Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Migration Mechanism for Service Function Chain in Operator Networks
-
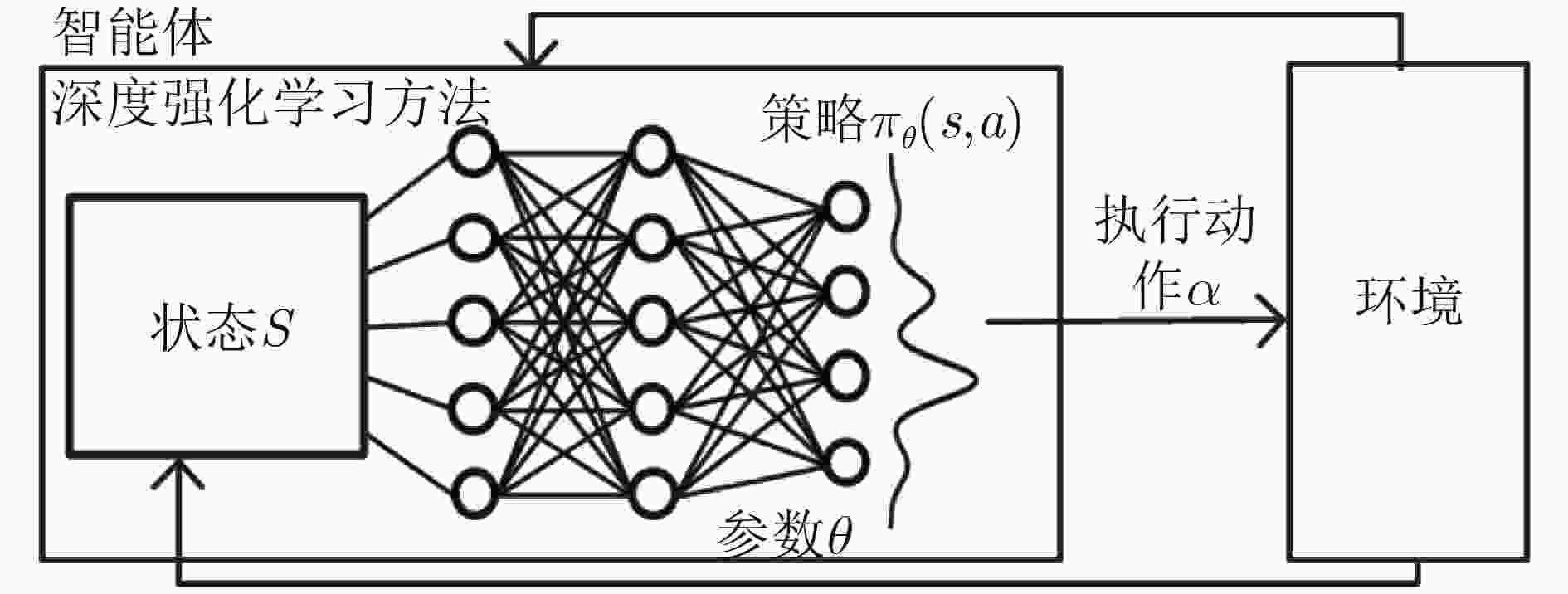
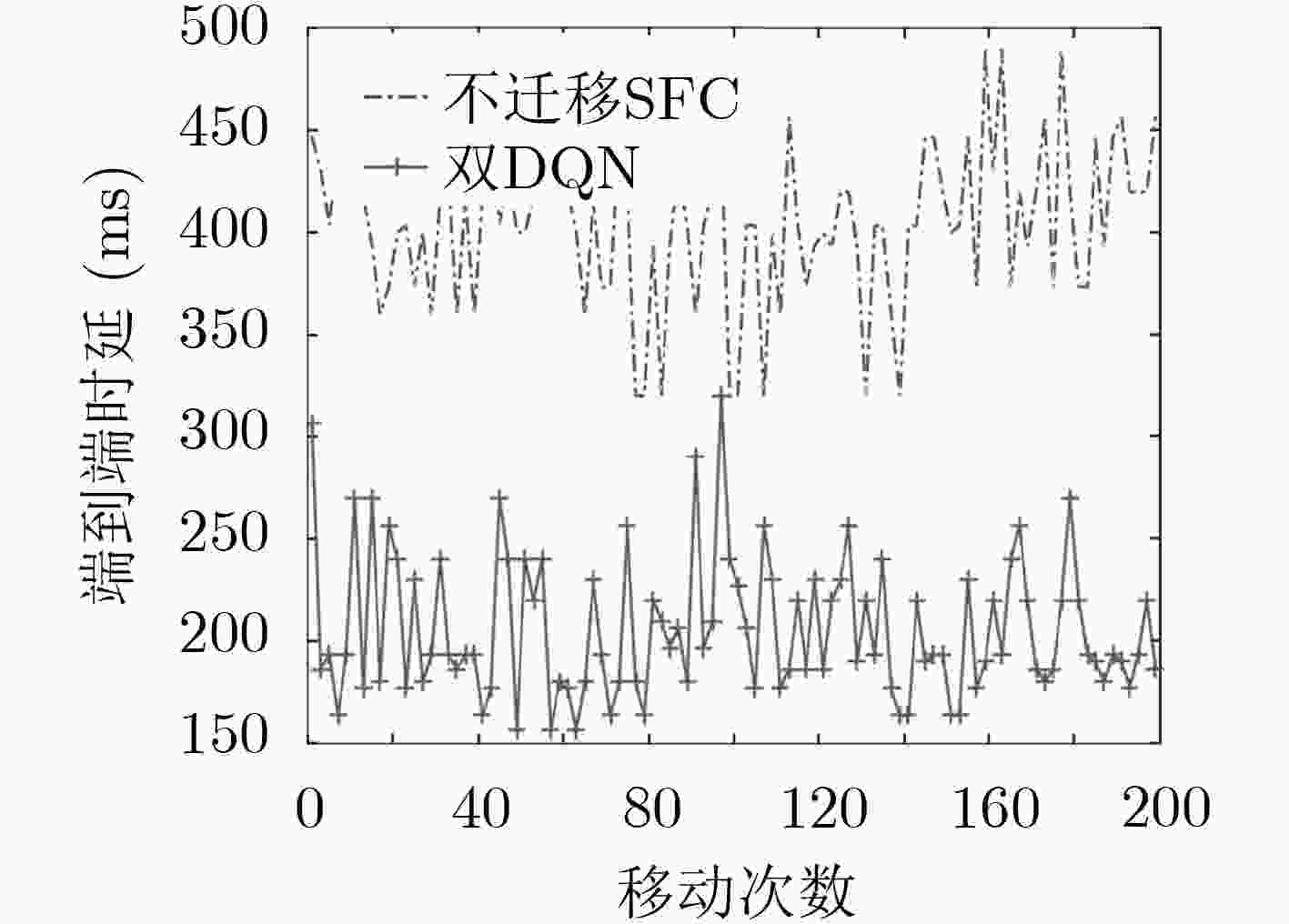
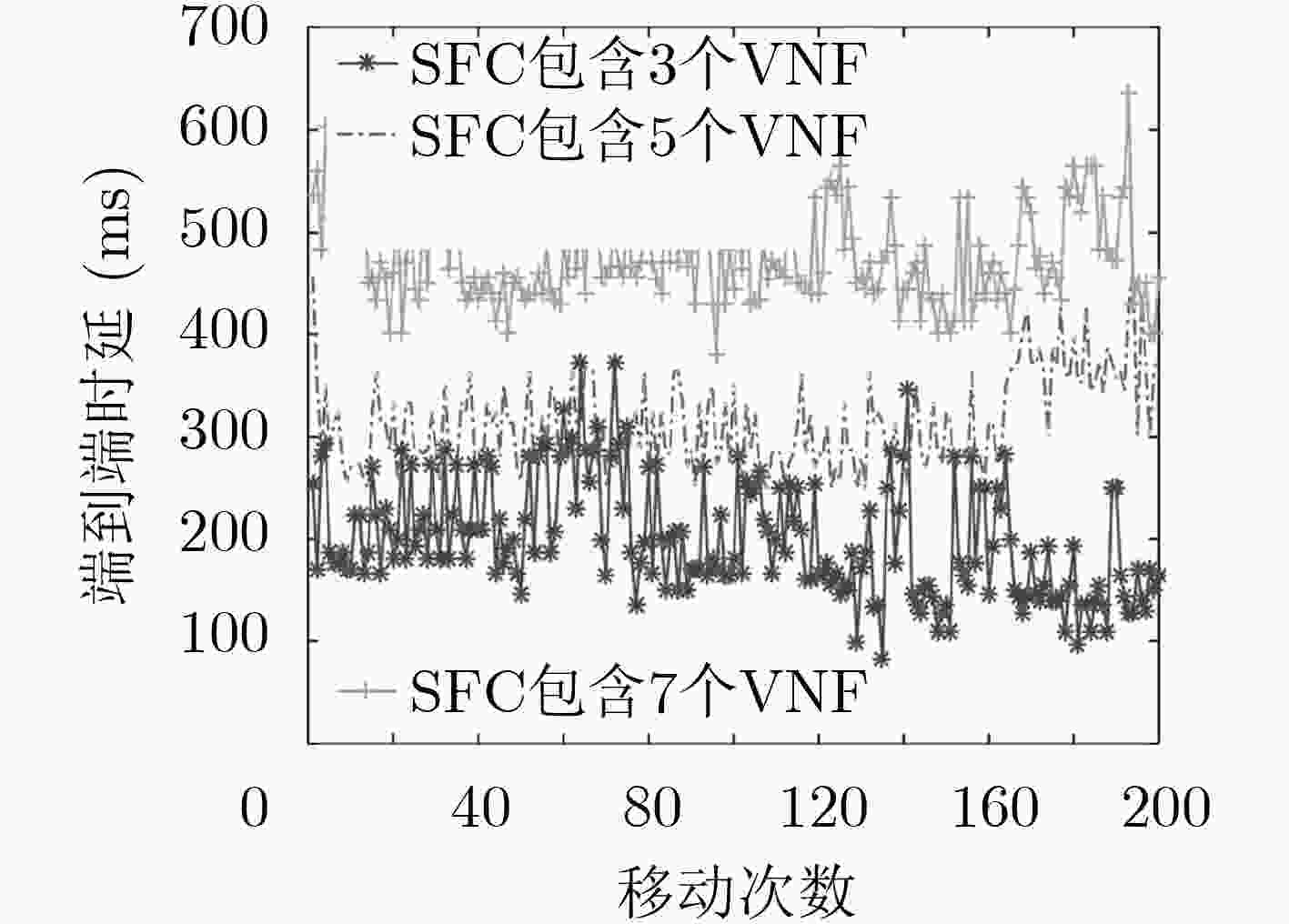
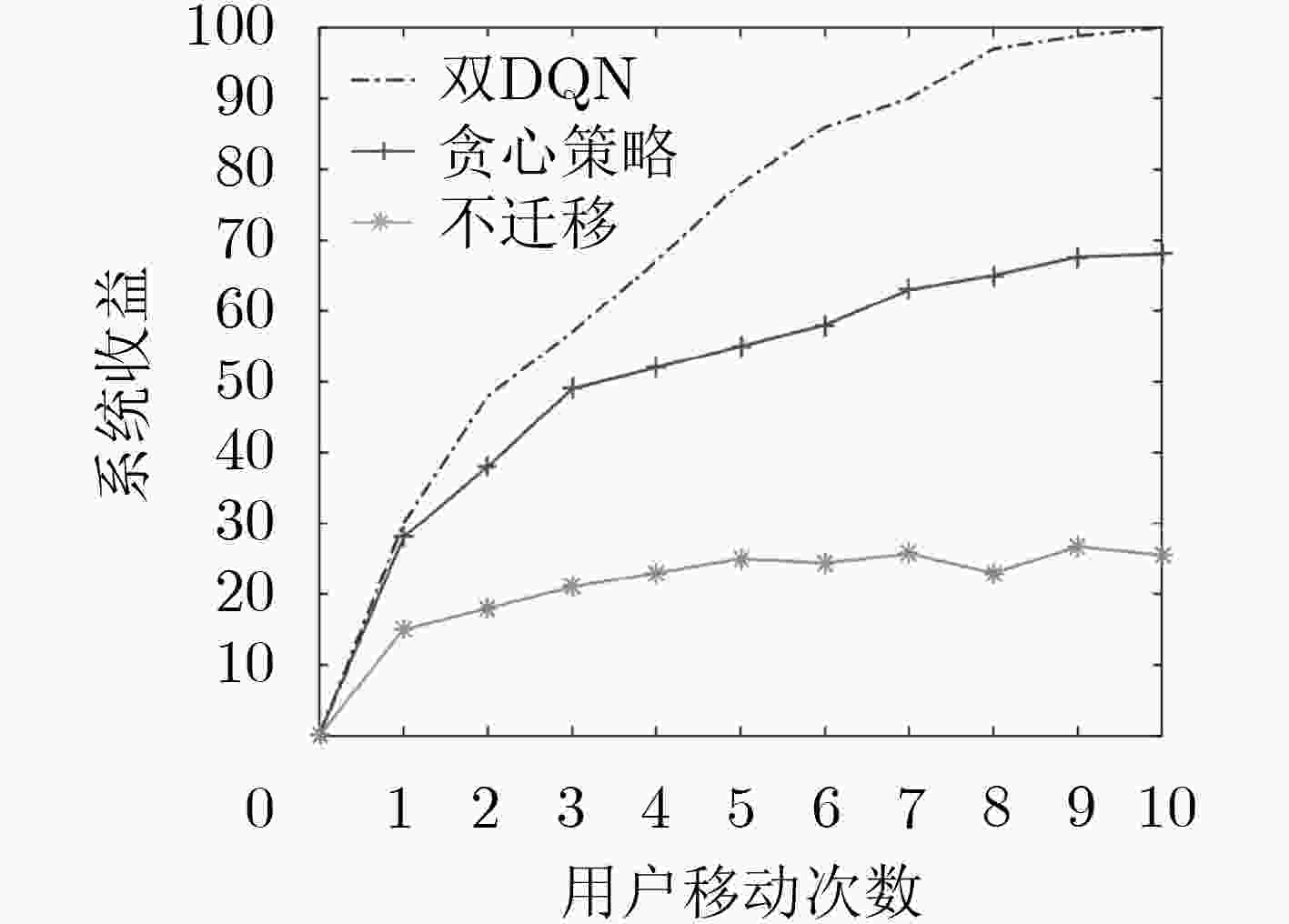
摘要: 为改善运营商网络提供的移动服务体验,该文研究服务功能链(SFC)的在线迁移问题。首先基于马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)对服务功能链中的多个虚拟网络功能(VNF)在运营商网络中的驻留位置迁移进行模型化分析。通过将强化学习和深度神经网络相结合提出一种基于双深度Q网络(double DQN)的服务功能链迁移机制,该迁移方法能在连续时间下进行服务功能链的在线迁移决策并避免求解过程中的过度估计。实验结果表明,该文所提出的策略相比于固定部署算法和贪心算法在端到端时延和网络系统收益等方面优势明显,有助于运营商改善服务体验和资源的使用效率。Abstract: To improve the service experience provided by the operator network, this paper studies the online migration of Service Function Chain(SFC). Based on the Markov Decision Process(MDP), modeling analysis is performed on the migration of multiple Virtual Network Functions(VNF) in SFC. By combining reinforcement learning and deep neural networks, a double Deep Q-Network(double DQN) based service function chain migration mechanism is proposed. This method can make online migration decisions and avoid over-estimation. Experimental result shows that when compared with the fixed deployment algorithm and the greedy algorithm, the double DQN based SFC migration mechanism has obvious advantages in end-to-end delay and network system revenue, which can help the mobile operator to improve the quality of experience and the efficiency of resources usage.
-
表 1 基于双DQN的SFC迁移算法的伪码
输入:运营商网络拓扑$G = \left( {N,E} \right)$,服务功能链集合C,网络功
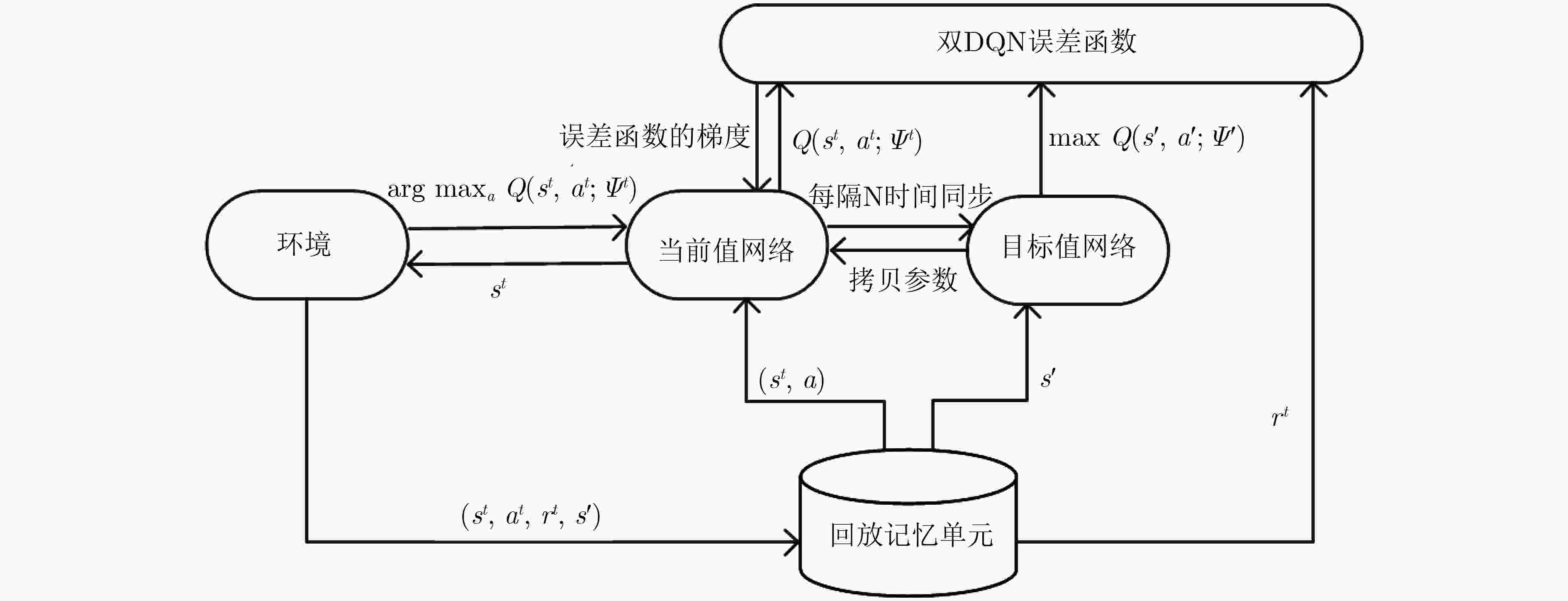
能集合F;输出:SFC迁移策略; 步骤1:初始化随机权重为$\psi $的神经网络; 步骤2:初始化动作值函数Q; 步骤3:初始化经验池(experience replay)存储器N; 步骤4:for episode = 1, 2, ···, M do, 观察初始状态${s^0}$, for t = 0, 1, ···, N–1 do, 以概率为$\varepsilon $选择一个随机动作${a^t}$, 否则选择动作${a^t} = \arg \max Q({s^t},a;{\psi ^t})$; 在仿真器中执行动作${a^t}$,并观察回报${R_{t + 1}}$和新状态${s_{t + 1}}$, 存储中间量$ < {s^t},{a^t},{r^t},{s^{t + 1}} > $到经验池存储器N中, 从经验池存储器N中获取一组样本, 计算损失函数$L({\psi ^t})$, 计算关于${\psi ^t}$的损失函数的梯度, 更新${\psi ^t} \leftarrow {\psi ^t} - \phi {{\text{∇}} _{ {\psi ^t} } }L({\psi ^t})$,其中$\phi $为学习率; end end -
CHATRAS B and OZOG F F. Network functions virtualization: The portability challenge[J]. IEEE Network, 2016, 30(4): 4–8. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2016.7513857 ZHANG Qixia, LIU Fangming, and ZENG Chaobing. Adaptive interference-aware VNF placement for service-customized 5G network slices[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 2019: 2449–2457. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2019.8737660. AGARWAL S, MALANDRINO F, CHIASSERINI C F, et al. Joint VNF placement and CPU allocation in 5G[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, USA, 2018: 1943–1951. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2018.8485943. KUO T W, LIOU B H, LIN K C J, et al. Deploying chains of virtual network functions: On the relation between link and server usage[C]. The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2016.7524565. TALEB T, KSENTINI A, and FRANGOUDIS P A. Follow-me cloud: When cloud services follow mobile users[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2019, 7(2): 369–382. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2016.2525987 ERAMO V, MIUCCI E, AMMAR M, et al. An approach for service function chain routing and virtual function network instance migration in network function virtualization architectures[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2017, 25(4): 2008–2025. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2017.2668470 HOUIDI O, SOUALAH O, LOUATI W, et al. An efficient algorithm for virtual network function scaling[C]. 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 2017: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2017.8254727. CHO D, TAHERI J, ZOMAYA A Y, et al. Real-time Virtual Network Function (VNF) migration toward low network latency in cloud environments[C]. The 10th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 798–801. doi: 10.1109/CLOUD.2017.118. 兰巨龙, 于倡和, 胡宇翔, 等. 基于深度增强学习的软件定义网络路由优化机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2669–2674. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180870LAN Julong, YU Changhe, HU Yuxiang, et al. A SDN routing optimization mechanism based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2669–2674. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180870 HUANG Xiaohong, YUAN Tingting, QIAO Guanhua, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for multimedia traffic control in software defined networking[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(6): 35–41. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1800097 LEE J W, MAZUMDAR R R, and SHROFF N B. Non-Convex optimization and rate control for multi-class services in the Internet[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2005, 13(4): 827–840. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2005.852876 李晨溪, 曹雷, 陈希亮, 等. 基于云推理模型的深度强化学习探索策略研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(1): 244–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170347LI Chenxi, CAO Lei, CHEN Xiliang, et al. Cloud reasoning model-based exploration for deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(1): 244–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170347 MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 GHAZNAVI M, KHAN A, SHAHRIAR N, et al. Elastic virtual network function placement[C]. The 4th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Networking, Niagara Falls, Canada, 2015: 255–260. doi: 10.1109/CloudNet.2015.7335318. SUGISONO K, FUKUOKA A, and YAMAZAKI H. Migration for VNF instances forming service chain[C]. The 7th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Networking, Tokyo, Japan, 2018: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/CloudNet.2018.8549194. LIN Tachun, ZHOU Zhili, TORNATORE M, et al. Demand-aware network function placement[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2016, 34(11): 2590–2600. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2016.2535401 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
