Automatic Decoding Algorithm of Morse Code Based on Deep Neural Network
-
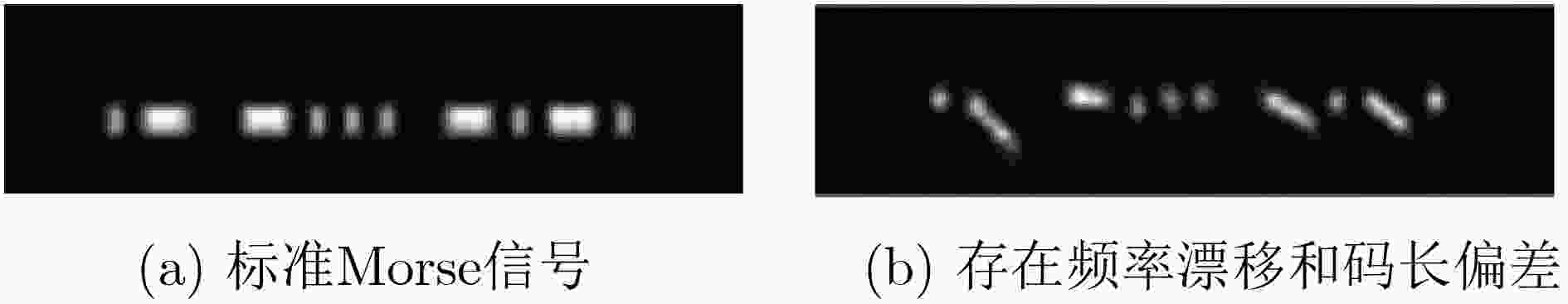
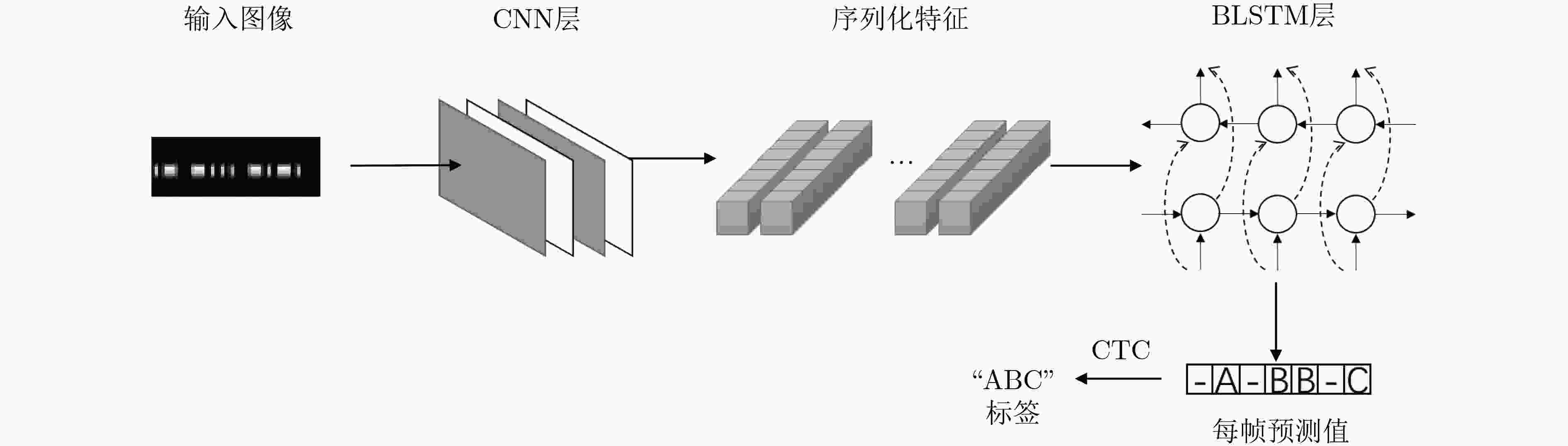
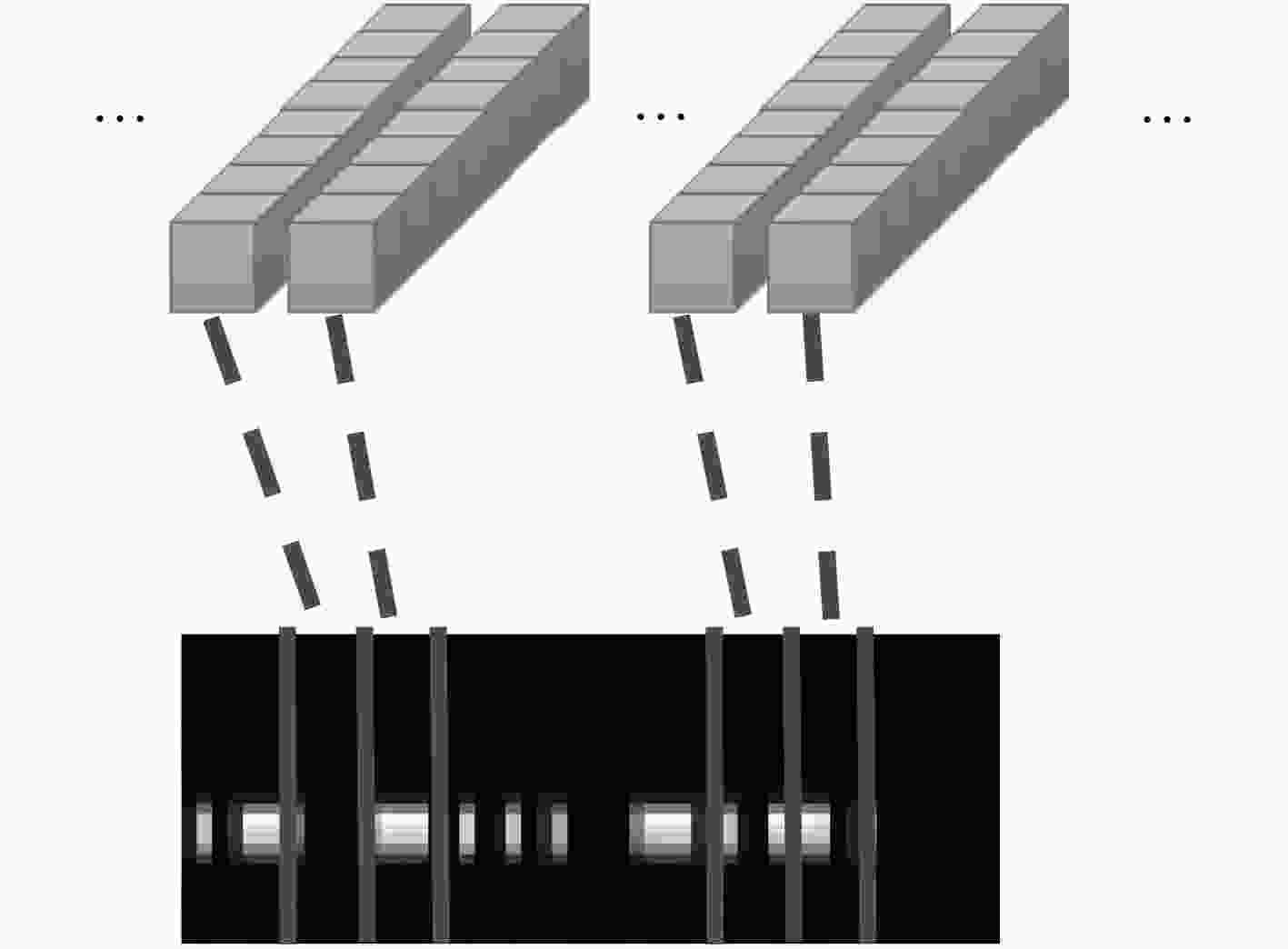
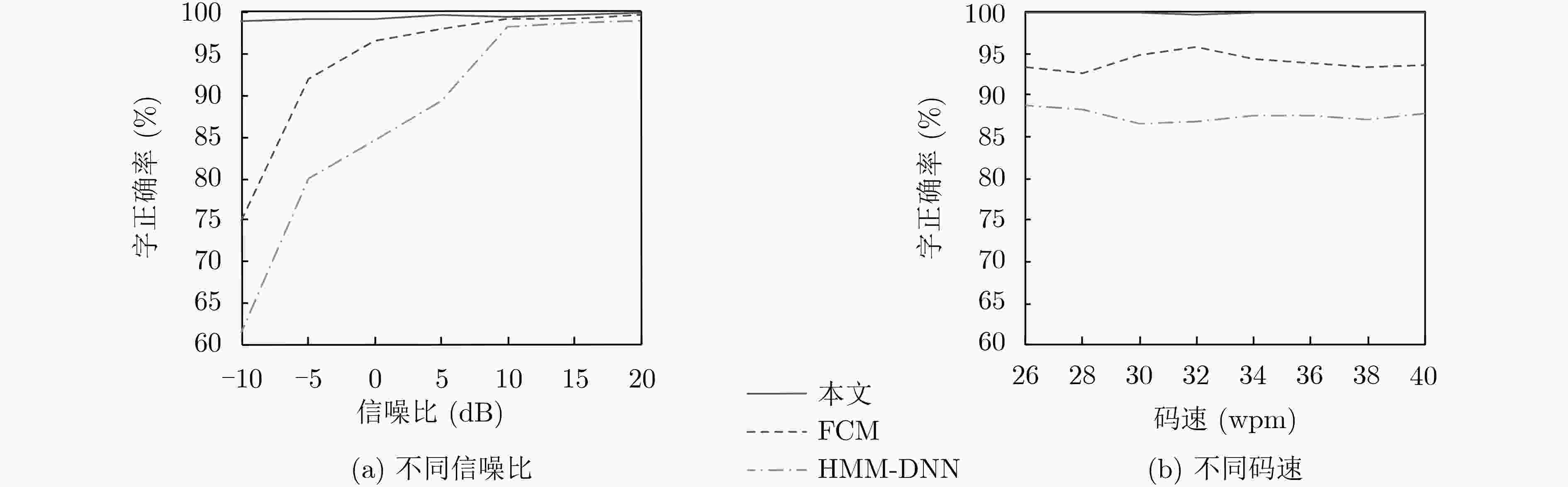
摘要: 在军用和民用领域,Morse电报一直是一种重要的短波通信手段,但目前的自动译码算法仍然存在准确率低、无法适应低信噪比和不稳定的信号等问题。该文引入深度学习方法构建了一个Morse码自动识别系统,神经网络模型由卷积神经网络、双向长短时记忆网络和连接时序分类层组成,结构简单,且能够实现端到端的训练。相关实验表明,该译码系统在不同信噪比、不同码速、信号出现频率漂移以及不同发报手法引起的码长偏差等情况下,均能取得较好的识别效果,性能优于传统的自动识别算法。Abstract: In the military and civilian fields, the Morse telegraph is always as an important means of short-wave communication, but the current automatic decoding algorithms still have problems such as low accuracy, inability to adapt to low signal-to-noise ratio and unstable signals. A deep learning method is introduced to construct a Morse code automatic recognition system. The neural network model consists of convolutional neural network, bidirectional long short-term memory network and connectionist temporal classification layer. The structure is simple and can implement end-to-end training. Related experiments show that the decoding system can achieve good recognition results under different signal-to-noise ratio, code rate, frequency drift and code length deviation caused by different sending manipulation, and the performance is better than the traditional recognition algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Morse code /
- Automatic decoding /
- Deep learning /
- Frequency drift /
- Code length deviation
-
表 1 CNN层设置
层名称 对应核大小 卷积层1 (5, 5, 1, 32),步长=(1, 1) 最大池化层1 (2, 2),步长=(2, 2) 卷积层2 (5, 5, 32, 64),步长=(1, 1) 最大池化层2 (2, 16),步长=(2, 2) 表 2 数据集组成
码速(wpm) 信噪比(dB) 数目 训练集 25, 30, 40 40, 30, 20, 10, 6, 3, –3, –6, –8, –10 25000/50000 验证集 25, 30, 40 40, 30, 20, 10, 6, 3, –3, –6, –8, –10 2500 测试集 25, 30, 40 40, 30, 20, 10, 6, 3, –3, –6, –8, –10 2500 表 3 频率漂移和码长偏差情况下的译码准确率
字准确率(%) 词准确率(%) 原始信号 99.92 99.65 频率漂移 96.23 91.71 频率漂移+码长偏差 95.88 90.40 表 4 有无频漂时去掉CNN前后译码性能
迭代次数 字准确率(%) 词准确率(%) 有CNN,无频漂 23 99.92 99.65 无CNN,无频漂 42 92.71 73.90 有CNN,有频漂 26 96.23 91.71 无CNN,有频漂 47 63.11 20.35 -
DEY S, CHUGG K M, and BEEREL P A. Morse code datasets for machine learning[C]. The 9th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Bangalore, India, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/icccnt.2018.8494011. SHIH C H and LUO C H. A Morse-code recognition system with LMS and matching algorithms for persons with disabilities[J]. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 1997, 44(3): 193–202. doi: 10.1016/s1386-5056(97)00020-8 HSIEH M C, LUO C H, and MAO Chiwu. Unstable Morse code recognition with adaptive variable-ratio threshold prediction for physically disabled persons[J]. IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, 2000, 8(3): 405–413. doi: 10.1109/86.867882 YANG Chenghong, LUO C H, JEANG Y L, et al. A novel approach to adaptive Morse code recognition for disabled persons[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2000, 54(1/3): 23–32. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4754(00)00180-4 GOLD B. Machine recognition of hand-sent Morse code[J]. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 1959, 5(1): 17–24. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1959.1057478 WU Chungmin and LUO Chinghsing. Morse code recognition system with fuzzy algorithm for disabled persons[J]. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology, 2002, 26(5): 202–207. doi: 10.1080/03091900210156904 WANG Yaqi, SUN Zhonghua, and JIA Kebin. An automatic decoding method for Morse signal based on clustering algorithm[C]. The 12th International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Kaohsiung, China, 2017: 235–242. 王亚琦, 孙中华, 贾克斌. Morse报自动译码算法研究[J]. 信号处理, 2017, 33(11): 1451–1456.WANG Yaqi, SUN Zhonghua, and JIA Kebin. Research on automatic decoding algorithm of Morse telegraph[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 33(11): 1451–1456. LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 WANG Xianyu, ZHAO Qi, MA Cheng, et al. Automatic Morse code recognition under low SNR[C]. 2018 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic, Control and Automation Engineering (MECAE 2018), Qingdao, China, 2018: 46–51. doi: 10.2991/mecae-18.2018.46. SHI Baoguang, BAI Xiang, and YAO Cong. An end-to-end trainable neural network for image-based sequence recognition and its application to scene text recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(11): 2298–2304. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2646371 韦醒超. 摩尔斯短波无线通信系统的设计与实现研究[D]. [硕士论文], 湖南大学, 2017.WEI Xingchao. Research on the design and implementation of Morse shortwave wireless communication system[D]. [Master dissertation], Hunan University, 2017. CABAL-YEPEZ E, GARCIA-RAMIREZ A G, ROMERO-TRONCOSO R J, et al. Reconfigurable monitoring system for time-frequency analysis on industrial equipment through STFT and DWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(2): 760–771. doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2221131 SAINATH T N, KINGSBURY B, SAON G, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for large-scale speech tasks[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 64: 39–48. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.08.005 GRAVES A and SCHMIDHUBER J. Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures[J]. Neural Networks, 2005, 18(5/6): 602–610. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.06.042 GRAVES A, FERNÁNDEZ S, and GOMEZ F. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, USA, 2006: 369–367. 刘宏哲, 杨少鹏, 袁家政, 等. 基于单一神经网络的多尺度人脸检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2598–2605. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180163LIU Hongzhe, YANG Shaopeng, YUAN Jiazheng, et al. Multi-scale face detection based on single neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2598–2605. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180163 -





 下载:
下载:
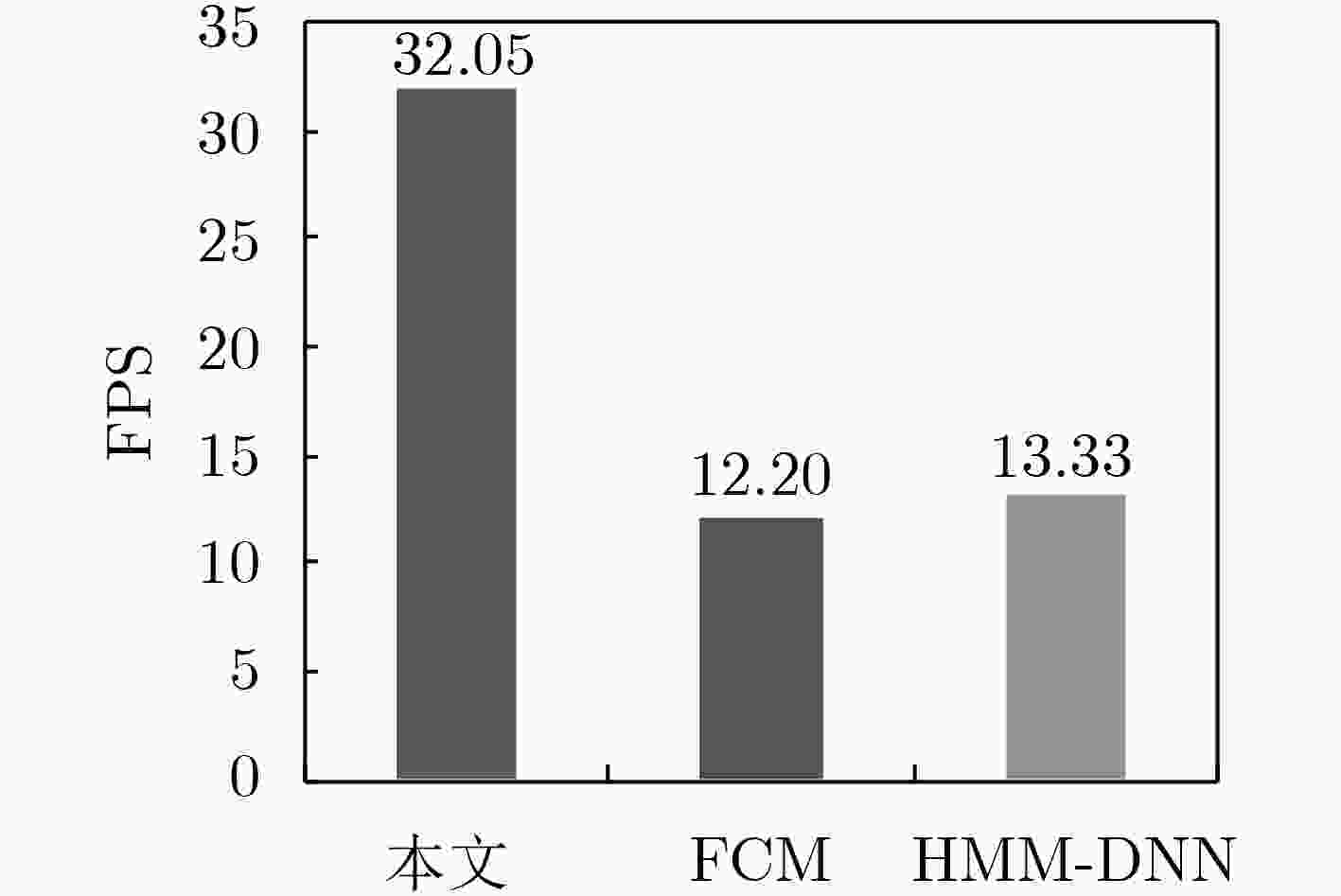



 下载:
下载:
