RGB-D Image Saliency Detection Based on Multi-modal Feature-fused Supervision
-
摘要:
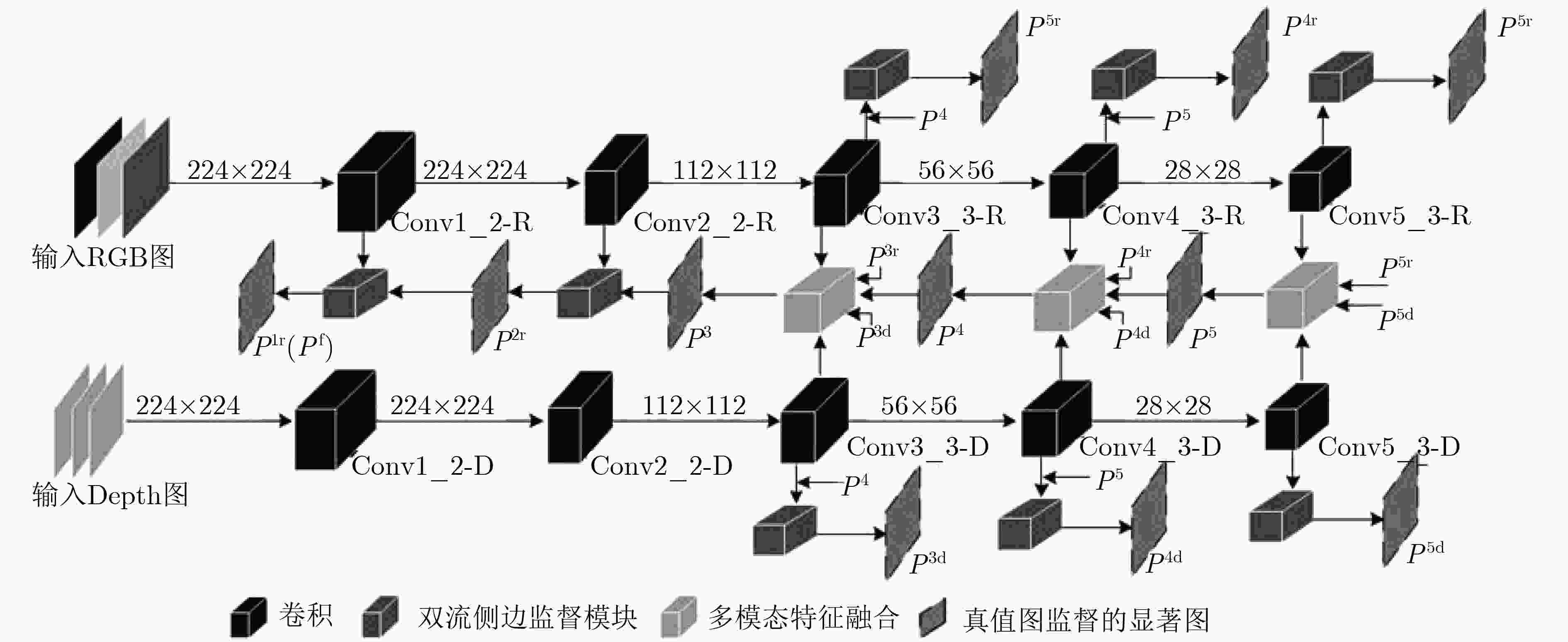
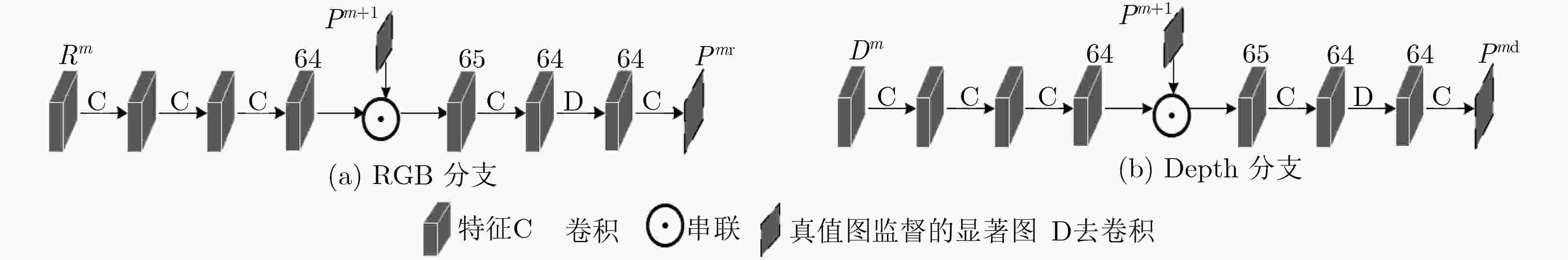
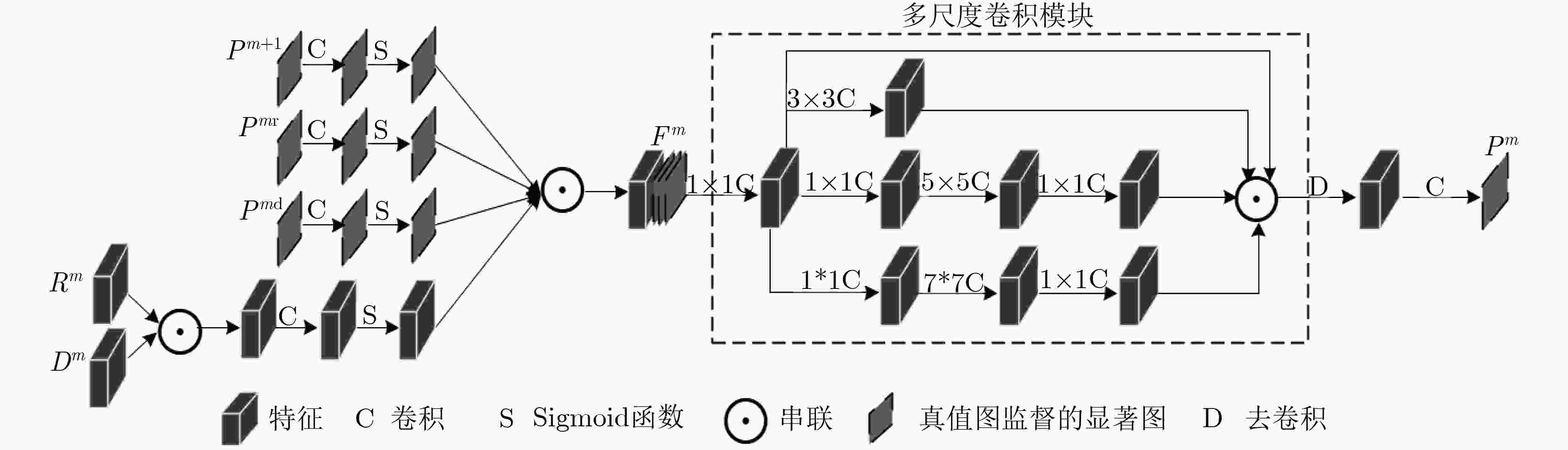
RGB-D图像显著性检测是在一组成对的RGB和Depth图中识别出视觉上最显著突出的目标区域。已有的双流网络,同等对待多模态的RGB和Depth图像数据,在提取特征方面几乎一致。然而,低层的Depth特征存在较大噪声,不能很好地表征图像特征。因此,该文提出一种多模态特征融合监督的RGB-D图像显著性检测网络,通过两个独立流分别学习RGB和Depth数据,使用双流侧边监督模块分别获取网络各层基于RGB和Depth特征的显著图,然后采用多模态特征融合模块来融合后3层RGB和Depth高维信息生成高层显著预测结果。网络从第1层至第5层逐步生成RGB和Depth各模态特征,然后从第5层到第3层,利用高层指导低层的方式产生多模态融合特征,接着从第2层到第1层,利用第3层产生的融合特征去逐步地优化前两层的RGB特征,最终输出既包含RGB低层信息又融合RGB-D高层多模态信息的显著图。在3个公开数据集上的实验表明,该文所提网络因为使用了双流侧边监督模块和多模态特征融合模块,其性能优于目前主流的RGB-D显著性检测模型,具有较强的鲁棒性。
-
关键词:
- RGB-D显著性检测 /
- 卷积神经网络 /
- 多模态 /
- 监督
Abstract:RGB-D saliency detection identifies the most visually attentive target areas in a pair of RGB and Depth images. Existing two-stream networks, which treat RGB and Depth data equally, are almost identical in feature extraction. As the lower layers Depth features with a lot of noise, it causes image features not be well characterized. Therefore, a multi-modal feature-fused supervision of RGB-D saliency detection network is proposed, RGB and Depth data are studied independently through two-stream , double-side supervision module is used respectively to obtain saliency maps of each layer, and then the multi-modal feature-fused module is used to later three layers of the fused RGB and Depth of higher dimensional information to generate saliency predicted results. Finally, the information of lower layers is fused to generate the ultimate saliency maps. Experiments on three open data sets show that the proposed network has better performance and stronger robustness than the current RGB-D saliency detection models.
-
Key words:
- RGB-D saliency detection /
- Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) /
- Multi-modal /
- Supervision
-
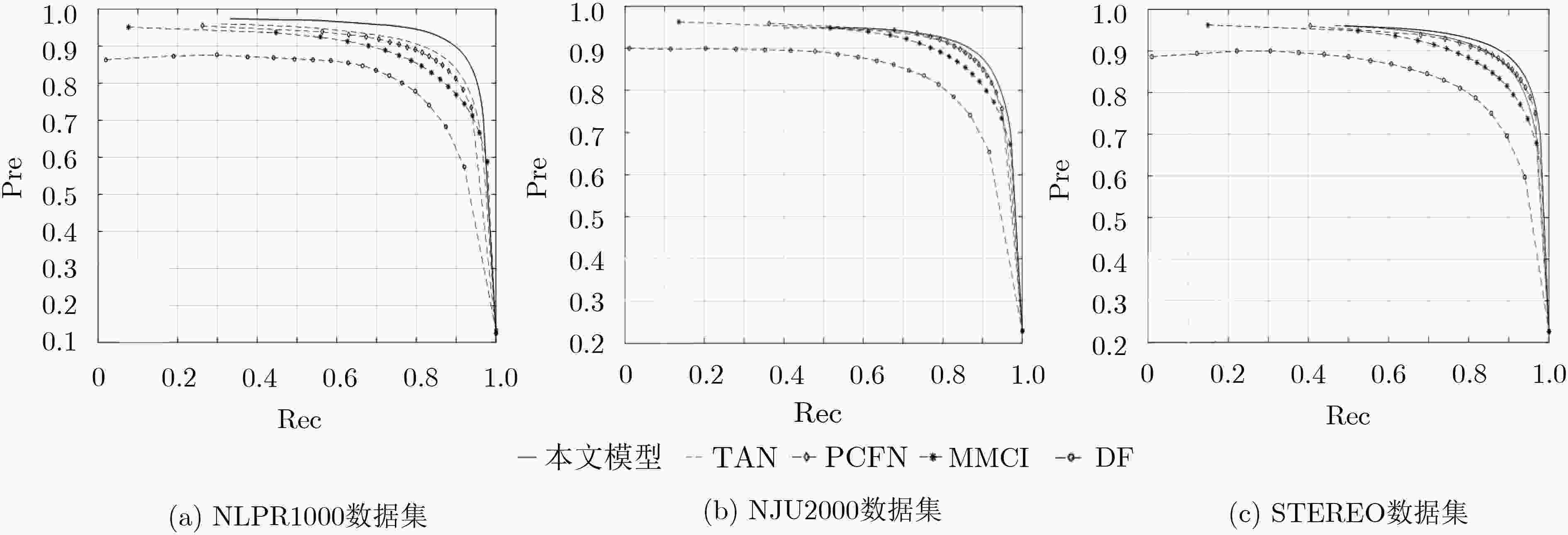
表 1 在F-measure, MAE, S-measure, E-measure上与其他模型的对比
算法 NLPR1000 NJU2000 STEREO F MAE S E F MAE S E F MAE S E TAN 0.7956 0.0410 0.8861 0.9161 0.8442 0.0605 0.8785 0.8932 0.8489 0.0591 0.8775 0.9108 PCFN 0.7948 0.0437 0.8736 0.9163 0.8440 0.0591 0.8770 0.8966 0.8450 0.0606 0.8800 0.9054 MMCI 0.7299 0.0591 0.8557 0.8717 0.8122 0.0790 0.8581 0.8775 0.8120 0.0796 0.8599 0.8896 DF 0.7348 0.0891 0.7909 0.8600 0.7703 0.1406 0.7596 0.8383 0.7650 0.1395 0.7664 0.8438 本文模型 0.8629 0.0318 0.9117 0.9464 0.8578 0.0541 0.8852 0.8956 0.8622 0.0519 0.8894 0.9130 表 2 双流侧边监督模块有效性实验对比结果
算法 NLPR1000 NJU2000 STEREO F MAE S E F MAE S E F MAE S E NDS 0.8358 0.0340 0.9085 0.9336 0.8502 0.0568 0.8848 0.8902 0.8524 0.0552 0.8879 0.9066 本文模型(DS) 0.8629 0.0318 0.9117 0.9464 0.8578 0.0541 0.8852 0.8956 0.8622 0.0519 0.8894 0.9130 表 3 多尺度模块有效性实验对比结果
算法 NLPR1000 NJU2000 STEREO F MAE S E F MAE S E F MAE S E BN 0.8488 0.0340 0.9059 0.9398 0.8504 0.0566 0.8814 0.8928 0.8573 0.0547 0.8848 0.9093 本文模型 0.8629 0.0318 0.9117 0.9464 0.8578 0.0541 0.8852 0.8956 0.8622 0.0519 0.8894 0.9130 表 4 低维Depth特征实验对比结果
算法 NLPR1000 NJU2000 STEREO F MAE S E F MAE S E F MAE S E DY 0.8715 0.1087 0.8187 0.9479 0.8250 0.1310 0.8414 0.8785 0.8355 0.1277 0.8541 0.8984 本文模型 0.8629 0.0318 0.9117 0.9464 0.8578 0.0541 0.8852 0.8956 0.8622 0.0519 0.8894 0.9130 -
SHAO Ling and BRADY M. Specific object retrieval based on salient regions[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2006, 39(10): 1932–1948. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2006.04.010 GUO Chenlei and ZHANG Liming. A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(1): 185–198. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2030969 MAHADEVAN V and VASCONCELOS N. Biologically inspired object tracking using center-surround saliency mechanisms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(3): 541–554. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.98 QU Liangqiong, HE Shengfeng, ZHANG Jiawei, et al. RGBD salient object detection via deep fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(5): 2274–2285. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2682981 CHEN Hao, LI Youfu, and SU Dan. Multi-modal fusion network with multi-scale multi-path and cross-modal interactions for RGB-D salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 86: 376–385. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.08.007 HAN Junwei, CHEN Hao, LIU Nian, et al. CNNs-Based RGB-D saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(11): 3171–3183. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2761775 CHEN Hao, LI Youfu, and SU Dan. RGB-D saliency detection by multi-stream late fusion network[C]. The 11th International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, Shenzhen, China, 2017: 459-468. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-68345-4_41. CHEN Hao and LI Youfu. Progressively complementarity-aware fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3051–3060. SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 2015 International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1150–1210. LEE C Y, XIE Saining, GALLAGHER P, et al. Deeply-supervised nets[C]. The 18th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, San Diego, USA, 2015: 562–570. XIE Saining and TU Zhuowen. Holistically-nested edge detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 125(1/3): 3–18. doi: 10.1007/s11263-017-1004-z HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, HU Xiaowei, et al. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(4): 815–828. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2815688 DU Dapeng, XU Xiangyang, REN Tongwei, et al. Depth images could tell us more: Enhancing depth discriminability for RGB-D scene recognition[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, San Diego, USA, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICME.2018.8486573. SONG Xinhang, HERRANZ L, and JIANG Shuqiang. Depth CNNs for RGB-D scene recognition: Learning from scratch better than transferring from RGB-CNNs[C]. The 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4271–4277. LIU Nian and HAN Junwei. DHSnet: Deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 678–686. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.80. KIM H J, DUNN E, and FRAHM J M. Learned contextual feature reweighting for image geo-localization[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3251–3260. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.346. PENG Houwen, LI Bing, XIONG Weihua, et al. RGBD salient object detection: A benchmark and algorithms[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 92–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10578-9_7. JU Ran, GE Ling, GENG Wenjing, et al. Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 2014: 1115–1119. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2014.7025222. NIU Yuzhen, GENG Yujie, LI Xueqing, et al. Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 454–461. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247708. MARTIN D R, FOWLKES C C, and MALIK J. Learning to detect natural image boundaries using local brightness, color, and texture cues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(5): 530–549. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.1273918 FAN Dengping, CHENG Mingming, LIU Yun, et al. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4558–4567. FAN Dengping, GONG Cheng, CAO Yang, et al. Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation[C]. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, 2018: 698–704. FAN Dengping, CHENG Mingming, LIU Jiangjiang, et al. Salient objects in clutter: Bringing salient object detection to the foreground[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 186–202. JIA Yangqing, SHELHAMER E, DONAHUE J, et al. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding[C]. The 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, USA, 2014: 675–678. doi: 10.1145/2647868.2654889. CHEN Hao and LI Youfu. Three-stream attention-aware network for RGB-D salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(6): 2825–2835. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2891104 -





 下载:
下载:
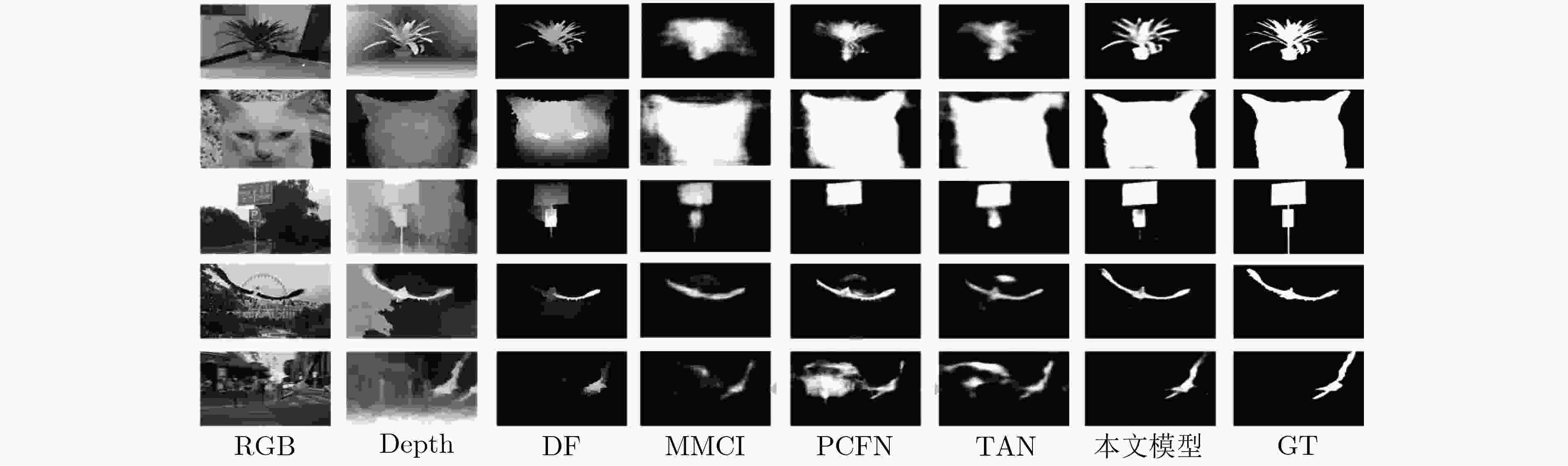
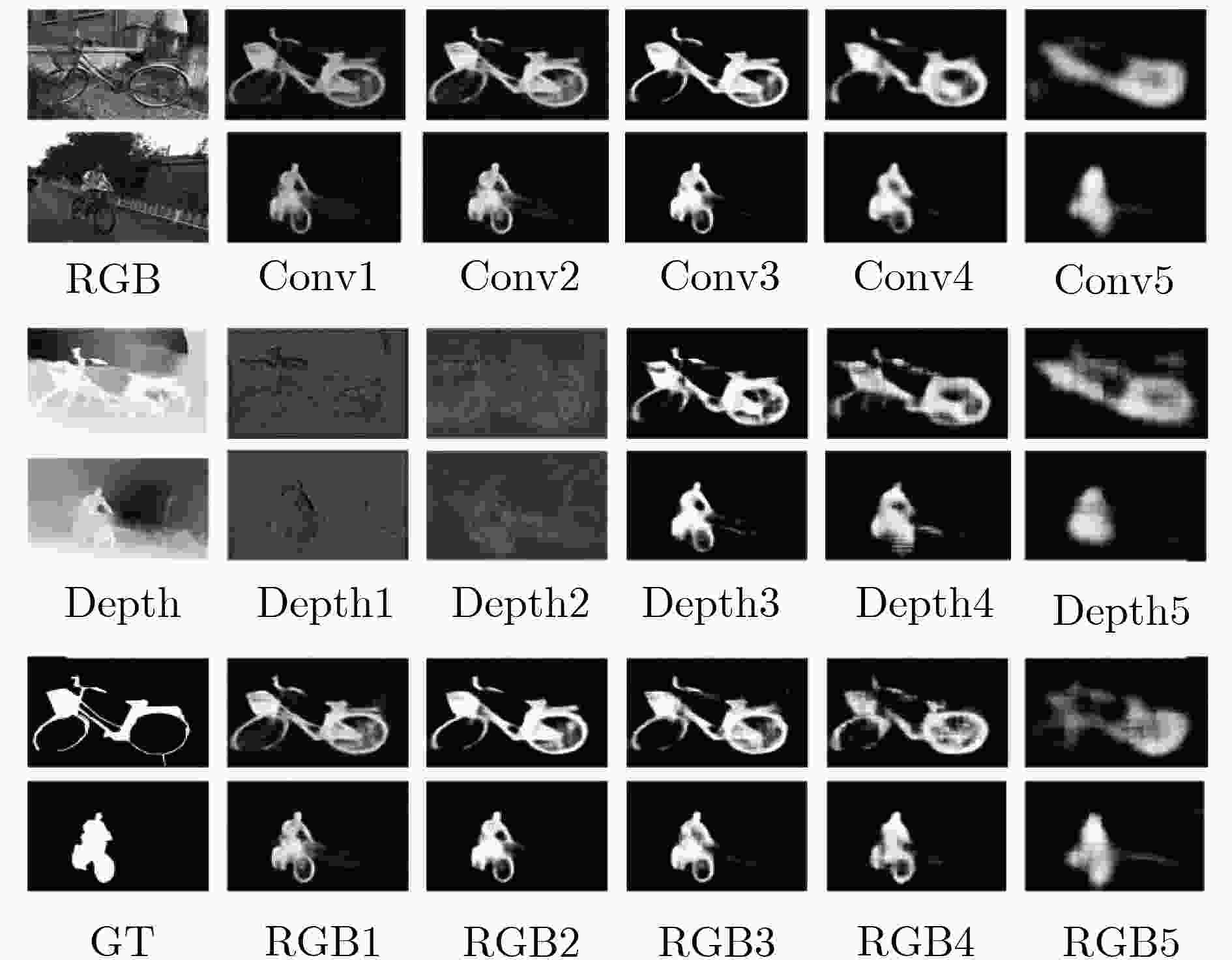
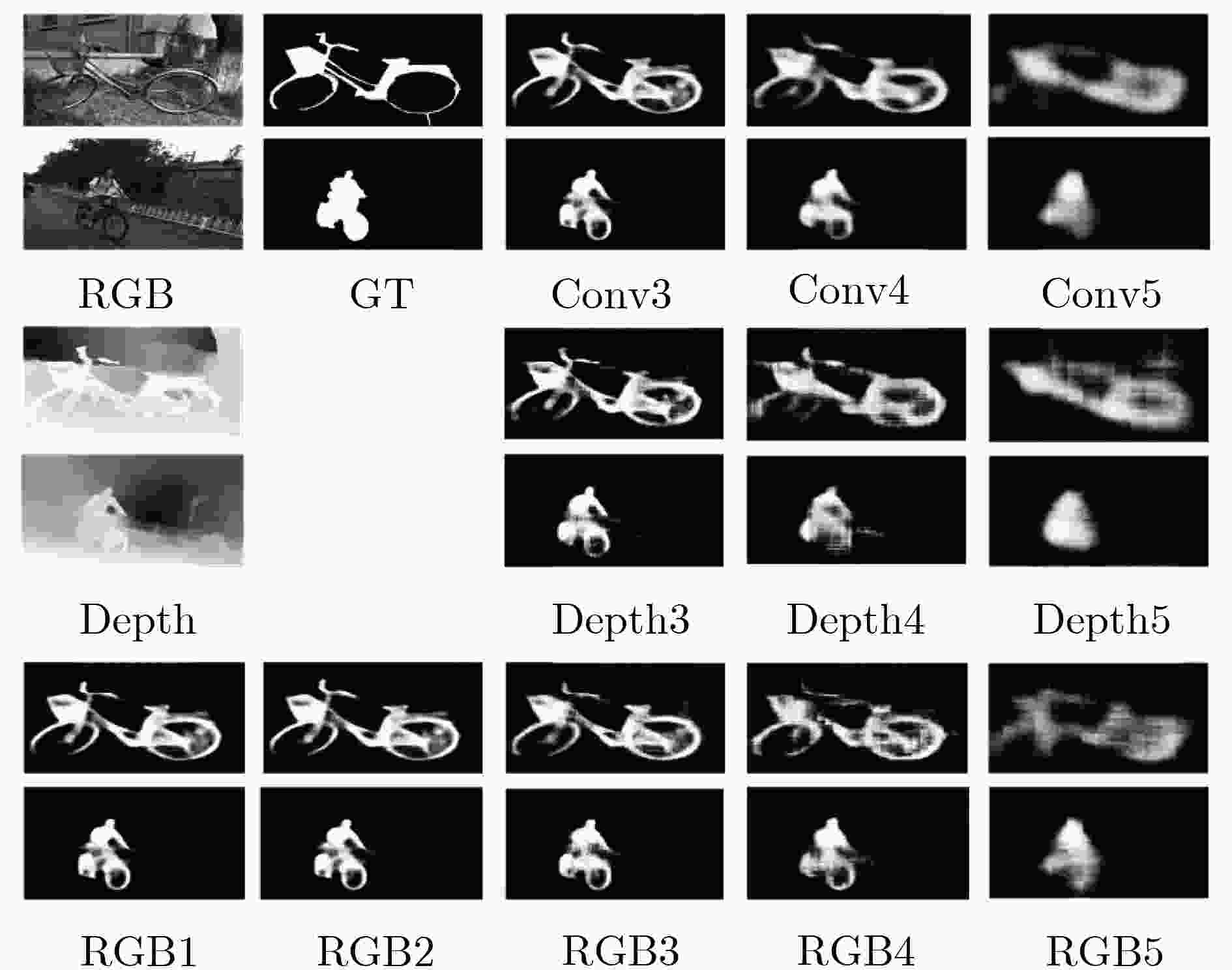


 下载:
下载:
