Range Spread Target Detection Based on OnlineEstimation of Strong Scattering Points
-
摘要:
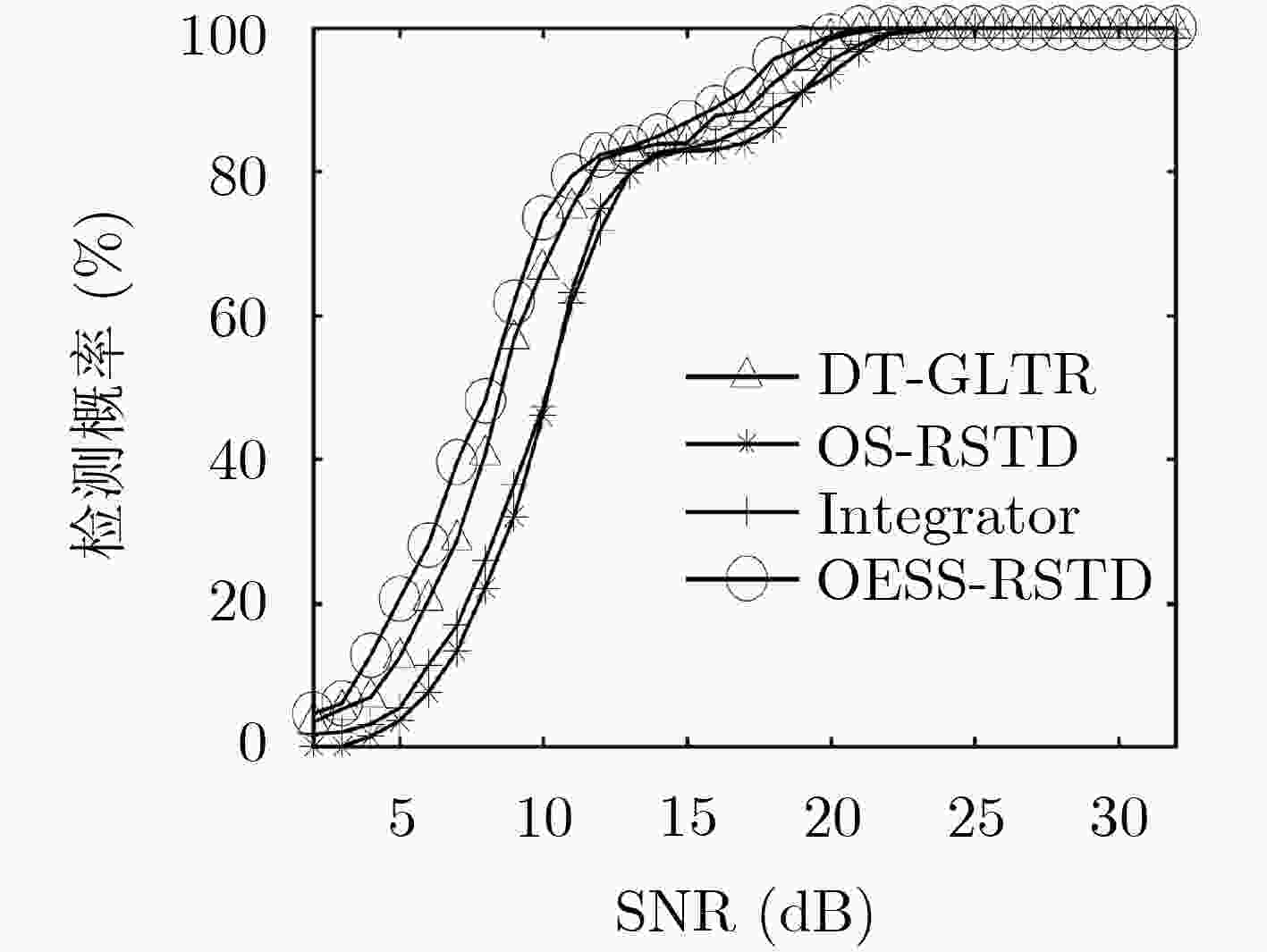
传统的距离扩展目标检测一般在散射点密度或散射点数量先验条件下完成,在目标散射点信息完全未知时检测性能会大幅降低。针对这个问题,该文提出一种基于强散射点在线估计的距离扩展目标检测方法(OESS-RSTD),该方法利用机器学习中的无监督聚类算法在线估计强散射点数量以及首次检测门限,然后再结合虚警率,确定2次检测门限,最后通过两次门限检测完成目标有无的判决。该文分别利用仿真数据和实测数据进行了试验验证,并和其他算法进行了试验对比,通过虚警概率一定时的信噪比(SNR)-检测概率曲线验证了该文所提方法相对于传统算法有更高的稳健性,且该方法不需要目标散射点的任何先验信息。
Abstract:The traditional range-extended target detection is usually completed under the condition of scattering point density or scattering point number priori. The detection performance is greatly reduced when the scattering point information of the target is completely unknown. To solve this problem, a Range Spread Target Detection method based on Online Estimation of Strong Scattering(OESS-RSTD) points is proposed. Firstly, the unsupervised clustering algorithm in machine learning is used to estimate the number of strong scattering points and the first detection threshold adaptively. Then, the second detection threshold is determined according to false alarm rate. Finally, the existence of the target is determined through two detection thresholds. The simulation data and the measured data are used to verify and compare with other algorithms. By comparing the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) -detection probability curves of various methods with a given false alarm probability, it is verified that the proposed method has higher robustness than the traditional algorithm, and the method does not need any priori information of target scattering points.
-
表 1 4种典型散射点模型
编号 散射点分布特点 名称 模型1 1个强散射点,占全部能量 单散射点 模型2 10个散射点,一个强散射点占50%能量,其他散射点占各占5.556%能量 稀疏多散射点 模型3 32个散射点,两个强散射点各占25%,其他散射点占各占1.66%能量 密集非均匀多散射点 模型4 32个散射点,均匀分布,各占3.125%能量 密集均匀散射点 -
JIANG Yuan, LI Yang, CAI Jinjian, et al. Robust automatic target recognition via HRRP sequence based on scatterer matching[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): No. 593, 1–19. doi: 10.3390/s18020593 DANIYAN A, LAMBOTHARAN S, DELIGIANNIS A, et al. Bayesian multiple extended target tracking using labeled random finite Sets and Splines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(22): 6076–6091. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2873537 HU Qi, JI Hongbing, and ZHANG Yongquan. Tracking of maneuvering non-ellipsoidal extended target with varying number of sub-objects[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 99: 262–284. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.06.013 HUGHES P K. A high-resolution radar detection strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1983, AES-19(5): 663–667. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1983.309368 GERLACH K and STEINER M J. Adaptive detection of range distributed targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1999, 47(7): 1844–1851. doi: 10.1109/78.771034 顾新锋, 简涛, 何友. 距离扩展目标的双门限恒虚警检测器及性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(6): 1318–1323. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01094GU Xinfeng, JIAN Tao, and HE You. Double threshold CFAR detector of range-spread target and its performance analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(6): 1318–1323. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01094 ROUFFET T, VALLET P, GRIVEL E, et al. Analysis of a GLRT for the detection of an extended target[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485281. LIU Jun, LIU Weijian, TANG Bo, et al. Distributed target detection exploiting persymmetry in Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(4): 1022–1033. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2887405 高彦钊, 占荣辉, 万建伟. KK分布杂波下的距离扩展目标检测算法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2015, 37(1): 118–124. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201501020GAO Yanzhao, ZHAN Ronghui, and WAN Jianwei. Range-spread target detection in KK-distributed clutter[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2015, 37(1): 118–124. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201501020 戴奉周, 刘宏伟, 吴顺君. 一种基于顺序统计量的距离扩展目标检测器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(10): 2488–2492.DAI Fengzhou, LIU Hongwei, and WU Shunjun. Order-statistic-based detector for range spread target[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(10): 2488–2492. LONG Teng, ZHENG Le, LI Yang, et al. Improved double threshold detector for spatially distributed target[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2012, E95.B(4): 1475–1478. doi: 10.1587/transcom.e95.b.1475 陈新亮, 王丽, 柳树林, 等. 高分辨雷达扩展目标检测算法研究[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2012, 42(8): 1007–1018. doi: 10.1360/112011-457CHEN Xinliang, WANG Li, LIU Shulin, et al. Research on extended target detection for high resolution radar[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2012, 42(8): 1007–1018. doi: 10.1360/112011-457 LONG Teng, LIANG Zhennan, and LIU Quanhua. Advanced technology of high-resolution radar: Target detection, tracking, imaging, and recognition[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(4): 40301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9811-0 XU Shuwen, SHI Xingyu, XUE Jian, et al. Maneuvering range-spread target detection in white Gaussian noise using multiple-pulse combined waveform contrast[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xiamen, China, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCC.2017.8242373. ARTHUR D and VASSILVITSKII S. k-means++: The advantages of careful seeding[C]. The 18th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, USA, 2007: 1027–1035. KANUNGO T, MOUNT D M, NETANYAHU N S, et al. An efficient k-Means clustering algorithm: Analysis and implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 881–892. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2002.1017616 CHEN YEWANG, TANG SHENGYU, BOUGUILA N, et al. A fast clustering algorithm based on pruning unnecessary distance computations in DBSCAN for high-dimensional data[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 83: 375–387. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.05.030 NGUYEN B and DE BAETS B. Kernel-based distance metric learning for supervised k-Means clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(10): 3084–3095. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2890021 -





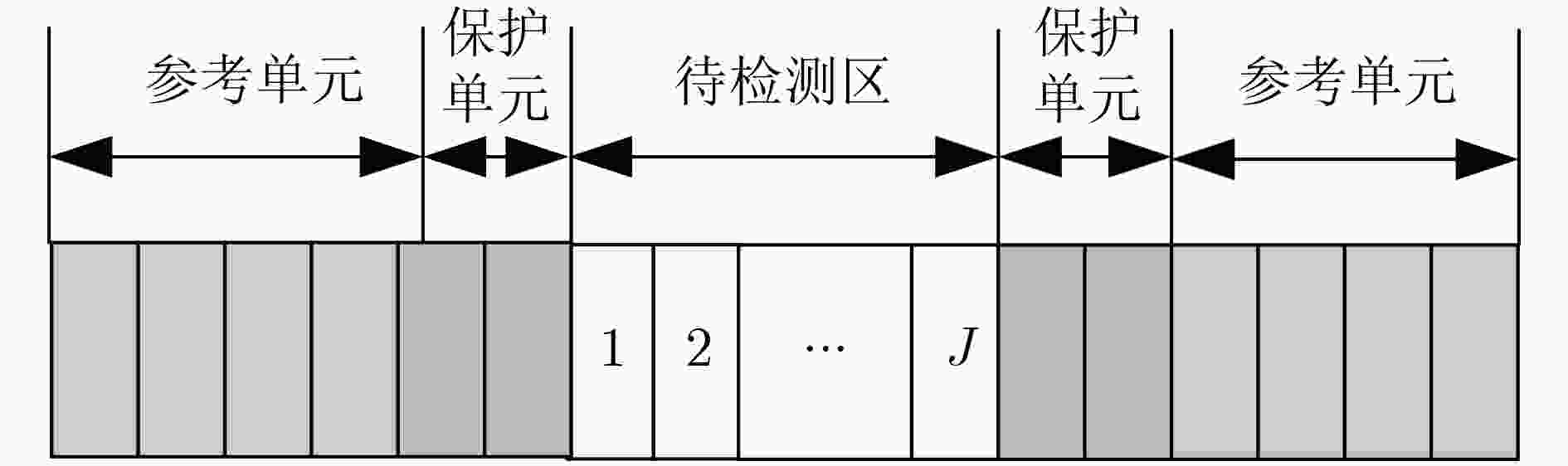
 下载:
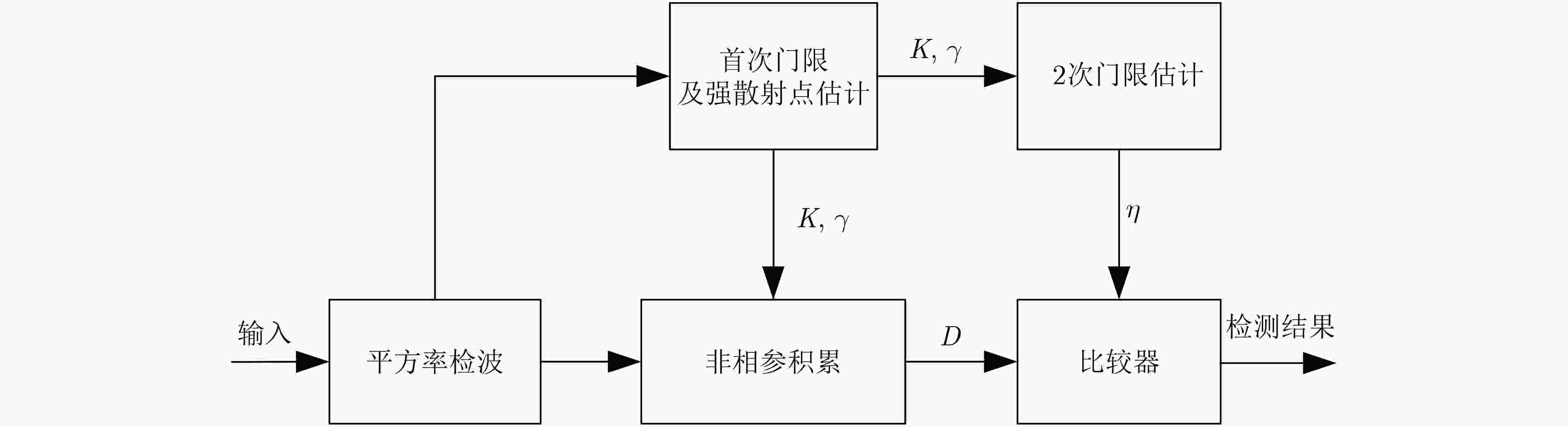
下载:
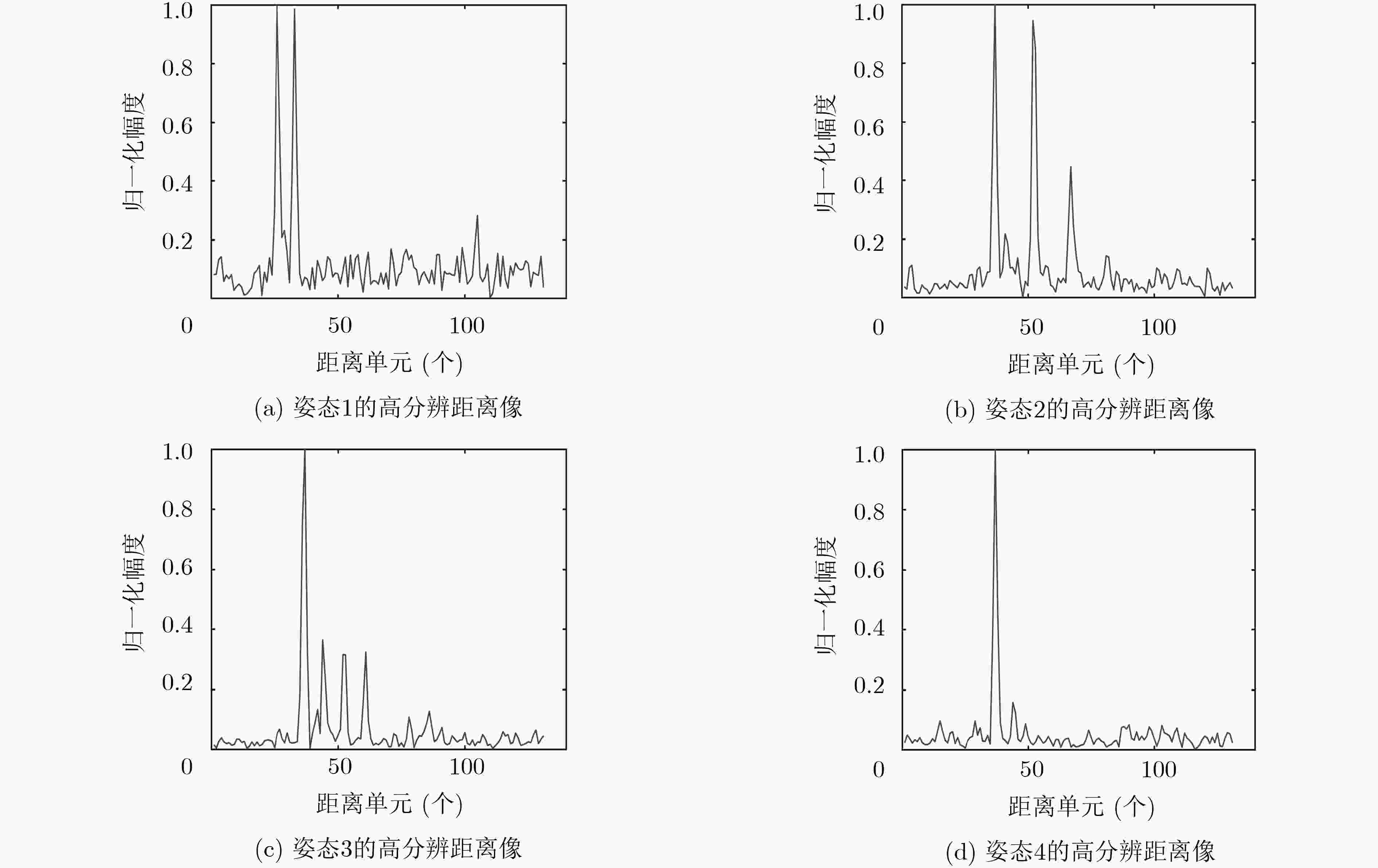
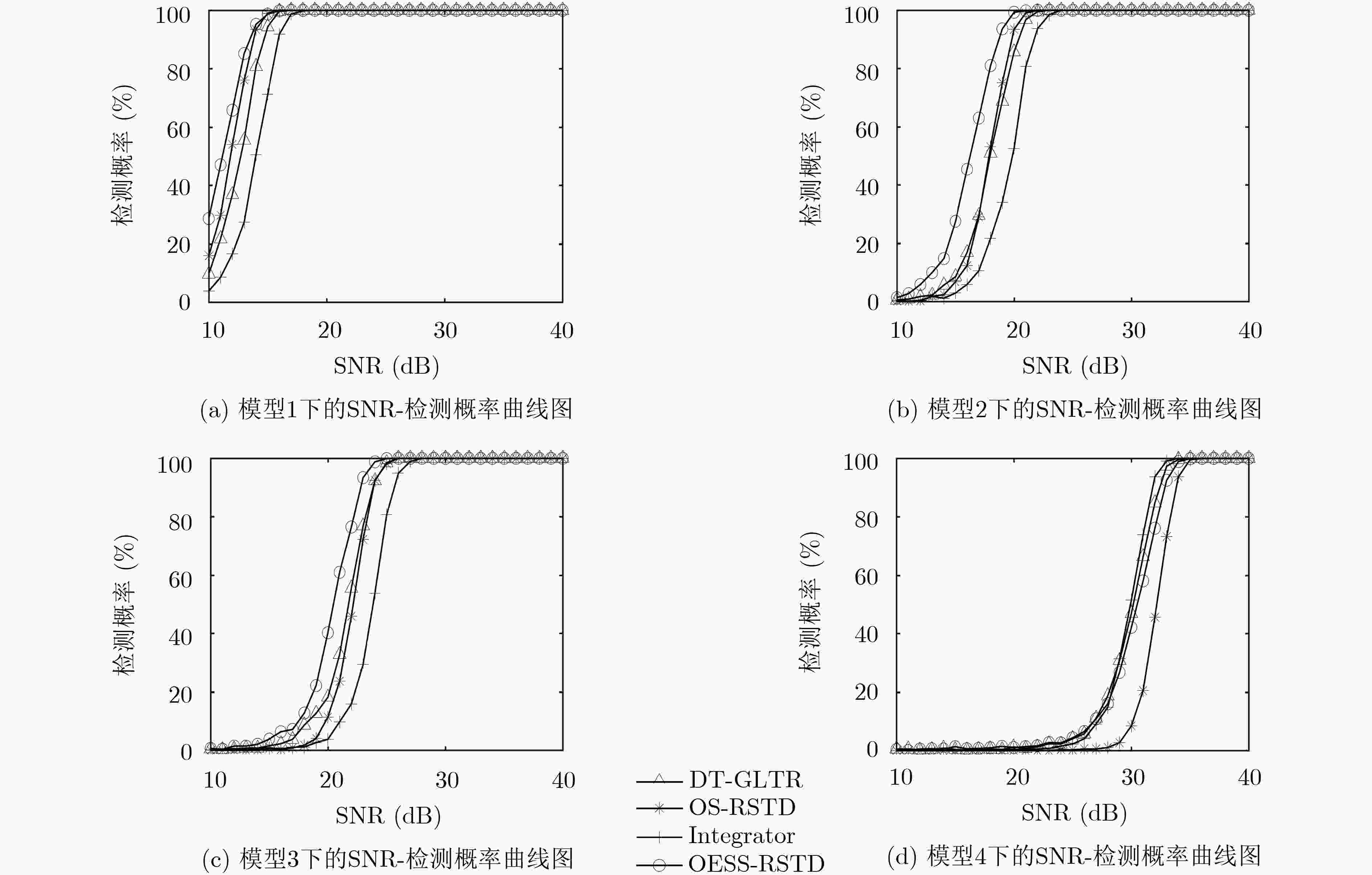


 下载:
下载:
