Double Encryption Method Based on Neural Network and Composite Discrete Chaotic System
-
摘要:
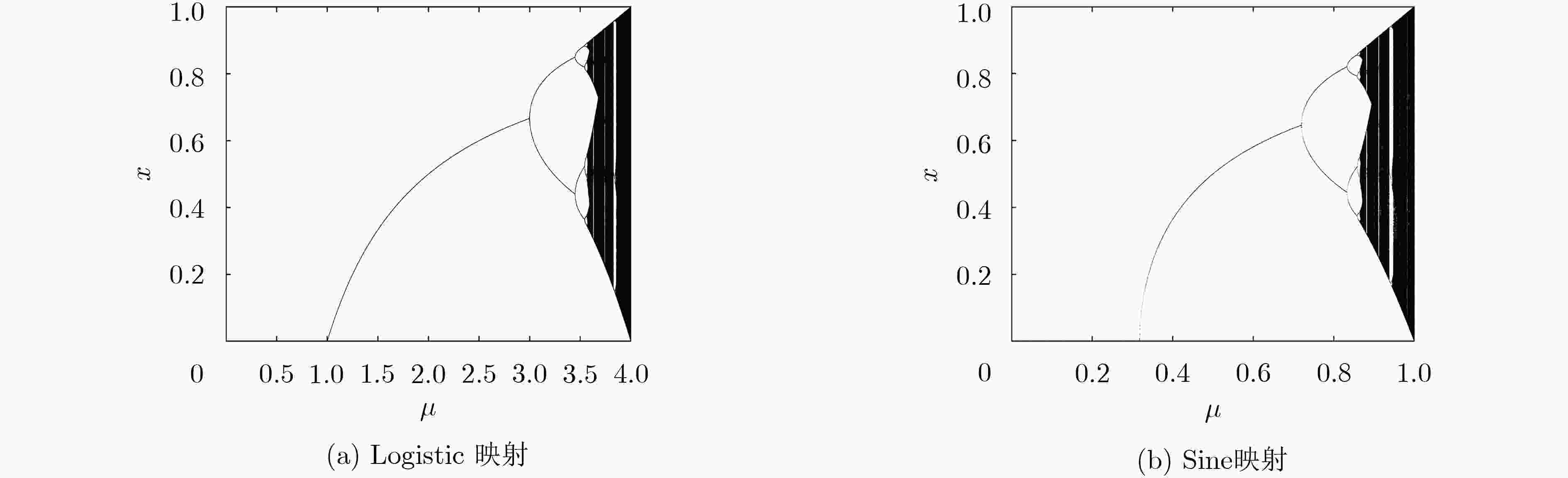
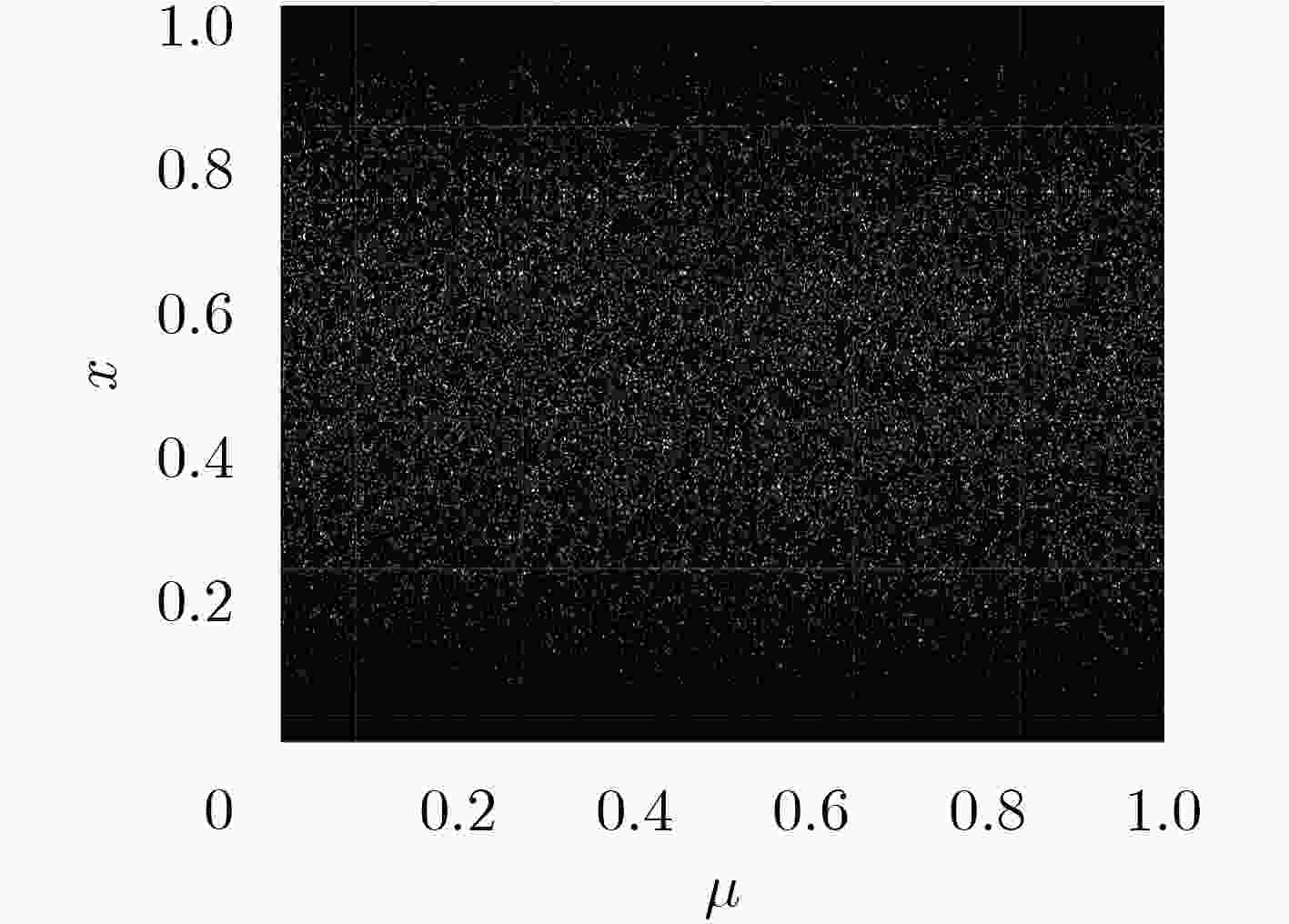
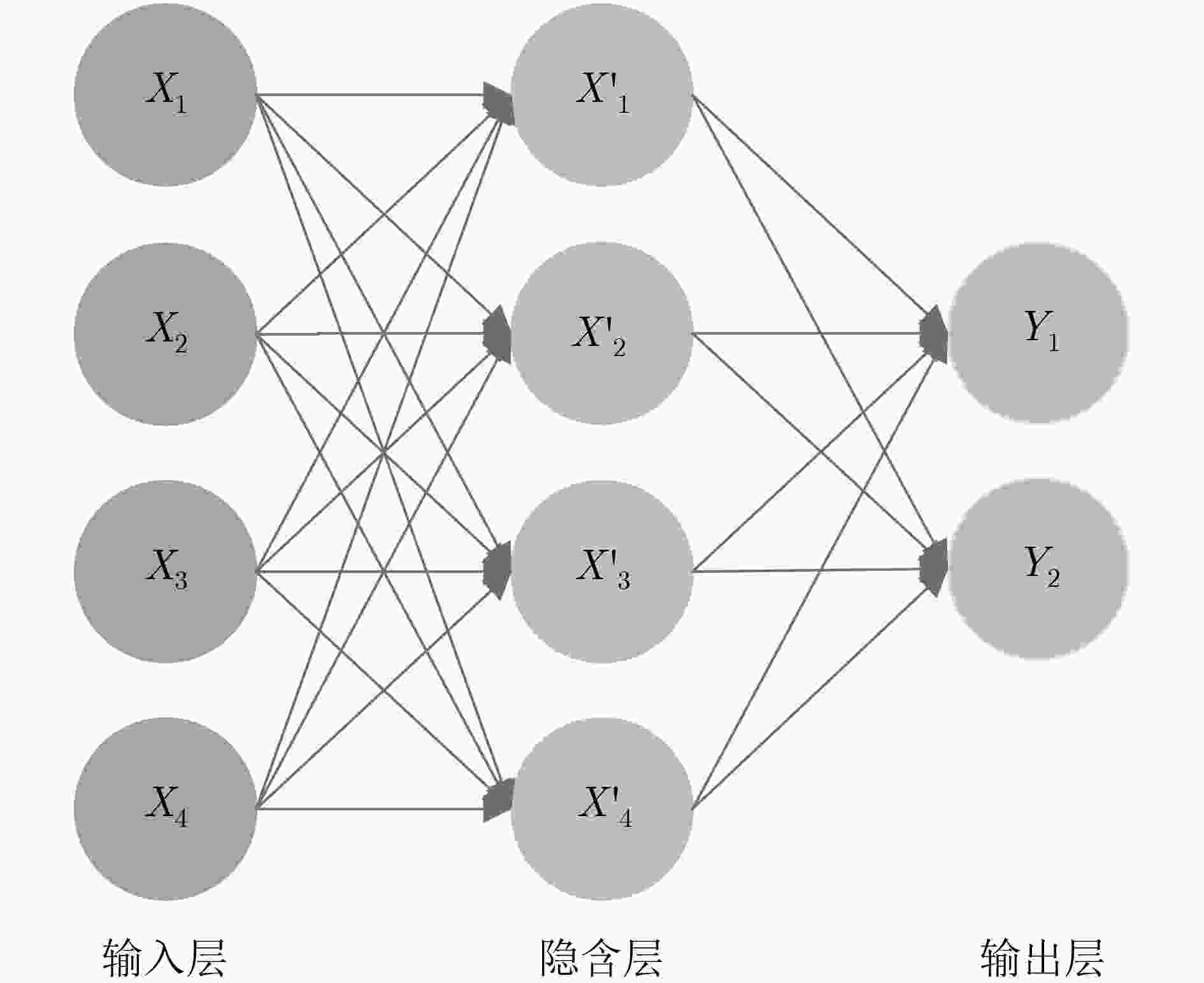
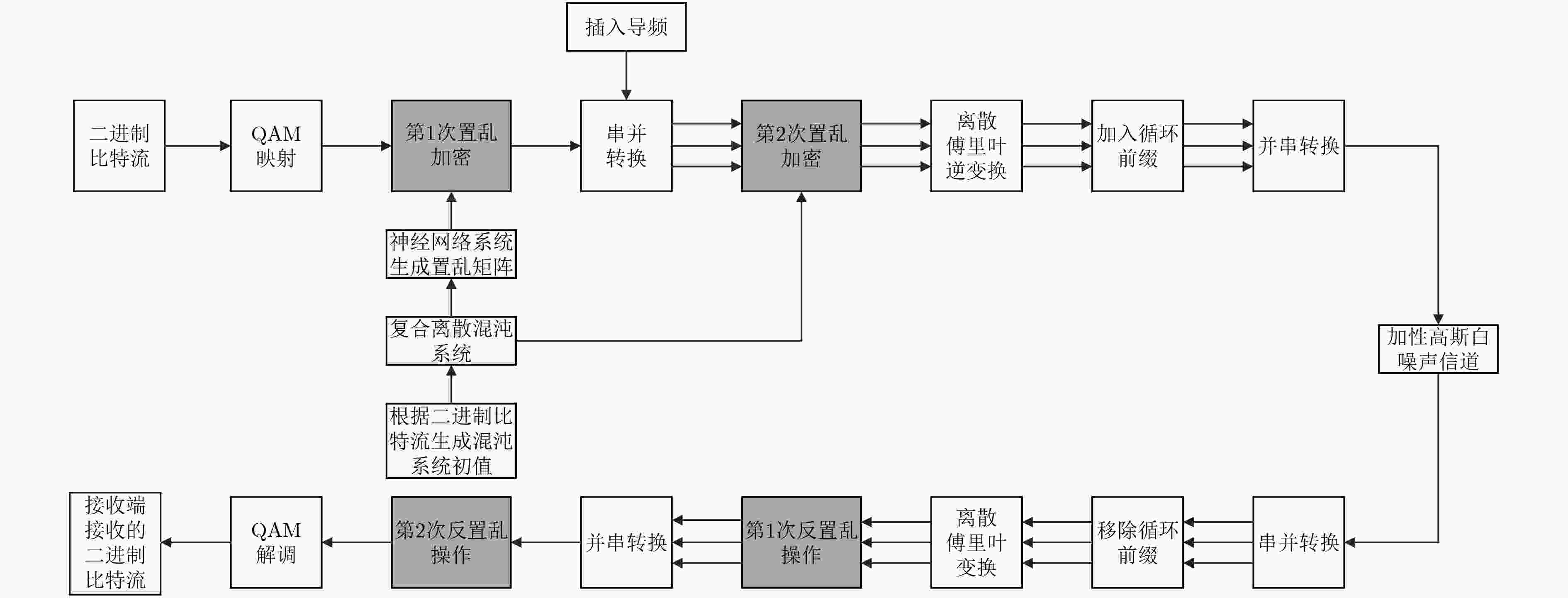
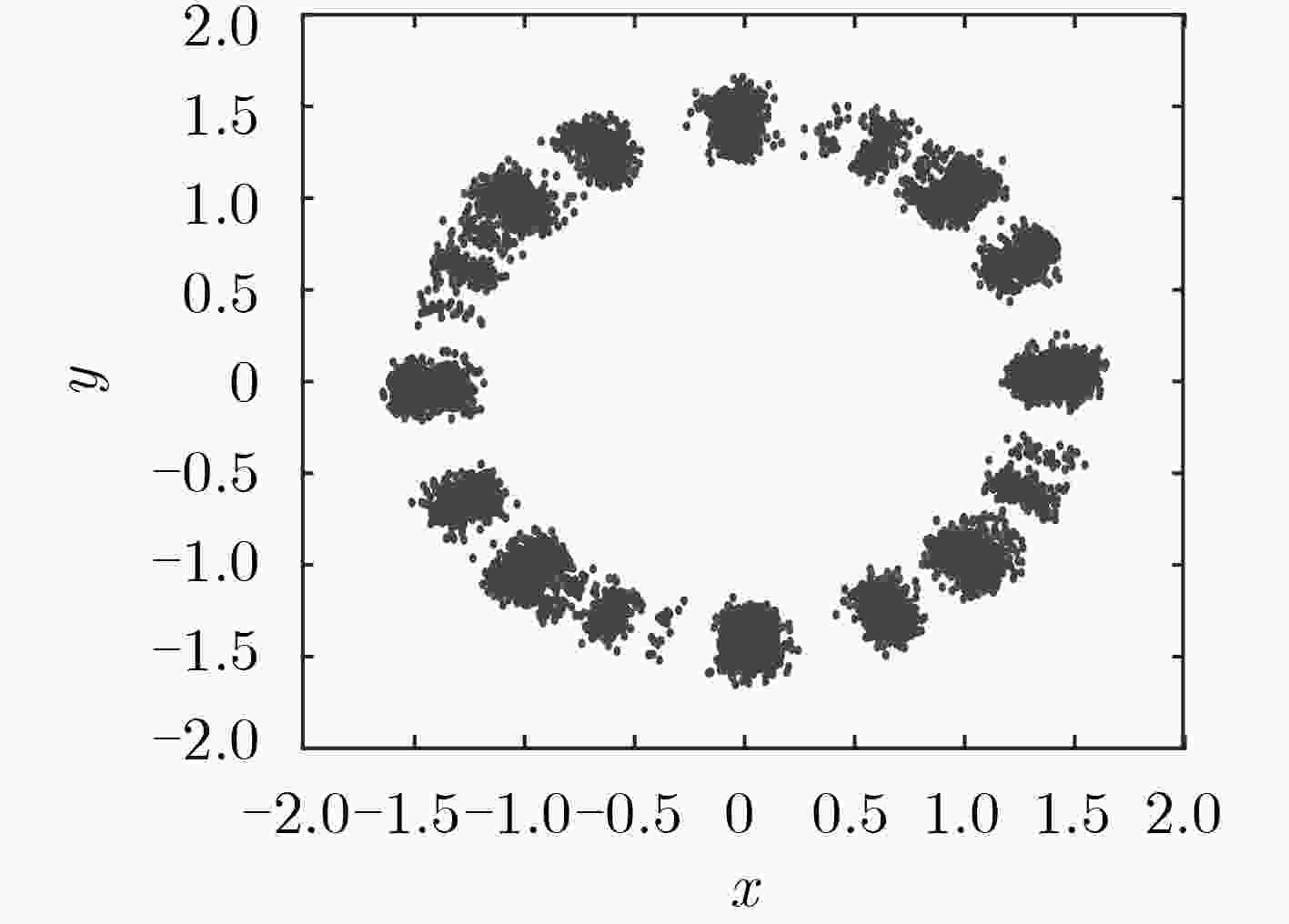
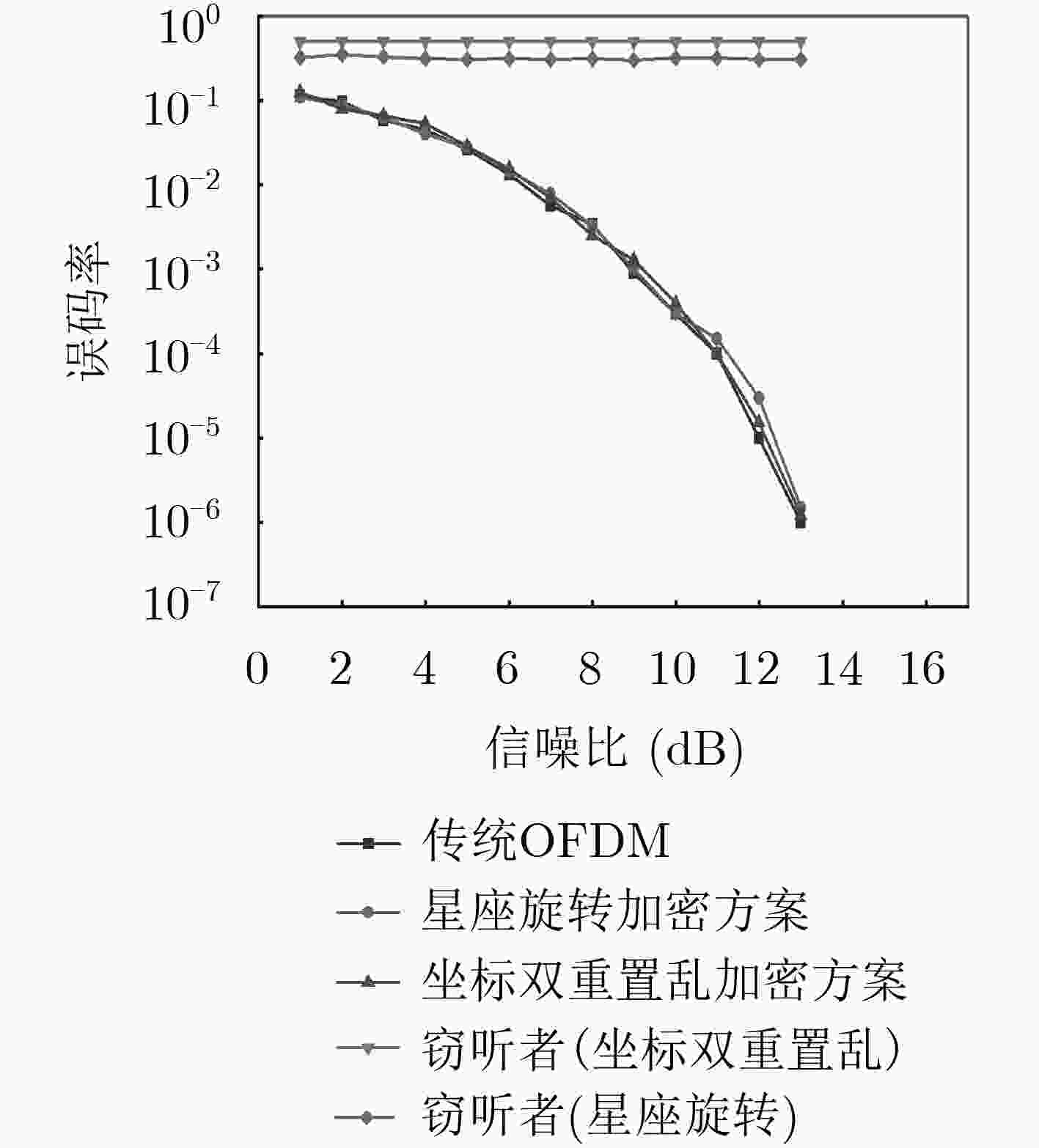
正交频分复用(OFDM)已被广泛应用于无线通信系统,其数据传输安全具有一定的实际意义。该文提出了一种双重加密方案,采用神经网络生成置乱矩阵实现第1次加密,通过基于Logistic映射与Sine映射的复合离散混沌系统产生的混沌序列进行第2次加密。该双重加密方案极大提升了OFDM通信系统的保密性,可以有效地防止暴力攻击。相比于单一的1维Logistic映射的混沌系统,基于Logistic映射与Sine映射的复合离散混沌系统具有更大的密钥空间。该文运用Lyapunov指数与NIST测试验证了该混沌系统的混沌特性及随机性,并仿真验证了双重加密方案的保密性能。仿真结果表明,该文所提出的加密方案密钥空间为4×1093,Lyapunov指数提高到0.9850,NIST测试中最大P值为0.9995。该双重加密方案可在不影响传输性能下极大提升OFDM通信系统的安全性。
Abstract:Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing(OFDM) is widely used in wireless communication systems, and its data transmission security has certain practical significance. A double encryption scheme is proposed which enhances the confidentiality of the OFDM communication system and can prevent brute force attacks significantly. Specifically, the first encryption is achieved by using neural network to generate the scrambling matrix, and the second encryption is implemented by chaotic sequence generating by composite discrete chaotic system based on Logistic mapping and Sine mapping. Moreover, it has larger secret key space compared with the single one-dimensional Logistic mapping chaotic system. The performance of double encryption is measured by verifying its chaotic characteristics and randomness (Lyapunov exponent and NIST) as well as its security performance in simulation. The results show that Lyapunov index is increased to 0.9850, and the maximum P-value in the NIST test is 0.9995 by using the proposed double encryption in this paper. It indicates such double encryption significantly improve the confidentiality of the OFDM communication system without affecting the transmission performance.
-
表 1 混沌系统Lyapunov指数
混沌系统 Logistic映射 Sine映射 复合离散混沌系统 Lyapunov指数 0.6118 0.5381 0.9850 表 2 NIST测试结果
序号 测试项目 P 值 测试结果 1 Frequency 0.7188 Success 2 Block Frequency 0.3721 Success 3 Cumulative Sums 0.5153 Success 4 Runs 0.9995 Success 5 Longest Run of Ones 0.6147 Success 6 Rank 0.8624 Success 7 Discrete Fourier Transform 0.9268 Success 8 Nonperiodic Template Matchings 0.9889 Success 9 Overlapping Template Matchings 0.7125 Success 10 Universal Statistical 0.6124 Success 11 Approximate Entropy 0.1522 Success 12 Random Excursions 0.4998 Success 13 Random Excurisions Variant 0.3114 Success 14 Serial 0.2962 Success 15 Linear Complexity 0.9855 Success 表 3 OFDM系统参数
特性 参数 特性 参数 调制方式 4QAM FFT点数 128 数据子载波 128 内插导频 4 循环前缀 4 OFDM符号数 100 信道类型 AWGN – – -
禹思敏, 吕金虎, 李澄清. 混沌密码及其在多媒体保密通信中应用的进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(3): 735–752. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151356YU Simin, LÜ Jinhu, and LI Chengqing. Chaos cipher and its application in multimedia secure communication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(3): 735–752. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151356 ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Chongfu, CHEN Chen, et al. Brownian motion encryption for physical-layer security improvement in CO-OFDM-PON[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(12): 1023–1026. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2702159 ZHANG Lijia, XIN Xiangjun, LIU Bo, et al. Physical secure enhancement in optical OFDMA-PON based on two-dimensional scrambling[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(26): B32–B37. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.000B32 ZHANG Chongfu, ZHANG Wei, CHEN Chen, et al. Physical-Enhanced secure strategy for OFDMA-PON using chaos and deoxyribonucleic acid encoding[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2018, 36(9): 1706–1712. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2018.2789435 ZHONG Ju, YANG Xuelin, and HU Weisheng. Performance-Improved secure OFDM transmission using chaotic active constellation extension[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(12): 991–994. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2700861 HAJOMER A A E, YANG Xuelin, and HU Weisheng. Chaotic walsh-hadamard transform for physical layer security in OFDM-PON[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(6): 527–530. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2663400 ZHANG Lijia, LIU Bo, and XIN Xiangjun. Secure optical generalized filter bank multi-carrier system based on cubic constellation masked method[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(12): 2711–2714. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.002711 ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Chongfu, CHEN Chen, et al. Joint PAPR reduction and physical layer security enhancement in OFDMA-PON[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2016, 28(9): 998–1001. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2522965 ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Chongfu, CHEN Chen, et al. Hybrid chaotic confusion and diffusion for physical layer security in OFDM-PON[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2017, 9(2): 7201010. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2017.2683501 臧鸿雁, 黄慧芳, 柴宏玉. 一类2次多项式混沌系统的均匀化方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1618–1624. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180735ZANG Hongyan, HUANG Huifang, and CHAI Hongyu. Homogenization method for the quadratic polynomial chaotic system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1618–1624. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180735 ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Chongfu, JIN Wei, et al. Chaos coding-based QAM IQ-Encryption for improved security in OFDMA-PON[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2014, 26(19): 1964–1967. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2343616 MA Ruifeng, DAI Linglong, WANG Zhaocheng, et al. Secure communication in TDS-OFDM system using constellation rotation and noise insertion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2010, 56(3): 1328–1332. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2010.5606266 LI Hao, WANG Xianbin, and ZOU Yulong. Dynamic subcarrier coordinate interleaving for eavesdropping prevention in OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(6): 1059–1062. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2315648 WANG Huiming, YIN Qinye, and XIA Xianggen. Distributed beamforming for physical-layer security of two-way relay networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3532–3545. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2191543 El SHAFIE A, TOURKI K, and AL-DHAHIR N. An artificial-noise-aided hybrid TS/PS scheme for OFDM-Based SWIPT systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(3): 632–635. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2642105 DING Zhiguo, LEUNG K K, GOECKEL D L, et al. On the application of cooperative transmission to secrecy communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2012, 30(2): 359–368. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2012.120215 CHENG M, DENG L, WANG X, et al. Enhanced secure strategy for OFDM-PON system by using hyperchaotic system and fractional fourier transformation[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2014, 6(6): 7903409. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2014.2363427 SHEN Zanwei, YANG XueLin, HE Hao, et al. Secure transmission of optical DFT-S-OFDM data encrypted by digital chaos[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2016, 8(3): 7904609. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2016.2564438 HU Zhouyi and CHAN C K. A 7-D hyperchaotic system-based encryption scheme for secure Fast-OFDM-PON[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2018, 36(16): 3373–3381. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2018.2841042 ALVAREZ G and LI Shujun. Some basic cryptographic requirements for chaos-based cryptosystems[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2006, 16(8): 2129–2151. doi: 10.1142/S0218127406015970 RUKHIN A, SOTO J, NECHVATAL J, et al. A statistical test suite for Random and pseudorandom number generators for cryptographic applications[R]. Special Publication 800-22 Revision 1a, 2010. IEEE Computer Society. ANSI/IEEE Std 754-1985 IEEE standard for binary floating-point arithmetic[S]. New York: IEEE Computer Society, 1985. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
