Detection of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Based on Kernel Sparse Coding
-
摘要:
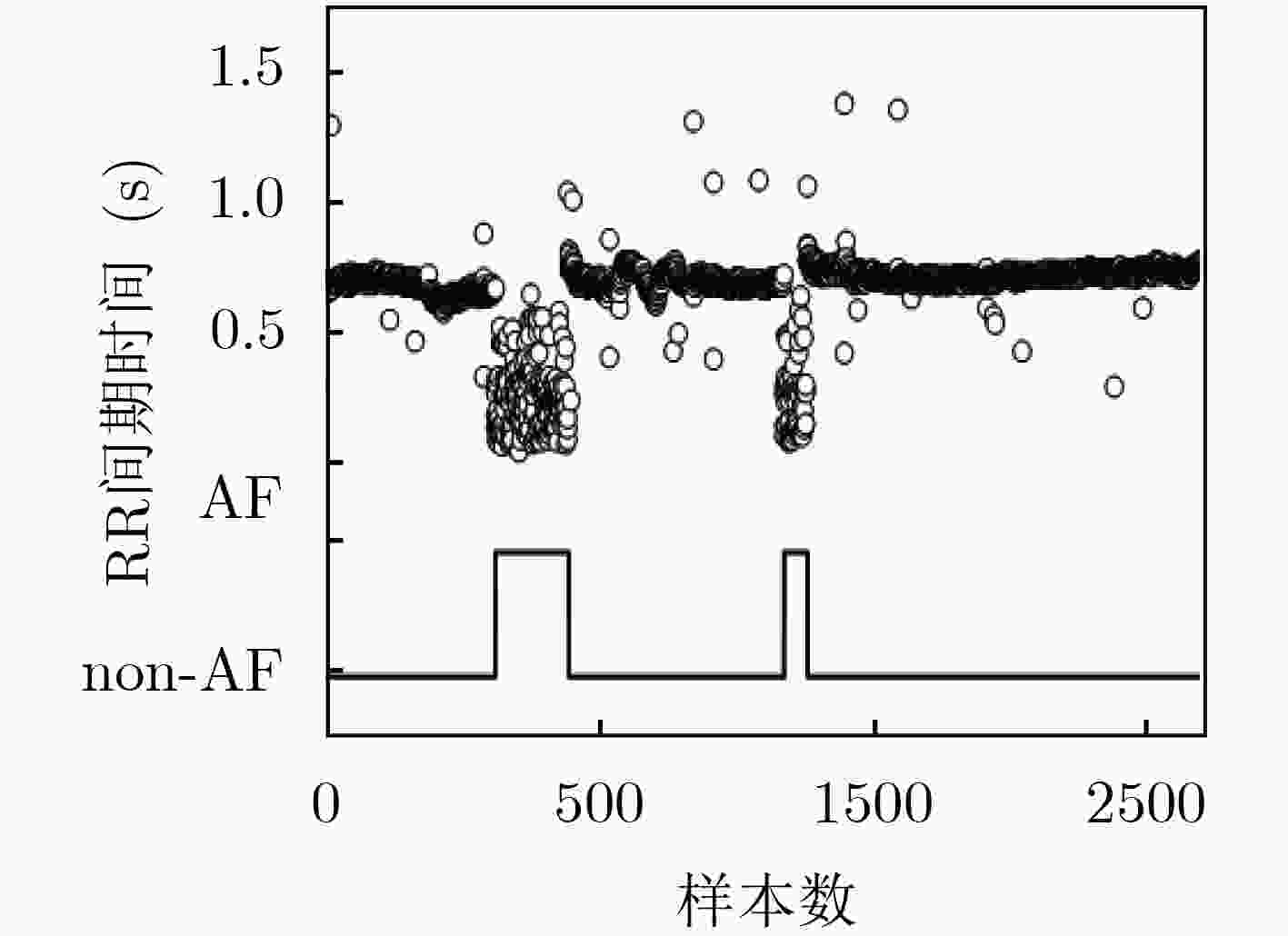
阵发性房颤(PAF)是一种具有偶发性的心律失常,其较高的漏检率导致心脏相关疾病的增加。该文提出了一种基于核稀疏编码的自动检测方法,可以仅根据较短RR间期数据识别PAF发作。该方法采用特殊几何结构来分析数据高维特性,通过计算协方差矩阵作为特征描述子,找到蕴含在数据中的黎曼流形结构;然后基于Log-Euclid框架,利用核方法将流形空间映射到高维可再生核希尔伯特空间,以获取更准确的稀疏表示来快速识别PAF。经麻省理工学院-贝斯以色列医院房颤数据库验证,获得98.71%的敏感性、98.43%的特异度和98.57%的总准确率。因此,该研究对检测短暂发作的PAF有实质性的改善,在临床监测和治疗方面显示出良好的潜力。
Abstract:Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (PAF) is a kind of accidental arrhythmia, and its high missed detection rate leads to the increase of heart-related diseases. An automatic detection method is proposed based on kernel sparse coding, which can identify PAF attacks based only on short RR interval data. A special geometric structure is presented to analyze the high-dimensional characteristics of the data, and the covariance matrix is calculated as a feature descriptor to find the Riemannian manifold structure contained in the data; Based on the Log-Euclidean framework, a manifold method is used to map the manifold space to a high-dimensional renewable kernel Hilbert space to obtain a more accurate sparse representation to identify quickly PAF. After verification by the Massa-chusetts Institute of Technology-Beth Israel Hospital atrial fibrillation database, the sensitivity is 98.71%, the specificity is 98.43%, and the total accuracy rate is 98.57%. Therefore, this study has a substantial improvement in the detection of transient PAF and shows good potential for clinical monitoring and treatment.
-
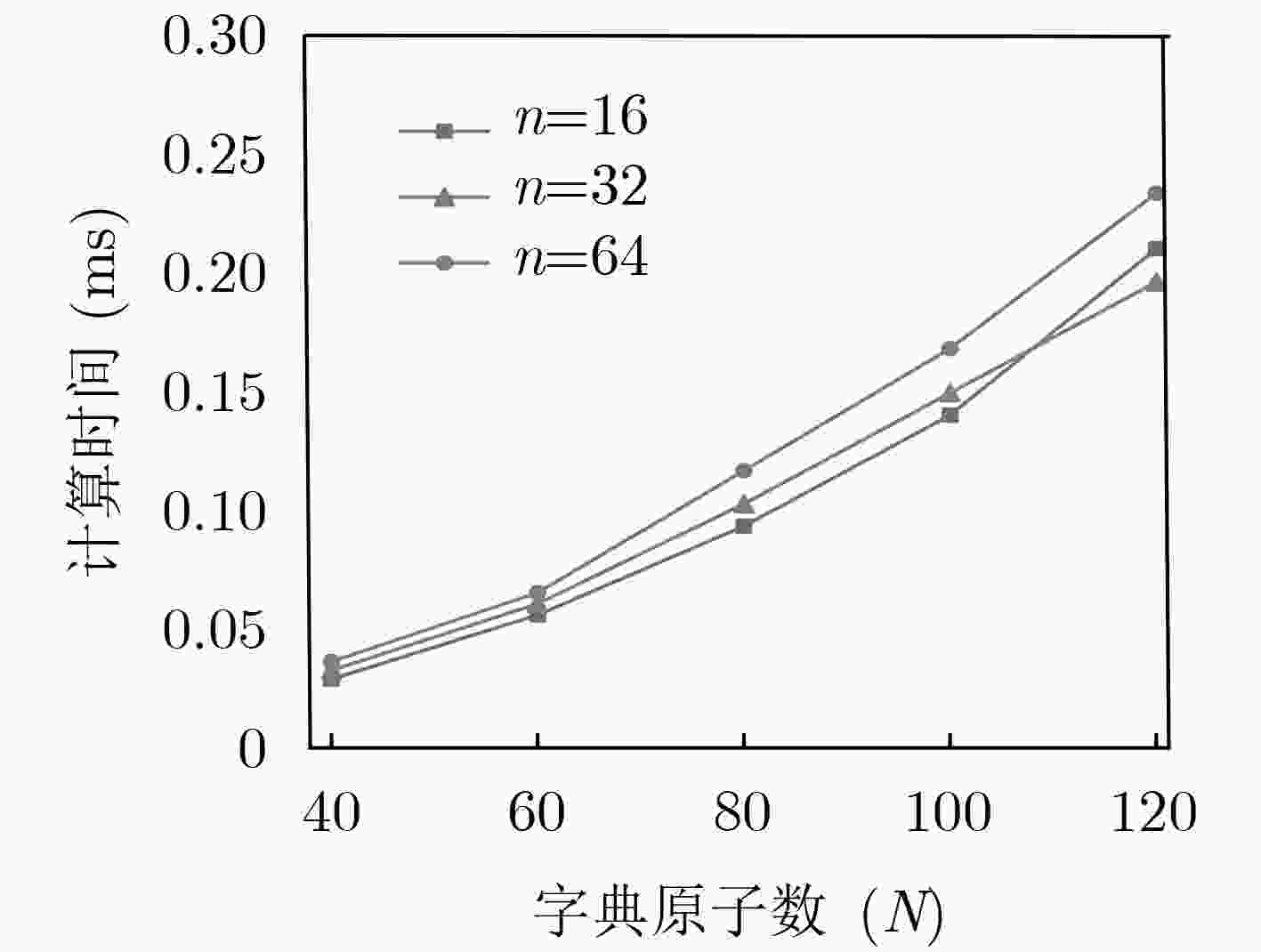
表 1 参数变化的检测性能(%)
字典原子数(N) 重复交叉验证 分割滑动窗口(n) 16 32 64 Se Sp Acc Se Sp Acc Se Sp Acc 40 数据集1 97.99 96.63 97.32 98.44 97.95 98.19 98.86 97.75 98.30 数据集2 97.95 97.42 97.68 98.74 98.15 98.44 98.67 98.43 98.55 数据集3 98.00 97.99 97.99 98.65 98.51 98.51 98.97 98.30 98.64 数据集4 97.38 98.44 97.91 98.50 98.67 98.59 98.78 98.57 98.67 数据集5 98.36 98.34 98.35 98.49 98.55 98.52 98.89 98.57 98.73 平均 97.94 97.76 97.85 98.56 98.37 98.45 98.83 98.32 98.58 60 数据集1 98.15 96.91 97.53 98.38 98.31 98.34 98.97 96.04 97.51 数据集2 98.26 97.32 97.79 98.06 98.12 98.09 98.46 94.26 96.36 数据集3 98.32 97.10 97.71 98.19 98.52 98.36 98.97 98.40 98.68 数据集4 97.76 98.41 98.09 98.78 98.52 98.65 98.91 98.64 98.78 数据集5 98.03 98.67 98.35 98.57 98.60 98.58 98.86 98.53 98.69 平均 98.10 97.68 97.89 98.39 98.41 98.40 98.83 97.17 98.00 80 数据集1 98.15 97.26 97.70 98.52 98.24 98.38 98.97 98.17 98.57 数据集2 97.99 97.43 97.71 98.81 98.27 98.54 98.97 98.35 98.66 数据集3 97.98 97.96 97.97 98.86 98.31 98.58 99.00 98.48 98.74 数据集4 97.39 98.24 97.81 98.73 98.66 98.69 98.93 98.44 98.69 数据集5 97.60 98.62 98.11 98.65 98.66 98.65 98.88 98.67 98.78 平均 97.82 97.90 97.86 98.71 98.43 98.57 98.95 98.42 98.69 100 数据集1 98.29 97.29 97.79 98.77 98.23 98.50 99.00 97.01 98.01 数据集2 98.13 97.72 97.92 98.81 98.09 98.45 98.94 98.56 98.75 数据集3 97.70 97.72 97.71 97.52 98.51 98.01 98.94 98.80 98.87 数据集4 97.90 98.38 98.14 98.60 98.72 98.66 98.94 98.80 98.87 数据集5 98.35 98.47 98.41 98.70 98.68 98.69 98.97 98.63 98.80 平均 98.07 97.92 97.95 98.48 98.45 98.46 98.96 98.36 98.66 120 数据集1 96.64 94.03 95.33 97.87 95.86 96.86 98.89 97.10 97.99 数据集2 98.11 93.22 95.66 98.81 97.74 98.28 97.73 97.84 97.79 数据集3 97.59 97.49 97.04 98.79 98.54 98.66 99.00 97.36 98.18 数据集4 98.24 98.10 98.17 98.50 98.59 98.54 98.94 98.46 98.70 数据集5 98.23 98.44 98.34 98.34 98.68 98.51 98.80 98.54 98.67 平均 97.76 96.26 96.91 98.46 97.88 98.17 98.67 97.86 98.27 -
HAQQANI H M, CHAN K H, GREGORY A T, et al. Atrial fibrillation: State of the art in 2017-shifting paradigms in pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and prevention[J]. Heart, Lung and Circulation, 2017, 26(9): 867–869. doi: 10.1016/s1443-9506(17)31276-3 DE SISTI A, LECLERCQ J F, HALIMI F, et al. Evaluation of time course and predicting factors of progression of paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation to permanent atrial fibrillation[J]. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 2014, 37(3): 345–355. doi: 10.1111/pace.12264 ZHOU Xiaolin, DING Hongxia, UNG B, et al. Automatic online detection of atrial fibrillation based on symbolic dynamics and Shannon entropy[J]. BioMedical Engineering OnLine, 2014, 13(1): 18. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-13-18 SEPULVEDA-SUESCUN J P, MURILLO-ESCOBAR J, URDA-BENITEZ R D, et al. Atrial Fibrillation Detection Through Heart Rate Variability Using a Machine Learning Approach and Poincare Plot Features[M]. TORRES I, BUSTAMANTE J, and SIERRA D A. VII Latin American Congress on Biomedical Engineering CLAIB 2016, Bucaramanga, Santander, Colombia. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd, 2016: 565–568. ANDERSEN R S, PEIMANKAR A, and PUTHUSSERYPADY S. A deep learning approach for real-time detection of atrial fibrillation[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 115: 465–473. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.08.011 季虎, 孙即祥, 王春光. 基于小波变换的自适应QRS-T对消P波检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(8): 1868–1871. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00117JI Hu, SUN Jixiang, and WANG Chunguang. An adaptive QRS-T cancellation based on wavelet transform for P-wave detection[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(8): 1868–1871. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00117 PETRĖNAS A, SÖRNMO L, LUKOŠEVIČIUS, et al. Detection of occult paroxysmal atrial fibrillation[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2015, 53(4): 287–297. doi: 10.1007/s11517-014-1234-y CUI Xingran, CHANG E, YANG Wenhuang, et al. Automated detection of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using an information-based similarity approach[J]. Entropy, 2017, 19(12): 677. doi: 10.3390/e19120677 XIN Yi and ZHAO Yizhang. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation recognition based on multi-scale wavelet α-entropy[J]. BioMedical Engineering OnLine, 2017, 16(1): 121. doi: 10.1186/s12938-017-0406-z TUZEL O, PORIKLI F, and MEER P. Region covariance: A fast descriptor for detection and classification[C]. Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 2006: 589–600. ZHANG Yingying, YANG Cai, and ZHANG Ping. Two-stage sparse coding of region covariance via Log-Euclidean kernels to detect saliency[J]. Neural Networks, 2017, 89: 84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2017.02.012 ARSIGNY V, FILLARD P, PENNEC X, et al. Geometric means in a novel vector space structure on symmetric positive-definite matrices[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2007, 29(1): 328–347. doi: 10.1137/050637996 SCHÖLKOPF B and SMOLA A J. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond[M]. Cambridge, USA: MIT Press, 2018: 13. doi: 10.7551/mitpress/4175.003.0018. LI Peihua, WANG Qilong, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Log-Euclidean kernels for sparse representation and dictionary learning[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. New York, USA, 2013: 1601–1608. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.202. GOLDBERGER A L, AMARAl L A N, GLASS L, et al. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals[J]. Circulation, 2000, 101(23): e215–e220. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215 HARANDI M T, SANDERSON C, HARTLEY R, et al. Sparse coding and dictionary learning for symmetric positive definite matrices: A kernel approach[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 216-229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33709-3_16. HUANG Chao, YE Shuming, CHEN Hang, et al. A novel method for detection of the transition between atrial fibrillation and sinus rhythm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 58(4): 1113–1119. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2096506 ZHOU Xiaolin, DING Hongxia, WU Wanqing, et al. A real-time atrial fibrillation detection algorithm based on the instantaneous state of heart rate[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(9): e0136544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136544 LIAN Jie, WANG Lian, and MUESSIG D. A simple method to detect atrial fibrillation using RR intervals[J]. The American Journal of Cardiology, 2011, 107(10): 1494–1497. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.01.028 LEE J, NAM Y, MCMANUS D D, et al. Time-varying coherence function for atrial fibrillation detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2013, 60(10): 2783–2793. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2013.2264721 -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
