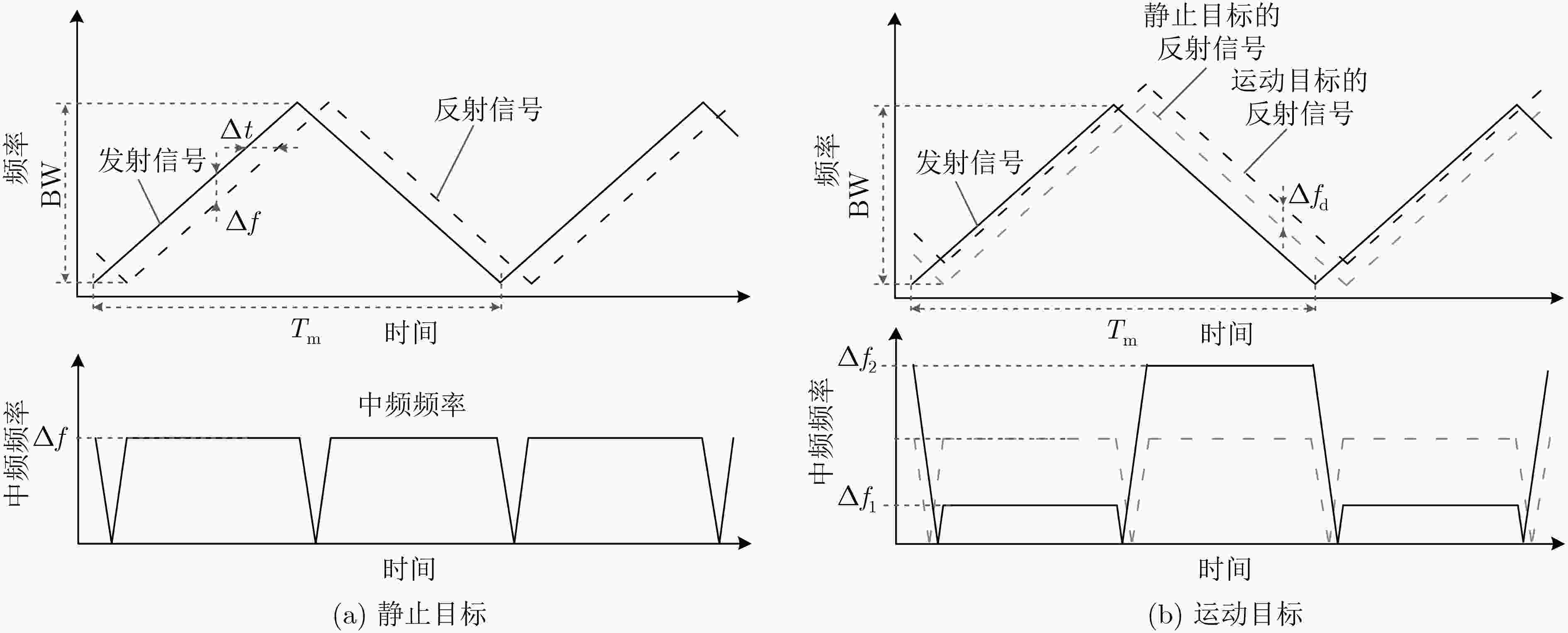
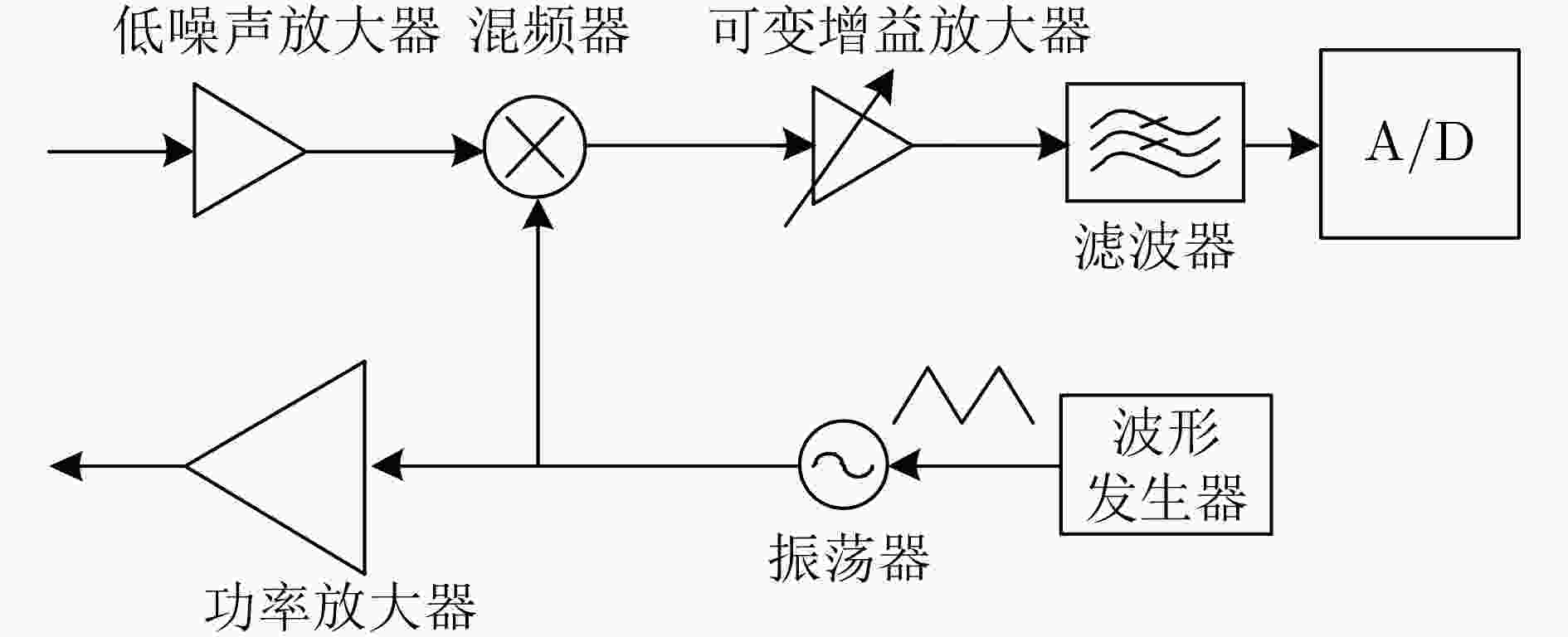



 下载:
下载:
