Research on Synchronous Excitation and Detection Method for Synthetic Multi-frequency Magnetic Induction Signals
-
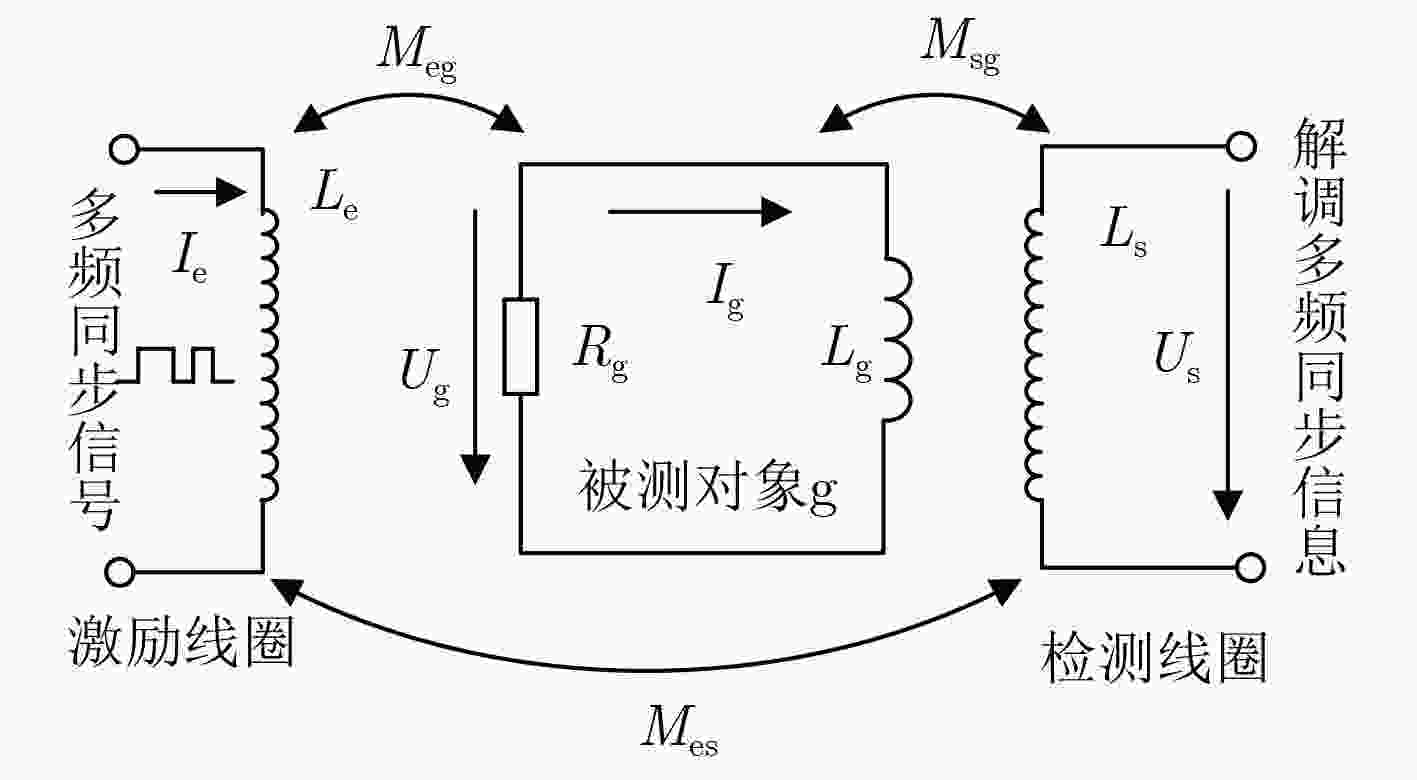
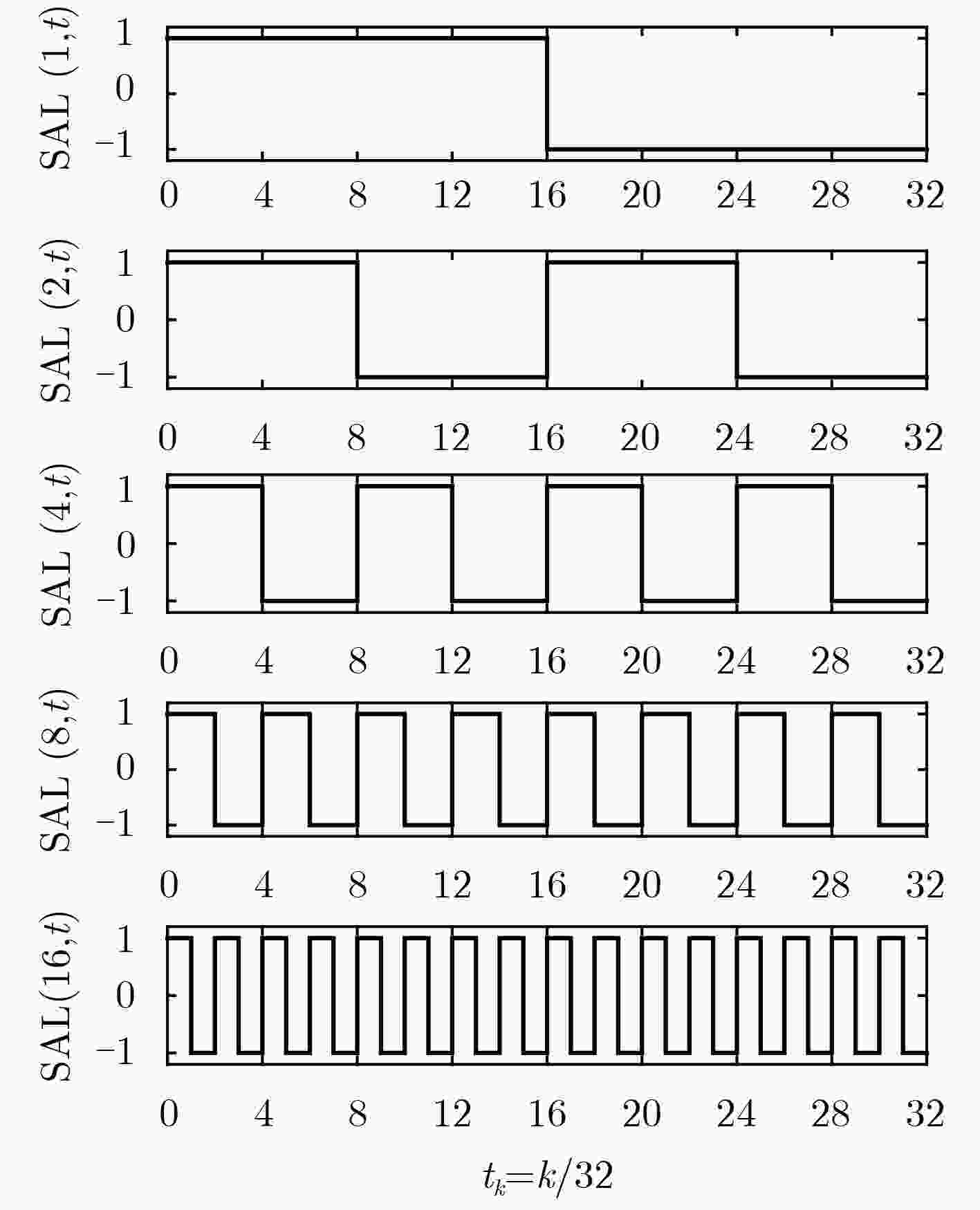
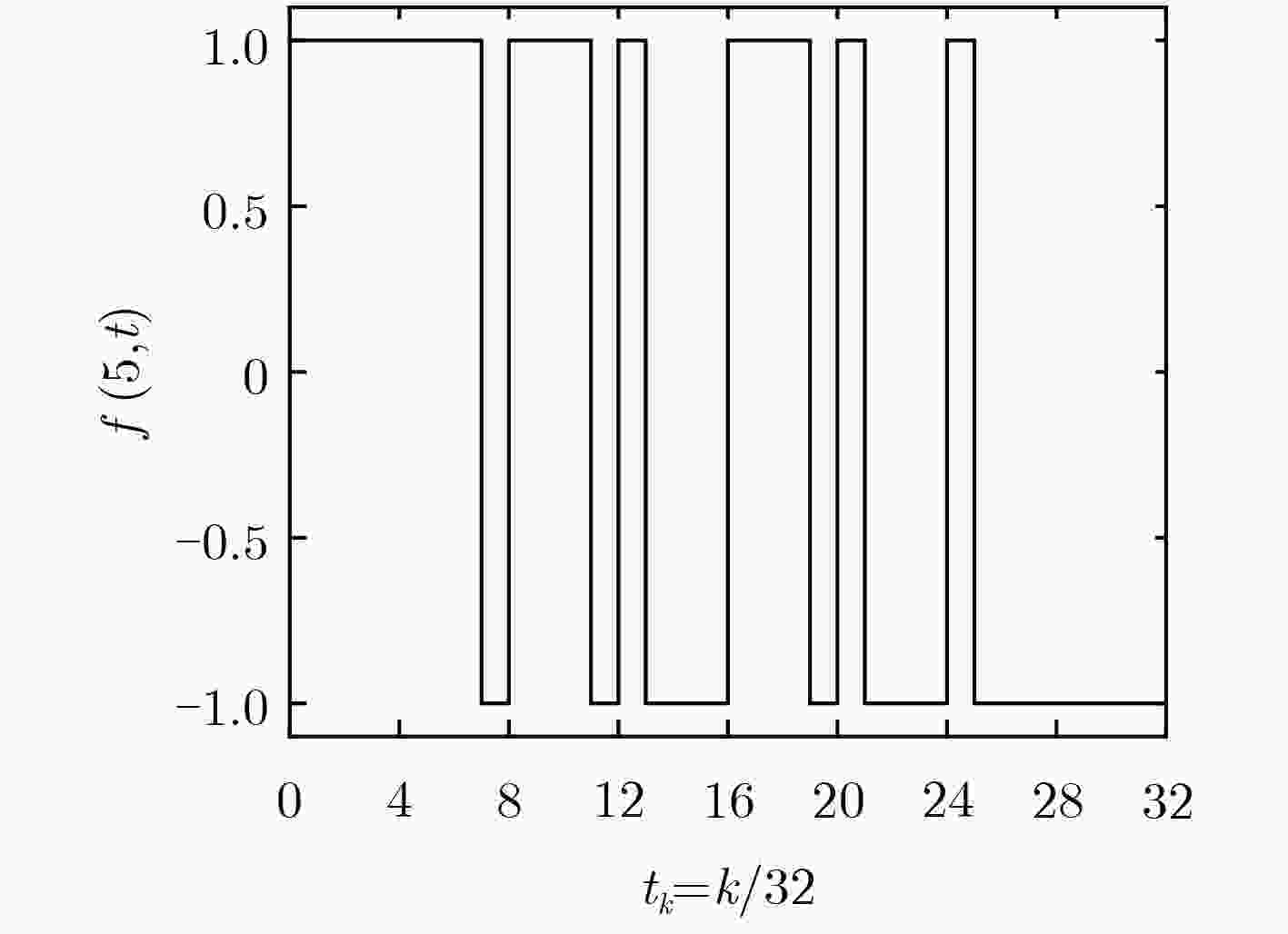
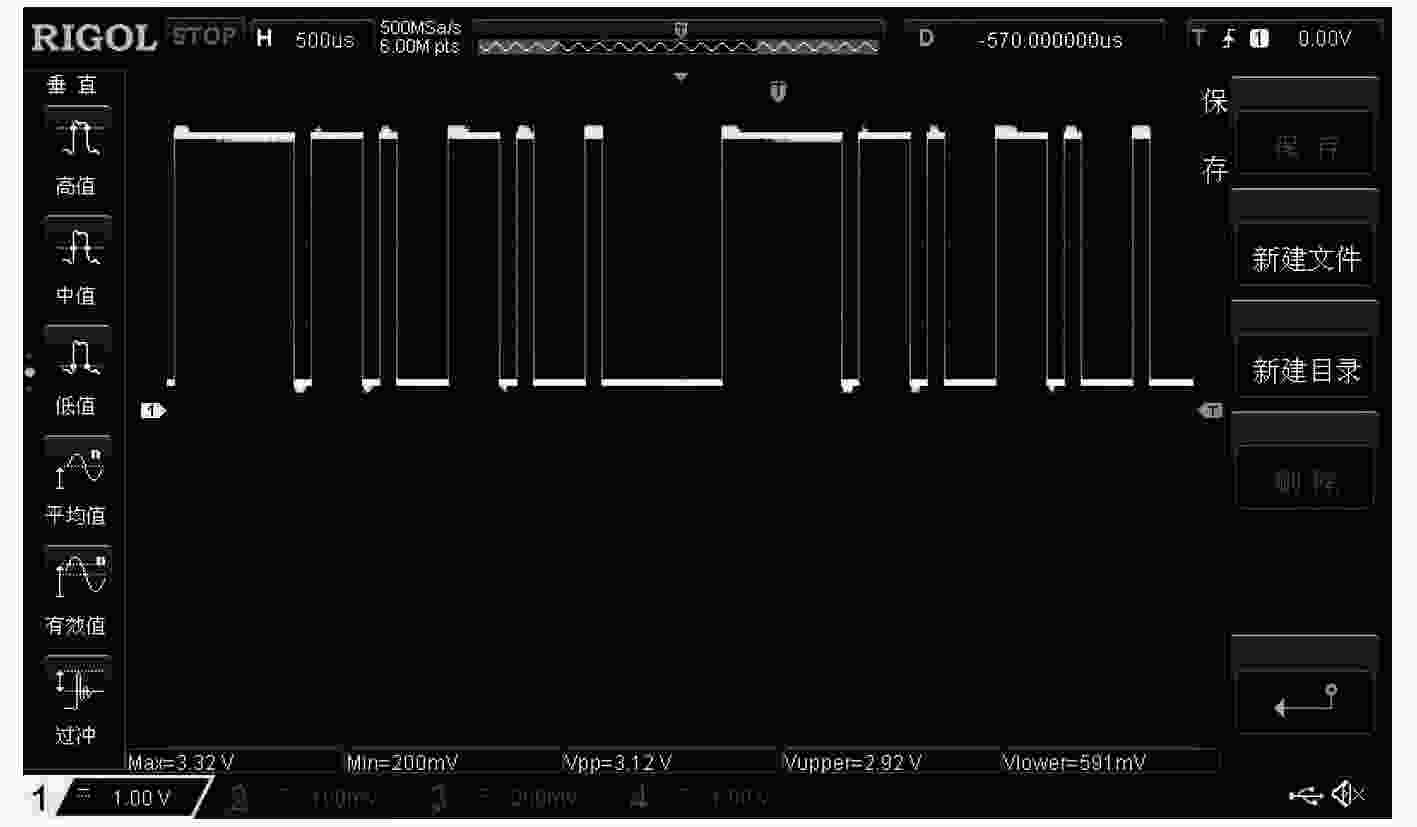
摘要: 磁感应检测技术是一种非接触、无创的电阻抗检测技术,多频率同步检测可同时获得不同频率下被测对象的阻抗信息。该文首先研究了磁感应信号多频率同步激励与检测原理,基于Walsh函数合成了5频率激励信号。其次分析了合成多频率同步检测性能,设计了合成多频磁感应信号同步检测系统。最后,通过合成5频率激励信号与同步检测系统进行不同电导率NaCl溶液的检测实验,结果表明:合成5频率激励信号5个主谐波的测量结果都具有很好的线性度,为磁感应信号多频率同步检测提供了激励-检测方法。Abstract: Magnetic induction detection technology is a non-contact and non-invasive electrical impedance detection technology. Multi-frequency synchronous detection can simultaneously obtain the impedance information of the tested object at different frequencies. Firstly, the principle of multi-frequency synchronous excitation and detection of magnetic induction signal are studied. Five-frequency excitation signal is synthesized based on Walsh function. Secondly, the performance of synthesized multi-frequency synchronous detection is analyzed, and a synthesized multi-frequency magnetic induction signal synchronous detection system is designed. Finally, the detection experiments of NaCl solution with different conductivities are carried out by synthesizing five-frequency excitation signal and synchronous detection system. The results show that the measurement results of five main harmonics of synthesized five-frequency excitation signal have good linearity. It provides an excitation-detection method for multi-frequency synchronous detection of magnetic induction signal.
-
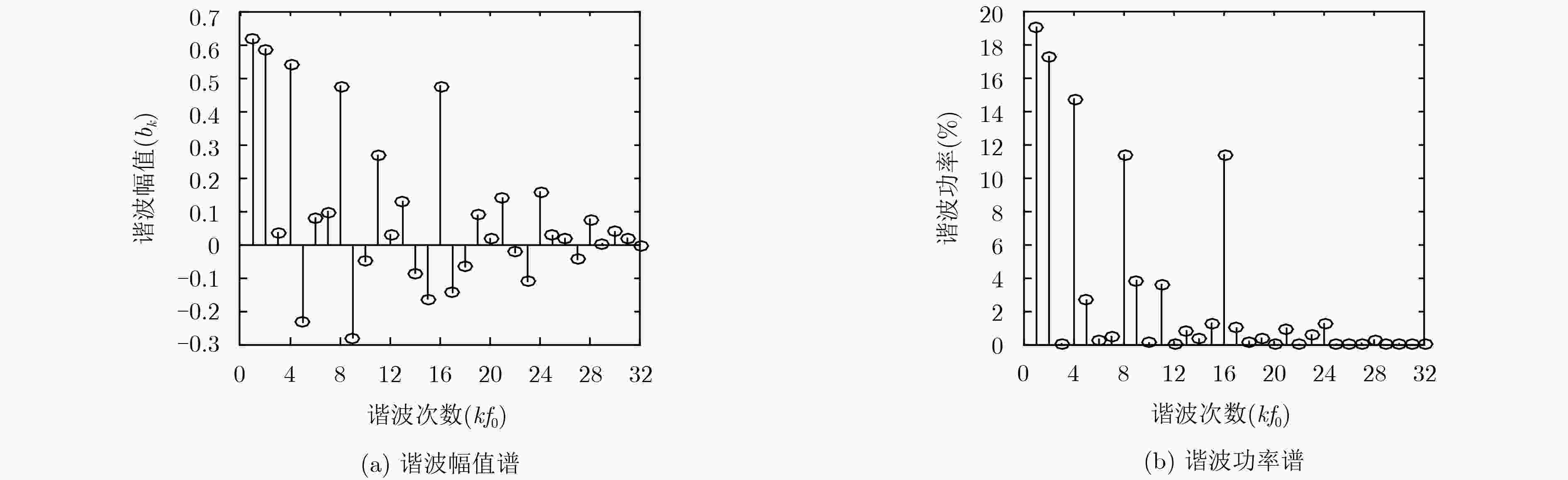
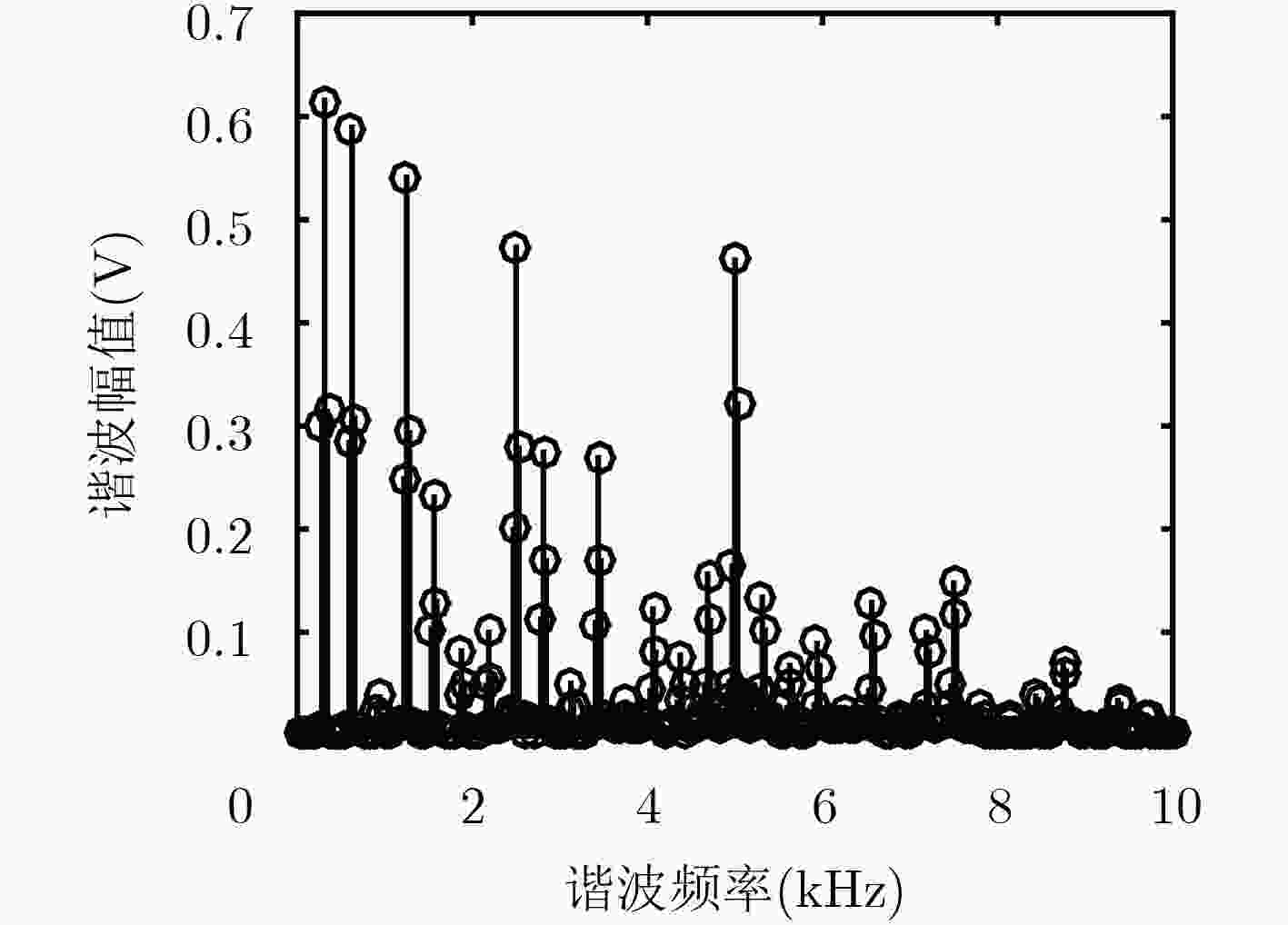
表 1 合成5频率同步信号f(5, t)的主谐波Hk频谱特性
Hk f0 2f0 4f0 8f0 16f0 总和 bk(V) 0.6173 0.5882 0.5443 0.4775 0.4775 Pk(%) 19.05 17.30 14.76 11.40 11.40 73.91 表 2 合成5频率激励信号f(5, t)的主谐波Hk频率值
Hk f0 2f0 4f0 8f0 16f0 Tclk=100 μs 312.5 Hz 625 Hz 1.25 kHz 2.5 kHz 5 kHz Tclk=50 μs 625 Hz 1.25 kHz 2.5 kHz 5 kHz 10 kHz 表 3 电导率与NaCl溶液浓度关系表
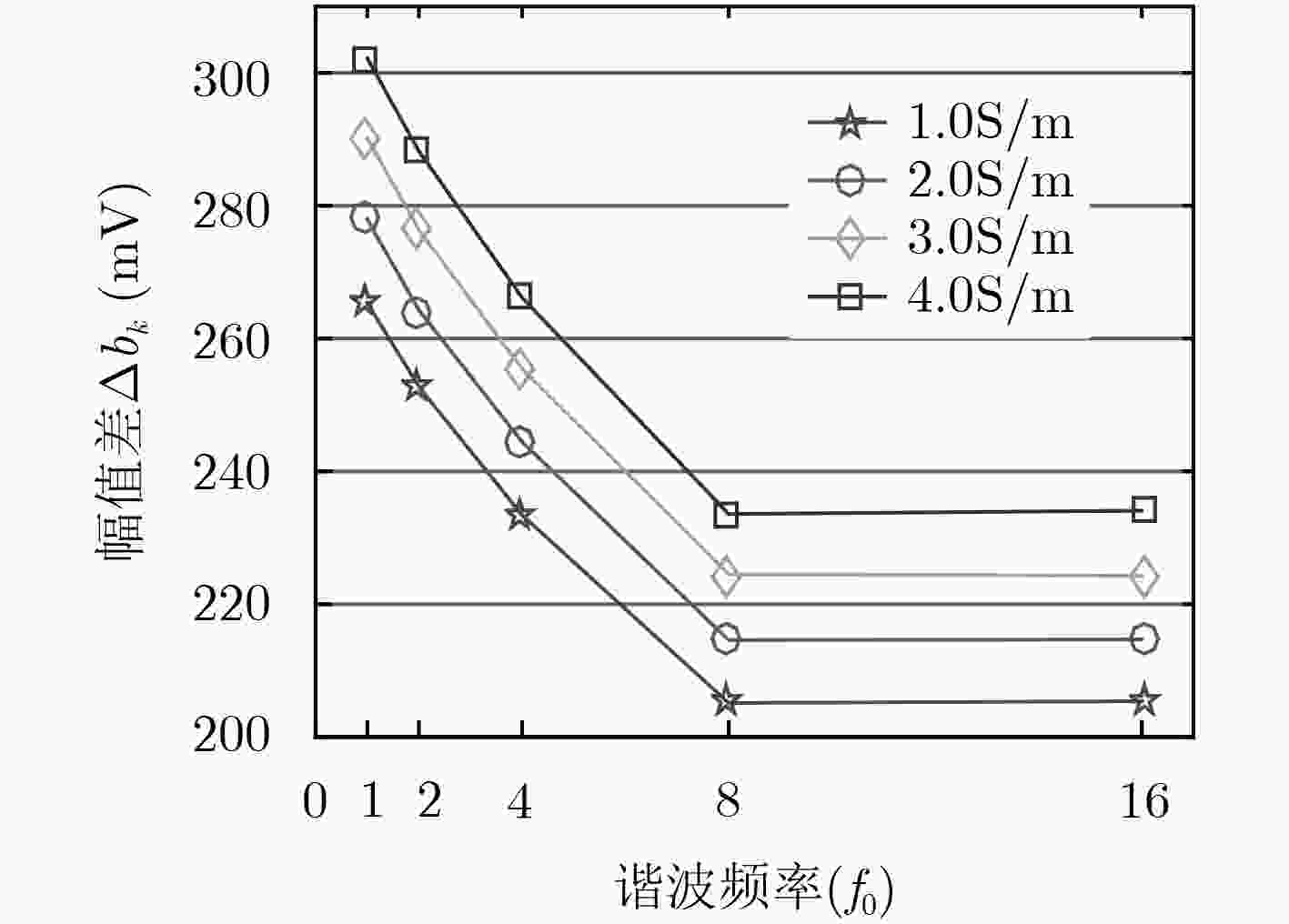
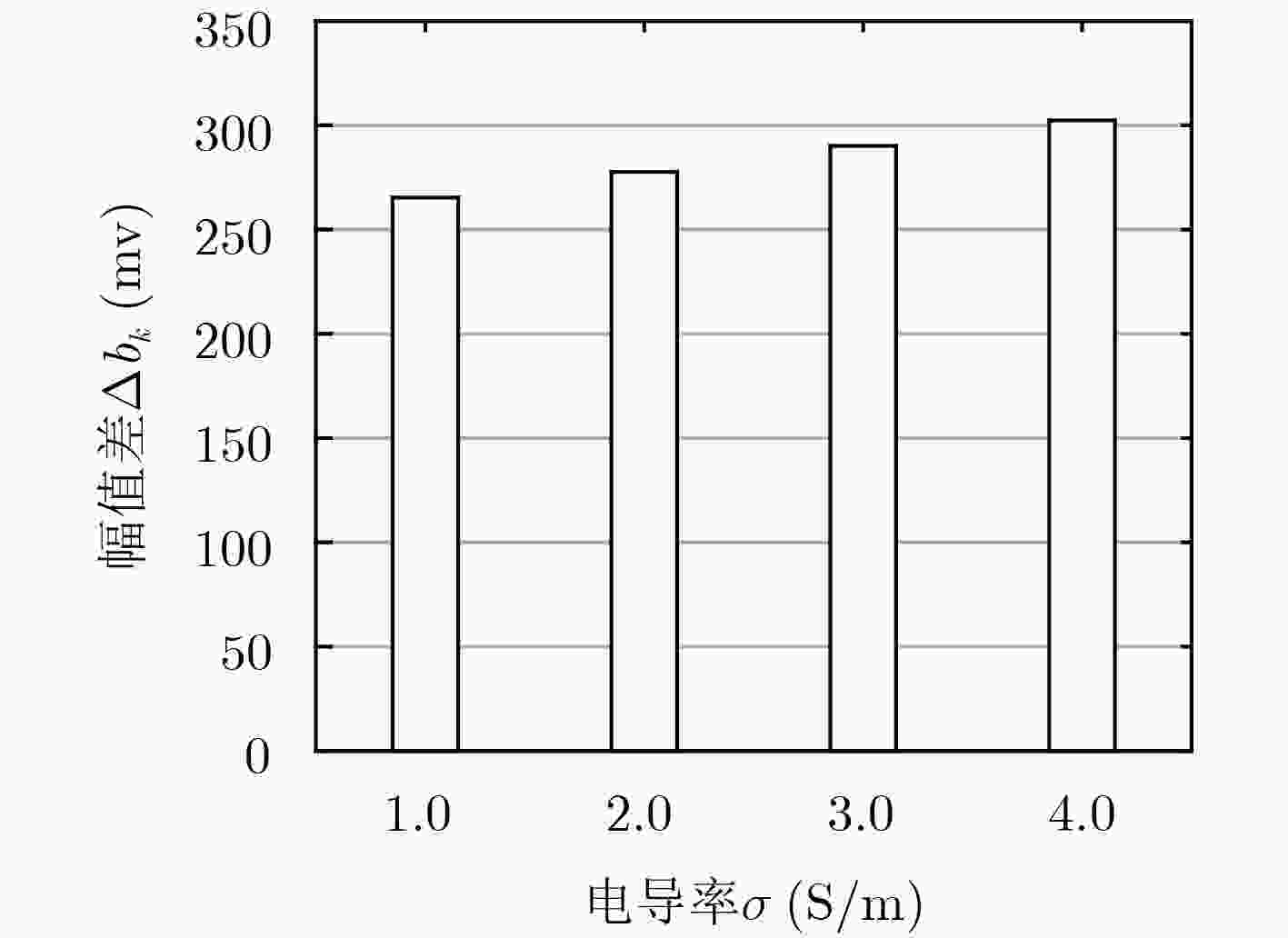
电导率$\sigma $(S/m) 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 ppm(mg/L) 5439 11476 17624 23713 表 4 不同电导率NaCl溶液同步检测结果
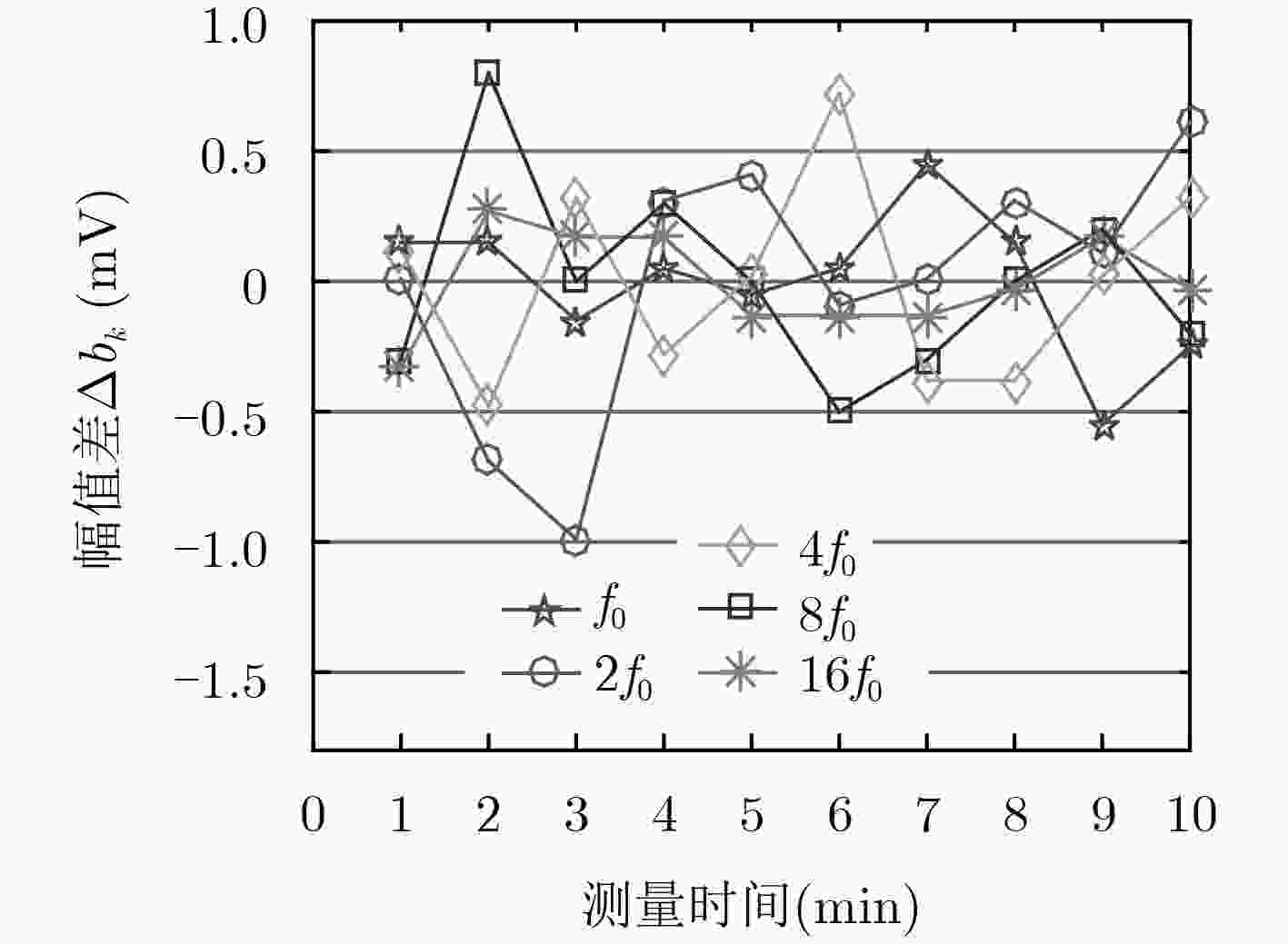
$\Delta {b_k}$(mV) f0 2f0 4f0 8f0 16f0 1.0 S/m 265.355 252.738 233.404 205.126 205.396 2.0 S/m 277.931 264.274 244.421 214.596 214.693 3.0 S/m 290.190 276.316 255.436 224.515 224.252 4.0 S/m 302.210 288.198 266.145 233.576 234.086 表 5 各谐波归一化系数
Hk f0 2f0 4f0 8f0 16f0 归一化系数 1.000 1.050 1.136 1.293 1.293 表 6 归一化处理后不同电导率NaCl溶液同步检测结果
$\Delta {b_k}$(mV) f0 2f0 4f0 8f0 16f0 平均值 1.0 S/m 265.355 265.269 265.160 265.210 265.560 265.311 2.0 S/m 277.931 277.377 277.677 277.454 277.579 277.603 3.0 S/m 290.190 290.016 290.190 290.279 289.939 290.123 4.0 S/m 302.210 302.487 302.356 301.993 302.653 302.340 -
GRIFFITHS H. Magnetic induction tomography[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2001, 12(8): 1126–1131. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/12/8/319 YAN Qingguang, JIN Gui, QIN Mingxin, et al. Experimental study on the detection of rabbit intracranial hemorrhage using four coil structures based on magnetic induction phase shift[J]. Biomedizinische Technik Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 62(1): 1–14. doi: 10.1515/bmt-2015-0129 柯丽, 刘欢, 杜强, 等. 基于滤波反投影的脑磁感应迭代重建算法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 31(11): 2445–2451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.11.005KE Li, LIU Huan, DU Qiang, et al. Study on iterative reconstruction algorithm for brain magnetic induction based on filtered back-projection[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 31(11): 2445–2451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.11.005 罗海军, 廖勇, 潘海涛, 等. 导数法峰值锐化算法提高磁感应成像图像分辨率[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1847–1852. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171102LUO Haijun, LIAO Yong, PAN Haitao, et al. Derivative method peak sharpening algorithm improves image resolution of magnetic induction tomography[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1847–1852. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171102 YIN Wuliang and PEYTON A J. Sensitivity formulation including velocity effects for electromagnetic induction systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2010, 46(5): 1172–1176. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2009.2038275 MELLERT F, WINKLER K, SCHNEIDER C, et al. Detection of (reversible) myocardial ischemic injury by means of electrical bioimpedance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2010, 58(6): 1511–1518. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2054090 SUN T, HOLMES D, GAWAD S, et al. High speed multi-frequency impedance analysis of single particles in a microfluidic cytometer using maximum length sequences[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2007, 7(8): 1034–1040. doi: 10.1039/b703546b 鞠康, 何为, 何传红, 等. 基于直接数字频率合成的混合频率恒流源设计[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2010, 31(9): 2109–2114. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2010.09.030JU Kang, HE Wei, HE Chuanhong, et al. Design of mixing frequency constant current source based on direct digital synthesizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2010, 31(9): 2109–2114. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2010.09.030 BRUNNER P, MERWA R, MISSNER A, et al. Reconstruction of the shape of conductivity spectra using differential multi-frequency magnetic induction tomography[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2006, 27: 237–248. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/27/5/S20 GURSOY D and SCHARFETTER H. Feasibility of head imaging using multi-frequency magnetic induction tomography[C]. Biomedical Engineering Meeting, Heidelberg, Germany, 2009, 525–528. XIAO Zhili, TAN Chao, and DONG Feng. Effect of inter-tissue inductive coupling on multi-frequency imaging of intracranial hemorrhage by magnetic induction tomography[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2017, 28(8): 1–11. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aa7504 MA Lu and SOLEIMANI M. Magnetic induction tomography methods and applications: A review[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2017, 28(7): 072001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aa7107 吕轶, 王旭, 杨丹, 等. 一种磁感应成像中生物组织涡流信号的新型测量方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(9): 2258–2262. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01422LÜ Yi, WANG Xu, YANG Dan, et al. A new measurement method of eddy current for biological tissue in magnetic induction tomography[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(9): 2258–2262. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01422 王超, 郎健, 王化祥. 用于生物阻抗测量的混频激励电流源[J]. 计量学报, 2006, 27(4): 392–396. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1158.2006.04.023WANG Chao, LANG Jian, and WANG Huaxiang. Mixing frequency excitation current source used in bioelectric impedance measuring system[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2006, 27(4): 392–396. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1158.2006.04.023 杨宇祥, 乔洋. 一种多频率同步信号激励电流源设计[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2013, 34(4): 908–913. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2013.04.029YANG Yuxiang and QIAO Yang. Design of a multi-frequency synchronized signal excitation current source[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2013, 34(4): 908–913. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2013.04.029 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
