WLAN Indoor Intrusion Detection Approach Based on Multiple Kernel Maximum Mean Discrepancy Transfer Learning
-
摘要:
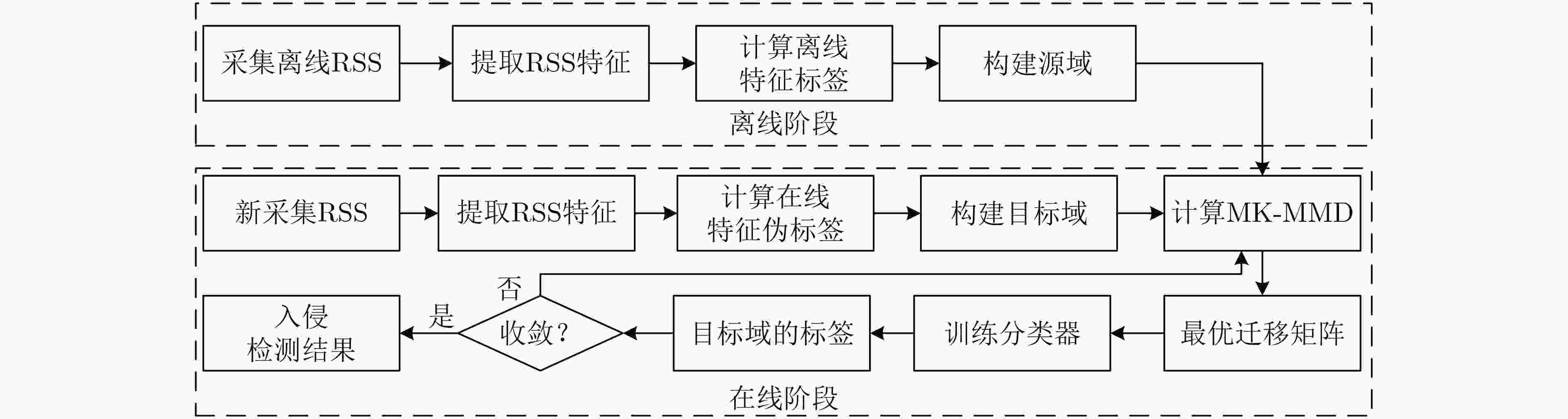
无线局域网(WLAN)室内入侵检测技术是目前智能检测领域的研究热点之一,而传统基于数据库构建的入侵检测技术没有考虑复杂室内环境中WLAN信号的时变性,从而导致WLAN室内入侵检测系统的鲁棒性较差。为了解决这一问题,该文提出一种基于多核最大均值差异(MKMMD)迁移学习的WLAN室内入侵检测方法。该方法首先利用离线有标记和在线伪标记的接收信号强度(RSS)特征来分别构建源域和目标域;其次,通过构造最优迁移矩阵以最小化源域和目标域RSS特征混合分布之间的MKMMD;再次,利用迁移后的源域RSS特征与对应标签来训练分类器,并将其用于对迁移后的目标域RSS特征进行分类以得到目标域标签集;最后,迭代更新目标域标签集直至算法收敛,进而实现对目标环境的入侵检测。实验结果表明,该文所提方法在保证较高检测精度的同时,能够有效克服信号时变性对检测性能的影响。
Abstract:Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) indoor intrusion detection technique is one of the current research hotspots in the field of intelligent detection, but the conventional database construction based intrusion detection technique does not consider the time-variant property of WLAN signal in the complicated indoor environment, which results in the low robustness of WLAN indoor intrusion detection system. To address this problem, a Multiple Kernel Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MKMMD) transfer learning based WLAN indoor intrusion detection approach is proposed. First of all, the offline labeled and online pseudo-labeled Received Signal Strength (RSS) features are used to construct source and target domains respectively. Second, the optimal transfer matrix is constructed to minimize the MKMMD of the joint distributions of RSS features in source and target domains. Third, a classifier trained from the transferred RSS features and the corresponding labels in source domain is used to classify the transferred RSS features in target domain, and meanwhile the label set corresponding to target domain is obtained. Finally, the label set corresponding to target domain is updated in an iterative manner until the proposed algorithm converges, and then the intrusion detection in target environment is achieved. The experimental results indicate that the proposed approach is able to preserve high detection accuracy as well as overcome the impact of time-variant signal property on the detection performance.
-
表 1 不同分类器的检测性能(%)
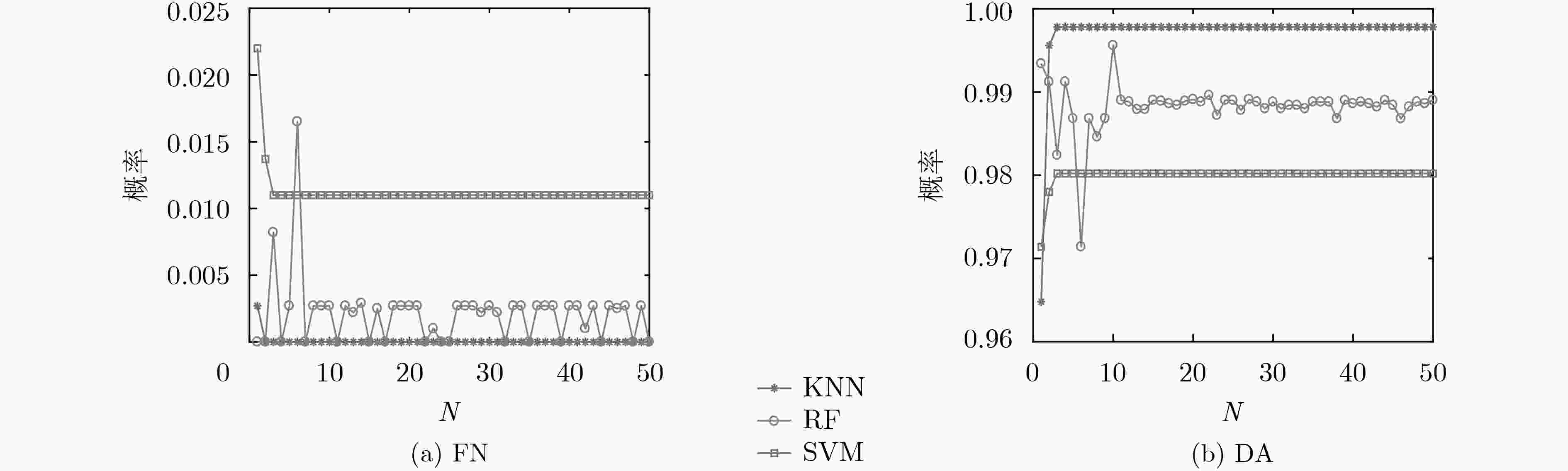
类别 FP FN DA KNN(迁移前) 35.92 0 75.60 KNN(迁移后) 0 0 99.78 RF(迁移前) 6.67 1.92 83.96 RF(迁移后) 0 0 98.90 SVM(迁移前) 18.02 0 93.85 SVM(迁移后) 0 1.10 98.02 表 2 不同方法的检测性能(%)
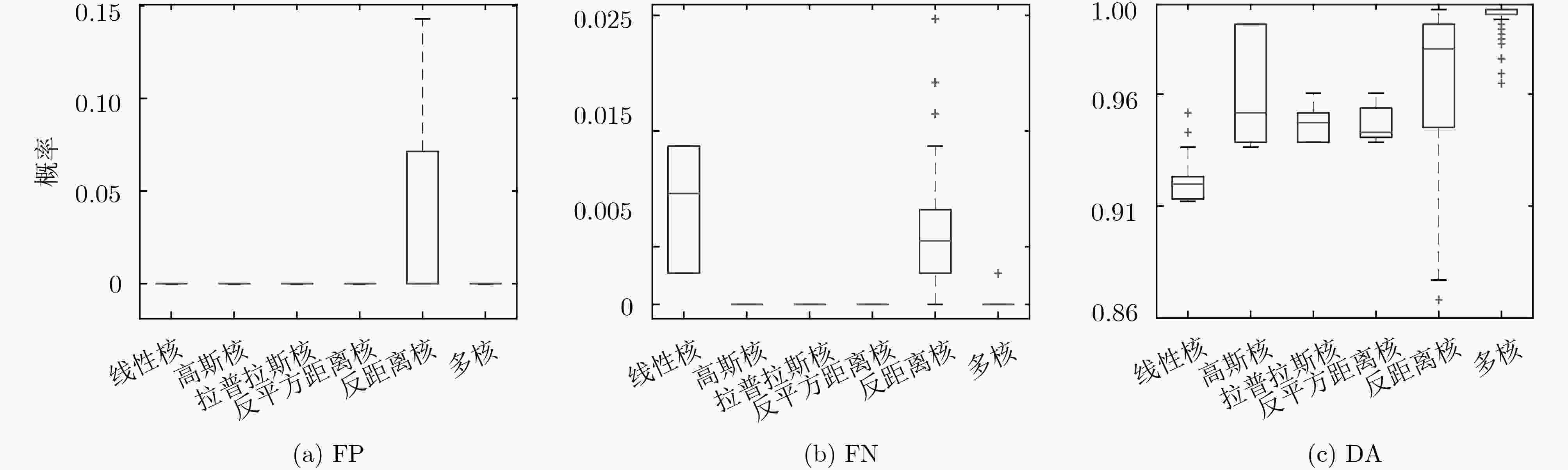
指标 RASID PNN PRNN 本文方法 FP 6.72 3.42 0 0 FN 3.31 2.92 0 0 DA 93.46 94.40 95.60 99.78 -
周培培, 丁庆海, 罗海波, 等. 视频监控中的人群异常行为检测与定位[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(8): 0815007. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0815007ZHOU Peipei, DING Qinghai, LUO Haibo, et al. Anomaly detection and location in crowded surveillance videos[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(8): 0815007. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0815007 程卫东, 董永贵. 利用热释电红外传感器探测人体运动特征[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2008, 29(5): 1020–1023. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2008.05.025CHENG Weidong and DONG Yonggui. Detection of human body motion features using pyroelectric infrared sensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2008, 29(5): 1020–1023. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2008.05.025 WANG Hongpeng, LIU Jingtai, SUN Lei, et al. Indoor intrusion detection using an intelligent sensor network[C]. 2008 IEEE World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Chongqing, China, 2008: 2396–2401. doi: 10.1109/WCICA.2008.4593298. TIAN Zengshan, LI Yong, ZHOU Mu, et al. WiFi-based adaptive indoor passive intrusion detection[C]. 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICDSP.2018.8631613. YOUSSEF M, MAH M, and AGRAWALA A. Challenges: Device-free passive localization for wireless environments[C]. The 13th Annual ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Montréal, Canada, 2007: 222–229. doi: 10.1145/1287853.1287880. ZHOU Rui, CHEN Jiesong, LU Xiang, et al. CSI fingerprinting with SVM regression to achieve device-free passive localization[C]. The 18th IEEE International Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks, Macau, China, 2017: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/WoWMoM.2017.7974313. KOSBA A E, SAEED A, and YOUSSEF M. RASID: A robust WLAN device-free passive motion detection system[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Lugano, Switzerland, 2012: 180–189. doi: 10.1109/PerCom.2012.6199865. TIAN Zengshan, ZHOU Xiangdong, ZHOU Mu, et al. Indoor device-free passive localization for intrusion detection using multi-feature PNN[C]. 2015 International Conference on Communications and Networking in China, Shanghai, China, 2015: 272–277. doi: 10.1109/CHINACOM.2015.7497950. DEAK G, CURRAN K, CONDELL J, et al. Detection of multi-occupancy using device-free passive localisation[J]. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 2014, 4(3): 130–137. doi: 10.1049/iet-wss.2013.0031 LV Jiguang, MAN Dapeng, YANG Wu, et al. Robust WLAN-based indoor intrusion detection using PHY layer information[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 30117–30127. doi: 10.1109/access.2017.2785444 TAN Qingqing, HAN Chong, SUN Lijuan, et al. A CSI frequency domain fingerprint-based method for passive indoor human detection[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications/12th IEEE International Conference on Big Data Science and Engineering, New York, USA, 2018: 1832–1837. doi: 10.1109/TrustCom/BigDataSE.2018.00277. GRETTON A, SRIPERUMBUDUR B, SEJDINOVIC D, et al. Optimal kernel choice for large-scale two-sample tests[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1205–1213. LONG Mingsheng, WANG Jianmin, DING Guiguang, et al. Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 2200–2207. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.274. DUAN Lixin, TSANG I W, and XU Dong. Domain transfer multiple kernel learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(3): 465–479. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2011.114 BORGWARDT K M, GRETTON A, RASCH M J, et al. Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy[J]. Bioinformatics, 2006, 22(4): e49–e57. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl242 PAN S J, TSANG I W, KWOK J T, et al. Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(2): 199–210. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2091281 SCHOLKÖPF B, SMOLA A, and MÜLLER K R. Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem[J]. Neural Computation, 1998, 10(5): 1299–1319. doi: 10.1162/089976698300017467 汪洪桥, 孙富春, 蔡艳宁, 等. 多核学习方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(8): 1037–1050. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01037WANG Hongqiao, SUN Fuchun, CAI Yanning, et al. On multiple kernel learning methods[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(8): 1037–1050. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01037 COVER T and HART P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1967, 13(1): 21–27. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1967.1053964 BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 CORTES C and VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00994018 -





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
