Matrix Metric Learning for Person Re-identification Based on Bidirectional Reference Set
-
摘要:
针对行人再识别中由于外观差异不显著导致特征描述不准确的问题,该文提出一种基于双向参考集矩阵度量学习(BRM2L)的行人再识别算法。首先通过互近邻算法获得每个摄像头下的互近邻参考集,为保证参考集的鲁棒性,联合考虑各摄像头下的互近邻参考集获得双向参考集。通过双向参考集挖掘出困难样本进行特征描述,从而得到准确的外观差异描述。最后利用该特征描述进行更有效的矩阵度量学习。在多个公开数据集上的实验结果证明了该算法比现有算法具有更好的行人再识别性能。
Abstract:To solve the problem of inaccurate feature representation caused by indistinctive appearance difference in person re-identification domain, a new Matrix Metric Learning algerithm based on Bidirectional Reference (BRM2L) set is proposed. Firstly, reciprocal-neighbor reference sets in different camera views are respectively constructed by the reciprocal-neighbor scheme. To ensure the robustness of reference sets, the reference sets in different camera views are jointly considered to generate the Bidirectional Reference Set (BRS). With hard samples which are mined by the BRS to represent feature descriptors, accurate appearance difference representations could be obtained. Finally, these representations are utilized to conduct more effective matrix metric learning. Experimental results on several public datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method.
-
表 1 两个摄像头下参考集里的样本标签的重叠率
$\sigma $ (%)行人 行人1 行人2 行人3 行人4 重叠率$\sigma $ 20 50 10 25 表 2 在3个数据集上采用不同特征的匹配精度(%)
方法 VIPeR CHUK01 PRID450S Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-1 Rank-5 ${{\rm{L}}_{\rm{2}}}$范数(GoG) 19.00 38.00 24.17 51.33 32.44 60.00 F范数(GoG) 20.17 41.83 34.50 69.83 52.22 80.22 ${\rm{BR}}{{\rm{M}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{L}}$(GoG) 38.33 69.17 45.33 70.50 54.44 80.67 ${{\rm{L}}_{\rm{2}}}$范数(FCTNN) 29.00 46.00 37.44 58.00 31.73 57.96 F范数(FCTNN) 30.00 49.83 46.56 72.11 44.40 72.84 ${\rm{BR}}{{\rm{M}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{L}}$(FCTNN) 41.33 68.17 47.42 77.44 45.51 72.96 表 3 VIPeR数据集上的结果
方法 Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 Rank-20 PCCA[16] 19.3 48.9 64.9 80.3 KISSME[18] 19.6 48.0 62.2 77.0 BiCov[17] 20.6 43.2 56.1 68.0 eSDC[19] 26.3 46.4 58.6 72.8 DeepMetric[24] 28.2 59.3 73.4 86.4 Midfilter[21] 29.1 52.5 65.9 79.9 LADF[20] 30.0 64.0 80.0 92.0 FTCNN[15]+XQDA 31.2 59.8 74.0 83.5 RD[6] 33.3 65.1 78.3 88.5 GoG[14]+XQDA 37.3 67.4 77.2 89.6 SCNCD[22] 37.8 68.5 81.2 90.4 ${\rm{D}}{{\rm{M}}^{\rm{3}}}$[4] 38.3 67.2 77.0 89.3 DeepRanking[25] 38.4 69.2 81.3 90.4 LOMO+XQDA[23] 40.0 68.5 80.5 91.0 DeepList[26] 40.5 69.1 80.1 91.2 ${\rm{BR}}{{\rm{M}}^2}{\rm{L}}$(GoG) 38.33 69.17 81.50 89.50 ${\rm{BR}}{{\rm{M}}^2}{\rm{L}}$(FTCNN) 41.33 68.17 82.00 90.33 表 4 PRID 450S数据集上的结果
表 5 CUHK01数据集上的结果
方法 Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 Rank-20 SDALF[1] 9.9 22.6 30.3 41.0 TML[12] 20.0 43.5 56.0 69.3 MidFilter[21] 34.3 55.1 65.0 74.9 ImprovedDeep[31] 47.5 71.0 80.0 – RD[6] 31.1 – 68.5 79.1 ${\rm{D}}{{\rm{M}}^{\rm{3}}}$[4] 43.7 70.1 77.4 88.7 ${\rm{BR}}{{\rm{M}}^2}{\rm{L}}$(GoG) 45.33 70.50 86.50 90.00 ${\rm{BR}}{{\rm{M}}^2}{\rm{L}}$(FTCNN) 47.42 77.44 88.33 98.33 -
FARENZENA M, BAZZANI L, PERINA A, et al. Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2360–2367. 李幼蛟, 卓力, 张菁, 等. 行人再识别技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1554–1568. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170505LI Youjiao, ZHUO Li, ZHANG Jing, et al. A survey of person re-identification[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1554–1568. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170505 ZHENG Lilei, DUFFNER S, IDRISSI K, et al. Pairwise identity verification via linear concentrative metric learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(1): 324–335. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2634011 WANG Zheng, HU Ruimin, CHEN Chen, et al. Person reidentification via discrepancy matrix and matrix metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(10): 3006–3020. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2755044 CHEN Xiaojing, AN Le, and BHANU B. Reference set based appearance model for tracking across non-overlapping cameras[C]. 2013 International Conference on Distributed Smart Cameras, Palm Springs, USA, 2013: 1–6. AN Le, KAFAI M, YANG Songfan, et al. Person reidentification with reference descriptor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 26(4): 776–787. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2416561 LIAO Shengcai and LI S Z. Efficient PSD constrained asymmetric metric learning for person re-identification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3685–3693. ZHONG Zhun, ZHENG Liang, CAO Donglin, et al. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3652–3661. SUN Yipeng, TAO Xiaoming, LI Yang, et al. Robust two-dimensional principal component analysis via alternating optimization[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 340–344. GRAY D, BRENNAN S, and TAO Hai. Evaluating appearance models for recognition, reacquisition, and tracking[C]. The 10th IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation for Tracking and Surveillance, Rio de Janeiro, 2007: 1–7. ROTH P M, HIRZER M, KÖSTINGER M, et al. Mahalanobis Distance Learning For Person Re-identification[M]. London: Springer, 2014: 247–267. LI Wei, ZHAO Rui, and WANG Xiaogang. Human reidentification with transferred metric learning[C]. The 11th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Daejeon, Korea, 2012: 31–44. WANG Xiaogang, DORETTO G, SEBASTIAN T, et al. Shape and appearance context modeling[C]. The 11th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2007: 1–8. MATSUKAWA T, OKABE T, SUZUKI E, et al. Hierarchical gaussian descriptor for person re-identification[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1363–1372. MATSUKAWA T and SUZUKI E. Person re-identification using CNN features learned from combination of attributes[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cancun, Mexico, 2016: 2428–2433. MIGNON A and JURIE F. PCCA: A new approach for distance learning from sparse pairwise constraints[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2666–2672. MA Bingpeng, SU Yu, and JURIE F. Bicov: A novel image representation for person re-identification and face verification[C]. British Machive Vision Conference, Surrey, UK, 2012: 57. 1–57. KÖSTINGER M, HIRZER M, WOHLHART P, et al. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2288–2295. ZHAO Rui, OUYANG Wanli, and WANG Xiaogang. Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3586–3593. LI Zhen, CHANG Shiyu, LIANG Feng, et al. Learning locally-adaptive decision functions for person verification[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3610–3617. ZHAO Rui, OUYANG Wanli, and WANG Xiaogang. Learning mid-level filters for person re-identification[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 144–151. YANG Yang, YANG Jimei, YAN Junjie, et al. Salient color names for person re-identification[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 536–551. LIAO Shengcai, HU Yang, ZHU Xiangyu, et al. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 2197–2206. YI Dong, LEI Zhen, LIAO Shengcai, et al. Deep metric learning for person re-identification[C]. 2014 International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 2014: 34–39. CHEN Shizhe, GUO Chaochun, and LAI Jianhuang. Deep ranking for person re-identification via joint representation learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(5): 2353–2367. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2545929 WANG Jin, WANG Zheng, GAO Changxin, et al. DeepList: Learning deep features with adaptive listwise constraint for person reidentification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(3): 513–524. doi: 10.1109/tcsvt.2016.2586851 DE CARVALHO PRATES R F and SCHWARTZ W R. CBRA: Color-based ranking aggregation for person re-identification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Quebec City, Canada, 2015: 1975–1979. SHEN Yang, LIN Weiyao, YAN Junchi, et al. Person re-identification with correspondence structure learning[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3200–3208. CHEN Yingcong, ZHENG Weishi, and LAI Jianhuang. Mirror representation for modeling view-specific transform in person re-identification[C]. The 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015: 3402–3408. YAO Wenbin, WENG Zhenyu, and ZHU Yuesheng. Diversity regularized metric learning for person re-identification[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 4264–4268. AHMED E, JONES M, and MARKS T K. An improved deep learning architecture for person re-identification[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3908–3916. -





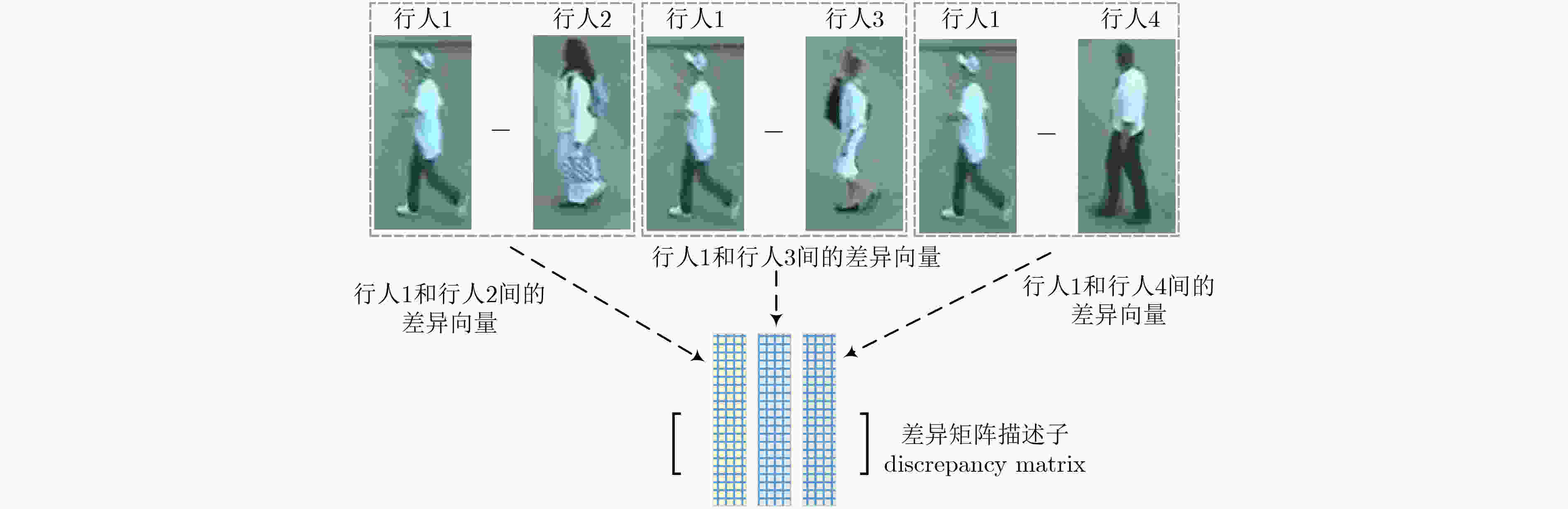
 下载:
下载:
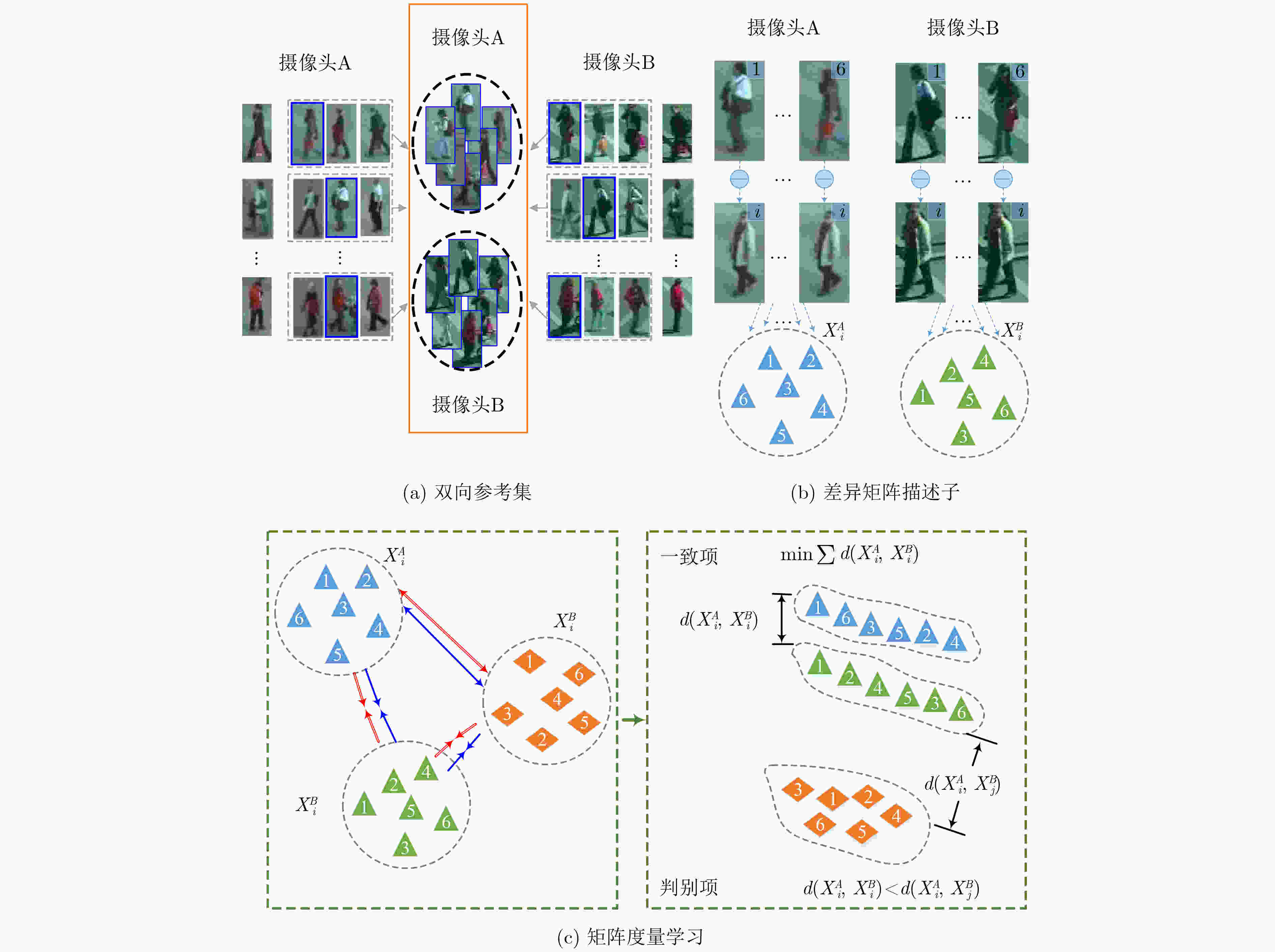
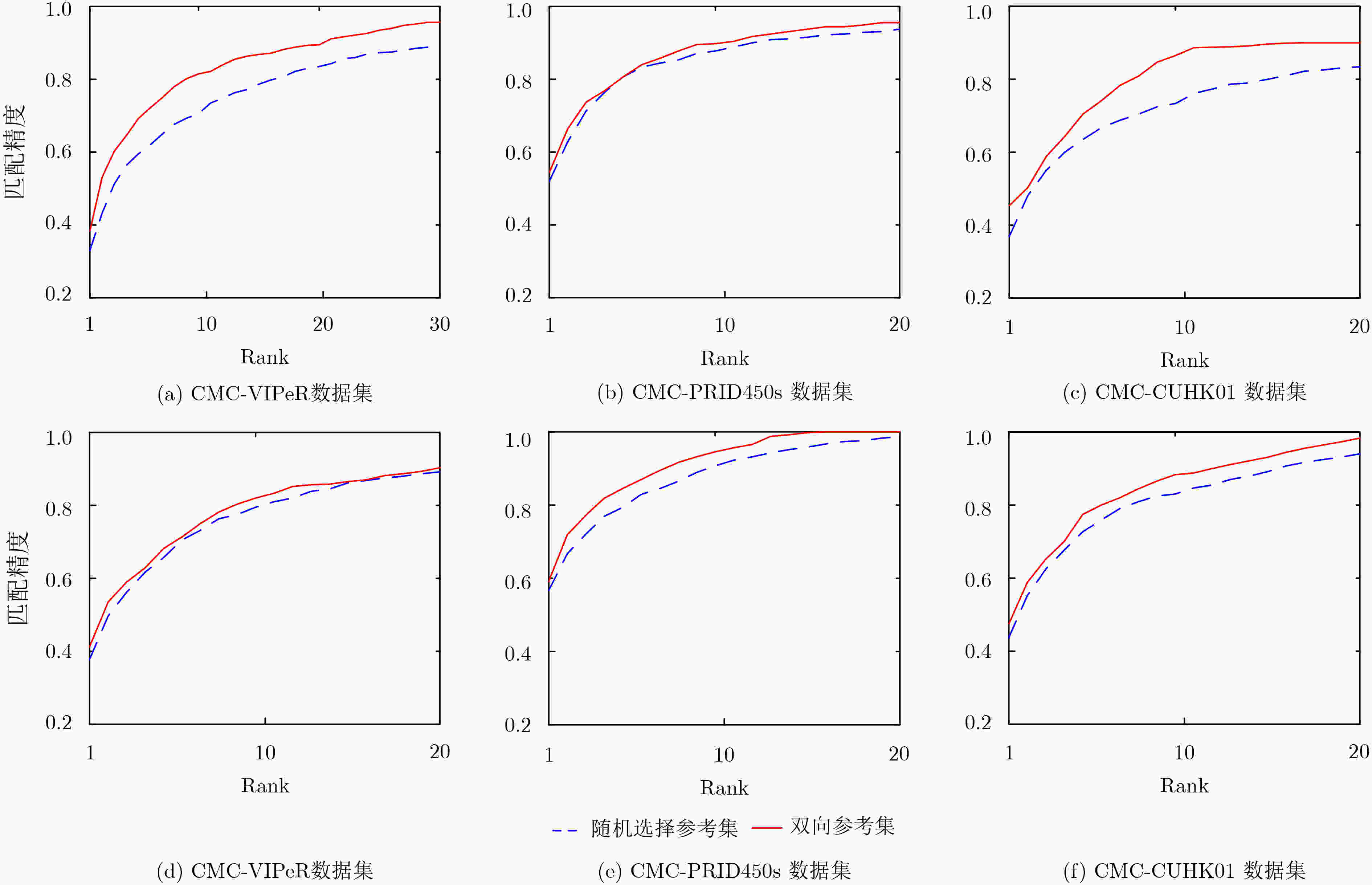



 下载:
下载:
