A Novel Radiometric Signature of Time-Division Multiple Access Signals and Its Application to Specific Emitter Identification
-
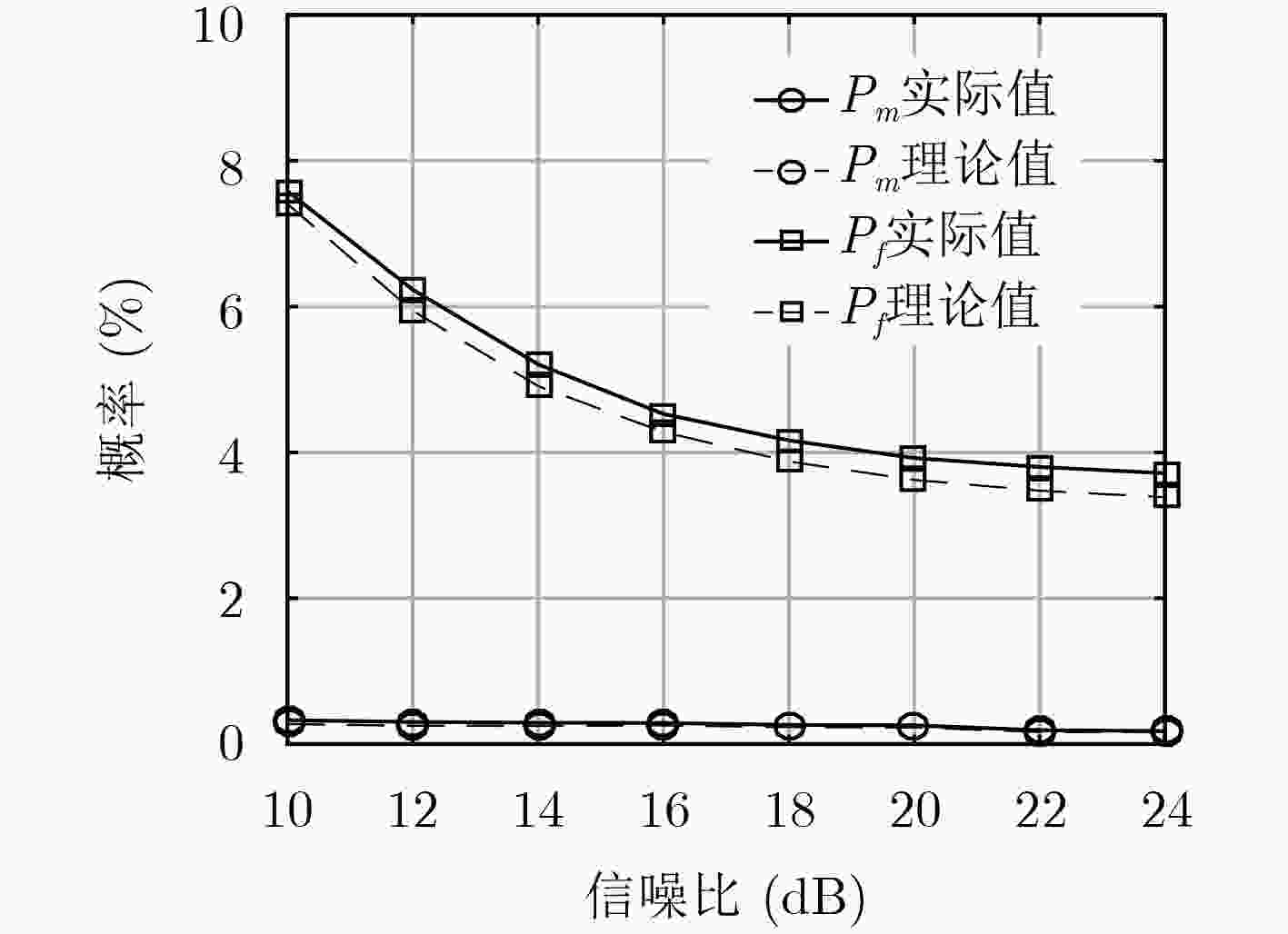
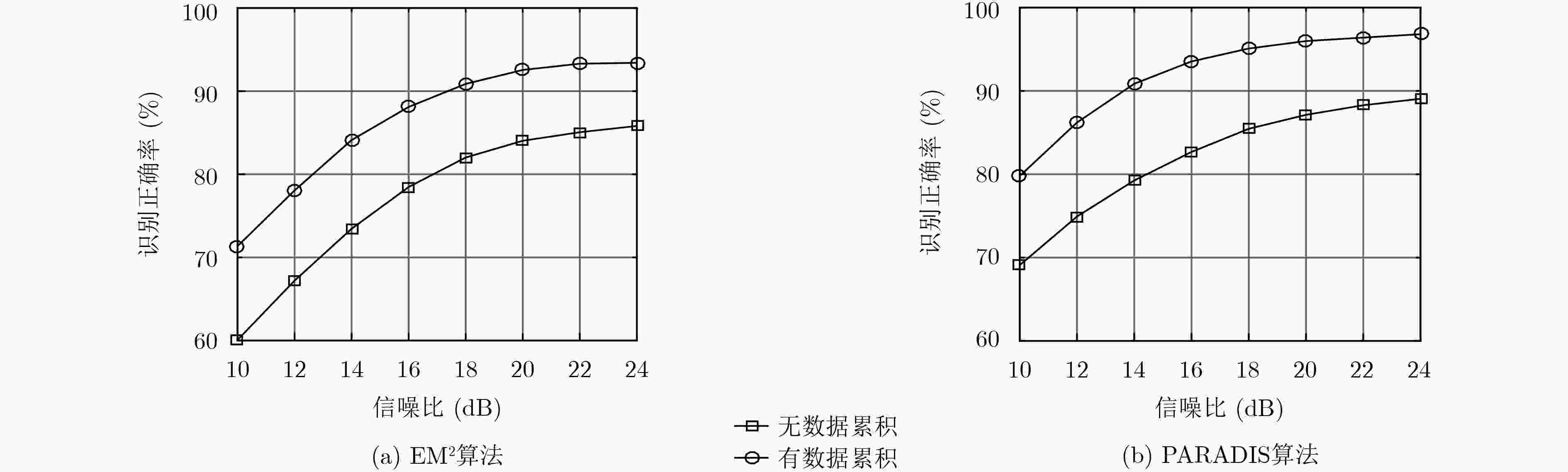
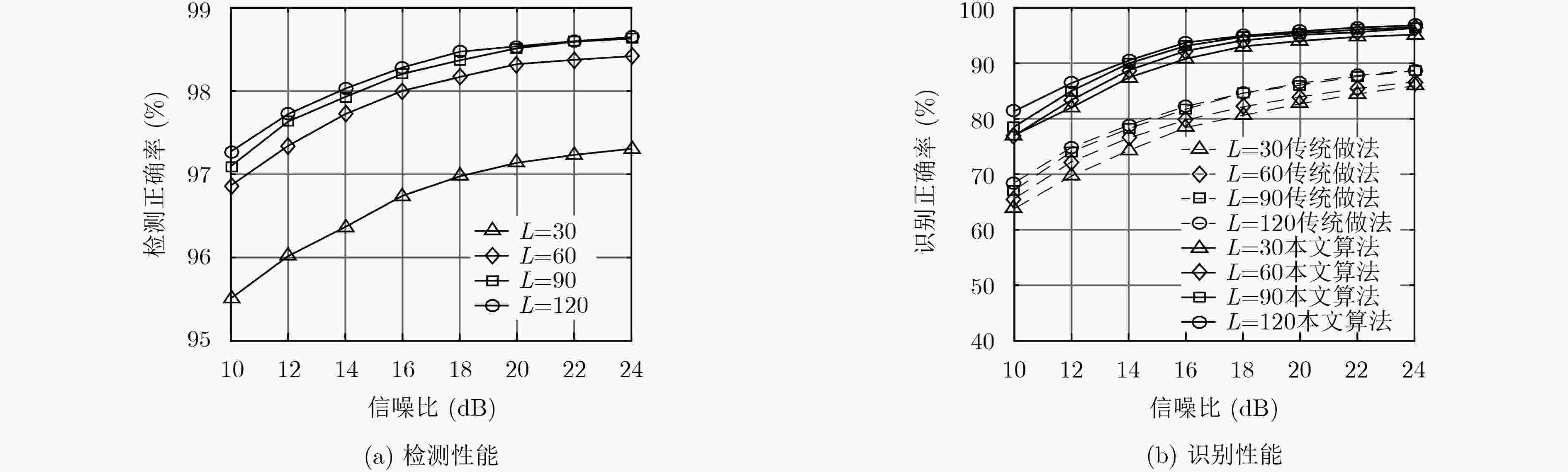
摘要: 时分多址(TDMA)信号特定辐射源识别(SEI)的性能主要受限于突发数据的长度。为此,该文提出一种新的射频特征,从载波相位上揭示了相邻时隙的用户是否相同,为相同用户的数据累积提供了依据。该文首先分析了特征的产生机理,并给出了提取方法;根据特征的统计特性,推导了自适应的判决门限,实现了相邻时隙用户身份的检测;在此基础上,设计了新的SEI处理流程,通过数据累积打破了每个时隙单独识别的传统思维。实验结果表明:该特征对噪声具备良好的鲁棒性,能够实现相邻时隙用户身份的准确检测;与传统做法相比,新的处理流程能够有效改善TDMA信号SEI的性能。Abstract: For Time-Division Multiple Access (TDMA) signals, the performance of Specific Emitter Identification (SEI) is primarily limited by burst duration. To remedy this shortcoming, a novel radiometric signature is presented, which reveals whether the users of the adjacent time slots are the same from a perspective of carrier phase, thereby providing the basis for data accumulation of the same user. First, the feature mechanism is introduced, as well as the extraction method. Thereafter, user identity detection of the adjacent slots is implemented with an adaptive threshold, which is derived from the distribution of the signature. Finally, a new SEI processing procedure is designed with data accumulation, which breaks the routine of identifying only one slot at a time. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed signature is resilient against the noise, and can accurately detect the user identity of the adjacent slots. Compared with the traditional processing procedure, the proposed one can effectively improve the SEI performance of TDMA signals.
-
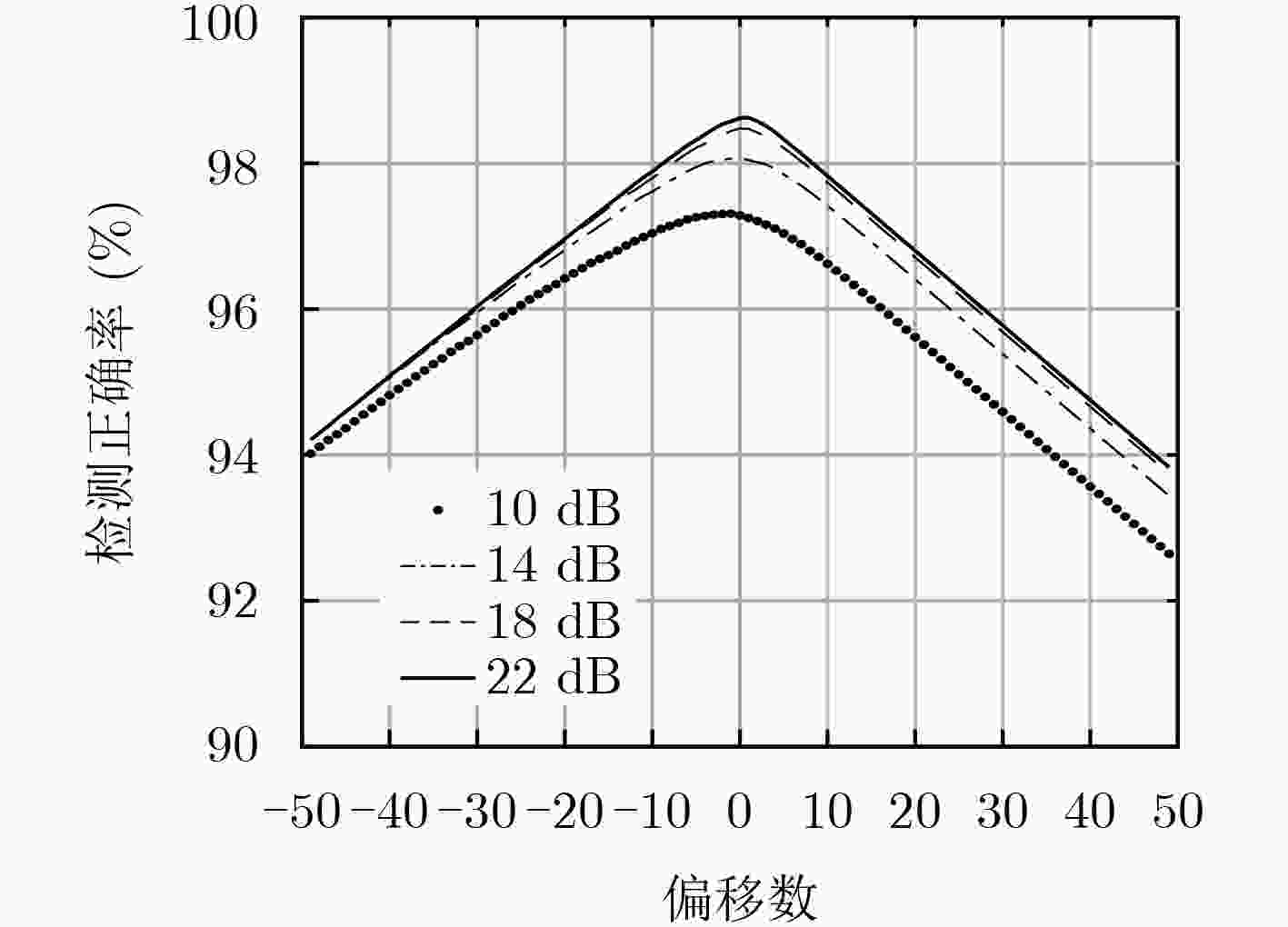
表 1 不同信噪比下的检测性能
信噪比${{{E_S}} / {{N_0}}}$(dB) 判决门限$\gamma $ 检测概率${P_{\rm{d}}}$(%) 检测正确率${P_{\rm{c}}}$(%) 10 0.0582 99.6723 97.2490 12 0.0467 99.6969 97.6732 14 0.0386 99.7077 98.0256 16 0.0336 99.7108 98.2951 18 0.0304 99.7369 98.4334 20 0.0285 99.7431 98.5184 22 0.0273 99.8092 98.6035 24 0.0266 99.8215 98.6404 -
DANEV B, ZANETTI D, and CAPKUN S. On physical-layer identification of wireless devices[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2012, 45(1): Article No.6. doi: 10.1145/2379776.2379782 SPEZIO A E. Electronic warfare systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(3): 633–644. doi: 10.1109/22.989948 MERCHANT K, REVAY S, STANTCHEV G, et al. Deep learning for RF device fingerprinting in cognitive communication networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 160–167. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2796446 DING Lida, WANG Shilian, WANG Fanggang, et al. Specific emitter identification via convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(12): 2591–2594. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2871465 KIM K, SPOONER C M, AKBAR I, et al. Specific emitter identification for cognitive radio with application to IEEE 802.11[C]. IEEE Global Telecommunications, New Orleans, USA, 2008: 1–5. HAN Jie, ZHANG Tao, REN Dongfang, et al. Communication emitter identification based on distribution of bispectrum amplitude and phase[J]. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2017, 11(8): 1104–1112. doi: 10.1049/iet-smt.2017.0024 BERTONCINI C, RUDD K, NOUSAIN B, et al. Wavelet fingerprinting of radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(12): 4843–4850. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2179276 ZHANG Jingwen, WANG Fanggang, DOBRE O A, et al. Specific emitter identification via Hilbert-Huang transform in single-hop and relaying scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(6): 1192–1205. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2520908 任东方, 张涛, 韩洁, 等. 基于ITD与纹理分析的特定辐射源识别方法[J]. 通信学报, 2017, 38(12): 160–168. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017299REN Dongfang, ZHANG Tao, HAN Jie, et al. Specific emitter identification based on ITD and texture analysis[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(12): 160–168. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017299 SATIJA U, TRIVEDI N, BISWAL G, et al. Specific emitter identification based on variational mode decomposition and spectral features in single hop and relaying scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(3): 581–591. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2855665 BRIK V, BANERJEE S, GRUTESER M, et al. Wireless device identification with radiometric signatures[C]. The 14th ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, New York, USA, 2008: 116–127. PENG Linning, HU Aiqun, ZHANG Junqing, et al. Design of a hybrid RF fingerprint extraction and device classification scheme[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(1): 349–360. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2838071 LIU Mingwei and DOHERTY J F. Specific emitter identification using nonlinear device estimation[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Sarnoff Symposium, Princeton, USA, 2008: 1–5. POLAK A C and GOECKEL D L. Wireless device identification based on RF oscillator imperfections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(12): 2492–2501. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2464778 ZHANG Yi. Wireless transmitter IQ balance and sideband suppression[EB/OL]. http://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/applicationnotes/AN-1100.pdf, 2018. 潘一苇, 彭华, 李天昀, 等. 针对特定辐射源识别的高精度符号同步方法[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 39(8): 106–112. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018132PAN Yiwei, PENG Hua, LI Tianyun, et al. High-precision symbol timing algorithm for specific emitter identification[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 39(8): 106–112. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018132 DE OLIVEIRA M C and BITMEAD R R. High-fidelity modulation parameter estimation of non-cooperative transmitters: Carrier frequency[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2011, 21(5): 632–637. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2011.03.002 CHANG C C and LIN C J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines[EB/OL]. http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm, 2018. -





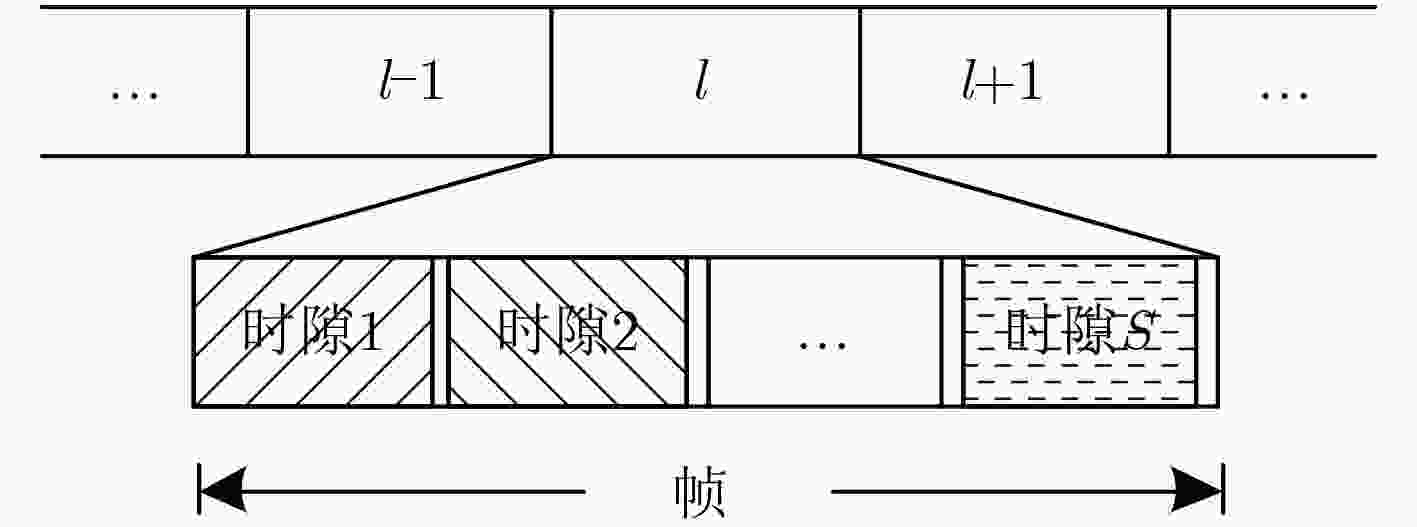
 下载:
下载:
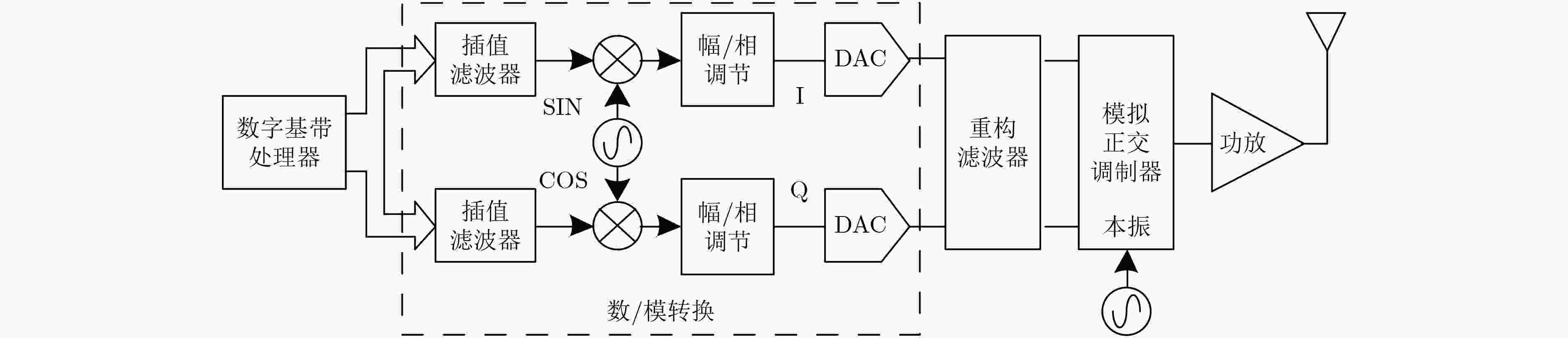
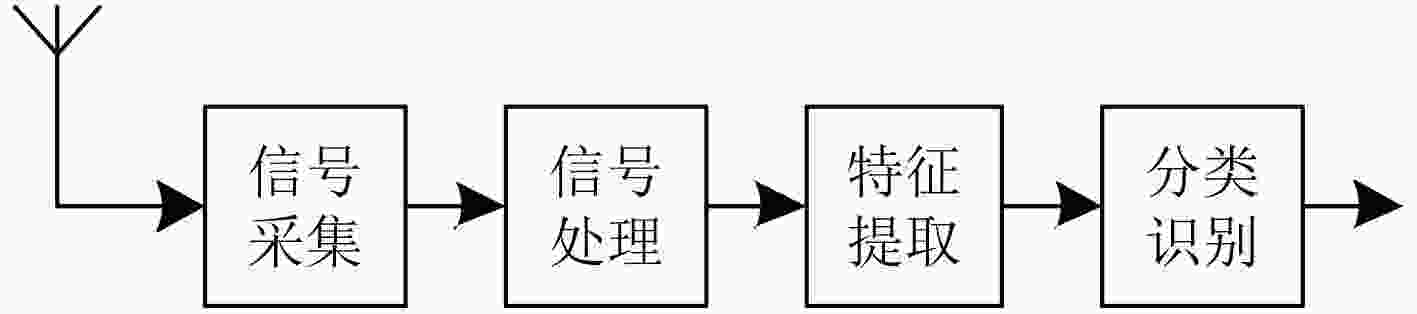
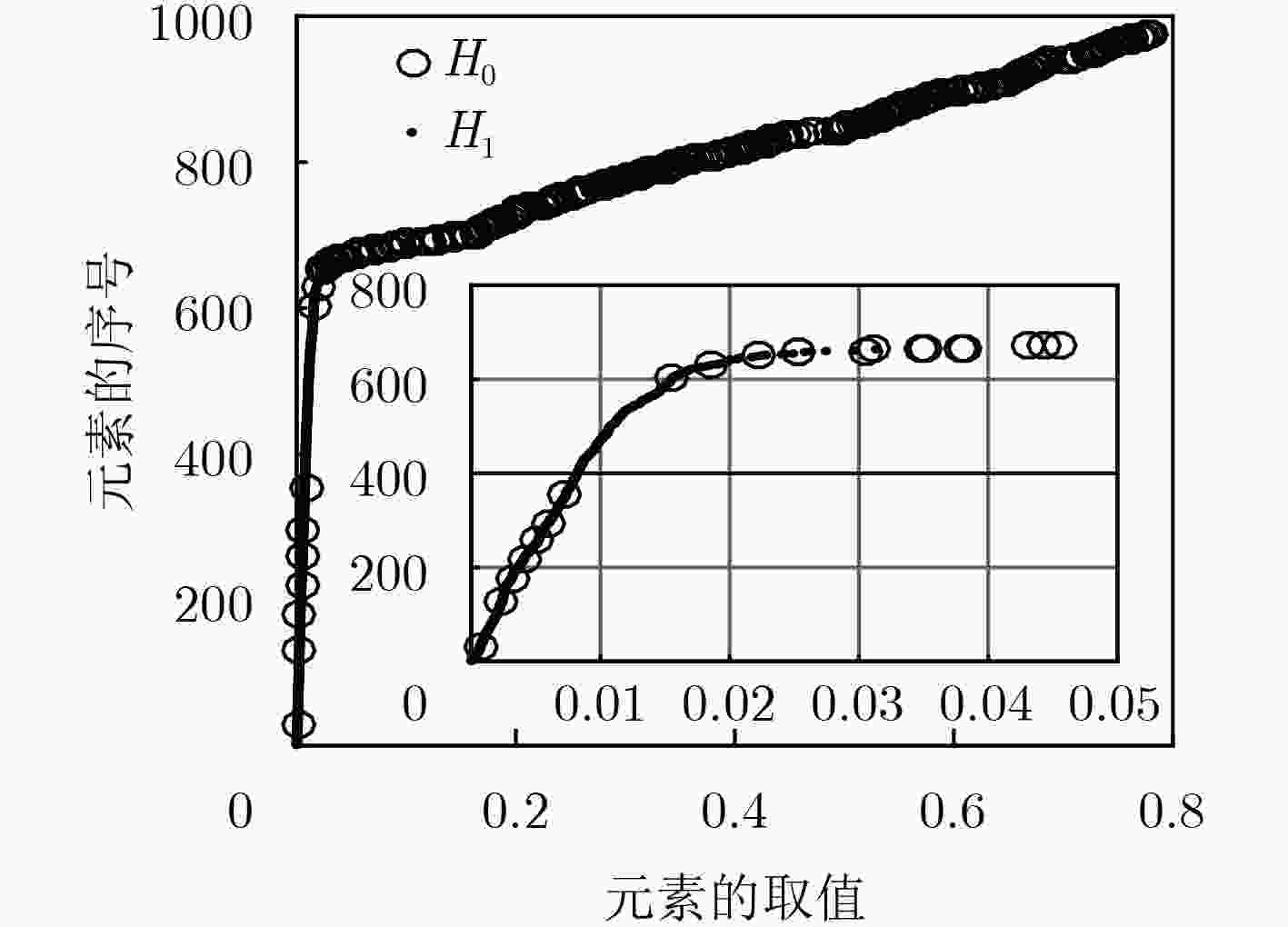



 下载:
下载:
