Candidate Label-Aware Partial Label Learning Algorithm
-
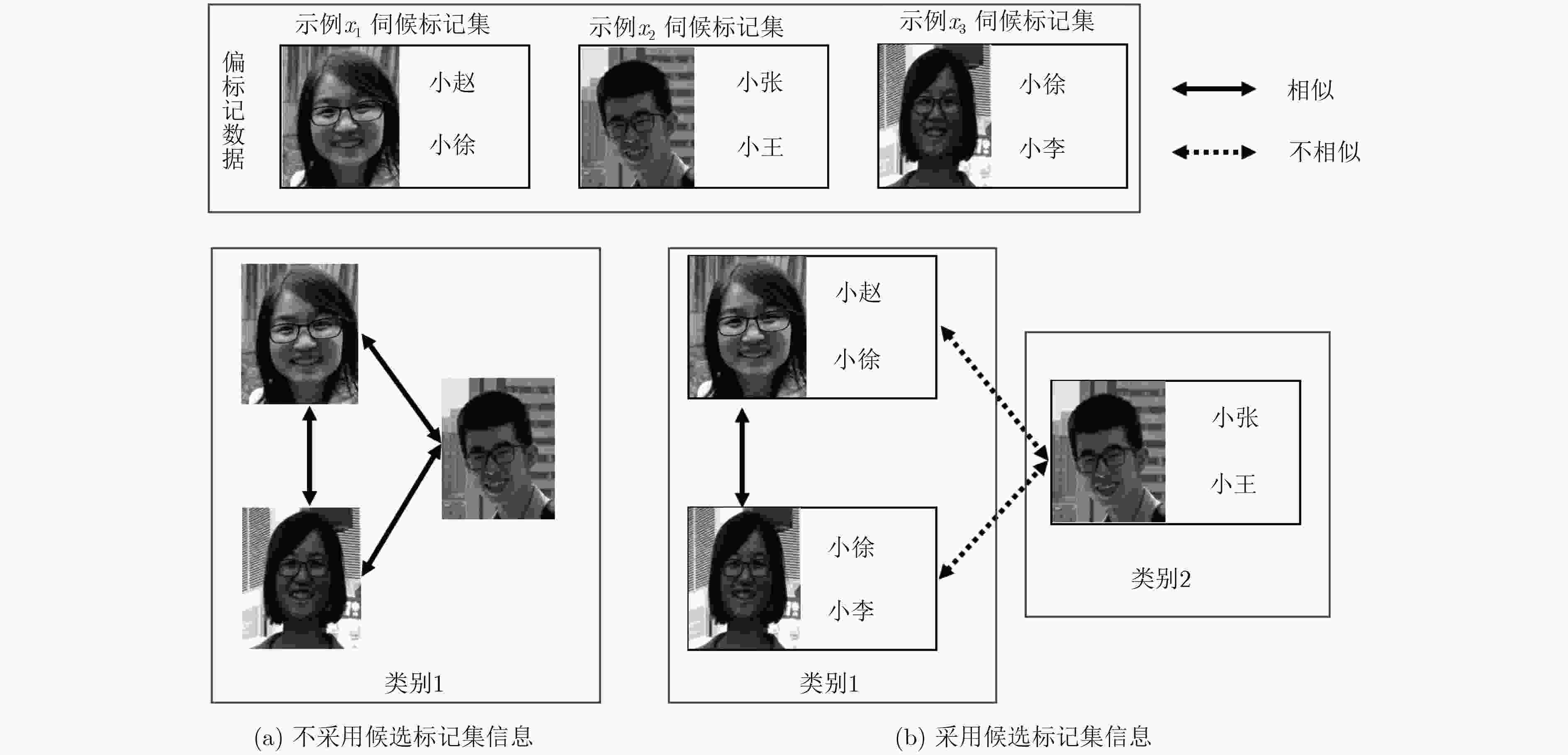
摘要: 在偏标记学习中,示例的真实标记隐藏在由一组候选标记组成的标记集中。现有的偏标记学习算法在衡量示例之间的相似度时,只基于示例的特征进行计算,缺乏对候选标记集信息的利用。该文提出一种候选标记感知的偏标记学习算法(CLAPLL),在构建图的阶段有效地结合候选标记集信息来衡量示例之间的相似度。首先,基于杰卡德距离和线性重构,计算出各个示例的标记集之间的相似度,然后结合示例相似度和标记集的相似度构建相似度图,并通过现有的基于图的偏标记学习算法进行学习和预测。3个合成数据集和6个真实数据集上实验结果表明,该文方法相比于基线算法消歧准确率提升了0.3%~16.5%,分类准确率提升了0.2%~2.8%。Abstract: In partial label learning, the true label of an instance is hidden in a label-set consisting of a group of candidate labels. The existing partial label learning algorithm only measures the similarity between instances based on feature vectors and lacks the utilization of the candidate labelset information. In this paper, a Candidate Label-Aware Partial Label Learning (CLAPLL) method is proposed, which combines effectively candidate label information to measure the similarity between instances during the graph construction phase. First, based on the jaccard distance and linear reconstruction, the similarity between the candidate labelsets of instances is calculated. Then, the similarity graph is constructed by combining the similarity of the instances and the label-sets, and then the existing graph-based partial label learning algorithm is presented for learning and prediction. The experimental results on 3 synthetic datasets and 6 real datasets show that disambiguation accuracy of the proposed method is 0.3%~16.5% higher than baseline algorithm, and the classification accuracy is increased by 0.2%~2.8%.
-
表 1 候选标记信息感知的偏标记学习算法伪代码
输入:偏标记数据集$D = \left\{ {({X_i},{S_i})|1 \le i \le m} \right\}$,最近邻样本数 $k$,标记相似度权重$\alpha $ 训练阶段: 1 对特征矩阵${\text{X}} \in {{\text{R}}^{m \times d}}$进行Z-score归一化; 2 根据式(1)求${{\text{w}}_j}$; 3 根据${{\text{w}} _j}$构建相似度图${G_i}(V,E)$; 4 switch v; case Jaccard:根据式(3)计算${{\text{u}}_j}$,并构建候选标记集相似度 图${G_{\rm{c}}}(i,j)$, (CAP-J算法); case linear:根据式(4)计算${{\text{u}}_j}$,并构建候选标记集相似度 图${G_{\rm{c}}}(i,j)$, (CAP-L算法); end switch 5 根据式(7)计算最终相似度图$G(i,j)$; 6 结合现有图模型偏标记学习算法进行消歧,得到消歧结果 $\mathop D\limits^ \wedge = \left\{ {({X_i},{{\widehat y}_i})|1 \le i \le m} \right\}$; 测试阶段: 7 对于未见示例${x^*}$,根据式(8)计算得分类结果; 输出:消歧结果$\mathop D\limits^ \wedge = \left\{ {({X_i},{{\widehat y}_i})|1 \le i \le m} \right\}$和分类结果${y^*}$。 表 2 基线算法和本文算法复杂度比较
算法复杂度 实际复杂度 基线算法 $O({d^{\,\; 2} }{n^3}\lg (n))$ $O({d^{\,\; 2} }{n^3}\lg (n))$ 本文算法(CAP-J) $O({d^{\,\; 2} }{n^3}\lg (n) + (s + 1){k^2})$ $O({d^{\,\; 2} }{n^3}\lg (n))$ 本文算法(CAP-L) $O({d^{\,\; 2} }{n^3}\lg (n) + (sk + 1){k^2})$ $O({d^{\,\; 2} }{n^3}\lg (n))$ 表 3 真实偏标记数据集的特征
数据集 样本数 特征数 类别标记数 候选标记数 平均 最小 最大 Lost 1122 108 16 2.23 1 3 Birdsong 4998 38 13 2.18 1 4 MSRSCv2 1758 48 23 3.16 1 7 FG-NET 1002 262 78 7.48 2 11 Yahoo! News 22991 163 219 1.91 1 5 Soccer Player 17472 279 171 2.09 1 11 表 4 合成偏标记数据集的特征
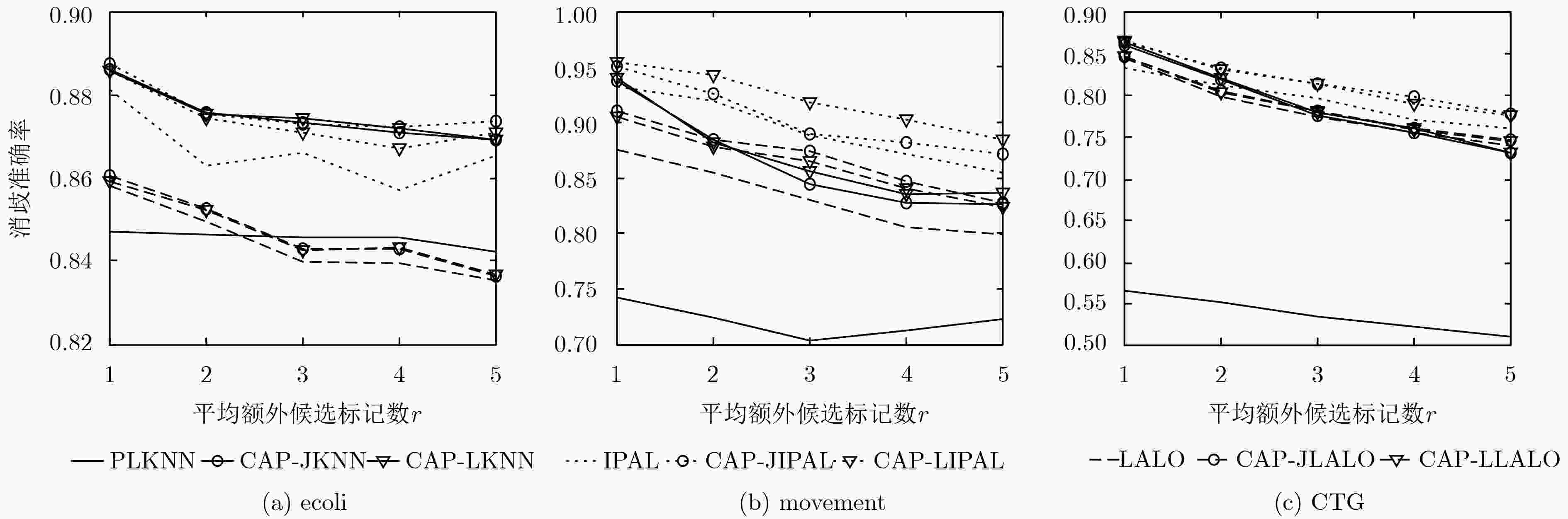
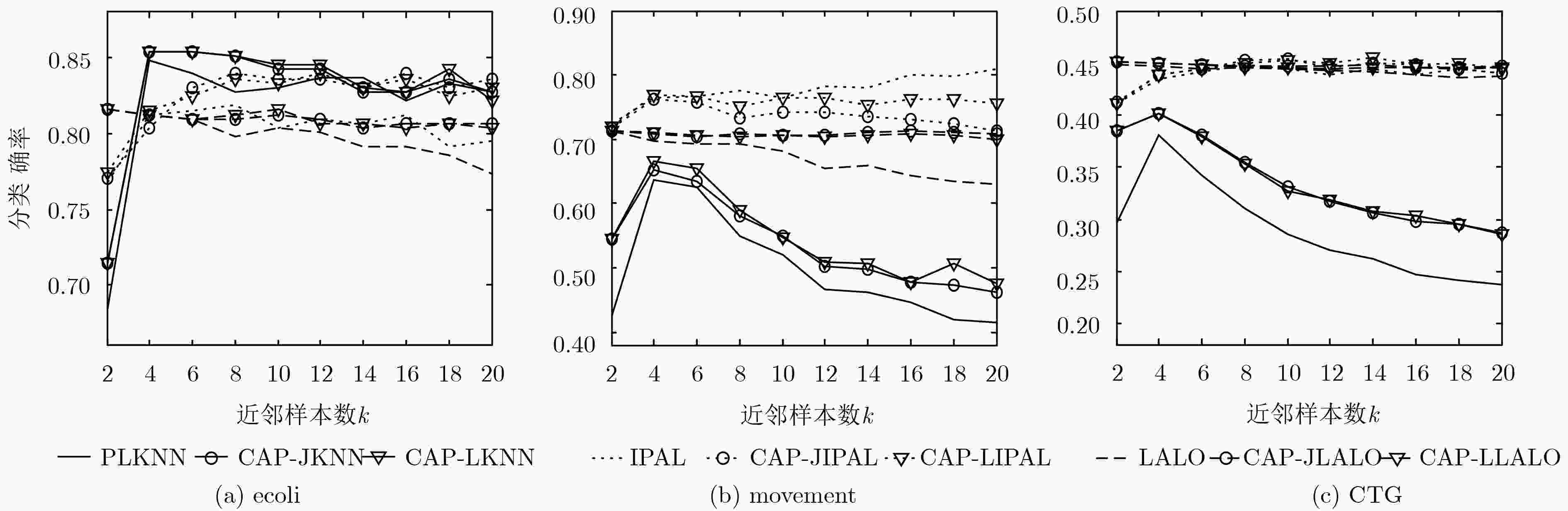
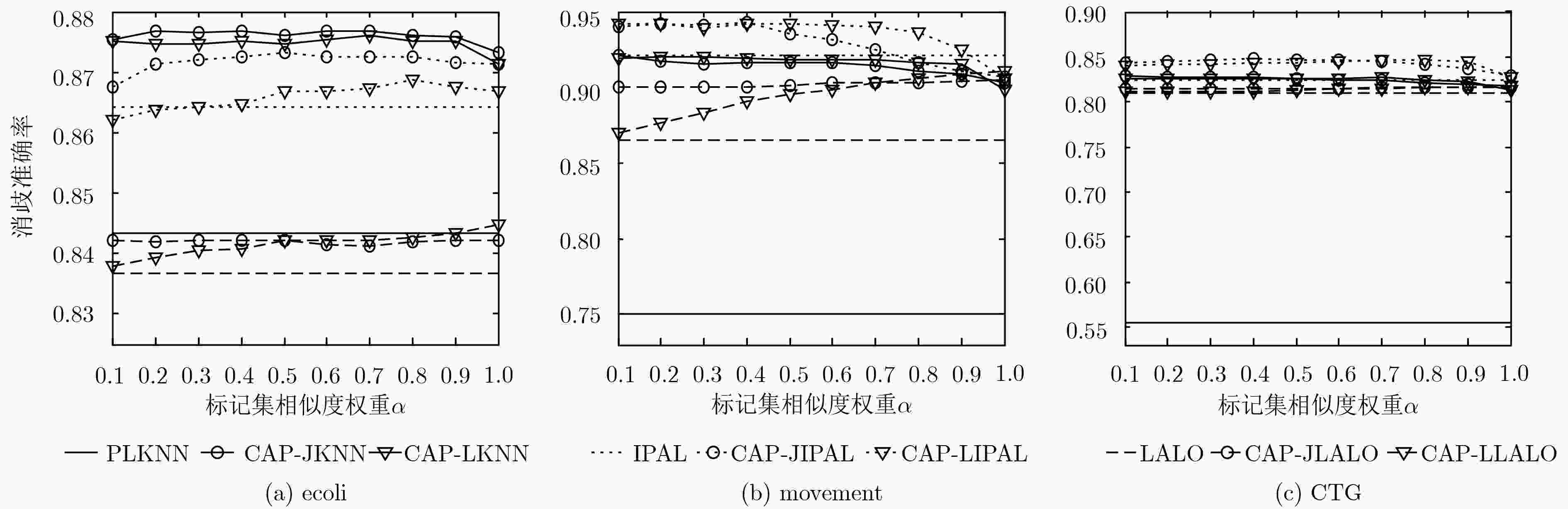
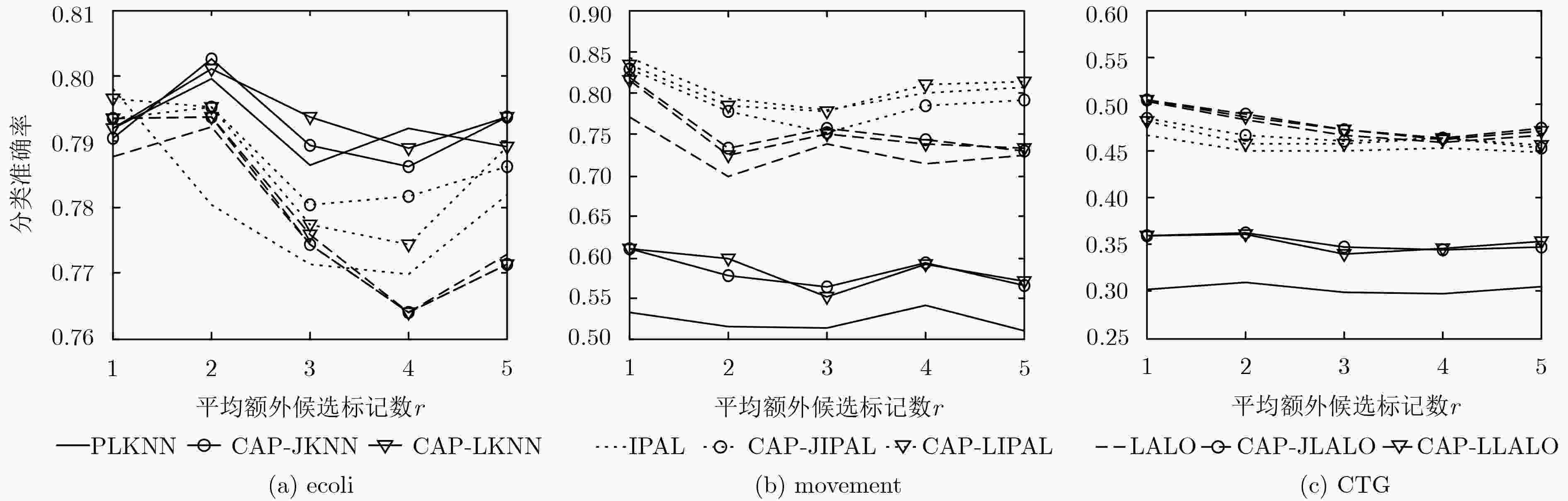
数据集 样本数 特征数 类别标记数 参数设置 Ecoli 336 7 8 p={0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4,0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8} r={1, 2, 3, 4, 5} Movement 360 90 15 CTG 2126 21 10 表 5 不同算法在真实偏标记数据集上的消歧准确率(%)
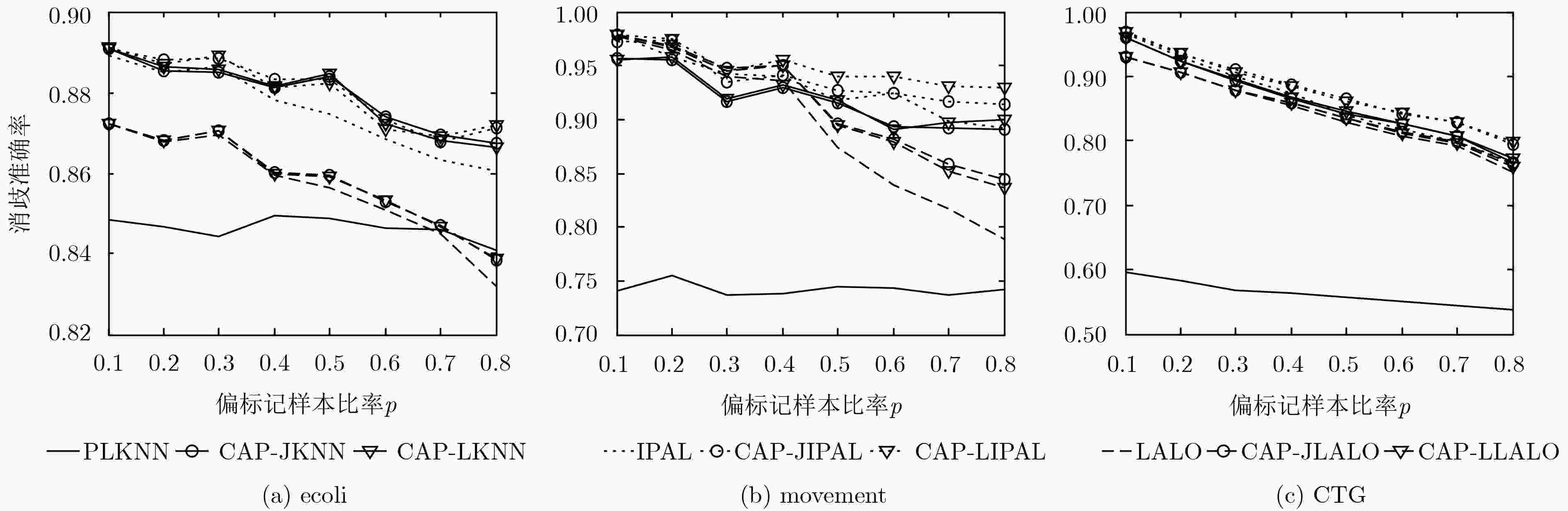
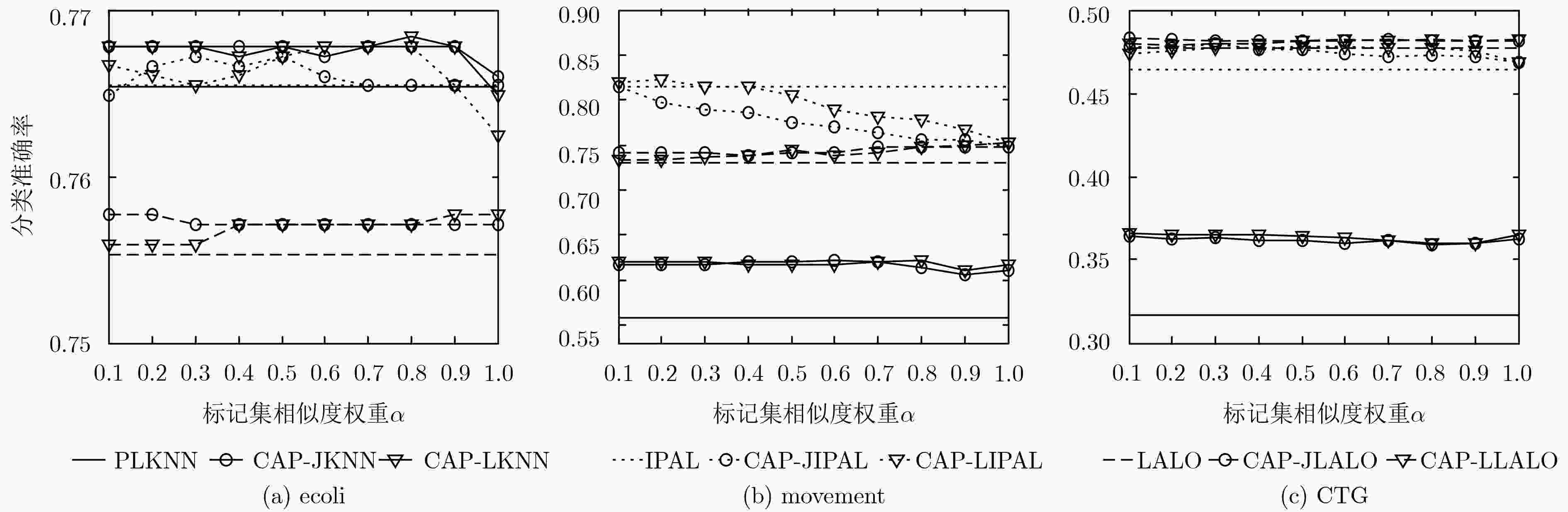
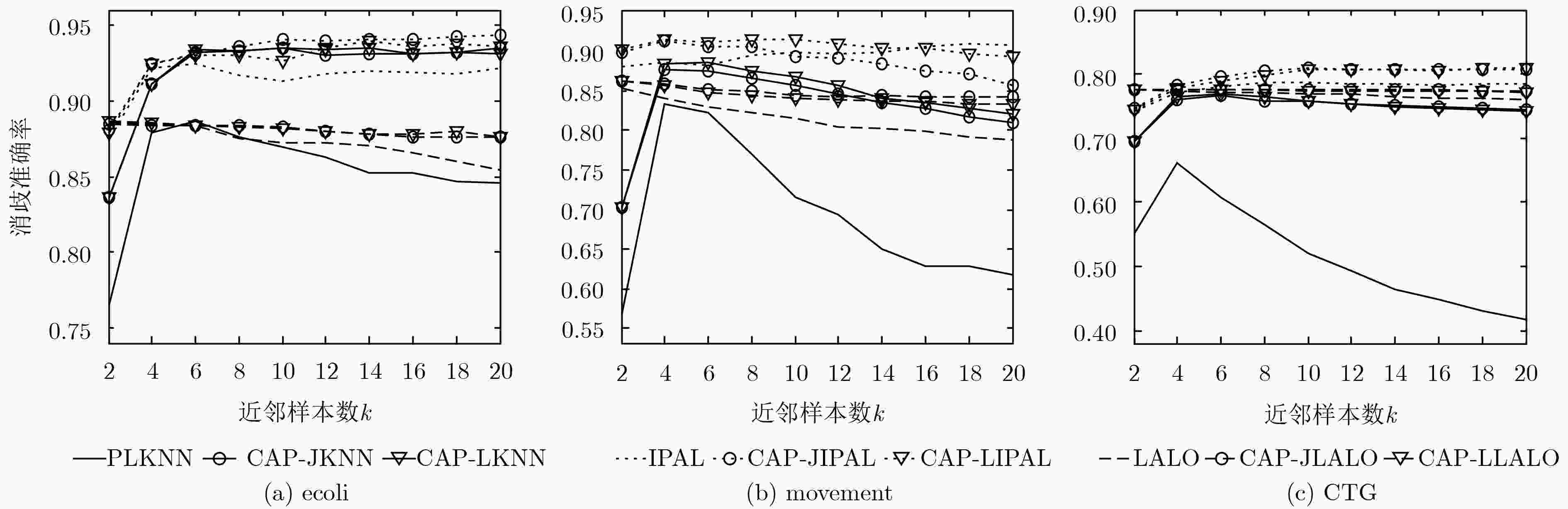
数据集 消歧准确率(mean±std.) Lost MSRCv2 BirdSong FG-NET Soccer Player Yahoo! News PLKNN 67.54±0.09 51.00±0.09 68.69±0.04 11.06±0.13 52.60±0.02 66.06±0.02 CAP-JKNN 73.60±0.10 62.19±0.08 77.14±0.04 14.71±0.15 69.55±0.01 80.00±0.02 CAP-LKNN 73.38±0.13 61.88±0.09 76.67±0.04 14.81±0.17 69.22±0.02 79.78±0.05 PLKNN(监督) 84.93±0.04 73.07±0.02 84.29±0.14 14.94±0.05 90.65±0.03 91.21±0.03 IPAL 84.01±0.15 70.58±0.15 83.61±0.04 15.28±0.19 67.65±0.03 84.99±0.05 CAP-JIPAL 85.58±0.17 71.25±0.20 84.22±0.04 15.40±0.19 67.94±0.02 85.33±0.04 CAP-LIPAL 85.39±0.24 70.92±0.12 84.40±0.05 14.86±0.17 67.89±0.07 85.21±0.03 IPAL(监督) 85.43±0.32 76.43±0.22 85.92±0.10 15.53±0.18 71.43±0.05 86.43±0.06 LALO 75.05±1.24 59.42±0.89 78.14±0.75 15.92±0.69 – – CAP-JLALO 76.80±1.11 59.48±1.09 78.02±0.81 15.69±0.75 – – CAP-LLALO 80.22±1.08 59.72±0.82 78.24±0.64 15.76±0.94 – – LALO(监督) 84.53±1.53 60.04±1.14 79.25±0.88 16.13±0.62 – – 表 6 不同算法在真实偏标记数据集上的分类准确率(%)
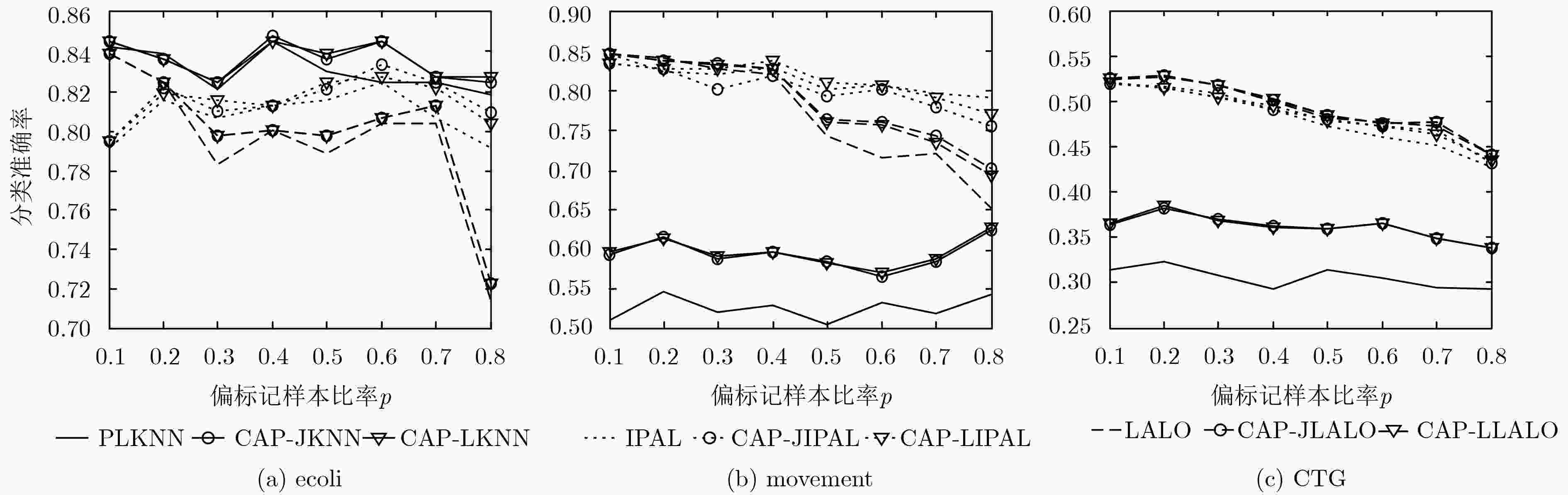
数据集 消歧准确率(mean±std.) Lost MSRCv2 BirdSong FG-NET Soccer Player Yahoo! News PLKNN 61.48±0.78 44.12±0.36 64.66±0.23 5.58±0.42 49.55±0.04 58.30±0.06 CAP-JKNN 64.01±0.65 46.35±0.38 66.01±0.26 6.24±0.38 50.77±0.09 61.18±0.05 CAP-LKNN 63.58±0.72 46.14±0.48 65.88±0.21 5.74±0.56 50.43±0.09 60.50±0.12 PLKNN(监督) 69.26±0.48 51.33±0.30 68.49±0.13 6.98±0.21 54.26±0.05 61.53±0.08 IPAL 73.18±0.79 53.08±0.33 71.09±0.33 5.28±0.55 54.84±0.10 65.88±0.14 CAP-JIPAL 73.95±0.68 53.35±0.50 71.34±0.30 5.45±0.60 55.00±0.10 66.02±0.16 CAP-LIPAL 73.44±0.68 52.61±0.71 71.60±0.26 5.89±0.57 54.46±0.18 66.02±0.18 IPAL (监督) 75.04±0.82 55.71±0.46 72.05±0.27 5.95±0.62 55.38±0.13 66.83±0.15 LALO 72.15±3.04 50.13±2.03 72.99±1.54 6.11±1.61 – – CAP-JLALO 73.02±2.88 49.23±2.10 73.00±1.62 5.96±1.19 – – CAP-LLALO 74.84±2.20 50.27±3.19 73.37±1.50 6.76±1.64 – – LALO(监督) 76.68±2.19 52.31±2.49 74.87±1.26 7.03±1.29 – – -
HÜLLERMEIER E and BERINGER J. Learning from ambiguously labeled examples[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2006, 10(5): 419–439. doi: 10.3233/IDA-2006-10503 SONG Jingqi, LIU Hui, GENG Fenghuan, et al. Weakly-supervised classification of pulmonary nodules based on shape characters[C]. The 14th International Conference on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, The 14th International Conference on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, The 2nd International Conference on Big Data Intelligence and Computing and Cyber Science and Technology Congress, Auckland, New Zealand, 2016: 228–232. TANG Caizhi and ZHANG Minling. Confidence-rated discriminative partial label learning[C]. The 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 2611–2617. TODA T, INOUE S, and UEDA N. Mobile activity recognition through training labels with inaccurate activity segments[C]. The 13th International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services, Hiroshima, Japan, 2016: 57–64. YU Fei and ZHANG Minling. Maximum margin partial label learning[J]. Machine Learning, 2017, 106(4): 573–593. doi: 10.1007/s10994-016-5606-4 LUO Jie and ORABONA F. Learning from candidate labeling sets[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2010: 1504–1512. ZHANG Minling and YU Fei. Solving the partial label learning problem: An instance-based approach[C]. The 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015: 4048–4054. FENG Lei and AN Bo. Leveraging latent label distributions for partial label learning[C]. The Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 2107–2113. COUR T, SAPP B, and TASKAR B. Learning from partial labels[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 1501–1536. ZHOU Zhihua. A brief introduction to weakly supervised learning[J]. National Science Review, 2018, 5(1): 44–53. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx106 TOLDO R and FUSIELLO A. Robust multiple structures estimation with J-linkage[C]. The 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 2008: 537–547. DUA D and TANISKIDOU E K. UCI machine learning repository[EB/OL]. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml, 2017. ZENG Zinan, XIAO Shijie, JIA Kui, et al. Learning by associating ambiguously labeled images[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 708–715. GUILLAUMIN M, VERBEEK J, and SCHMID C. Multiple instance metric learning from automatically labeled bags of faces[C]. The 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 2010: 634–647. ZHANG Minling, ZHOU Binbin, and LIU Xuying. Partial label learning via feature-aware disambiguation[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1335–1344. BRIGGS F, FERN X Z, and RAICH R. Rank-loss support instance machines for MIML instance annotation[C]. The 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Beijing, China, 2012: 534–542. LIU Liping and DIETTERICH T G. A conditional multinomial mixture model for superset label learning[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 548–556. ZHANG Minling, YU Fei, and TANG Caizhi. Disambiguation-free partial label learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2017, 29(10): 2155–2167. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2721942 ZHANG Minling and YU Fei. Solving the partial label learning problem: An instance-based approach[C]. The 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015: 4048–4054. -





 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:
