Energy Efficiency and System Capacity Based Multi-Objective Radio Resource Management in M2M Communications
-
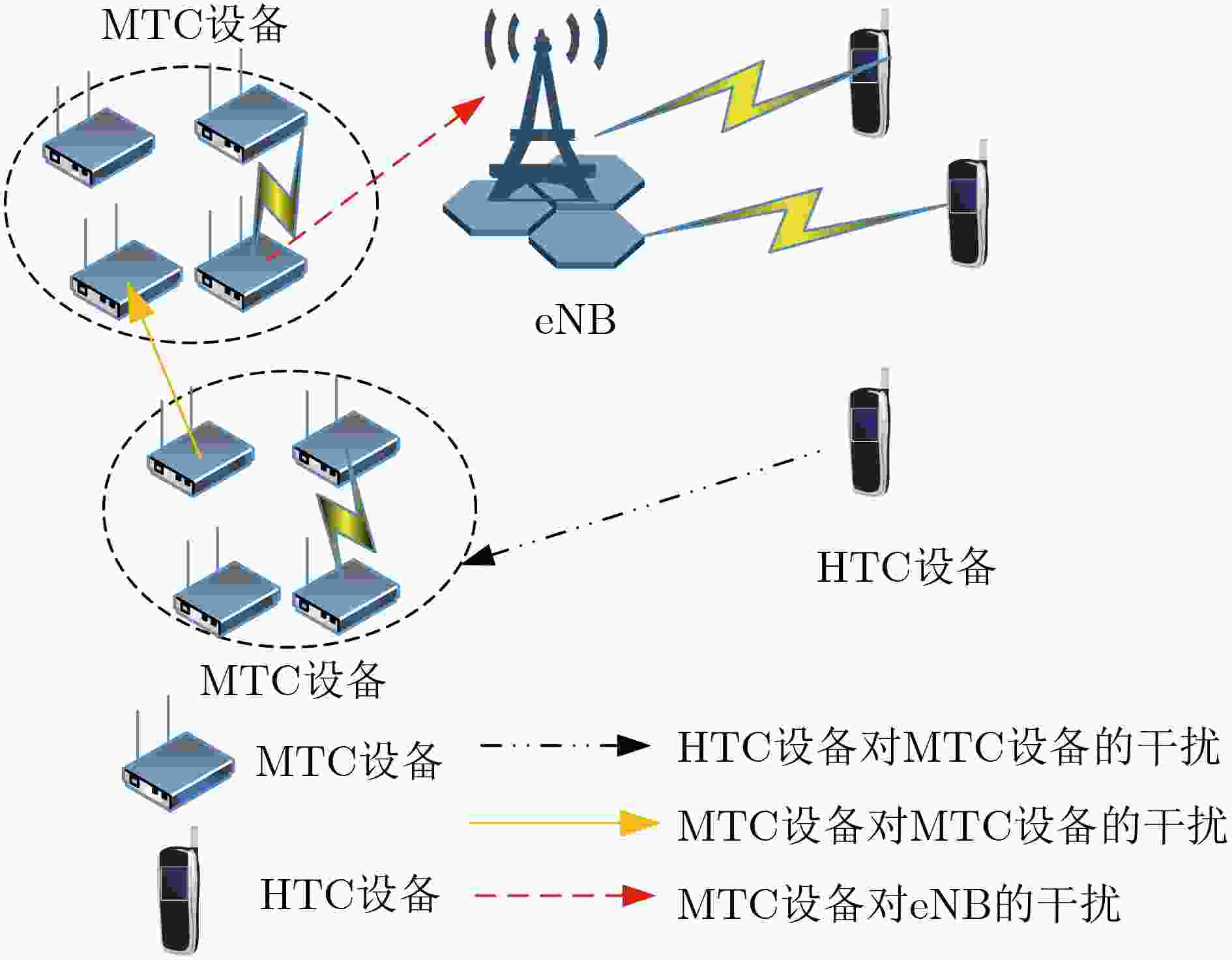
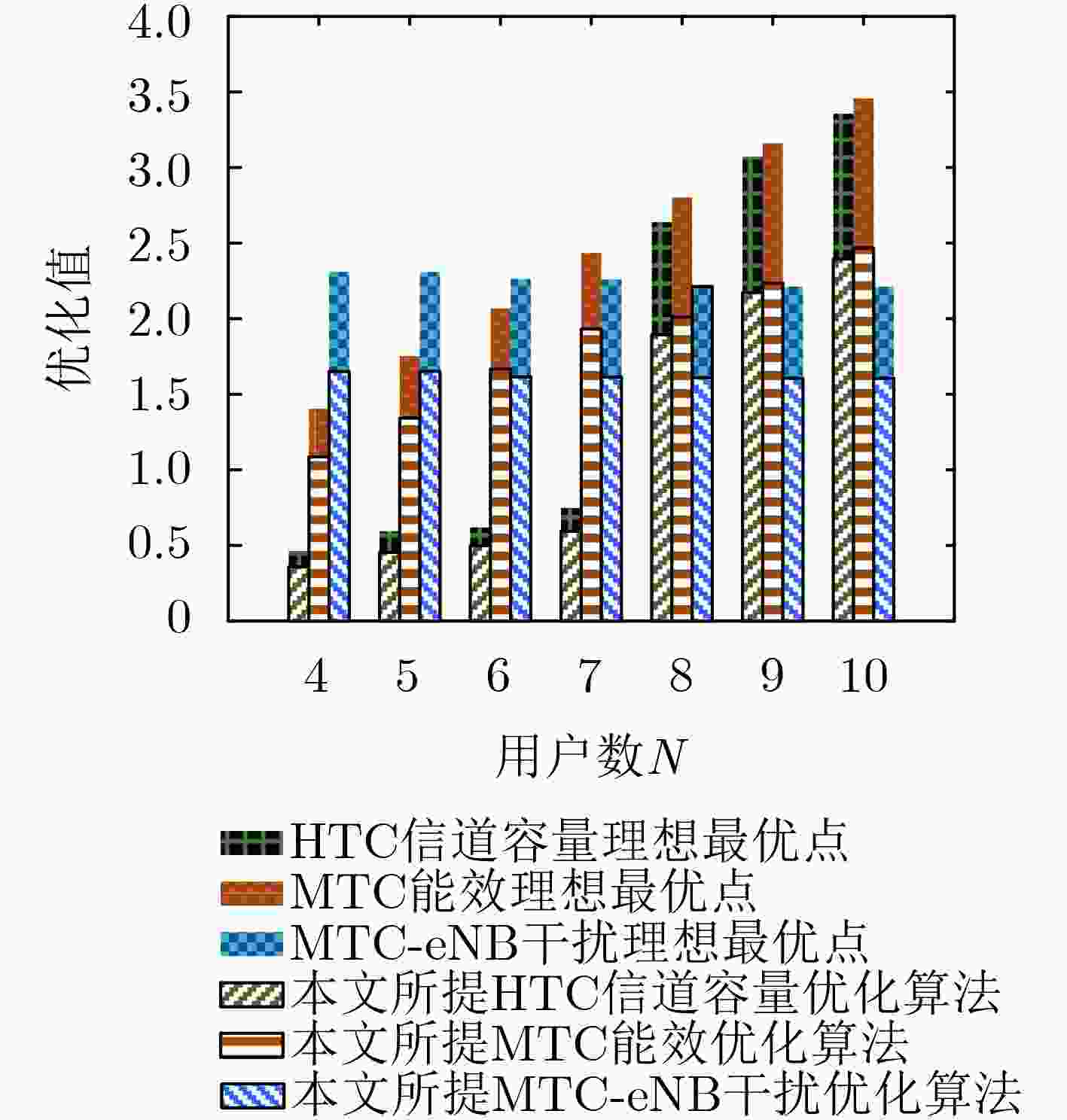
摘要: 机器对机器(M2M)通信和设备到设备(D2D)通信都是5G中的关键技术。而M2M通信特别需要考虑提高设备的能量效率(EE)以延长设备的生存周期。该文将M2M技术与D2D技术相结合,考虑M2M设备使用D2D技术进行通信,同时M2M设备复用蜂窝网络中的人对人(H2H)通信的频谱资源。为了同时保证两种系统的服务质量(QoS)需求,建立了最大化M2M的能量效率,最大化H2H系统容量和,以及最小化M2M系统对H2H系统干扰的多目标优化问题(MOOP)。为了解决该问题,采用惩罚函数的方法将二进制变量松弛约束,进而采用凹凸过程(CCCP)方法将非凸的单目标优化问题转化为凸优化问题,并最终通过加权切比雪夫算法得到原多目标优化问题的Pareto最优解。通过与传统的加权和算法进行比较,仿真结果证明了该算法的有效性。Abstract: Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and Device-to-Device (D2D) communications are both key technologies in the Fifth Generation (5G) mobile communication systems. In M2M communications, the Energy Efficiency (EE) especially needs to be improved to extend the life cycle of the M2M equipment. In this paper, the M2M and D2D technologies are combined and the D2D technology is used to realize M2M transmission. At the same time, M2M users are allowed to reuse spectrum resources with Human-to-Human (H2H) devices in the cellular networks. To guarantee the Quality of Service (QoS) of these two systems simultaneously, a Multi-Objective Optimization Problem (MOOP) is then formulated to maximize the sum throughput of H2H systems, and the sum EE of M2M systems and to minimize the interference from M2M communications to H2H networks. To solve this MOOP, the penalty function method is firstly adopted to relax the original binary variables, and then the ConCave-Convex Procedure (CCCP) method is used to convert the non-convex single-objective problems into convex problems. Finally, the weighted Tchebyshev algorithm is utilized to obtain the Pareto solution of the original MOOP. By comparing with the traditional weighted sum method, the effectiveness of the proposed method is proved by simulation results.
-
表 1 仿真参数
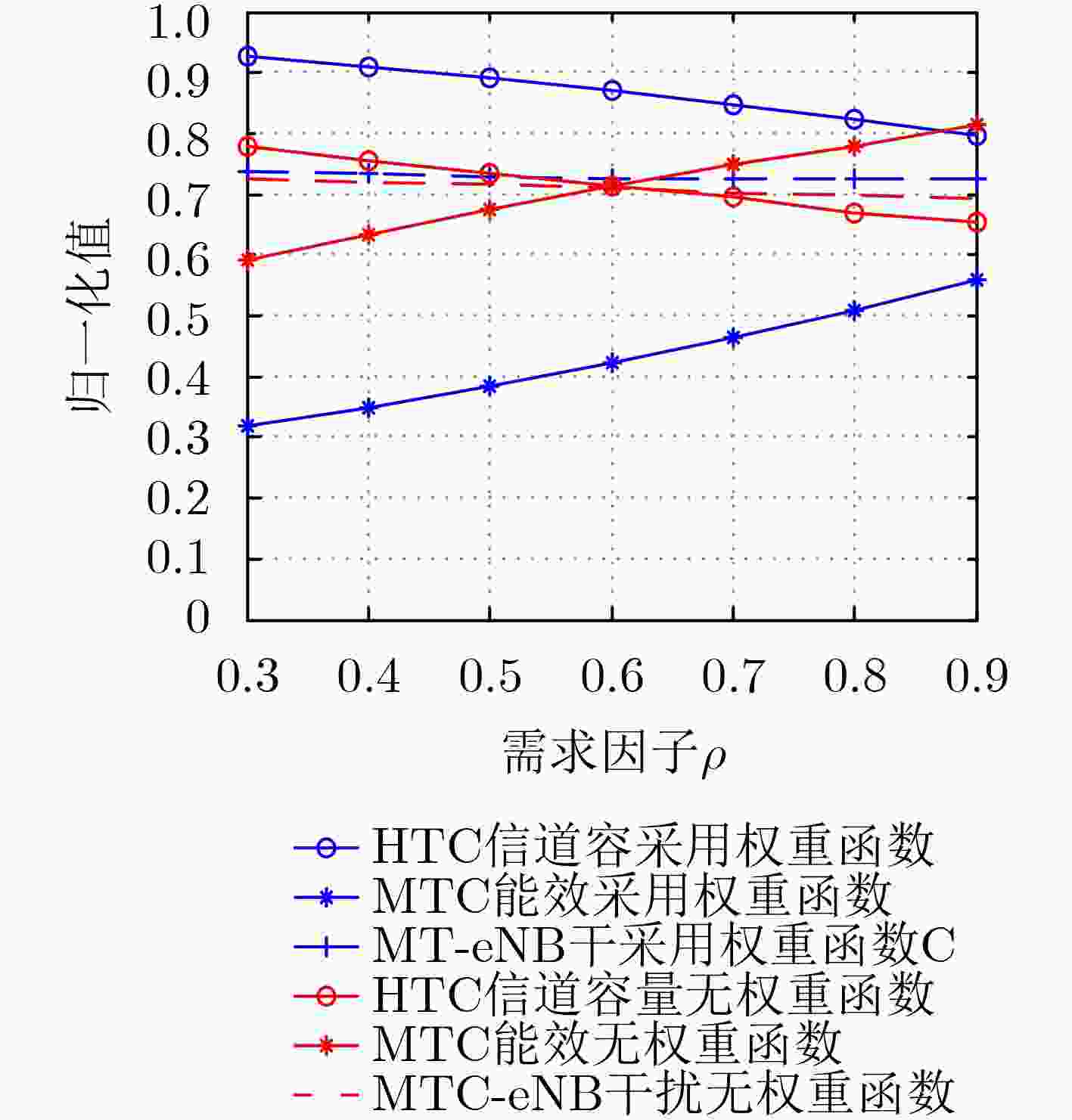
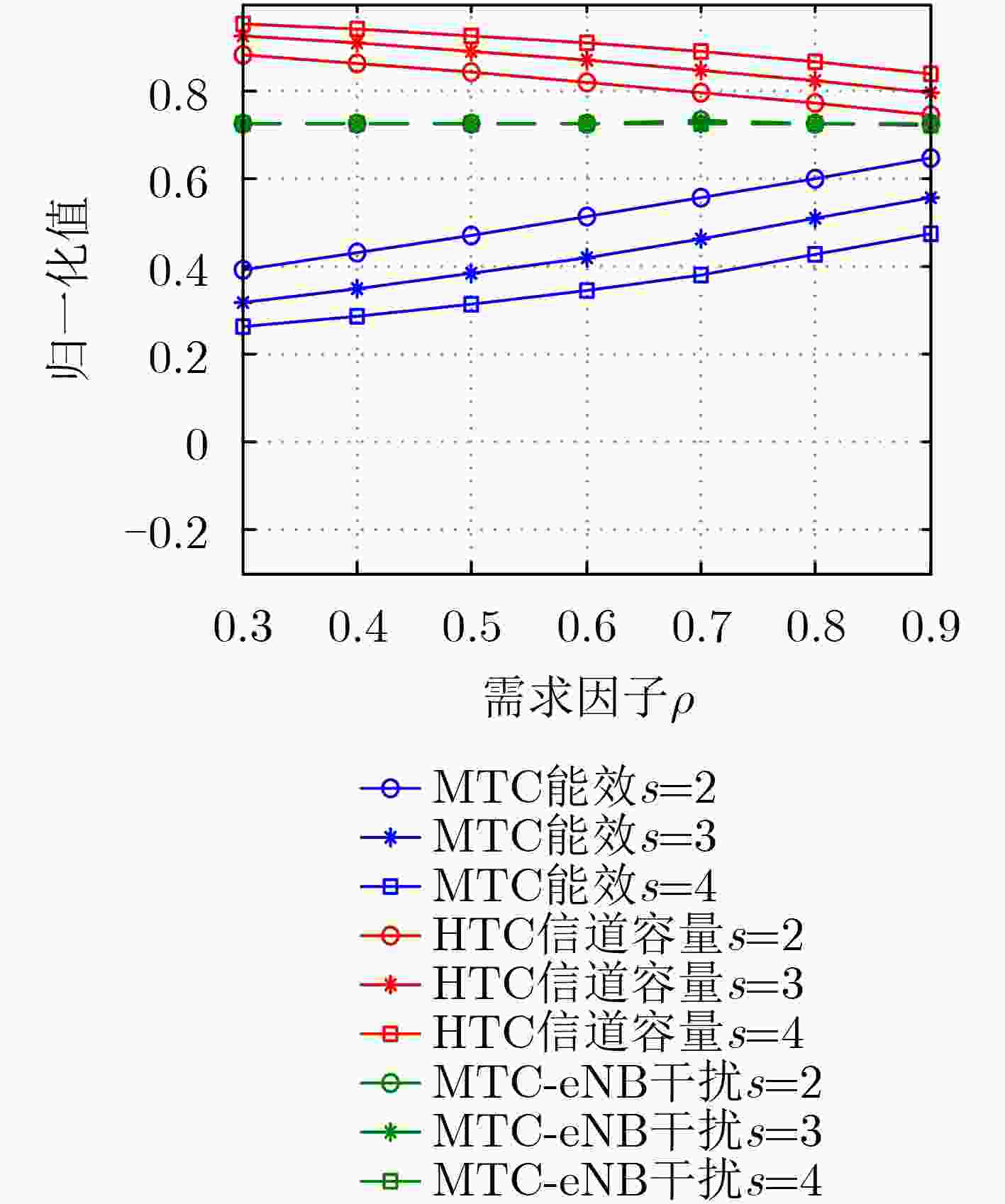
仿真参数 参数值 小区半径 500 m 簇半径 100 m 噪声功率谱密度 –174 dBm/Hz 每个簇内的MTC设备个数Nj 10 每个小区的HTC设备个数M 10 MTC的传输功率上限PUn 15 dBm HTC的传输功率上限PUm 23 dBm 子信道个数K 50 单位子信道带宽W 180 kHz 簇1内MTC设备速率/时延约束 320 kbps/20 ms 簇2内MTC设备速率/时延约束 1000 kbps/40 ms 簇3内MTC设备速率/时延约束 200 kbps/3000 ms HTC设备最小传输速率Rth 1 Mbit/s 电路功率消耗Pc 0.1 W 参数s 3.0 -
XIA Nian, CHEN H H, and YANG C S. Radio resource management in machine-to-machine communications—A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(1): 791–828. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2765344 CHANG C W and CHEN J C. UM paging: Unified M2M paging with optimal DRX cycle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(3): 886–900. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2575835 HUANG Jun, XING Congcong, SHIN S Y, et al. Optimizing M2M communications and quality of services in the IoT for sustainable smart cities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Computing, 2018, 3(1): 4–15. doi: 10.1109/TSUSC.2017.2702589 ZHANG Guopeng, LI Ao, YANG Kun, et al. Optimal power control for delay-constraint machine type communications over cellular uplinks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(6): 1168–1171. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2535145 TIAN Hui, XU Youyun, XU Kui, et al. Energy-efficient user association in heterogeneous networks with M2M/H2H coexistence under QoS guarantees[J]. China Communications, 2015, 12(Suppl): 93–103. doi: 10.1109/CC.2015.7386157 AIJAZ A, TSHANGINI M, NAKHAI M R, et al. Energy-efficient uplink resource allocation in LTE networks with M2M/H2H co-existence under statistical QoS guarantees[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2014, 62(7): 2353–2365. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2014.2328338 HAMDOUN S, RACHEDI A, and GHAMRI-DOUDANE Y. Radio resource sharing for mtc in lte-a: An interference-aware bipartite graph approach[C]. 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2015.7417719. XU Shaoyi and GAO Shuai. Multi-objective optimization for balancing energy efficiency and channel capacity for machine type communications in LTE networks[C]. The IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, Montreal, Canada, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2017.8292578. NG D W K, LO E S, and SCHOBER R. Multiobjective resource allocation for secure communication in cognitive radio networks with wireless information and power transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(5): 3166–3184. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2436334 KHAMIDEHI B, RAHMATI A, and SABBAGHIAN M. Joint sub-channel assignment and power allocation in heterogeneous networks: An efficient optimization method[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(12): 2490–2493. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2597147 BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 215–273. XU Lukai, YU Guanding, and JIANG Yuhuan. Energy-efficient resource allocation in single-cell OFDMA systems: Multi-objective approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(10): 5848–5858. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2443104 -





 下载:
下载:
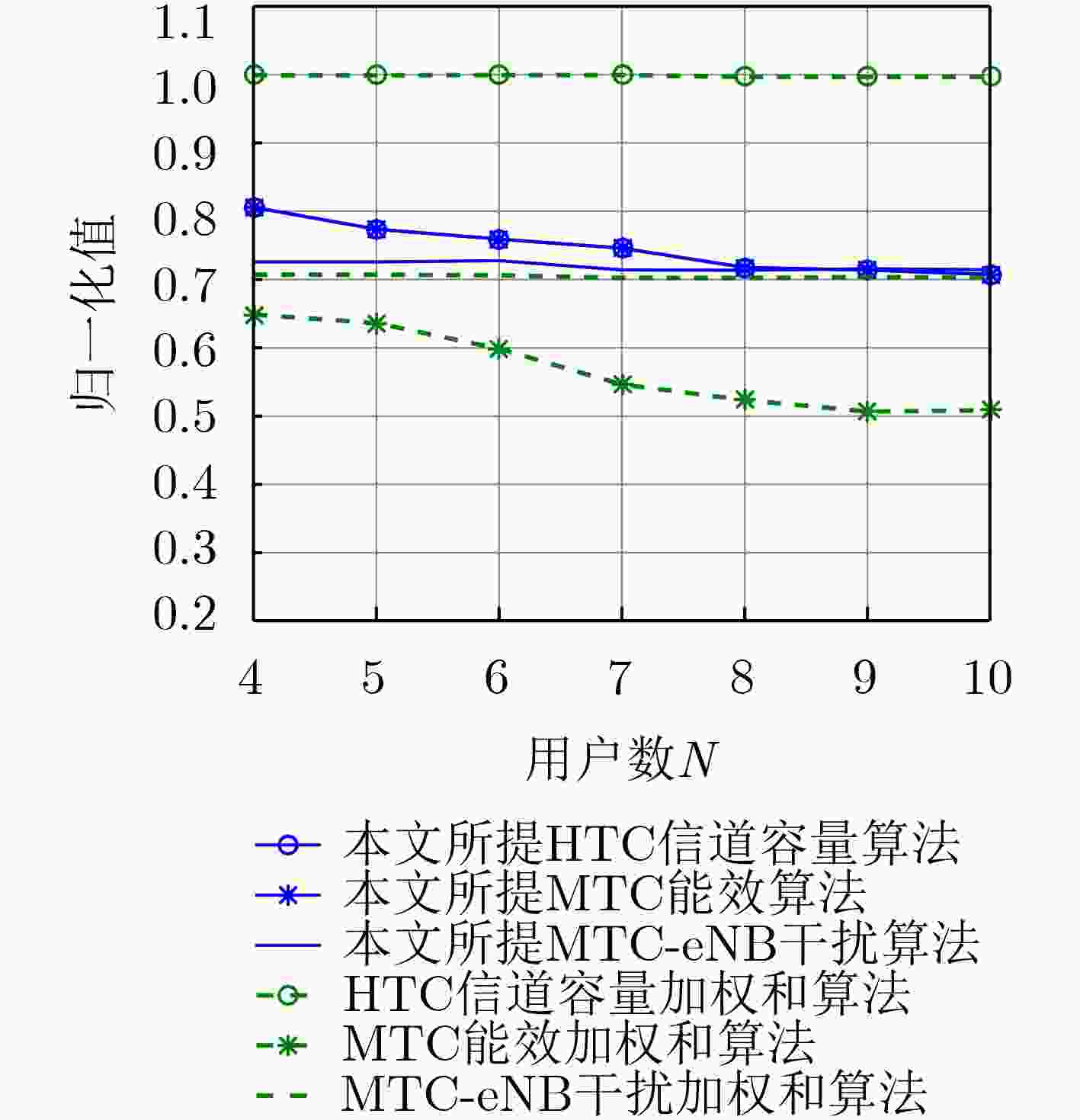


 下载:
下载:
