Quality of Service-aware Elastic Flow Aggregation Based on Enhanced Rough K-Means
-
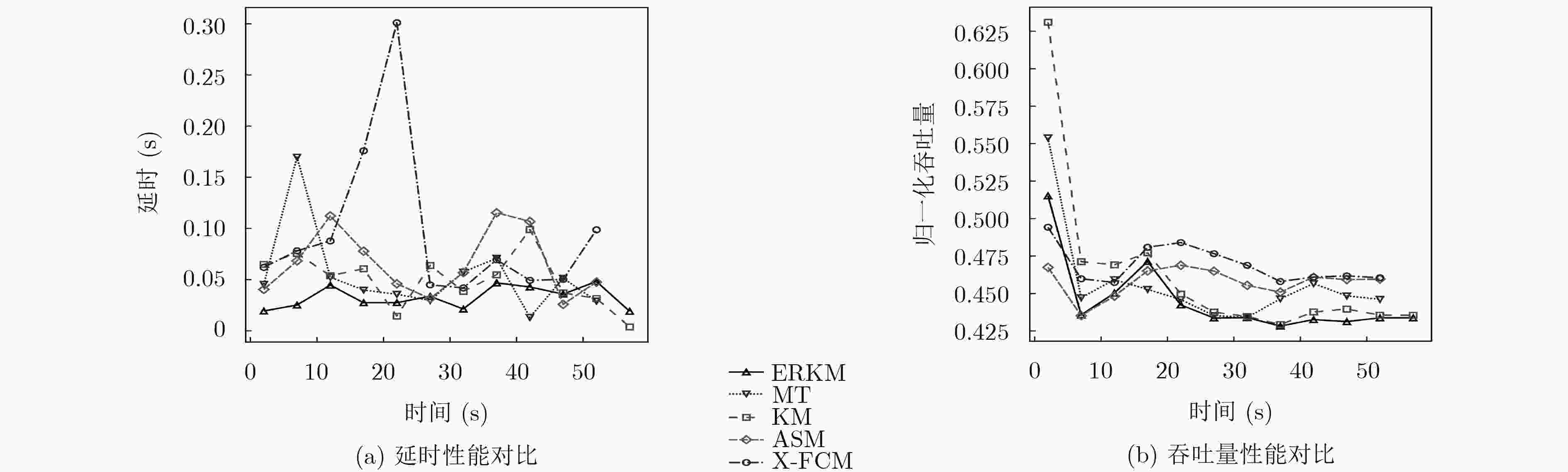
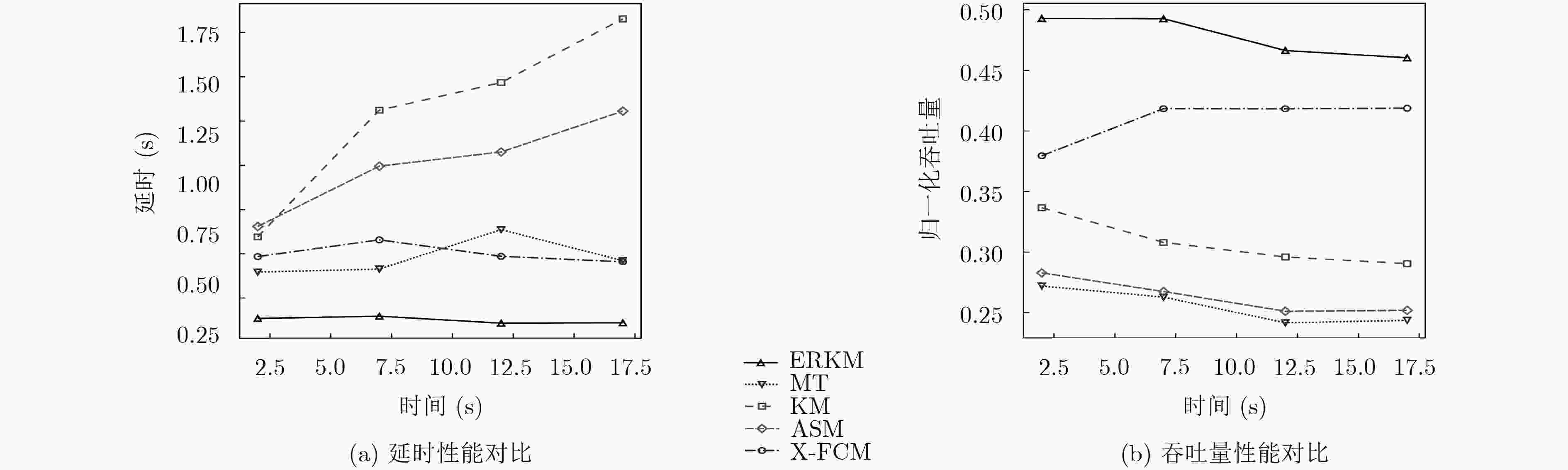
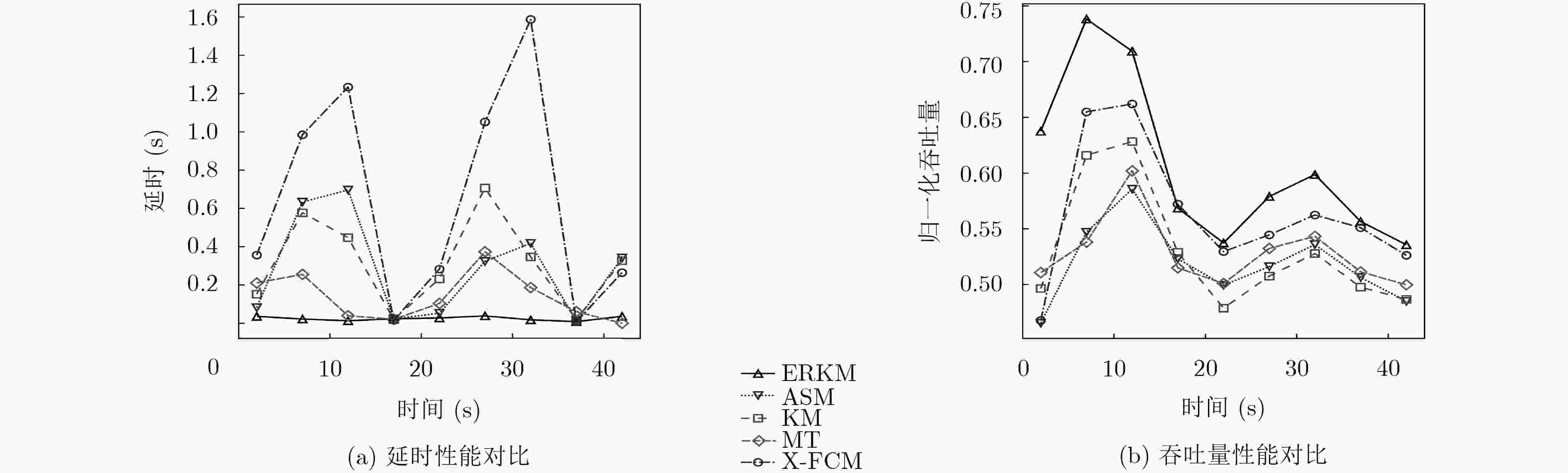
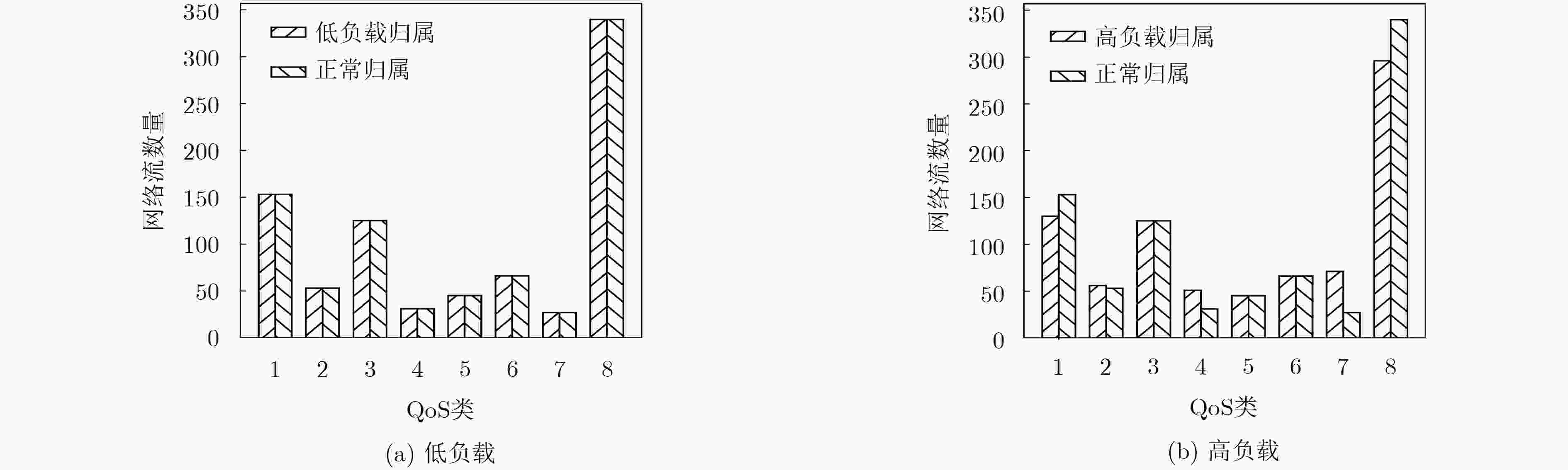
摘要: 面对多变的网络环境,现有的网络服务质量(QoS)映射中流聚集方法缺乏灵活性。针对现有聚集方法的缺陷,该文提出一种动态聚集方法。使用增强粗糙K均值算法(ERKM),按照网络流的QoS属性将网络流进行合理聚集,并且在网络处于高负载状况时,通过隶属度弹性聚集网络流,从而适应网络的变化,使得网络流聚集具有灵活性。最后进行了网络流聚集实验和调度实验。实验表明,相比于现有的方法,该方法能够更加弹性地应对不同网络状态,并且更好地保障网络流的QoS指标。此外,还进一步验证了该文方法在不同网络环境下的QoS类聚集的一致性。
-
关键词:
- 网络流聚集 /
- 增强粗糙K-Means /
- 服务质量映射 /
- 隶属度
Abstract: Facing changeable network environment, current Quality of Service (QoS)-aware flow aggregation scheme is lack of flexibility. A dynamic flow aggregation method to overcome present problems is proposed. An Enhanced Rough K-Means (ERKM) algorithm is used to aggregate network flows properly. Importantly, it is able to adjust degree of membership to face ever-changing internet environment to make algorithm more flexible. Internet scheduler experiment is carried out and a comparison is made with existing methods. Experimental results suggest that proposed method has advantages not only on flexibility of aggregation, but also on assurance of QoS of Internet flows. In addition, the consistency of QoS allocation under different network environment is investigated. -
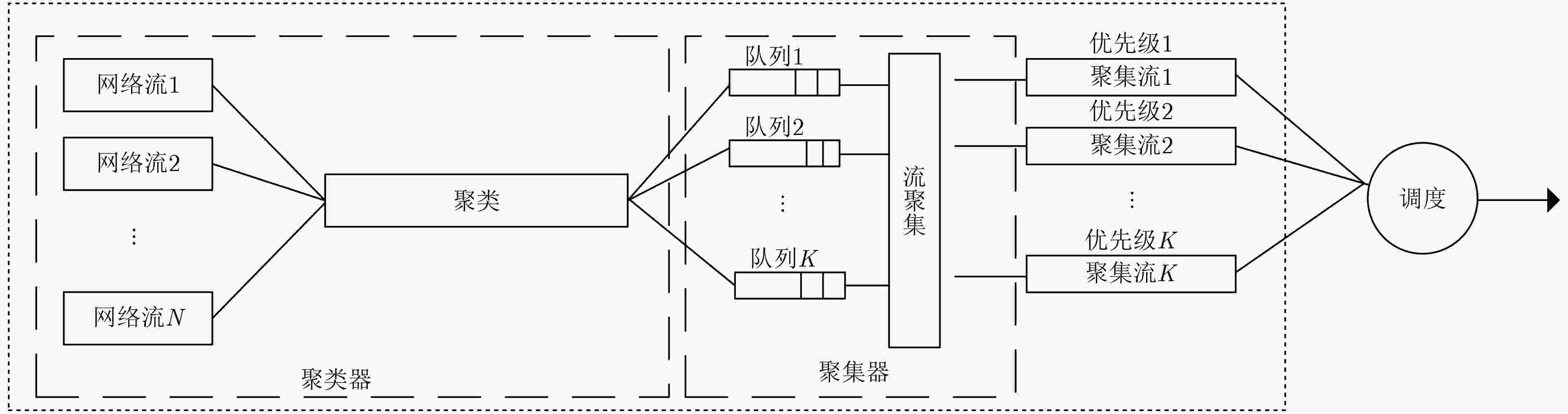
表 1 聚集方法
算法1:聚集方法 (1) 接受进入的网络流,使用该流的第1个网络包p代表网络流
f;(2) 如果p是进入聚集器的第1条网络流,则将aggr_id写入p,
否则绕过;(3) 从p中提取信息$(x,h,{s_{{\rm{up}},}})$; (4) 判断队列h是否溢出: (5) 如果溢出,则执行(6),否则将流f推进到队列h中,执行
(7);(6) 以隶属度为优先原则,根据${s_{{\rm{up}}}}$将p推进到无溢出队列中,若
${s_{{\rm{up}}}}$中候选队列均存在溢出,则将p丢弃;(7) 聚集流通过调度器进行调度。 表 2 数据集描述
类型 大小(GB) 网络流条数 在线非直播视频(标清,高清) 59.46 240 HTTP下载视频 67.56 60 互动类视频音频通信 19.12 120 P2P视频共享 57.85 60 在线直播视频 61.91 120 -
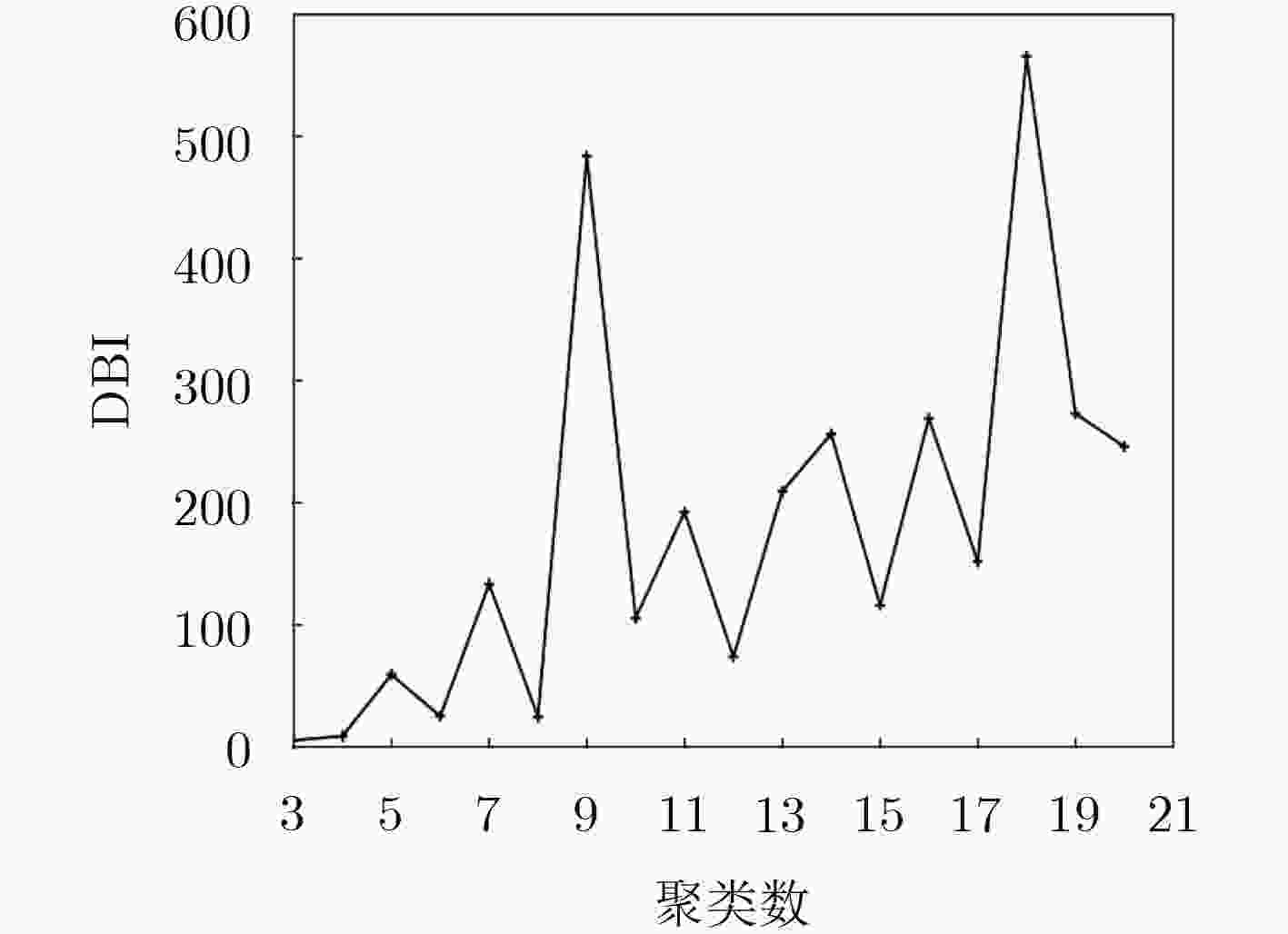
Cisco. Cisco: Complete-white-paper-c11-481360[EB/OL]. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/ip-ngn-ip-nexFt-generation-network/white_paper_c11-481360.html, 2018. KAMIYAMA N, TAKAHASHI Y, ISHIBASHI K, et al. Flow aggregation for traffic engineering[C]. 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014: 1936–1941. DOMŻAŁ J, JURKIEWICZ P, GAWLOWICZ P, et al. Flow aggregation mechanism for flow-aware multi-topology adaptive routing[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(12): 2582–2585. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2748101 ESHETE A and JIANG Yuming. Flow aggregation using dynamic packet state[C]. The 16th Meeting of the European Network of Universities and Companies in Information and Communication Engineering, Trondheim, Norway, 2010: 263–265. WANG Zaijian, DONG Yuning, and WANG Xinheng. A dynamic service class mapping scheme for different QoS domains using flow aggregation[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2015, 9(4): 1299–1310. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2014.2351825 STANKIEWICZ R, CHOLDA P, and JAJSZCZYK A. QoX: What is it really?[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2011, 49(4): 148–158. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2011.5741159 AL-SHAIKHLI A, ESMAILPOUR A, and NASSER N. Quality of service interworking over heterogeneous networks in 5G[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016: 1–6. 王再见, 董育宁, 张晖, 等. 一种异构网络多媒体业务QoS类弹性映射方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(3): 709–714. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00890WANG Zaijian, DONG Yuning, ZHANG Hui, et al. An elastic QoS class mapping method for multimedia traffic in heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(3): 709–714. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00890 HAMZA N B, REKHIS S, and BOUDRIGA N. Cooperative architecture for QoS management in wireless 4G networks[C]. 2011 IEEE Symposium on Computers & Informatics, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2011: 559–564. JAIN A and TOKEKAR S. QoS mapping approach for UMTS-WLAN integrated network[C]. 2016 Second International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology, Ghaziabad, India, 2016: 237–241. RYU M, KIM Y, and PARK H. Systematic QoS class mapping framework over multiple heterogeneous networks[C]. The 8th International Conference on Next Generation Wired/Wireless Networking, Petersburg, Russia, 2008: 212–221. ITO Y. Calculation of necessary QoS for user satisfaction with a QoS mapping matrix[C]. The 10th IEEE/IPSJ International Symposium on Applications and the Internet, Seoul, South Korea, 2010: 233–236. doi: 10.1109/SAINT.2010.95. SANTOS E C. Autonomous QoS-based mechanism for resource allocation in LTE-Advanced Pro networks[C]. 2018 IEEE Colombian Conference on Communications and Computing, Medellin, Colombia, 2018: 1–6. 张腾飞, 陈龙, 李云. 基于簇内不平衡度量的粗糙K-means聚类算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2013, 28(10): 1479–1484. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2013.10.017ZHANG Tengfei, CHEN Long, and LI Yun. Rough K-means clustering based on unbalanced degree of cluster[J]. Control and Decision, 2013, 28(10): 1479–1484. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2013.10.017 MARDANI A, JUSOH A, and ZAVADSKAS E K. Fuzzy multiple criteria decision-making techniques and applications - two decades review from 1994 to 2014[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(8): 4126–4148. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.01.003 TANG Jiliang, ALELYANI S, and LIU Huan. Feature Selection for Classification: A Review[M]. AGGARWAL C C. Data Classification: Algorithms and Applications. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2014: 1–29. FAHAD A, ALSHATRI N, TARI Z, et al. A survey of clustering algorithms for big data: Taxonomy and empirical analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2014, 2(3): 267–279. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2014.2330519 DAVIES D L and BOULDIN D W. A cluster separation measure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1979, PAMI-1(2): 224–227. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1979.4766909 HOTTMAR V and ADAMEC B. Analytical model of a weighted round robin service system[J]. Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2012, 2012: 374961. doi: 10.1155/2012/374961 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
