Application of SVM Machine Learning to Hardware Trojan Detection Using Side-channel Analysis
-
摘要:
集成电路(ICs)面临着硬件木马(HTs)造成的严峻威胁。传统的旁路检测手段中黄金模型不易获得,且隐秘的木马可以利用固硬件联合操作将恶意行为隐藏在常规的芯片运行中,更难以检测。针对这种情况,该文提出利用机器学习支持向量机(SVM)算法从系统操作层次对旁路分析检测方法进行改进。使用现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)验证的实验结果表明,存在黄金模型时,有监督SVM可得到86.8%的训练及测试综合的平均检测准确率,进一步采用分组和归一化去离群点方法可将检测率提升4%。若黄金模型无法获得,则可使用半监督SVM方法进行检测,平均检测率为52.9%~79.5%。与现有同类方法相比,验证了SVM算法在指令级木马检测中的有效性,明确了分类学习条件与检测性能的关系。
Abstract:Integrated Circuits (ICs) are suffering severer threats caused by Hardware Trojans (HTs), some of which hide in routine operations by coercing firmware or hardware. Along with conventional side-channel detection not always getting golden-chip, HTs become more difficult to detect. An improved Support Vector Machine (SVM) machine learning frameworks for this is proposed using system-level side-channel analysis. Cross validation experimental results on Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) show that in the condition of golden-chip, supervised SVM achieves 85.8% test accuracy in average. After grouping, outlier-removing and normalization, it rises by 4%. Even if golden-chip is out of hand, semi-supervised SVM has accuracy to judge HTs existence, averaging in 52.9%-79.5% under different test modes. Comparing with existing researches, this work verifies the efficiency of SVM for HT detection in instruction level, and points out the relationship between diversified learning conditions with detection performance.
-
表 1 指令集
指令序号及名称 指令类型 描述 1-NOP 类型1 NOP 无操作 2-MOV_A_RR
5-MOV_RR_A
8-MOV_D_A3-MOV_A_D
6-MOV_RR_D
9-MOV_D_RR4- MOV_A_DATA
7-MOV_RR_DATA
10-MOV_D_DATA类型2 MOV 移动存储器,复制操作数2到操作数1 11-ADD_A_RR 12-ADD_A_D 13-ADD_A_DATA 类型3 ADD 加法器加操作,将操作数的值加到加法器上并存储 14-SUBB_A_RR 15-SUBB_A_D 16-SUBB_A_DATA 类型4 SUBB 从加法器中借位减操作 17-INC_A 18-INC_D 19-INC_RR 类型5 INC 增加操作数 20-JMP_A_DPTR 类型6 JMP 跳转至数据指针+ DPTR代表的加法器地址 21-JNC 类型7 JNC 跳转至相关地址如果进位没有设置 表 2 木马基准电路
名称 描述 HT1 MC8051-T200,这个木马在空闲模式激活8051内部计时器 HT2 MC8051-T300,这个木马在8051通过UART发送特定数据串时被触发。目的是通过UART收到任意信息 HT3 MC8051-T500,这个木马的触发器检测特定的命令,当木马激活后其负载可以替换特定的数据 HT4 MC8051-T600,这个木马使得微控制器上运行算法的任何跳转失效 HT5 MC8051-T700,这个木马用敌人预设数据替换一些输入数据 HT6 MC8051-T800,这个木马当UART接收特殊字符时篡改堆栈指针 表 3 SVM常用核函数
名称 表达式 参数 线性核 $\kappa ({{{x}}_i},{{{x}}_j}) = {{{x}}_i}^{\rm{T}}{{{x}}_j}$ 多项式核 $\kappa ({{{x}}_i},{{{x}}_j}) = {({{{x}}_i}^{\rm{T}}{{{x}}_j})^d}$ $d \ge 1$为多项式的次数 高斯核 $\kappa ({ {{x} }_i},{ {{x} }_j}) = \exp \left( - \dfrac{ { { {\left\| { { {{x} }_i} - { {{x} }_j} } \right\|}^2} } }{ {2{\sigma ^2} } }\right)$ $\sigma > 0$为高斯核的带宽 表 4 MOD1检测率及运行时间对比表
线性核函数准确率及运行时间 多项式核函数准确率及时间 高斯核函数准确率及时间 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 无预处理 83.30 100.00 0.02620 83.30 67.31 0.06912 83.30 57.24 0.10902 预处理+分组 98.00 83.30 0.01261 85.80 99.10 0.03929 98.00 83.30 0.02698 表 5 MOD3检测率及运行时间对比表
线性核函数准确率及时间 多项式核函数准确率及时间 高斯核函数准确率及时间 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 无预处理 83.30 100.00 0.06944 83.30 100.00 0.06193 83.30 100.00 0.06800 预处理+分组 98.80 83.30 0.06526 66.70 100.00 0.07183 88.00 84.90 0.07139 表 6 MOD4检测率及运行时间对比表
线性核函数准确率及时间 多项式核函数准确率及时间 高斯核函数准确率及时间 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 训练(%) 测试(%) 时间(s) 无预处理 85.94 85.08 0.02049 85.60 86.07 0.03807 85.83 85.38 0.05487 预处理+分组 97.80 97.80 0.01222 86.70 87.00 0.03904 97.60 98.40 0.03709 -
钟晶鑫, 王建业, 阚保强. 基于温度特征分析的硬件木马检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(3): 743–749. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170443ZHONG Jingxin, WANG Jianye, and KAN Baoqiang. Hardware Trojan detection through temperature characteristics analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(3): 743–749. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170443 RAD R M, WANG Xiaoxiao, TEHRANIPOOR M, et al. Power supply signal calibration techniques for improving detection resolution to hardware Trojans[C]. 2008 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, USA, 2008: 632–639. doi: 10.1109/ICCAD.2008.4681643. LAMECH C, AARESTAD J, PLUSQUELLIC J, et al. REBEL and TDC: Two embedded test structures for on-chip measurements of within-die path delay variations[C]. 2011 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, USA, 2011: 170–177. doi: 10.1109/ICCAD.2011.6105322. DU Dongdong, NARASIMHAN S, CHAKRABORTY R S, et al. Self-referencing: A scalable side-channel approach for hardware Trojan detection[C]. The 12th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Santa Barbara, USA, 2010: 173–187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-15031-9_12. HE Jiaji, ZHAO Yiqiang, GUO Xiaolong, et al. Hardware Trojan detection through chip-free electromagnetic side-channel statistical analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2017, 25(10): 2939–2948. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2017.2727985 NARASIMHAN S, DU Dongdong, CHAKRABORTY R S, et al. Multiple-parameter side-channel analysis: A non-invasive hardware Trojan detection approach[C]. 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust, Anaheim, USA, 2010: 13–18. doi: 10.1109/HST.2010.5513122. LIU Yu, JIN Yier, NOSRATINIA A, et al. Silicon demonstration of hardware Trojan design and detection in wireless cryptographic ICs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2017, 25(4): 1506–1519. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2016.2633348 FORTE D, BAO Chongxi, and SRIVASTAVA A. Temperature tracking: An innovative run-time approach for hardware Trojan detection[C]. 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, USA, 2013: 532–539. doi: 10.1109/ICCAD.2013.6691167. ZHAO Hong, KWIAT K, KAMHOUA C, et al. Applying chaos theory for runtime hardware Trojan detection[C]. 2015 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications, Verona, USA, 2015: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/CISDA.2015.7208642. JAP D, HE Wei, and BHASIN S. Supervised and unsupervised machine learning for side-channel based Trojan detection[C]. The 27th IEEE International Conference on Application-specific Systems, Architectures and Processors, London, UK, 2016: 17–24. doi: 10.1109/ASAP.2016.7760768. BAO Chongxi, FORTE D, and SRIVASTAVA A. On reverse engineering-based hardware Trojan detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2016, 35(1): 49–57. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2488495 INOUE T, HASEGAWA K, YANAGISAWA M, et al. Designing hardware Trojans and their detection based on a SVM-based approach[C]. The 12th IEEE International Conference on ASIC, Guiyang, China, 2017: 811–814. doi: 10.1109/ASICON.2017.8252600. KULKARNI A, PINO Y, and MOHSENIN T. SVM-based real-time hardware Trojan detection for many-core platform[C]. 2016 17th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, Santa Clara, USA, 2016: 362–367. doi: 10.1109/ISQED.2016.7479228. LODHI F K, HASAN S R, HASAN O, et al. Power profiling of microcontroller′s instruction set for runtime hardware Trojans detection without golden circuit models[C]. The Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2017: 294–297. doi: 10.23919/DATE.2017.7927002. TEHRANIPOOR M and SALAMANI H. trust-HUB[OL]. https://www.trust-hub.org/, 2018. 李莹, 周崟灏, 陈岚. 一种旁路检测方法及装置[P]. 中国专利, CN109684881A, 2019.LI Ying, ZHOU Yinhao, and CHEN Lan. A bypass detection method and device[P]. China patent, CN109684881A, 2019. -





 下载:
下载:
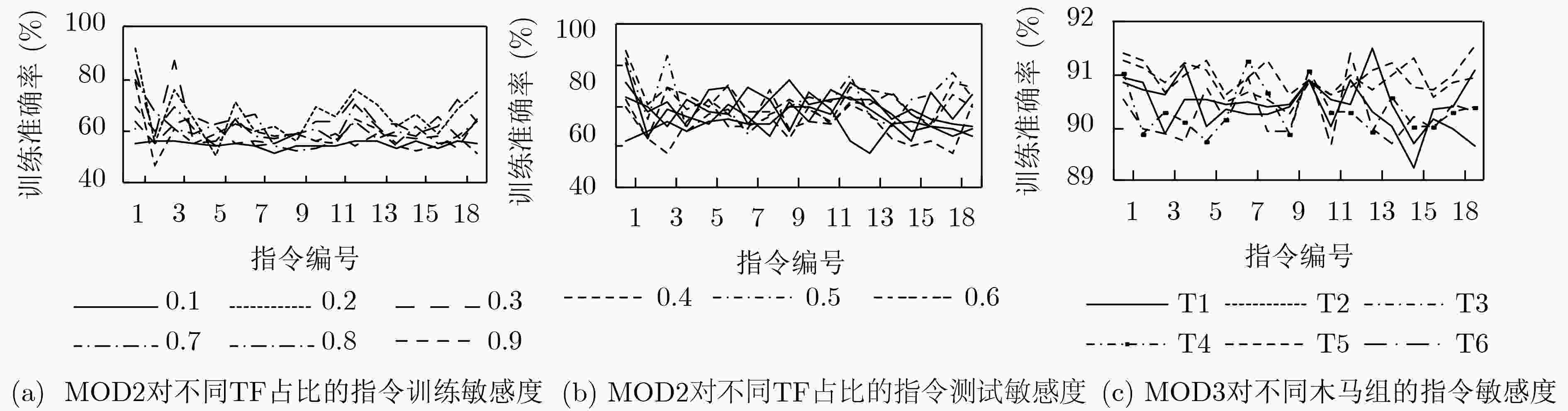
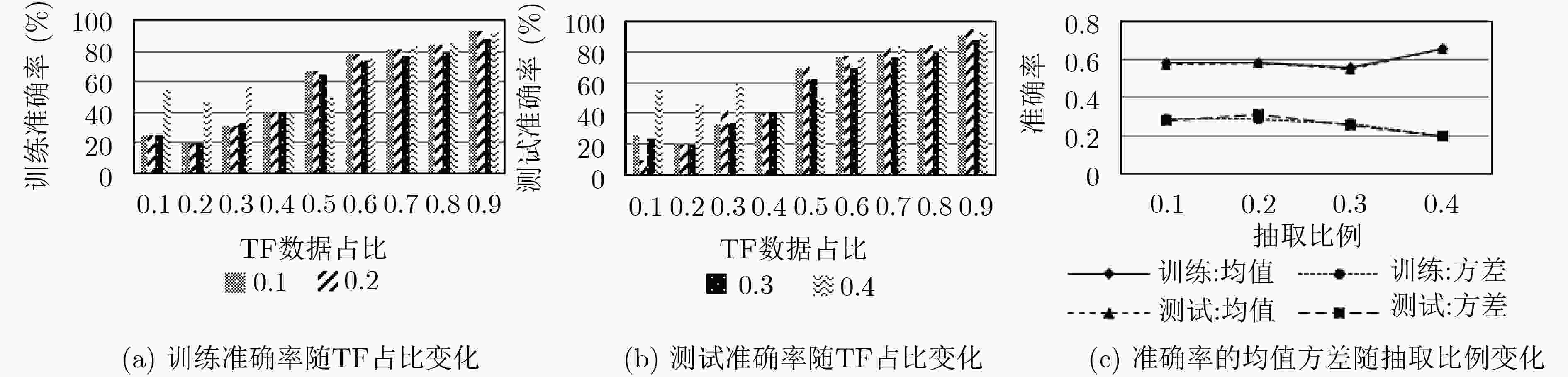


 下载:
下载:
