Image Semantic Segmentation Based on Region and Deep Residual Network
-
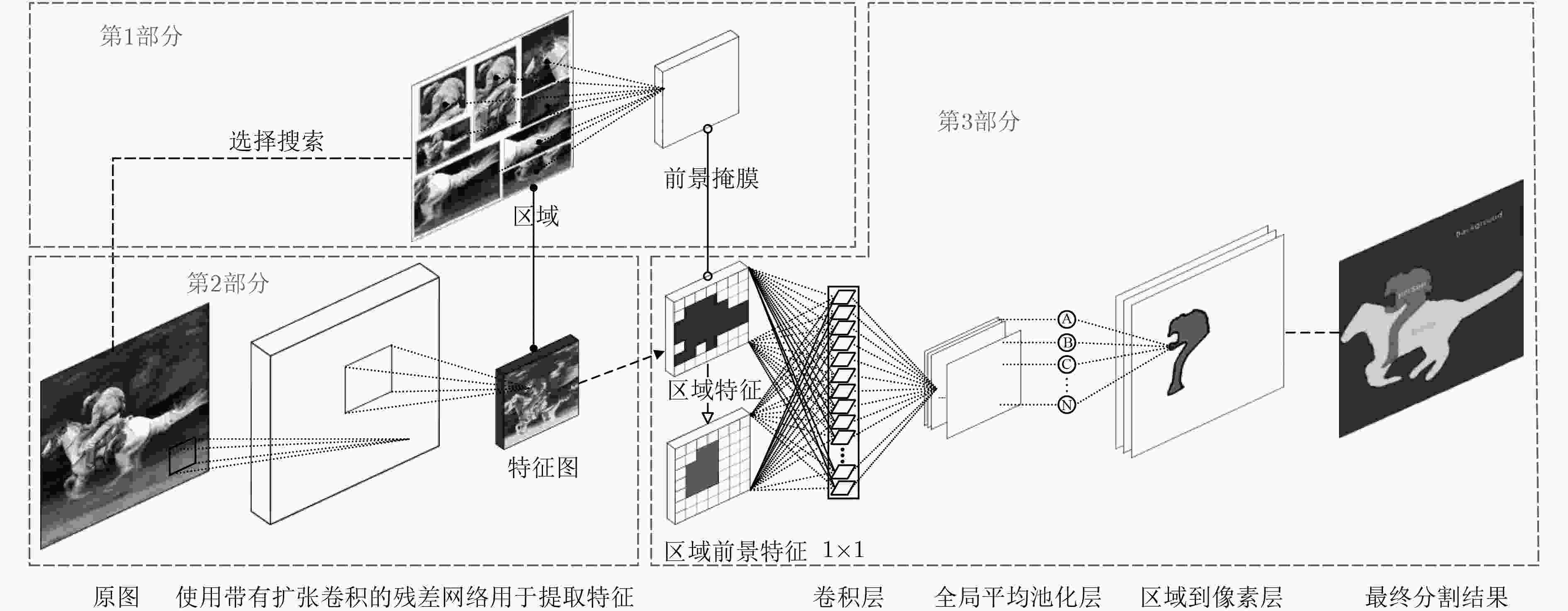
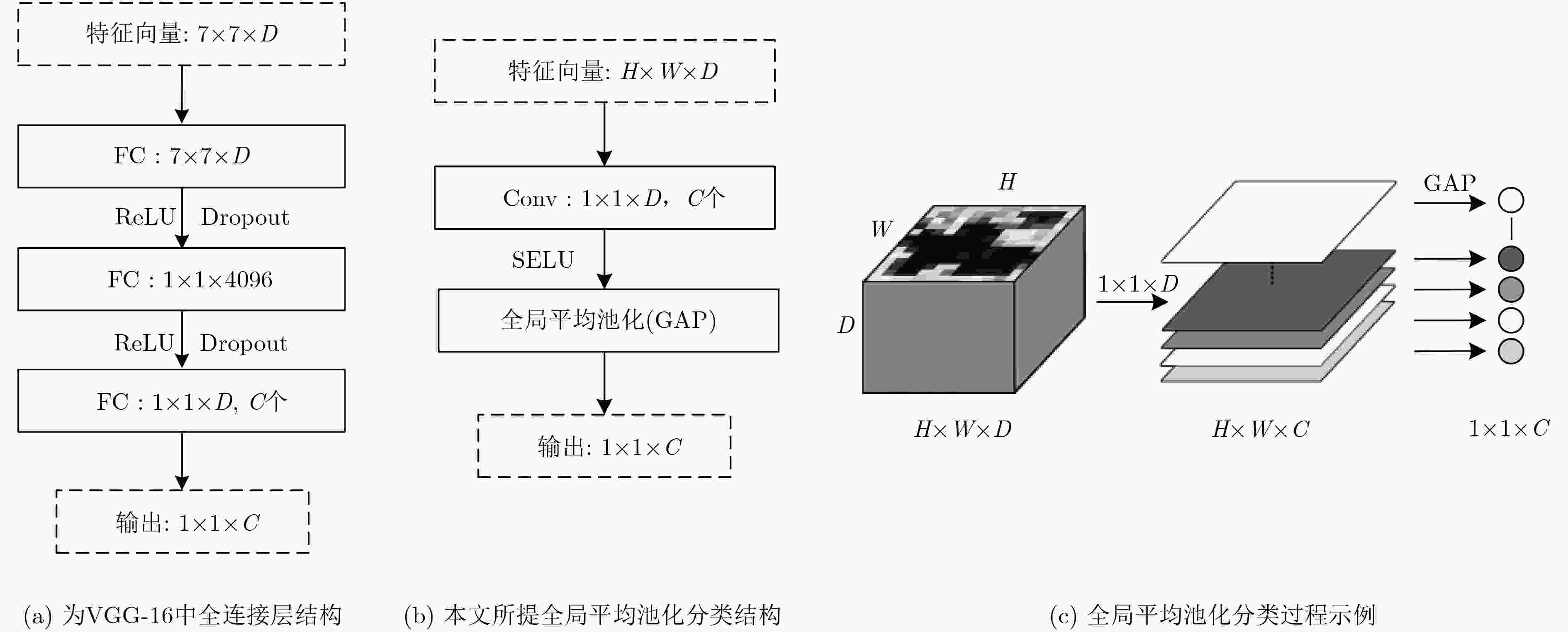
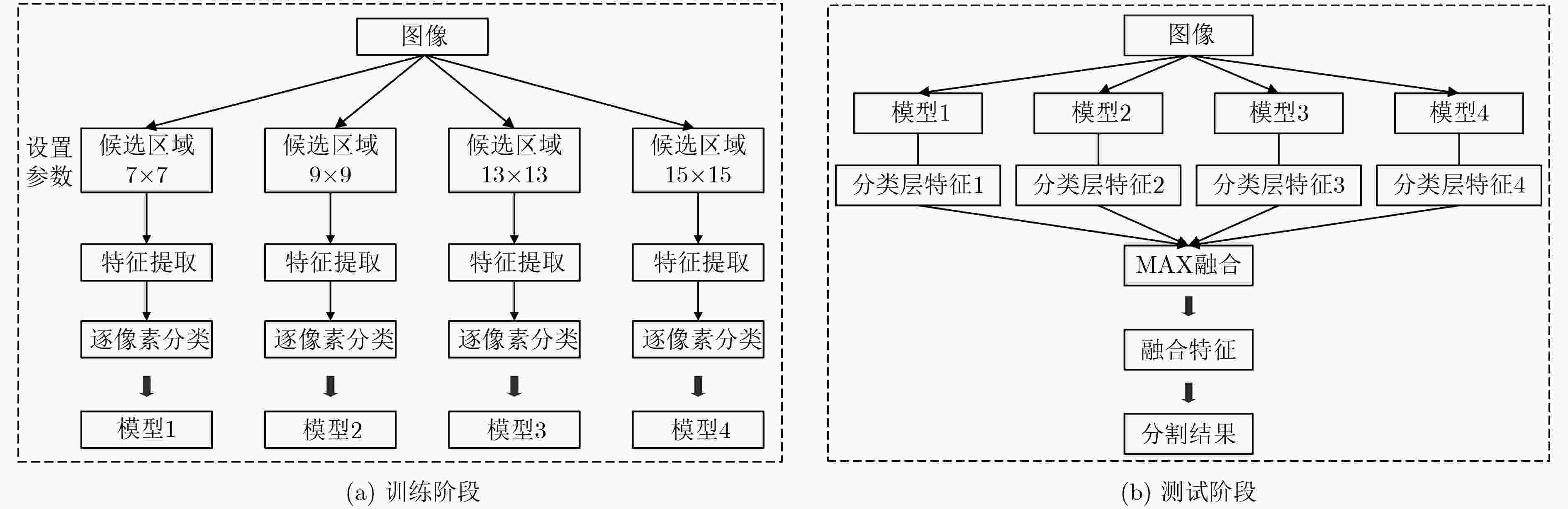
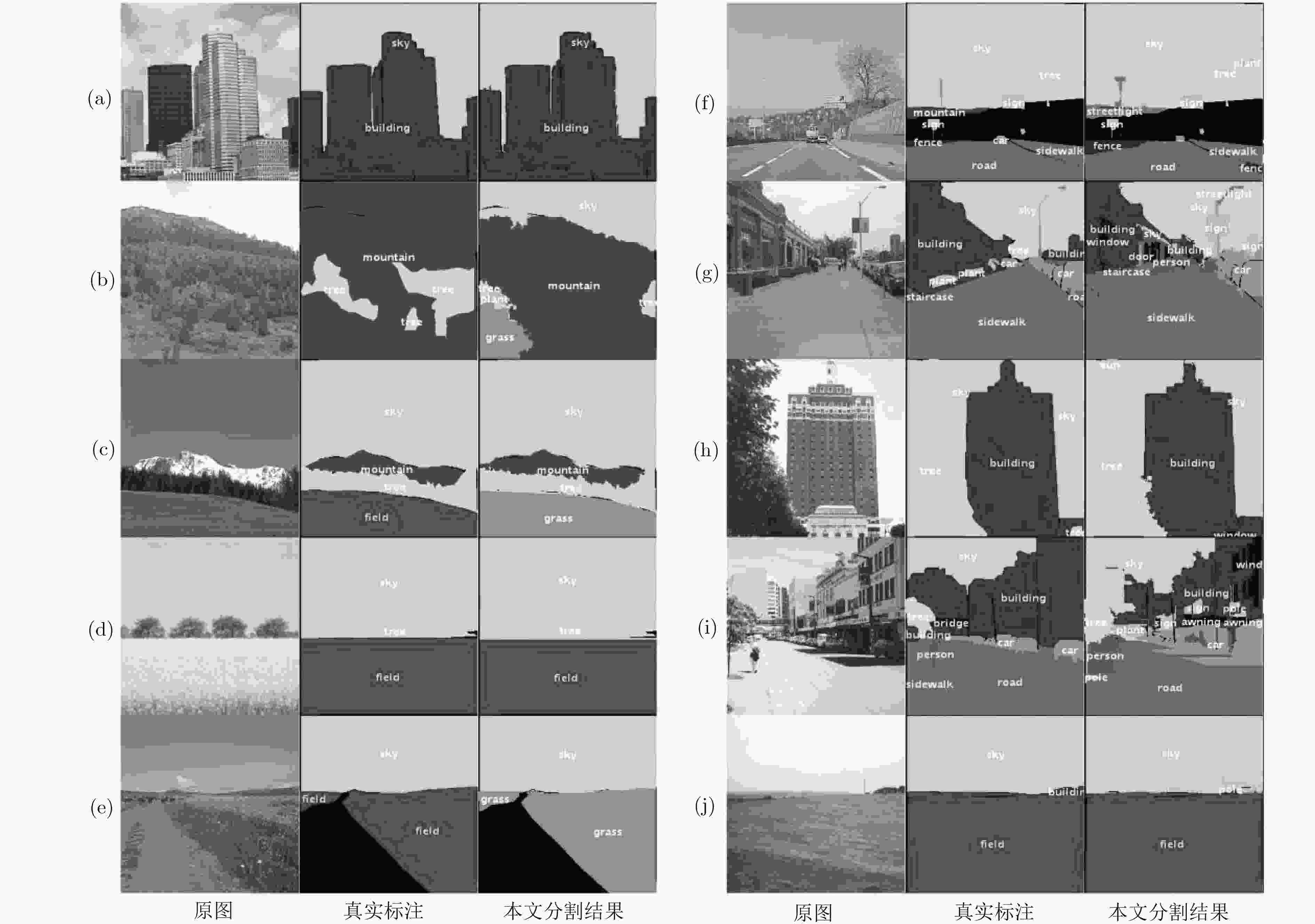
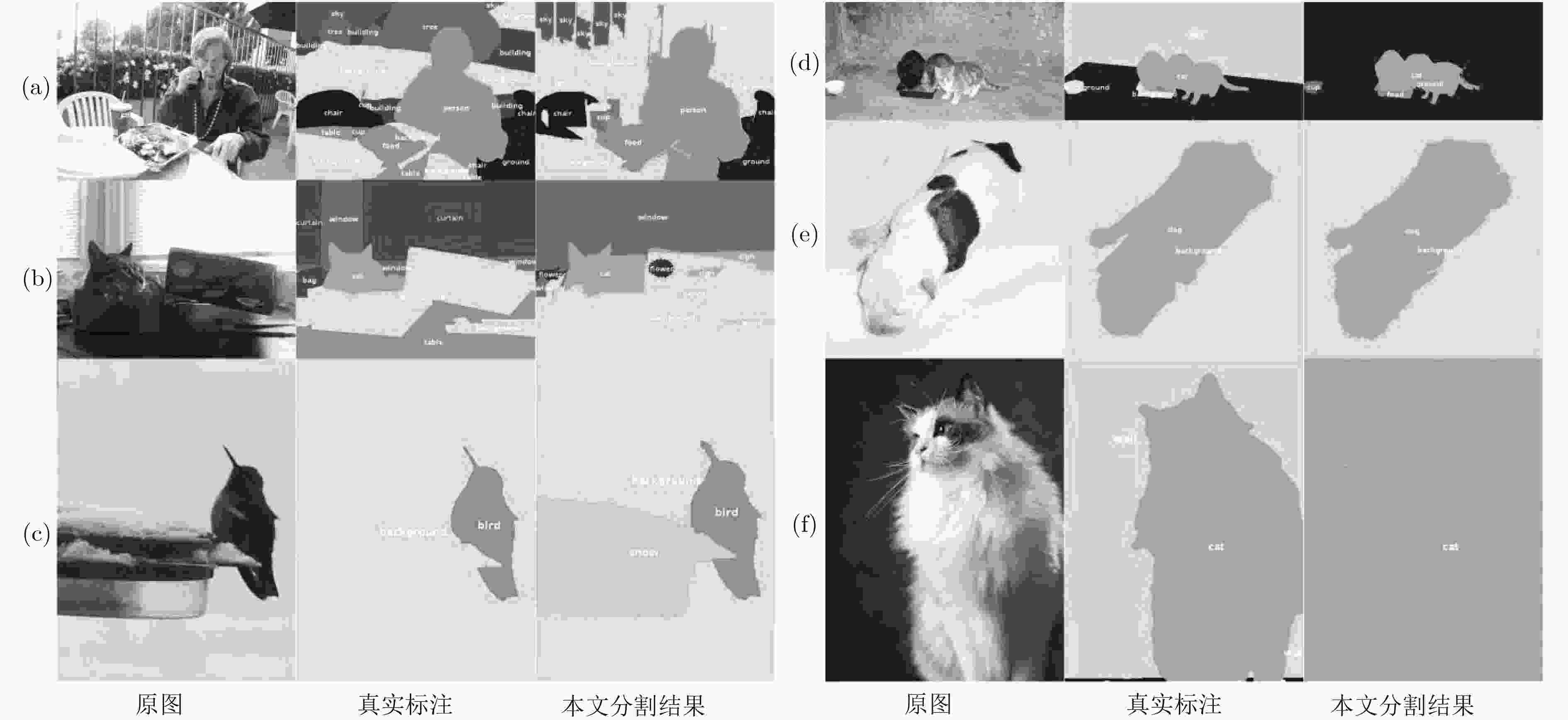
摘要: 该文提出了一种结合区域和深度残差网络的语义分割模型。基于区域的语义分割方法使用多尺度提取相互重叠的区域,可识别多种尺度的目标并得到精细的物体分割边界。基于全卷积网络的方法使用卷积神经网络(CNN)自主学习特征,可以针对逐像素分类任务进行端到端训练,但是这种方法通常会产生粗糙的分割边界。该文将两种方法的优点结合起来:首先使用区域生成网络在图像中生成候选区域,然后将图像通过带扩张卷积的深度残差网络进行特征提取得到特征图,结合候选区域以及特征图得到区域的特征,并将其映射到区域中每个像素上;最后使用全局平均池化层进行逐像素分类。该文还使用了多模型融合的方法,在相同的网络模型中设置不同的输入进行训练得到多个模型,然后在分类层进行特征融合,得到最终的分割结果。在SIFT FLOW和PASCAL Context数据集上的实验结果表明该文方法具有较高的平均准确率。Abstract: An image semantic segmentation model based on region and deep residual network is proposed. Region based methods use multi-scale to create overlapping regions, which can identify multi-scale objects and obtain fine object segmentation boundary. Fully convolutional methods learn features automatically by using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to perform end-to-end training for pixel classification tasks, but typically produce coarse segmentation boundaries. The advantages of these two methods are combined: firstly, candidate regions are generated by region generation network, and then the image is fed through the deep residual network with dilated convolution to obtain the feature map. Then the candidate regions and the feature maps are combined to get the features of the regions, and the features are mapped to each pixel in the regions. Finally, the global average pooling layer is used to classify pixels. Multiple different models are obtained by training with different sizes of candidate region inputs. When testing, the final segmentation are obtained by fusing the classification results of these models. The experimental results on SIFT FLOW and PASCAL Context datasets show that the proposed method has higher average accuracy than some state-of-the-art algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Semantic segmentation /
- Region /
- Deep residual network /
- Ensemble
-
表 1 本文算法与其他先进方法在SIFT FLOW数据集上的实验对比(%)
表 2 本文算法与其他先进方法在PASCAL Context数据集上的实验对比(%)
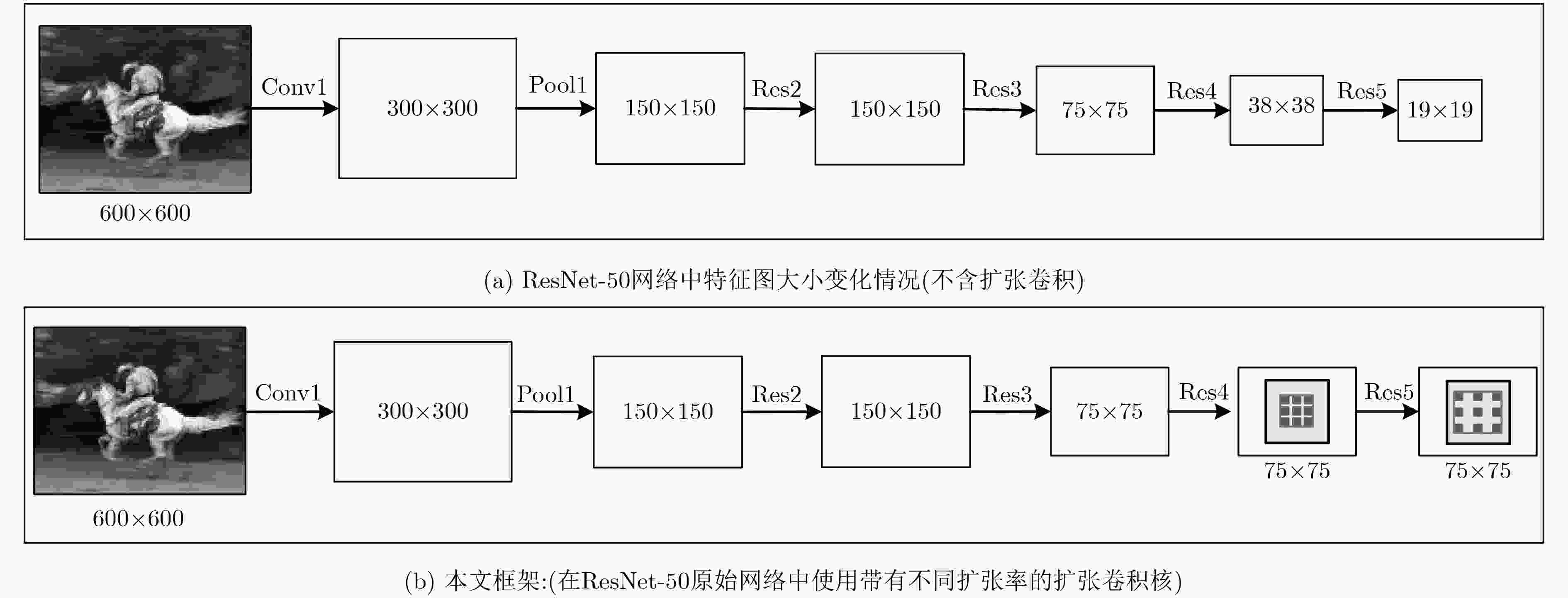
表 3 3种不同扩张卷积核使用方案的性能比较
实验 操作 最后卷积层输出大小 SIFT FLOW MA(%) 1 无操作 19×19 64.50 2 仅移除stride操作 仅Res4 (stride=1) 38×38 26.61 3 仅Res5 (stride=1) 38×38 37.47 4 Res4 (stride=1)+Res5 (stride=1) 75×75 39.76 5 +设置dilated 仅Res4(dilated=2) 38×38 64.20 6 仅Res5(dilated=4) 38×38 63.60 7 Res4(dilated=2)+Res5(dilated=4) 75×75 65.50 表 4 4个单模型以及融合模型在SIFT FLOW上的效果比较
模型序号 候选区域尺寸 SIFT FLOW MA(%) 1 7×7 64.20 2 9×9 64.80 3 13×13 65.30 4 15×15 65.20 融合模型3 4 – 65.70 融合模型3 4 – 66.00 融合模型1 2 3 4 – 66.20 -
魏云超, 赵耀. 基于DCNN的图像语义分割综述[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2016, 40(4): 82–91. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291WEI Yunchao and ZHAO Yao. A review on image semantic segmentation based on DCNN[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2016, 40(4): 82–91. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291 CARREIRA J, LI Fuxin, and SMINCHISESCU C. Object recognition by sequential figure-ground ranking[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2012, 98(3): 243–262. doi: 10.1007/s11263-011-0507-2 CARREIRA J, CASEIRO R, BATISTA J, et al. Semantic segmentation with second-order pooling[C]. Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision 2012, Berlin, Germany, 2012: 430–443. ARBELÁEZ P, HARIHARAN B, GU Chunhui, et al. Semantic segmentation using regions and parts[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 3378–3385. GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2014: 580–587. GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. SHELHAMER E, LONG J, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 39(4): 640–651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs[J]. Computer Science, 2015(4): 357–361. doi: 10.1080/17476938708814211 CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 UIJLINGS J R R, VAN DE SANDE K E A, GEVERS T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154–171. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0620-5 HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 YU Tianshu, YAN Junchi, ZHAO Jieyi, et al. Joint cuts and matching of partitions in one graph[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 705–713. HARIHARAN B, ARBELÁEZ P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Simultaneous detection and segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 297–312. DAI Jifeng, HE Kaiming, and SUN Jian. Convolutional feature masking for joint object and stuff segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3992–4000. CAESAR H, UIJLINGS J, and FERRARI V. Region-based semantic segmentation with end-to-end training[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 381–397. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. YU F and KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07122, 2015. LIN Min, CHEN Qiang, and YAN Shuicheng. Network in network[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.4400, 2014. LIU Ce, YUEN J, and TORRALBA A. Nonparametric scene parsing via label transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2368–2382. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.131 MOTTAGHI R, CHEN Xianjie, LIU Xiaobai, et al. The role of context for object detection and semantic segmentation in the wild[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 891–898. YANG Jimei, PRICE B, COHEN S, et al. Context driven scene parsing with attention to rare classes[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 3294–3301. EIGEN D and FERGUS R. Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 2650–2658. DAI Jifeng, HE Kaiming, and SUN Jian. Boxsup: exploiting bounding boxes to supervise convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1635–1643. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
