Binaural Target Sound Source Localization Based on Time-frequency Units Selection
-
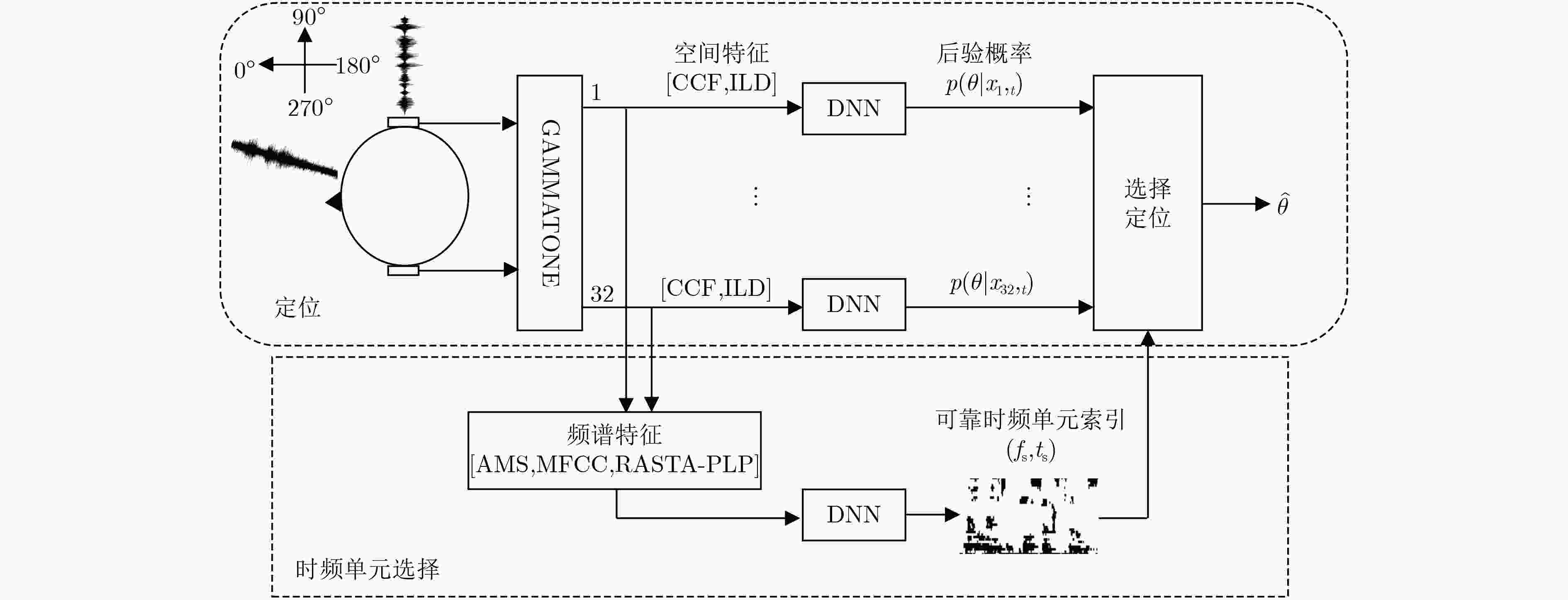
摘要: 针对复杂声学环境下,现有目标声源定位算法精度低的问题,该文提出了一种基于时频单元选择的双耳目标声源定位算法。该算法首先利用双耳目标声源的频谱特征训练1个基于深度学习的时频单元选择模型,然后使用时频单元选择器从双耳输入信号中提取可靠的时频单元,减少非目标时频单元对定位精度的负面影响。同时,基于深度神经网络的定位系统将双耳空间线索映射到方位角的后验概率。最后,依据与可靠时频单元相对应的后验概率完成目标语音的声源定位。实验结果表明,该算法在低信噪比和各种混响环境,特别是存在与目标声源类似的噪声环境下目标声源的定位精度得到明显改善,性能优于对比算法。Abstract: The performance of the existing target localization algorithms is not ideal in complex acoustic environment. In order to improve this problem, a novel target binaural sound localization algorithm is presented. First, the algorithm uses binaural spectral features as input of a time-frequency units selector based on deep learning. Then, to reduce the negative impact of the time-frequency unit belonging to noise on the localization accuracy, the selector is emploied to select the reliable time-frequency units from binaural input sound signal. At the same time, a Deep Neural Network (DNN)-based localization system maps the binaural cues of each time-frequency unit to the azimuth posterior probability. Finally, the target localization is completed according to the azimuth posterior probability belonging to the reliable time-frequency units. Experimental results show that the performance of the proposed algorithm is better than comparison algorithms and achieves a significant improvement in target localization accuracy in low Signal-to-Noise Ratio(SNR) and various reverberation environments, especially when there is noise similar to the target sound source.
-
Key words:
- Target sound localization /
- Deep learning /
- Time-frequency units selection
-
表 1 房间特性参数
房间 A B C D T60(s) 0.32 0.47 0.68 0.89 DRR(dB) 6.09 5.31 8.82 6.12 表 2 噪声类型与描述
噪声 噪声描述 symphony 弦乐器的声音,频率范围分布较广且与目标语音频率范围重叠 baby 与目标语音相比有更高的共振峰,且频率范围重叠 babble 随机选取于TIMIT数据集的32条语音混合形成,与目标语音频谱类似 alarm 信号能量大部分集中于2 kHz左右的窄带噪声 telephone 窄带噪声,能量集中于1 kHz与2 kHz附近 white 白噪声,能量在整个频带内均匀分布 表 3 目标声源定位精度
噪声 信噪比(dB) 房间A(%) 房间B(%) 房间C(%) 房间D(%) 对比
算法1对比
算法2本文
算法对比
算法1对比
算法2本文
算法对比
算法1对比
算法2本文
算法对比
算法1对比
算法2本文
算法symphony 6 85.3 97.9 96.8 83.2 97.8 98.0 82.1 100.0 97.9 85.3 98.9 98.8 0 69.8 95.7 96.8 71.6 96.8 97.9 78.8 96.8 96.8 74.7 98.9 96.9 –6 40.0 90.5 92.6 35.3 88.4 94.7 57.7 92.6 96.8 51.2 93.3 96.8 –12 13.7 64.8 77.9 8.4 55.2 72.9 11.6 67.1 75.8 21.1 70.7 76.8 baby 6 94.7 100.0 100.0 94.8 97.9 98.9 92.6 93.7 100.0 94.8 100.0 100.0 0 83.1 97.9 100.0 88.7 97.4 100.0 84.6 95.8 100.0 89.5 97.9 100.0 –6 75.7 95.2 96.8 80.6 92.6 95.8 79.8 92.6 94.9 80.0 94.7 97.9 –12 56.8 73.7 87.4 61.1 78.9 85.7 71.6 80.5 87.4 74.7 81.5 91.2 babble 6 81.1 92.6 98.9 85.2 93.7 100.0 82.1 89.5 97.9 85.3 94.7 97.8 0 66.2 87.4 97.8 68.7 88.4 97.9 73.6 88.4 98.6 72.5 92.6 98.9 –6 47.6 64.2 87.5 44.2 57.9 78.7 60.5 72.2 88.4 61.2 76.8 87.6 –12 44.5 58.2 67.4 34.7 53.4 75.7 57.9 64.7 71.6 52.6 61.2 78.9 alarm 6 95.8 100.0 98.9 94.7 100.0 97.9 91.6 98.9 94.7 94.7 98.9 98.9 0 89.7 98.9 98.9 87.4 96.8 97.9 84.2 97.9 94.7 90.5 98.9 98.9 –6 69.9 93.7 95.8 63.9 94.7 95.8 66.1 94.7 95.3 86.8 95.2 95.8 –12 21.1 86.3 84.2 30.5 85.2 91.6 43.2 83.2 88.4 64.2 85.3 83.2 telephone 6 69.5 100.0 98.9 75.8 100.0 98.7 70.5 100 100.0 83.2 100.0 100.0 0 48.3 91.5 91.6 52.4 99.1 97.8 46.9 95.8 96.8 62.4 97.9 98.9 –6 29.5 88.4 89.5 25.1 84.7 89.1 26.2 88.7 91.6 41.3 90.5 92.6 –12 16.8 77.6 88.4 10.5 81.1 86.7 14.7 77.9 89.7 21.1 84.2 85.9 white 6 64.2 85.3 89.5 60.0 90.5 95.8 54.7 84.2 84.2 66.3 83.2 93.7 0 41.1 78.9 82.1 38.9 82.1 83.2 26.3 76.8 83.2 45.3 82.6 86.4 –6 18.9 48.7 61.1 16.8 44.2 64.2 5.3 31.9 59.6 19.5 41.1 57.9 –12 10.5 18.9 44.2 7.4 14.7 35.9 2.1 7.4 12.6 8.4 13.7 27.4 -
MAY T, VAN DE PAR S, and KOHLRAUSCH A. A probabilistic model for robust localization based on a binaural auditory front-end[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2011, 19(1): 1–13. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2010.2042128 李如玮, 潘冬梅, 张爽, 等. 基于Gammatone滤波器分解的HRTF和GMM的双耳声源定位算法[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2018, 44(11): 1385–1390. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2017090015LI Ruwei, PAN Dongmei, ZHANG Shuang, et al. Binaural sound source localization algorithm based on HRTF and GMM Under Gammatone filter decomposition[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2018, 44(11): 1385–1390. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2017090015 WOODRUFF J and WANG Deliang. Binaural localization of multiple sources in reverberant and noisy environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2012, 20(5): 1503–1512. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2012.2183869 MA Ning, MAY T, and BROWN G J. Exploiting deep neural networks and head movements for robust binaural localization of multiple sources in reverberant environments[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2017, 25(12): 2444–2453. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2750760 MA Ning, GONZALEZ J A, and BROWN G J. Robust binaural localization of a target sound source by combining spectral source models and deep neural networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2018, 26(11): 2122–2131. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2018.2855960 WANG Yuxuan, HAN Kun, and WANG Deliang. Exploring monaural features for classification-based speech segregation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2013, 21(2): 270–279. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2012.2221459 JIANG Yi, WANG Deliang, LIU Runsheng, et al. Binaural classification for reverberant speech segregation using deep neural networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(12): 2112–2121. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2014.2361023 ZHANG Xueliang and WANG Deliang. Deep learning based binaural speech separation in reverberant environments[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2017, 25(5): 1075–1084. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2687104 WANG Deliang and CHEN Jitong. Supervised speech separation based on deep learning: An overview[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2018, 26(10): 1702–1726. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2018.2842159 WIERSTORF H, GEIER M, and SPORS S. A free database of head related impulse response measurements in the horizontal plane with multiple distances[C]. The Audio Engineering Society Convention 130, Berlin, Germany, 2011. HUMMERSONE C, MASON R, and BROOKES T. Dynamic precedence effect modeling for source separation in reverberant environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2010, 18(7): 1867–1871. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2010.2051354 MA Ning, BROWN G J, and GONZALEZ J A. Exploiting top-down source models to improve binaural localisation of multiple sources in reverberant environments[C]. The 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Dresden, Germany, 2015: 160–164. COOKE M, BARKER J, CUNNINGHAM S, et al. An audio-visual corpus for speech perception and automatic speech recognition[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2006, 120(5): 2421–2424. doi: 10.1121/1.2229005 MAY T, MA Ning, and BROWN G J. Robust localisation of multiple speakers exploiting head movements and multi-conditional training of binaural cues[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 2679–2683. MAY T. Robust speech dereverberation with a neural network-based post-filter that exploits multi-conditional training of binaural cues[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2018, 26(2): 406–414. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2765819 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
