An Improved Virtual Force Relocation Coverage Enhancement Algorithm
-
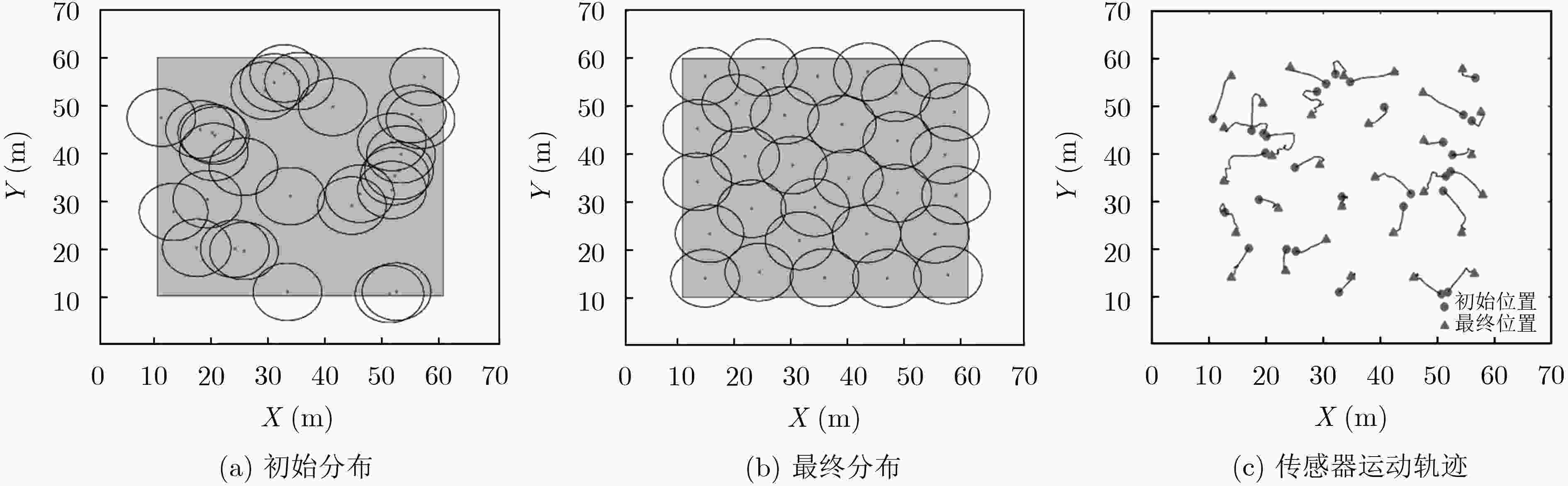
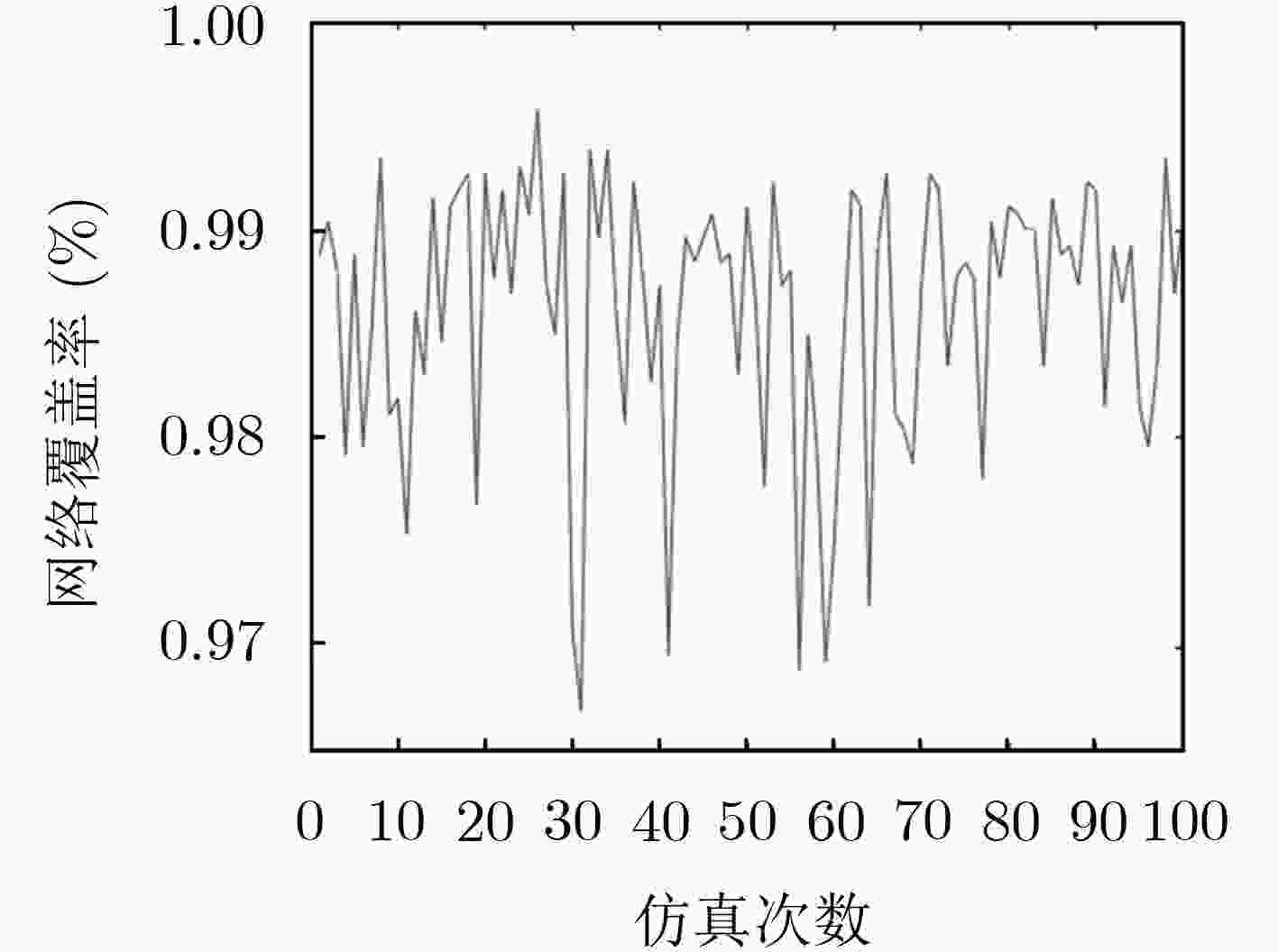
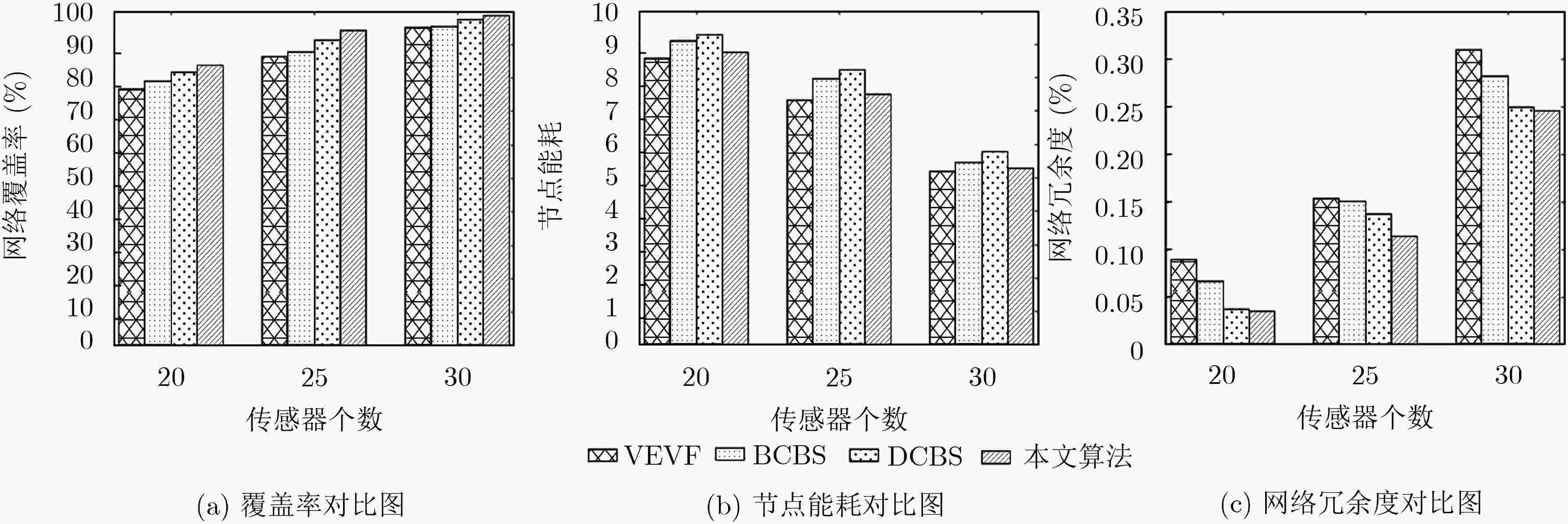
摘要: 在移动无线传感网络(MWSN)的部署问题中最关键的是如何提供最大的区域覆盖范围。针对现有的覆盖控制算法存在覆盖率不理想、部署效率低、能耗过高的问题,该文提出了一种高效部署策略。第1阶段利用Voronoi图获得整个网络的覆盖孔,检测Voronoi多边形内的未覆盖区域,并提供虚拟力驱动传感器移动,同时采用动态调整策略改变移动步长,从而减少能量损耗;第2阶段提出一种检测机制,利用Delaunay三角网检测传感器之间的局部覆盖孔并进行修复。仿真结果表明,该算法在提高网络覆盖率的同时加快了收敛速度,为部署移动无线传感网络提供了新的解决思路。
-
关键词:
- 移动无线传感网 /
- 网络覆盖 /
- 虚拟力 /
- voronoi图 /
- delaunay三角
Abstract: The most critical issue in the deployment of Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks (MWSN) is how to provide maximum regional coverage.To solve the problem that the existing coverage control algorithm has unsatisfactory coverage, low deployment efficiency and high energy consumption, an efficient deployment strategy is proposed.The first stage uses the Voronoi diagram to obtain the coverage hole of the entire network, and detects the uncovered area in the Voronoi polygon, and provides virtual force to drive the sensor movement, and uses the dynamic adjustment strategy to change the moving step size, thereby reducing energy loss;The second stage proposes a detection mechanism that uses a Delaunay triangulation to detect local coverage holes between sensors and repair them.The simulation results show that the algorithm accelerates the convergence speed while improving the network coverage, and provides a new solution for deploying mobile wireless sensor networks. -
表 1 基于Voronoi图的虚拟力重定位算法
Randomly deploy N sensors in the monitoring area; Repeat Construct Voronoi polygons based on the position of the
sensors;For each $i{\rm{ (} }1 \le i \le N)$ For each $j{\rm{ } }(1 \le j \le {\rm{vertex(} }i\rm{)})$// vertex: the number of
Voronoi polygon vertices;If ${{\rm dist(} }i,j{) < }{R_s}$ //case 1: Voronoi polygon vertices are
all covered;Calculate the force of the centroid on the sensor and
the position of the sensor;Else //case 2: Voronoi polygon vertices are not all
covered;Calculate ${F_{\rm{uncov}}}$ and the position of the sensor at the
next moment;// ${F_{\rm{uncov}}}$:the force of the uncovered grid
point on the sensor;End for End for Sensor location update; End for Until termination criterion is met 表 2 基于Delaunay三角的局部覆盖空洞修复算法
Construct a Delaunay triangulation based on the position of the
sensors;For each $j{\rm{ } }(1 \le j \le {\rm{TRI} }\left( i \right))$// TRI: the number of Delaunay
trianglesCalculate empty circle center coordinates and radius; If there is a gap between the sensors: Calculate the force of the centroid of the empty circle on
the sensor and the position of the sensor circle on the
sensor;If ${\rm{fitness} }(x(t)) \ge {\rm{fitness} }(x(t - {\rm{1} }))$ Sensor location update; Break; Else Sensor position unchanged; End if End if End for -
YUE Yinggao and HE Ping. A comprehensive survey on the reliability of mobile wireless sensor networks: Taxonomy, challenges, and future directions[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 44: 188–204. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.03.005 ETANCELIN J M, FABBRI A, GUINAND F, et al. DACYCLEM: A decentralized algorithm for maximizing coverage and lifetime in a mobile wireless sensor network[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2019, 87: 174–187. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2018.12.008 HACIOGLU G, KAND V F A, and SESLI E. Multi objective clustering for wireless sensor networks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 59: 86–100. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.016 ALIA O M and Al-AJOURI A. Maximizing wireless sensor network coverage with minimum cost using harmony search algorithm[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(3): 882–896. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2016.2633409 ABO-ZAHHAD M, SABOR N, SASAKI S, et al. A centralized immune-Voronoi deployment algorithm for coverage maximization and energy conservation in mobile wireless sensor networks[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 30: 36–51. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2015.11.005 XU Ying, DING Ou, QU Rong, et al. Hybrid multi-objective evolutionary algorithms based on decomposition for wireless sensor network coverage optimization[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 68: 268–282. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.03.053 ROUT M and ROY R. Dynamic deployment of randomly deployed mobile sensor nodes in the presence of obstacles[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2016, 46: 12–22. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2016.03.004 MAHBOUBI H and AGHDAM A G. Distributed deployment algorithms for coverage improvement in a network of wireless mobile sensors: Relocation by virtual force[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2017, 4(4): 736–748. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2016.2547579 HABIBI J, MAHBOUBI H, and AGHDAM A G. A gradient-based coverage optimization strategy for mobile sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2017, 4(3): 477–488. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2016.2515370 LEE H J, KIM Y H, HAN Y H, et al. Centroid-Based movement assisted sensor deployment schemes in wireless sensor networks[C]. The 70th Vehicular Technology Conference Fall, Anchorage, USA, 2009. doi: 10.1109/VETECF.2009.5379087. FANG Wei, SONG Xinhong, WU Xiaojun, et al. Novel efficient deployment schemes for sensor coverage in mobile wireless sensor networks[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 41: 25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.08.001 BARTOLINI N, BONGIOVANNI G, PORTA T L, et al. Voronoi-based deployment of mobile sensors in the face of adversaries[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Sydney, Australia, 2014: 532–537. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2014.6883373. QIU Chenxi and SHEN Haiying. A delaunay-based coordinate-free mechanism for full coverage in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(4): 828–839. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.134 LI Wei and ZHANG Wei. Coverage hole and boundary nodes detection in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2015, 48: 35–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2014.10.011 JOSHITHA K L and JAYASHRI S. A novel redundant hole identification and healing algorithm for a homogeneous distributed Wireless Sensor Network[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2019, 104(4): 1261–1282. doi: 10.1007/s11277-018-6079-5 SO-IN C, NGUYEN T G, and NGUYEN N G. An efficient coverage hole-healing algorithm for area-coverage improvements in mobile sensor networks[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2019, 12(3): 541–552. doi: 10.1007/s12083-018-0675-8 -





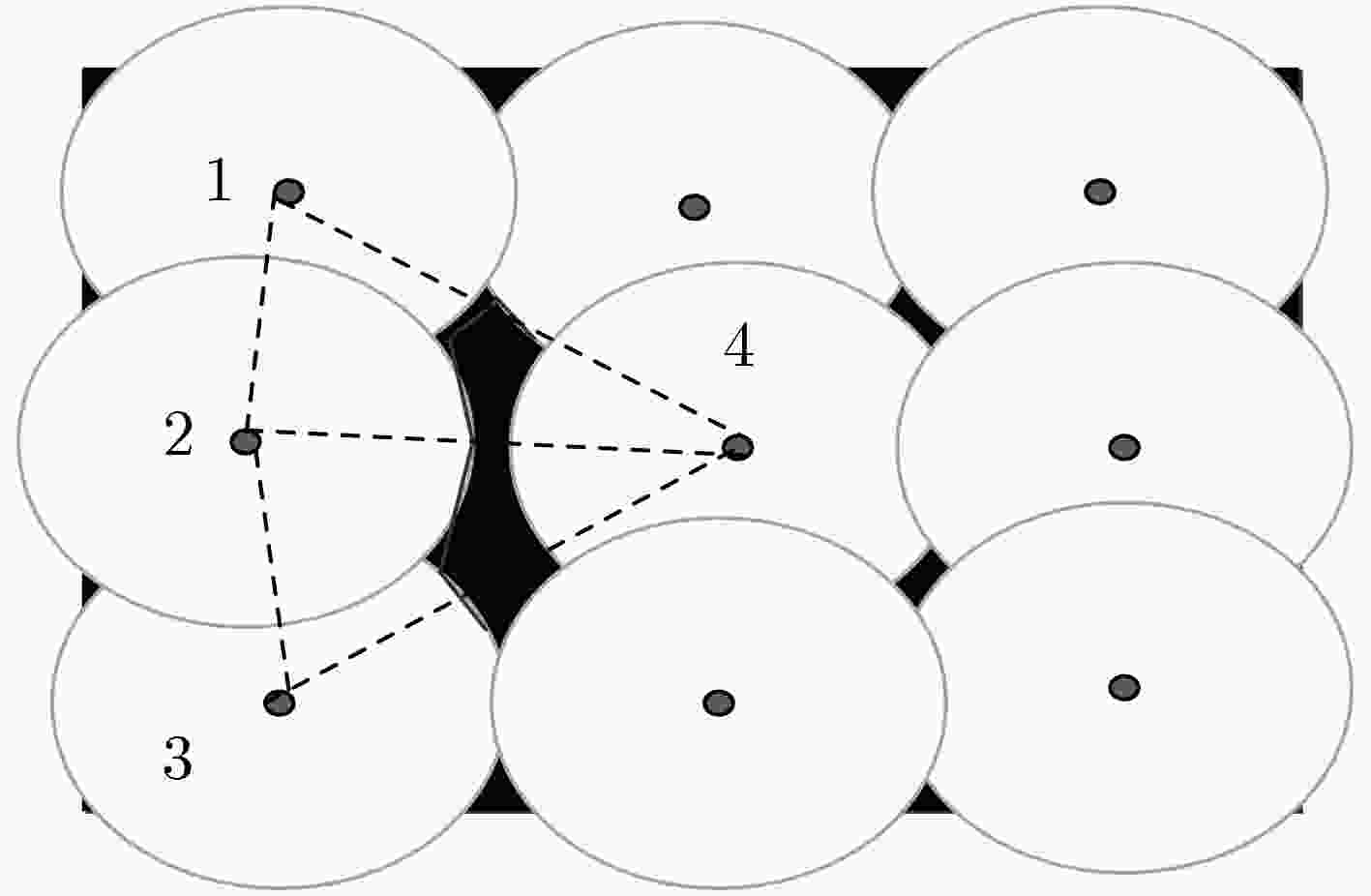
 下载:
下载:
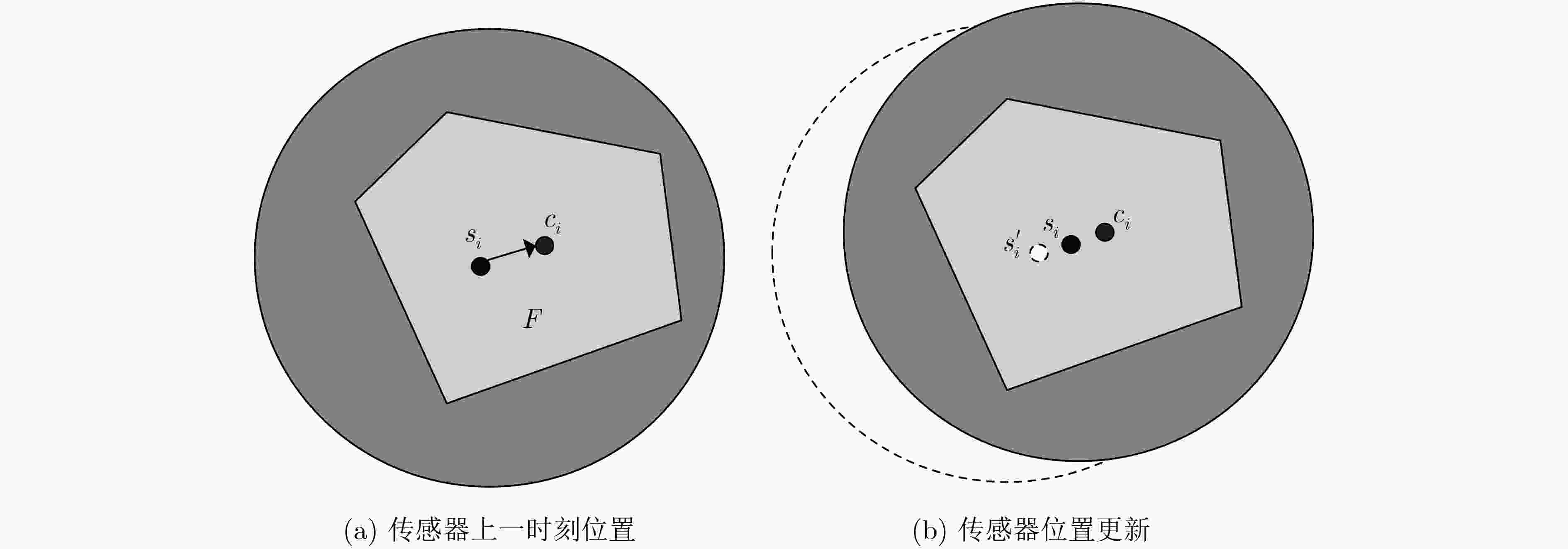
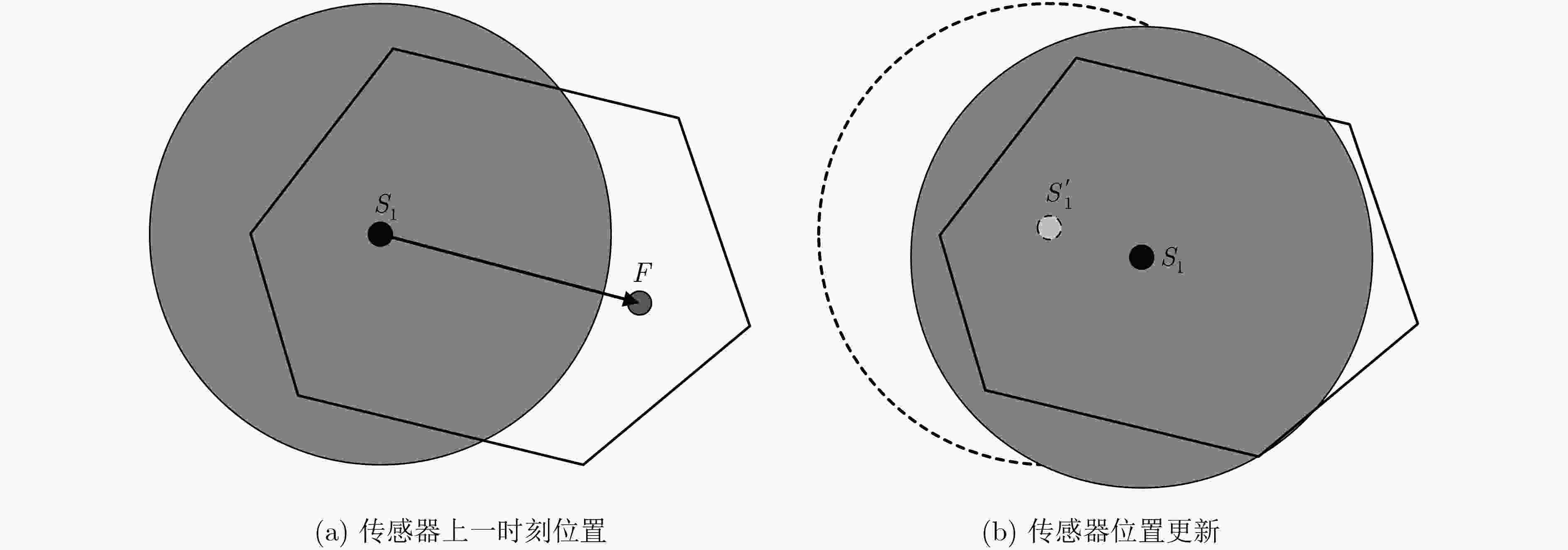
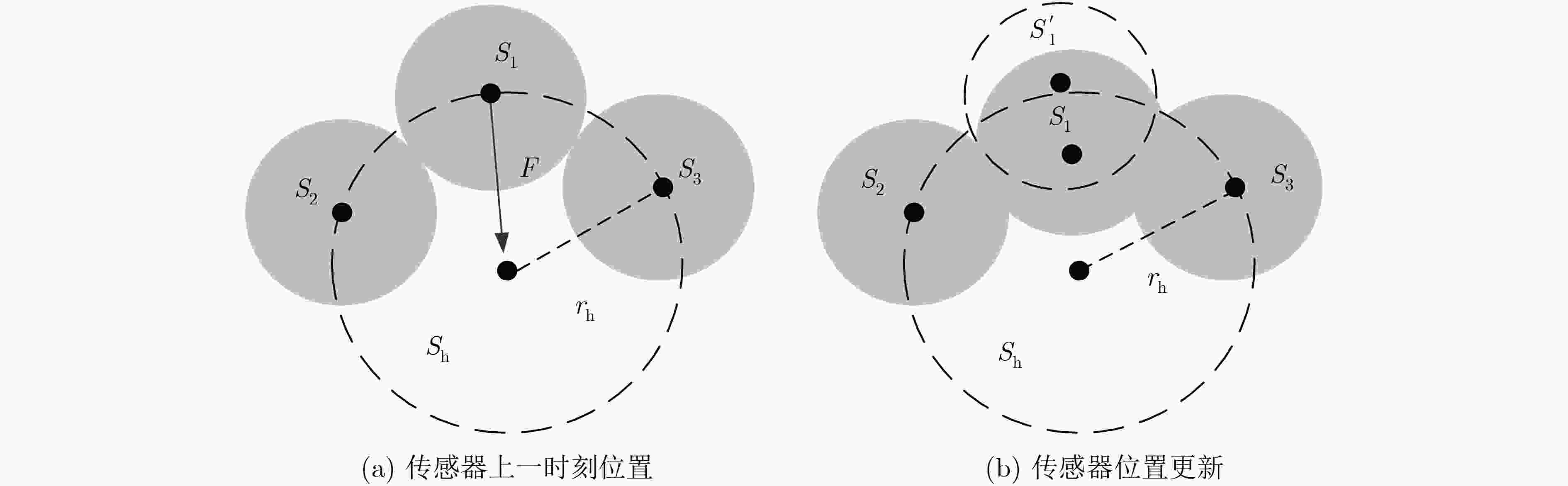



 下载:
下载:
