Development in Signal Processing Based on Correntropy and Cyclic Correntropy
-
摘要:
在无线电监测和目标定位等应用中,接收信号经常会受到脉冲噪声和同频带干扰等复杂电磁环境的影响,传统的基于2阶统计量的信号处理方法往往不能正常工作,基于分数低阶统计量的信号处理方法也由于对信号噪声统计先验知识的依赖性而遇到困难。近年来提出并受到信号处理领域普遍关注的相关熵和循环相关熵信号处理理论与方法,是解决复杂电磁环境下信号分析处理、参数估计、目标定位和其他应用问题的有效技术手段,有力促进了非高斯、非平稳信号处理理论方法和应用的发展。该文系统性地综述了相关熵和循环相关熵信号处理的基本理论和基本方法,包括相关熵与循环相关熵的起源背景、定义概念、性质特点,以及所包含的数学物理意义。该文还介绍了相关熵与循环相关熵信号处理在多个领域的应用问题,希望对非高斯、非平稳统计信号处理的研究和应用有所裨益。
Abstract:In radio monitoring and target location applications, the received signals are often affected by complex electromagnetic environment, such as impulsive noise and cochannel interference. Traditional signal processing methods based on second-order statistics often fail to work properly. The signal processing methods based on fractional lower order statistics also encounter difficulties due to their dependence on prior knowledge of signals and noises. In recent years, the theory and method of correntropy and cyclic correntropy signal processing, which are widely concerned in the field of signal processing, are put forward. They are effective technical means to solve the problems of signal analysis and processing, parameter estimation, target location and other applications to complex electromagnetic environment. They promote greatly the development of the theory and application of non-Gaussian and non-stationary signal processing. This paper reviews systematically the basic theory and methods of correntropy and cyclic correntropy signal processing, including the background, definition, properties and characteristics of correntropy and cyclic correntropy, as well as their mathematical and physical meanings. This paper introduces also the applications of correntropy and cyclic correntropy signal processing to many fields, hoping to benefit the research and application of non-Gaussian and non-stationary statistical signal processing.
-
Key words:
- Signal processing /
- Correntropy /
- Cyclic correntropy /
- Non-Gaussian /
- Non-stationary
-
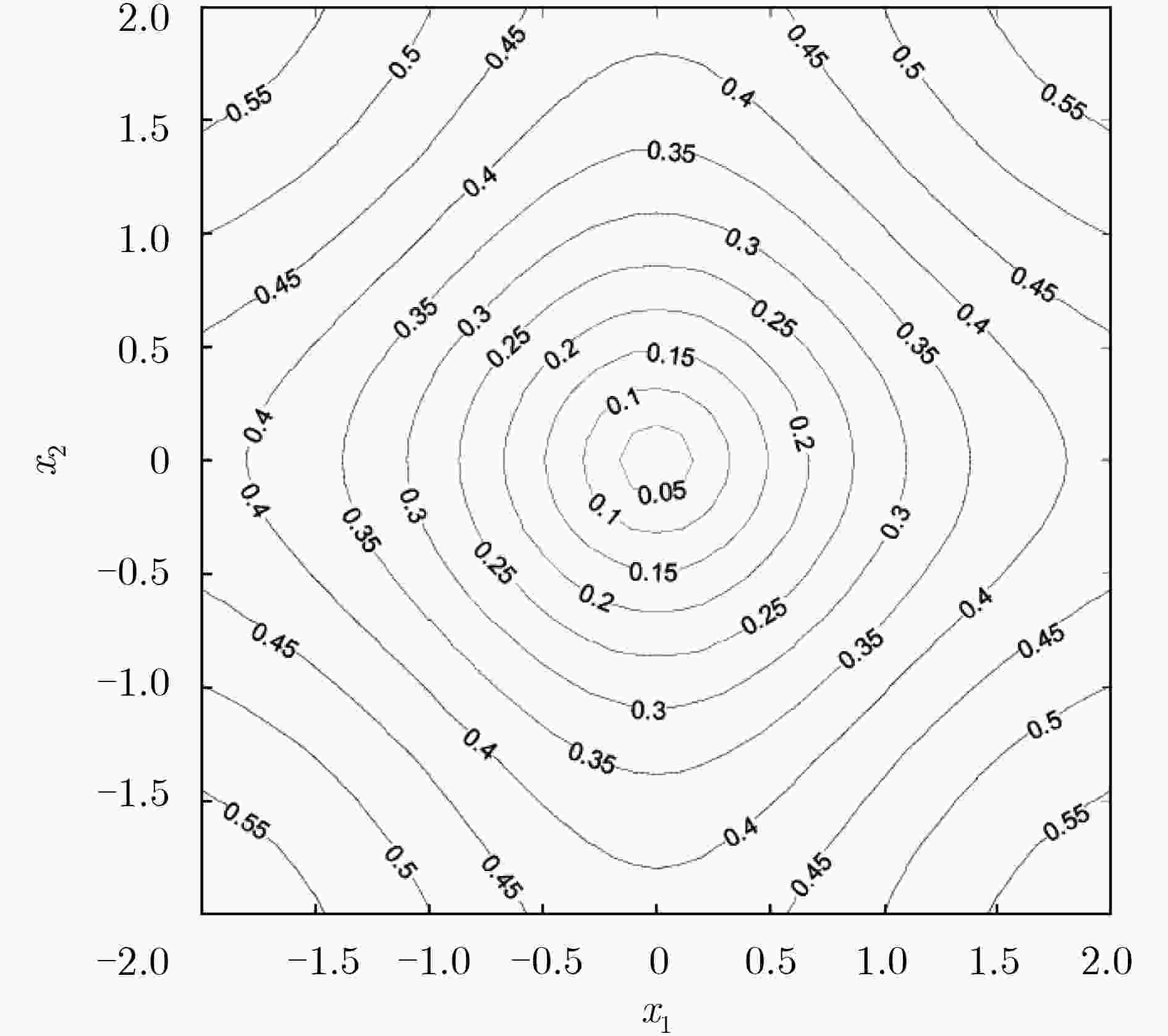
图 1 2D空间CIM等高线图[5]
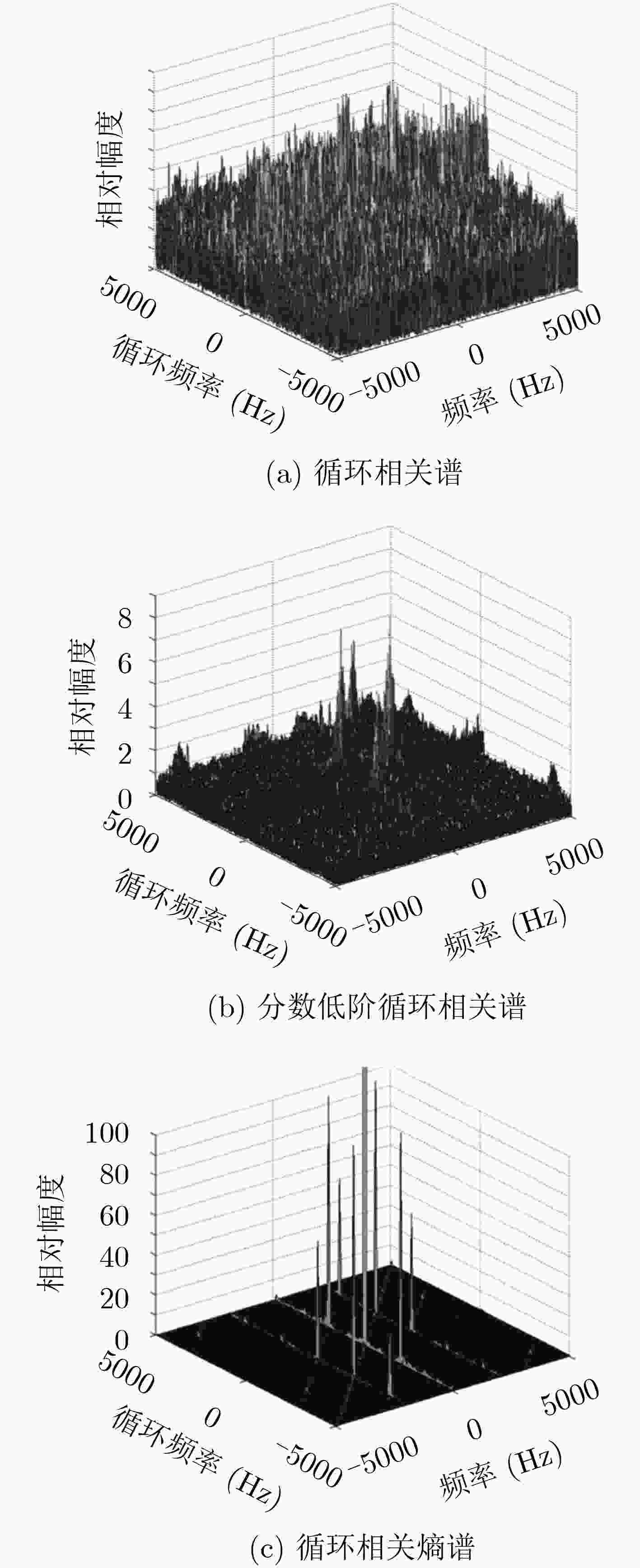
图 2 循环相关熵谱与常规的循环相关谱及分数低阶循环相关谱的对比[6]
-
SHAO M and NIKIAS C L. Signal processing with fractional lower order moments: Stable processes and their applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1993, 81(7): 986–1010. doi: 10.1109/5.231338 NIKIAS C L and SHAO M. Signal Processing with Alpha-Stable Distributions and Applications[M]. New York: Wiley, 1995: 1–3. LIU Weifeng, POKHAREL P P, and PRINCIPE J C. Correntropy: A localized similarity measure[C]. 2006 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Network Proceedings, Vancouver, Canada, 2006: 4919–4924. GUNDUZ A and PRINCIPE J C. Correntropy as a novel measure for nonlinearity tests[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 89(1): 14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.07.005 LIU Weifeng, POKHAREL P P, and PRINCIPE J C. Correntropy: Properties and applications in non-Gaussian signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(11): 5286–5298. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.896065 LUAN Shengyang, QIU Tianshuang, ZHU Yongjie, et al. Cyclic correntropy and its spectrum in frequency estimation in the presence of impulsive noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 1204: 503–508. FONTES A I R, REGO J B A, DE M MARTINS A, et al. Cyclostationary correntropy: Definition and applications[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 69: 110–117. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.10.029 MILLER G. Properties of certain symmetric stable distributions[J]. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 1978, 8(3): 346–360. doi: 10.1016/0047-259X(78)90058-1 CAMBANIS S and MILLER G. Linear problems in p-th order and stable processes[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1981, 41(1): 43–69. doi: 10.1137/0141005 郭莹, 邱天爽. 基于分数低阶统计量的盲多用户检测算法[J]. 电子学报, 2007, 35(9): 1670–1674. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.09.011GUO Ying and QIU Tianshuang. Blind multiuser detector based on FLOS in impulse noise environment[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(9): 1670–1674. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.09.011 MA Xinyu and NIKIAS C L. Joint estimation of time delay and frequency delay in impulsive noise using fractional lower order statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(11): 2669–2687. doi: 10.1109/78.542175 邱天爽, 王宏禹, 孙永梅. 一种基于分数低阶协方差的自适应EP潜伏期变化检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2004, 32(1): 91–95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.01.022QIU Tianshuang, WANG Hongyu, and SUN Yongmei. A fractional lower-order covariance based adaptive latency change detection for evoked potentials[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2004, 32(1): 91–95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.01.022 KONG Xuan and QIU Tianshuang. Adaptive estimation of latency change in evoked potentials by direct least mean p-norm time-delay estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1999, 46(8): 994–1003. doi: 10.1109/10.775410 LIU T H and MENDEL J M. A subspace-based direction finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2001, 49(8): 1605–1613. doi: 10.1109/78.934131 GEORGIOU P G, TSAKALIDES P, and KYRIAKAKIS C. Alpha-stable modeling of noise and robust time-delay estimation in the presence of impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 1999, 1(3): 291–301. doi: 10.1109/6046.784467 SANTAMARIA I, POKHAREL P P, and PRINCIPE J C. Generalized correlation function: Definition, properties, and application to blind equalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(6): 2187–2197. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.872524 VAPNIK V N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory[M]. New York: Springer Verlag, 1995: 2-4. BACH F R and JORDAN M I. Kernel independent component analysis[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2002, 3: 1–48. PRINCIPE J C. Information Theoretic Learning: Renyi’s Entropy and Kernel Perspectives[M]. New York: Wiley, 1988: 1. POKHAREL P P, LIU Weifeng, and PRINCIPE J C. A low complexity robust detector in impulsive noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 89(10): 1902–1909. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.03.027 PARZEN E. On estimation of a probability density function and mode[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1962, 33(3): 1065–1076. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177704472 HUBER P J. Robust Statistics[M]. New York: Wiley, 1981: 1–2. GARDE A, SÖRNMO L, JANÉ R, et al. Correntropy-based spectral characterization of respiratory patterns in patients with chronic heart failure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2010, 57(8): 1964–1972. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2044176 SINGH A and PRINCIPE J C. Using correntropy as a cost function in linear adaptive filters[C]. 2009 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Atlanta, USA, 2009: 2950–2955. 宋爱民, 邱天爽, 佟祉谏. 对称稳定分布的相关熵及其在时间延迟估计上的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(2): 494–498.SONG Aimin, QIU Tianshuang, and TONG Zhijian. Correntropy of the symmetric stable distribution and its application to the time delay estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(2): 494–498. WANG Lingfeng and PAN Chunhong. Robust level set image segmentation via a local correntropy-based K-means clustering[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(5): 1917–1925. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2013.11.014 JIN Fangxiao and QIU Tianshuang. Adaptive time delay estimation based on the maximum correntropy criterion[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 88: 23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.01.014 PENG Siyuan, CHEN Badong, SUN Lei, et al. Constrained maximum correntropy adaptive filtering[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 140: 116–126. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.05.009 LI Yingsong, JIANG Zhengxiong, SHI Wanlu, et al. Blocked maximum correntropy criterion algorithm for cluster-sparse system identifications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2019, 66(11): 1915–1919. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2019.2891654 GUIMARÃES J P F, FONTES A I R, REGO J B A, et al. Complex correntropy: Probabilistic interpretation and application to complex-valued data[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(1): 42–45. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2634534 朝乐蒙, 邱天爽, 李景春, 等. 广义复相关熵与相干分布式非圆信号DOA估计[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(5): 795–801.CHAO Lemeng, QIU Tianshuang, LI Jingchun, et al. Generalized complex correntropy and DOA estimation for coherently distributed noncircular sources[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(5): 795–801. CHEN Badong, XING Lei, ZHAO Haiquan, et al. Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(13): 3376–3387. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2539127 LUO Xiong, SUN Jiankun, WANG Long, et al. Short-term wind speed forecasting via stacked extreme learning machine with generalized correntropy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(11): 4963–4971. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2854549 ZHAO Ji and ZHANG Hongbin. Kernel recursive generalized maximum correntropy[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(12): 1832–1836. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2761886 CHEN Liangjun, QU Hua, and ZHAO Jihong. Generalized correntropy based deep learning in presence of non-Gaussian noises[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 278: 41–50. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.06.080 GIANNAKIS G B and ZHOU GUOTONG. Harmonics in multiplicative and additive noise: Parameter estimation using cyclic statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1995, 43(9): 2217–2221. doi: 10.1109/78.414790 GHOGHO M, SWAMI A, and GAREL B. Performance analysis of cyclic statistics for the estimation of harmonics in multiplicative and additive noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1999, 47(12): 3235–3249. doi: 10.1109/78.806069 NAPOLITANO A. Cyclostationarity: New trends and applications[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 120: 385–408. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.09.011 LIU Tao, QIU Tianshuang, and LUAN Shengyang. Cyclic Correntropy: Foundations and theories[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34659–34669. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2847346 MA Jitong and QIU Tianshuang. Automatic modulation classification using cyclic correntropy spectrum in impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(2): 440–443. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2875001 LIU Tao, QIU Tianshuang, and LUAN Shengyang. Cyclic frequency estimation by compressed cyclic correntropy spectrum in impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(6): 888–892. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2910928 JIN Fangxiao, QIU Tianshuang, and LIU Tao. Robust cyclic beamforming against cycle frequency error in Gaussian and impulsive noise environments[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2019, 99: 153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2018.11.035 GARDNER W A. The spectral correlation theory of cyclostationary time-series[J]. Signal Processing, 1986, 11(1): 13–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-1684(86)90092-7 GARDNER W A, NAPOLITANO A, and PAURA L. Cyclostationarity: Half a century of research[J]. Signal Processing, 2006, 86(4): 639–697. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.06.016 郭莹, 邱天爽, 张艳丽, 等. 脉冲噪声环境下基于分数低阶循环相关的自适应时延估计方法[J]. 通信学报, 2007, 28(3): 8–14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2007.03.002GUO Ying, QIU Tianshuang, ZHANG Yanli, et al. Novel adaptive time delay estimation method based on the fractional lower order cyclic correlation in impulsive noise environment[J]. Journal on Communications, 2007, 28(3): 8–14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2007.03.002 LIU Yang, QIU Tianshuang, and SHENG Hu. Time-difference-of-arrival estimation algorithms for cyclostationary signals in impulsive noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(9): 2238–2247. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.02.016 KWON H and NASRABADI N M. Hyperspectral target detection using kernel matched subspace detector[C]. 2004 International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Singapore, 2004: 3327–3330. ERDOGMUS D, AGRAWAL R, and PRINCIPE J C. A mutual information extension to the matched filter[J]. Signal Processing, 2005, 85(5): 927–935. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2004.11.018 JEONG K H, LIU Weifeng, HAN S, et al. The correntropy MACE filter[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2009, 42(5): 871–885. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2008.09.023 ZHAO Songlin, CHEN Badong, and PRÍNCIPE J C. Kernel adaptive filtering with maximum correntropy criterion[C]. 2011 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, San Jose, USA, 2011: 2012–2017. CHEN Badong and PRINCIPE J C. Maximum correntropy estimation is a smoothed MAP estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 19(8): 491–494. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2204435 CHEN Badong, XING Lei, LIANG Junli, et al. Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(7): 880–884. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2319308 WU Zongze, SHI Jiahao, ZHANG Xie, et al. Kernel recursive maximum correntropy[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 117: 11–16. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.04.024 CHEN Badong, LIU Xi, ZHAO Haiquan, et al. Maximum correntropy Kalman filter[J]. Automatica, 2017, 76: 70–77. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.10.004 LIU Xi, CHEN Badong, ZHAO Haiquan, et al. Maximum correntropy Kalman filter with state constraints[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 25846–25853. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2769965 LIU Xi, CHEN Badong, XU Bin, et al. Maximum correntropy unscented filter[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2017, 48(8): 1607–1615. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2016.1277407 LIU Xi, QU Hua, ZHAO Jihong, et al. Maximum correntropy unscented Kalman filter for spacecraft relative state estimation[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(9): 1530. doi: 10.3390/s16091530 KRIM H and VIBERG M. Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 1996, 13(4): 67–94. doi: 10.1109/79.526899 YOU Guohong, QIU Tianshuang, and YANG Jiao. A novel DOA estimation algorithm of cyclostationary signal based on UCA in impulsive noise[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2013, 67(6): 491–499. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2012.11.006 ZHANG Jingfeng, QIU Tianshuang, SONG Aimin, et al. A novel correntropy based DOA estimation algorithm in impulsive noise environments[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 104: 346–357. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.04.033 王鹏, 邱天爽, 任福全, 等. 对称稳定分布噪声下基于广义相关熵的DOA估计新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 2007–2013.WANG Peng, QIU Tianshuang, REN Fuquan, et al. A novel generalized correntropy based method for direction of arrival estimation in symmetric alpha stable noise environments[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 2007–2013. WANG Peng, QIU Tianshuang, REN Fuquan, et al. A robust DOA estimator based on the correntropy in alpha-stable noise environments[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 60: 242–251. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2016.10.002 王鹏, 邱天爽, 金芳晓, 等. 脉冲噪声下基于稀疏表示的韧性DOA估计方法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(7): 1537–1544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.07.001WANG Peng, QIU Tianhsuang, JIN Fangxiao, et al. A robust DOA estimation method based on sparse representation for impulsive noise environments[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(7): 1537–1544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.07.001 KNAPP C and CARTER G C. The generalized correlation method for estimation of time delay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1976, 24(4): 320–327. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1976.1162830 CARTER G C. Time delay estimation for passive sonar signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1981, 29(3): 463–470. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1981.1163560 WANG Gang and HO K C. Convex relaxation methods for unified near-field and far-field TDOA-based localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(4): 2346–2360. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2903037 YU Ling, QIU Tianshuang, and LUAN Shengyang. Fractional time delay estimation algorithm based on the maximum correntropy criterion and the Lagrange FDF[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 111: 222–229. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.12.018 LUO Yuanzhe, SUN Guolu, ZHANG Xiaotong, et al. Adaptive time-delay estimation based on normalized maximum correntropy criterion for near-field electromagnetic ranging[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2018, 67: 404–414. CHEN Xing, QIU Tianshuang, LIU Cheng, et al. TDOA estimation algorithm based on generalized cyclic correntropy in impulsive noise and cochannel interference[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2018, 101-A(10): 1625–1630. LI Sen, LIN Bin, DING Yabo, et al. Signal-selective time difference of arrival estimation based on generalized cyclic correntropy in impulsive noise environments[C]. The 13th International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications, Tianjin, China, 2018: 274–283. HE Ran, ZHENG Weishi, and HU Baogang. Maximum correntropy criterion for robust face recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(8): 1561–1576. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.220 ZHOU Sanping, WANG Jinjun, ZHANG Mengmeng, et al. Correntropy-based level set method for medical image segmentation and bias correction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 234: 216–229. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.013 PENG Jiangtao and DU Qian. Robust joint sparse representation based on maximum correntropy criterion for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7152–7164. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743110 HASSAN M, TERRIEN J, MARQUE C, et al. Comparison between approximate entropy, correntropy and time reversibility: Application to uterine electromyogram signals[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2011, 33(8): 980–986. BARQUERO-PÉREZ O, SÖRNMO L, GOYA-ESTEBAN R, et al. Fundamental frequency estimation in atrial fibrillation signals using correntropy and Fourier organization analysis[C]. The 3rd International Workshop on Cognitive Information Processing (CIP), Baiona, Spain, 2012: 1–6. NAPOLITANO A. Cyclostationarity: Limits and generalizations[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 120: 323–347. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.09.013 ZHAO Xuejun, QIN Yong, HE Changbo, et al. Rolling element bearing fault diagnosis under impulsive noise environment based on cyclic correntropy spectrum[J]. Entropy, 2019, 21(1): 50. doi: 10.3390/e21010050 HUIJSE P, ESTEVEZ P A, ZEGERS P, et al. Period estimation in astronomical time series using slotted correntropy[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2011, 18(6): 371–374. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2011.2141987 DUAN Jiandong, QIU Xinyu, MA Wentao, et al. Electricity consumption forecasting scheme via improved LSSVM with maximum correntropy criterion[J]. Entropy, 2018, 20(2): 112. doi: 10.3390/e20020112 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
