Recognition of Network Security Situation Elements Based on Depth Stack Encoder and Back Propagation Algorithm
-
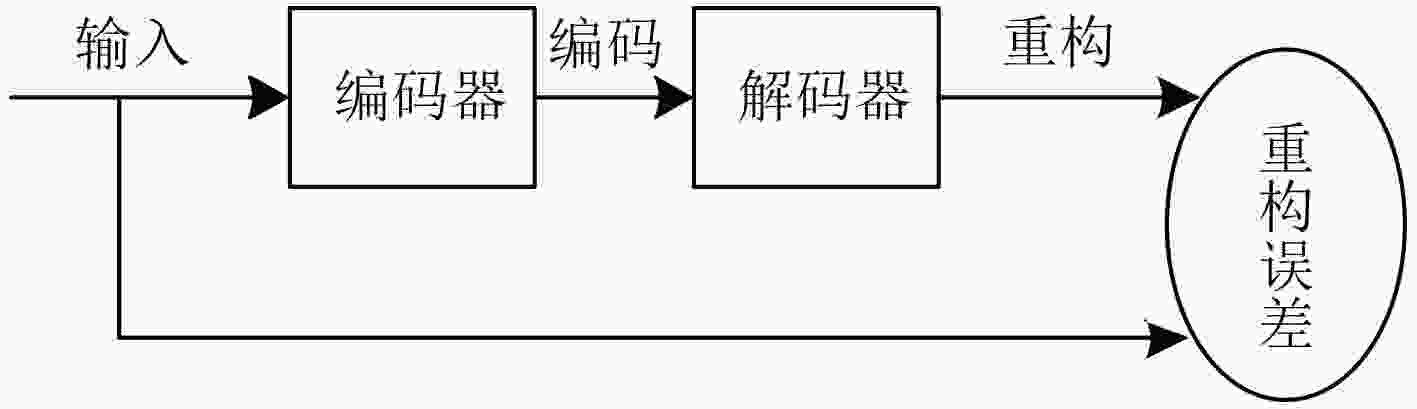
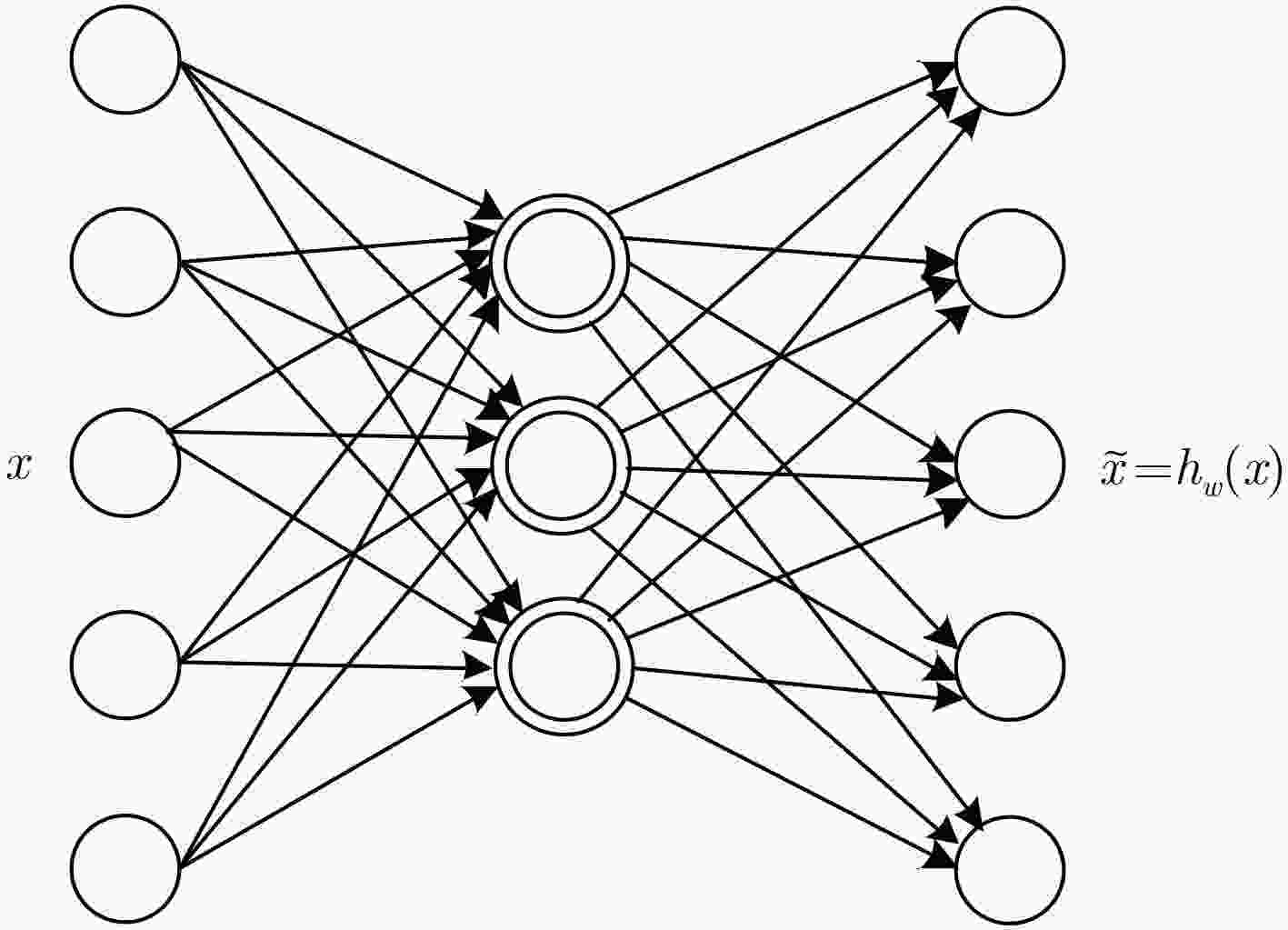
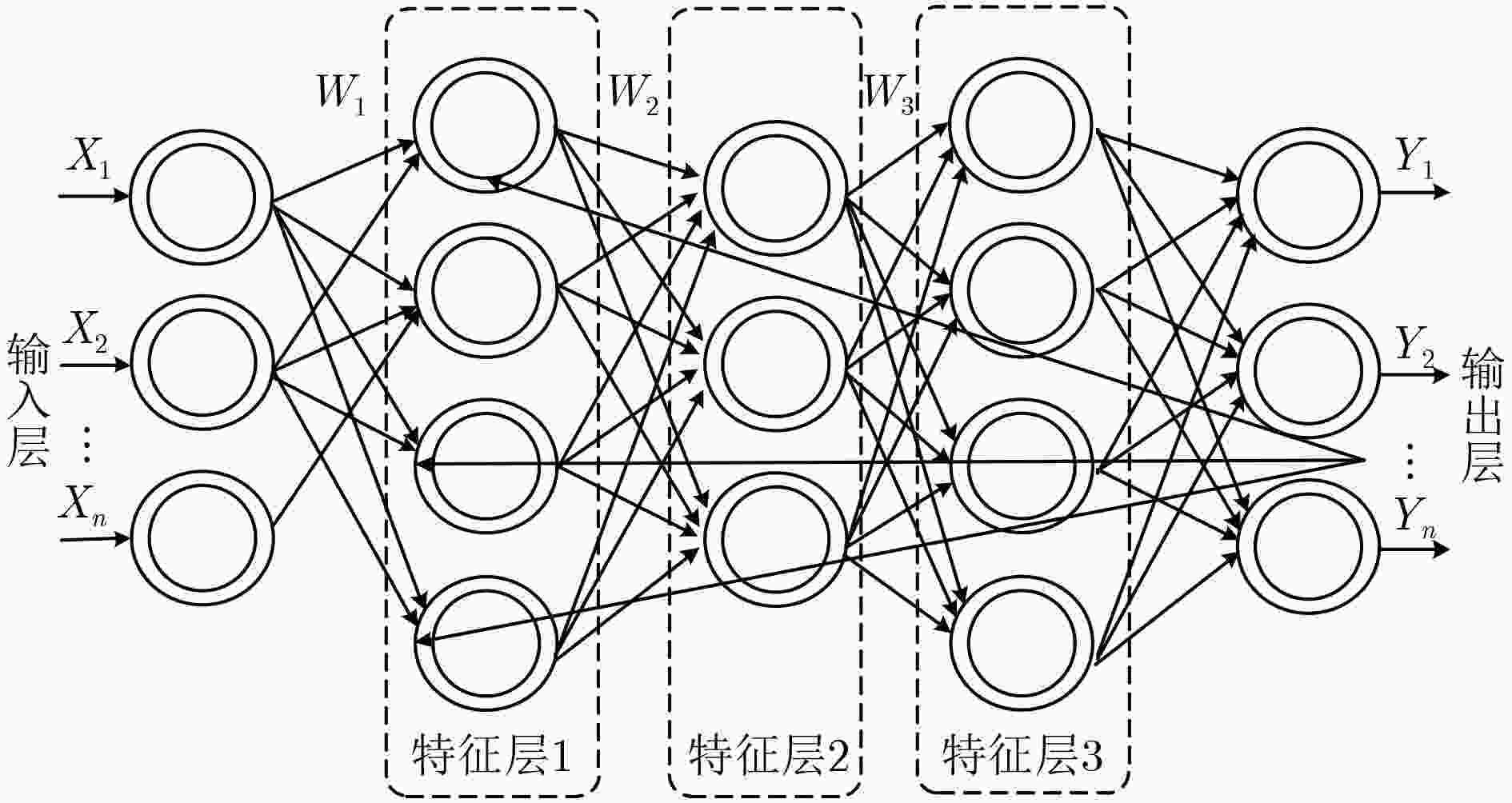
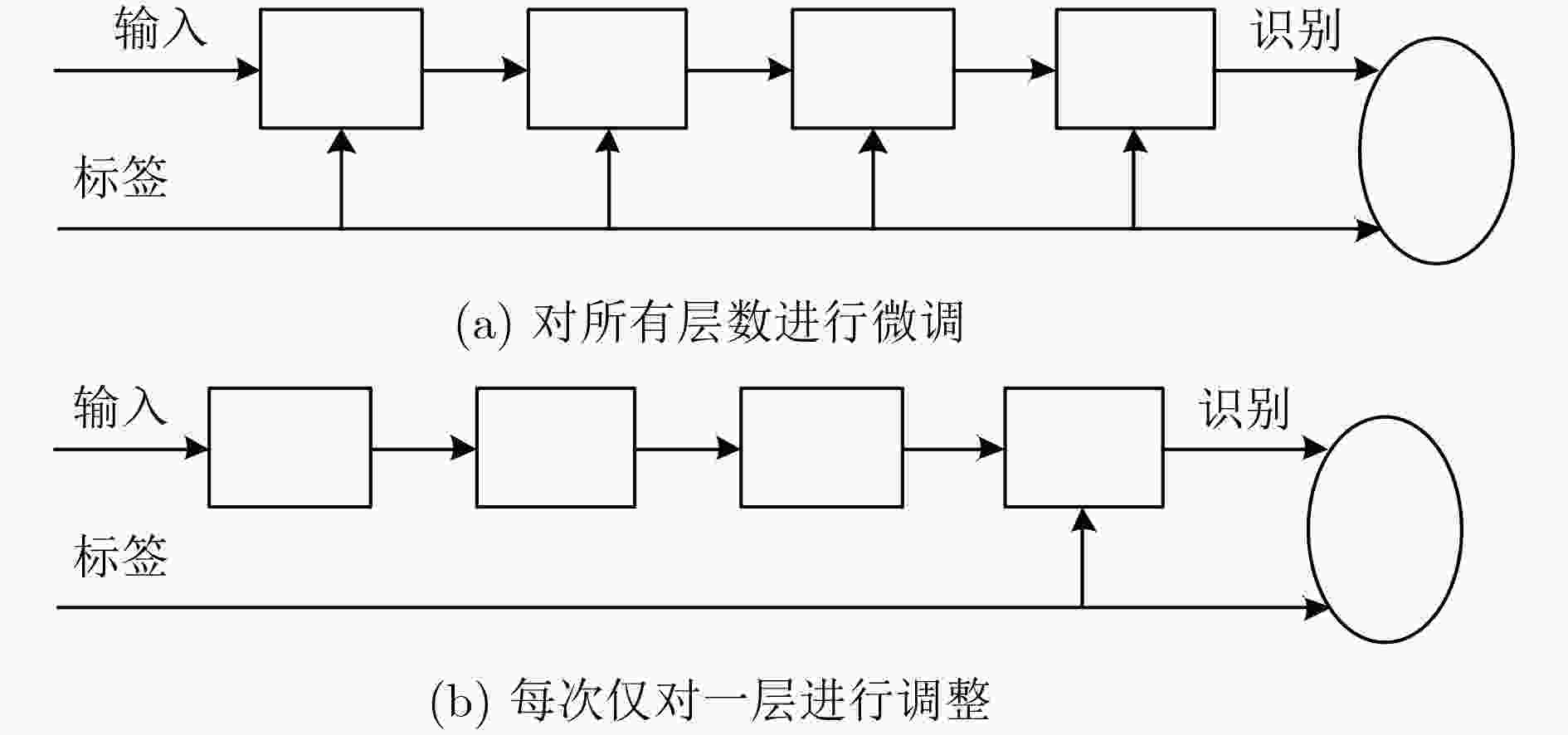
摘要: 网络安全态势要素识别的基础是对态势数据集进行有效的特征提取。针对反向传播(BP)神经网络对海量安全态势信息数据学习时过度依赖数据标签的问题,该文提出一种结合深度堆栈编码器和反向传播算法的网络安全态势要素识别方法,通过无监督学习算法逐层训练网络,在此基础上堆叠得到深度堆栈编码器,利用编码器提取数据集特征,实现了网络的无监督训练。仿真实验验证了该方法能有效提升安全态势感知的效能和准确度。Abstract: The basis of the identification of network security situation element is to perform the feature extraction of situation data effectively. Considering the problem that the Back Propagation(BP) neural networks have excessive dependence on data labels when it has a learning of massive security situation information data, a network security situation element identification method is proposed, which combines deep stack encoder and BP algorithm. It trains the network layer by layer through unsupervised learning algorithm. On this basis the deep track encoder by stacking can be obtained. The unsupervised training of the network is realized when using the encoder to extract the characteristic of the data sets. It is verified by simulation experiments that the method can improve the performance and accuracy of situational awareness effectively.
-
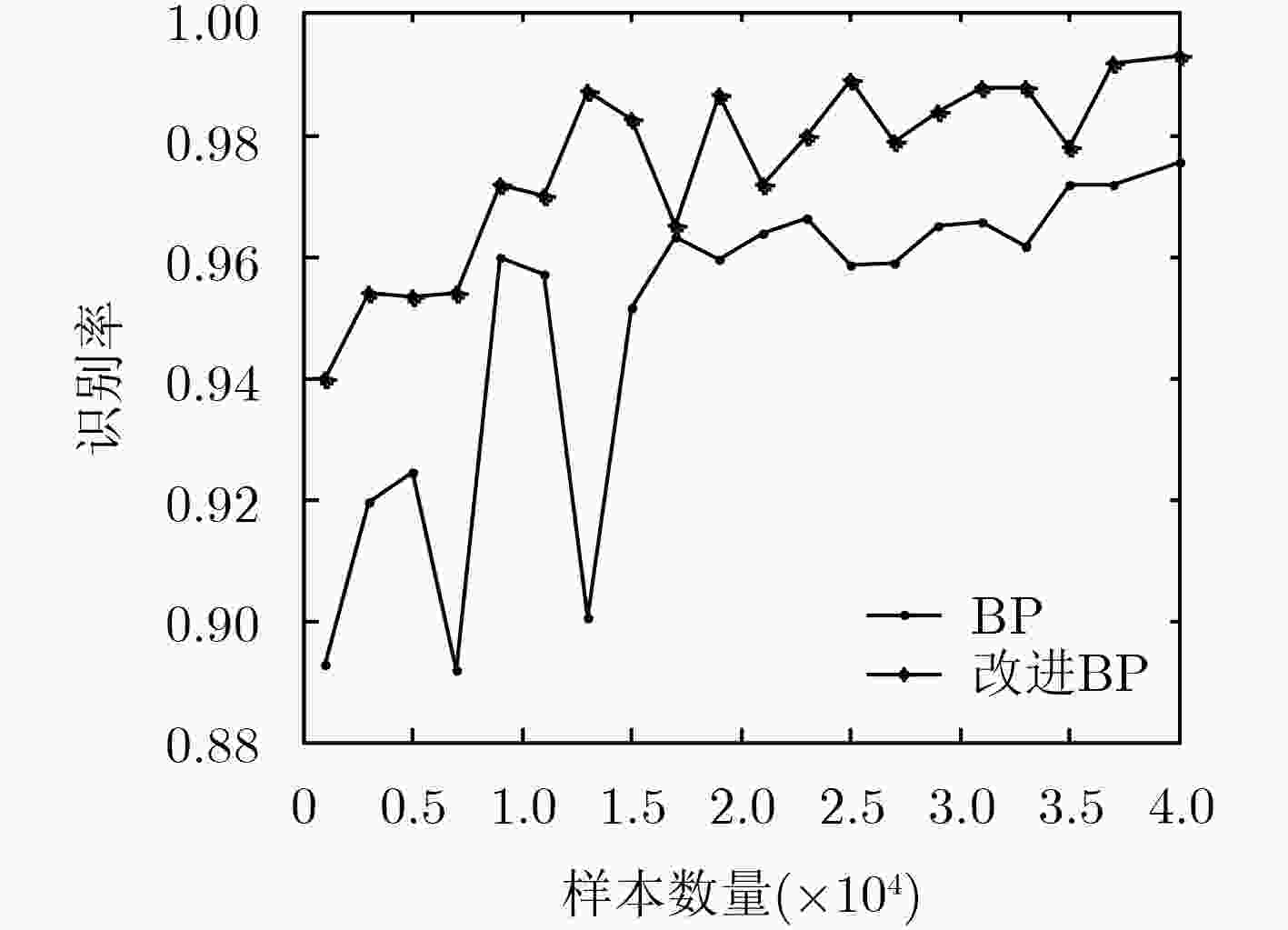
表 1 不同样本数量下的BP神经网络和改进型BP神经网络识别率结果
样本数量 识别率 BP 改进BP 1000 0.893 0.940 3000 0.919 0.954 5000 0.924 0.953 7000 0.892 0.954 9000 0.960 0.972 11000 0.957 0.970 13000 0.901 0.987 15000 0.952 0.982 17000 0.963 0.965 19000 0.959 0.986 21000 0.964 0.972 23000 0.966 0.980 25000 0.958 0.989 27000 0.959 0.979 29000 0.965 0.984 31000 0.965 0.988 33000 0.961 0.988 35000 0.972 0.978 37000 0.972 0.992 40000 0.975 0.993 表 2 不同标签占比下的BP神经网络和改进型BP神经网络识别率结果
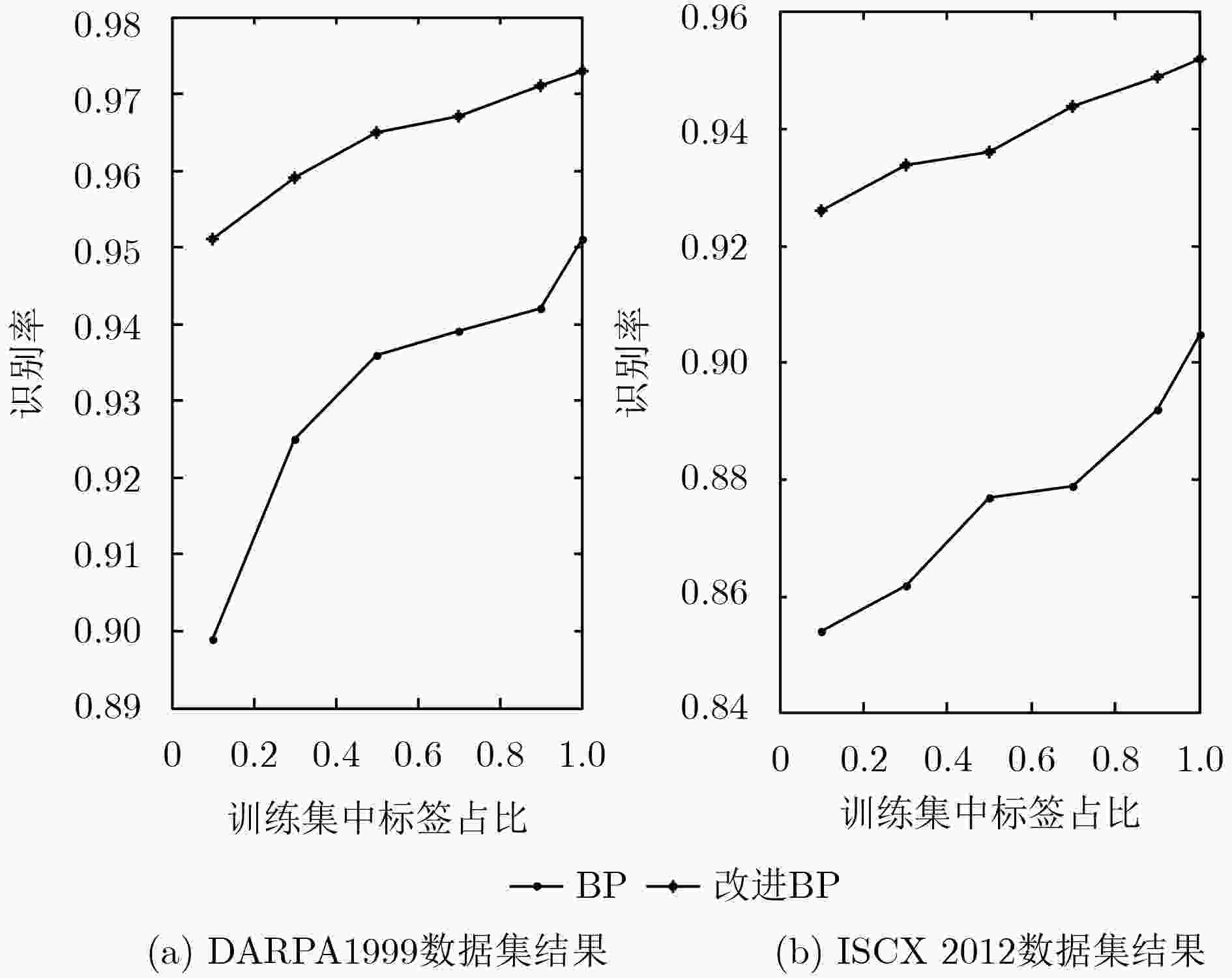
训练集中标签占比(%) 识别率(DARPA1999) 识别率(ISCX 2012) BP 改进BP BP 改进BP 10 0.899 0.951 0.854 0.926 30 0.925 0.959 0.862 0.934 50 0.936 0.965 0.877 0.936 70 0.939 0.967 0.879 0.944 90 0.942 0.971 0.892 0.949 100 0.951 0.973 0.905 0.952 -
国家计算机网络应急技术处理协调中心. 2017年我国互联网网络安全态势综述[EB/OL]. http://www.cert.org.cn/publish/main/upload/File/situation.pdf, 2018.National Internet Emergency Center. Summary of China’s Internet security situation in 2018[EB/OL]. http://www.cert.org.cn/publish/main/upload/File/situation.pdf, 2018. SRIHARI R K. Situation awareness through concept-based information extraction[EB/OL]. http://www.dawnbreaker.com/vas05, 2015. ZHANG Songmei, YAO Shan, YE Xin'en, et al. A network security situation analysis framework based on information fusion[C]. The 6th IEEE Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, Chongqing, China, 2011: 326-332. doi: 10.1109/ITAIC.2011.6030216. 韦勇, 连一峰, 冯登国. 基于信息融合的网络安全态势评估模型[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2009, 46(3): 353–362.WEI Yong, LIAN Yifeng, and FENG Dengguo. A network security situational awareness model based on information fusion[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2009, 46(3): 353–362. 陈秀真, 郑庆华, 管晓宏, 等. 层次化网络安全威胁态势量化评估方法[J]. 软件学报, 2006, 17(4): 885–897.CHEN Xiuzhen, ZHENG Qinghua, GUAN Xiaohong, et al. Quantitative hierarchical threat evaluation model for network security[J]. Journal of Software, 2006, 17(4): 885–897. LIU Zhiming, LI Sheng, HE Jin, et al. Complex network security analysis based on attack graph model[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, Harbin, China, 2012: 183–186. doi: 10.1109/IMCCC.2012.50. HINTON G E, OSINDERO S, and TEH Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527–1554. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 ERHAN D, BENGIO Y, COURVILLE A, et al. Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning?[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11: 625–660. BENGIO Y. Learning deep architectures for AI[J]. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1): 1–127. doi: 10.1561/2200000006 VINCENT P, LAROCHELLE H, LAJOIE I, et al. Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11: 3371–3408. RIFAI S, VINCENT P, MULLER X, et al. Contractive auto-encoders: Explicit invariance during feature extraction[C]. The 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2011: 122-132. EVANS R and GREFENSTETTE E. Learning explanatory rules from noisy data[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2018, 61: 1–64. doi: 10.1613/jair.5714 BRONSTEIN M M, BRUNA J, LECUN Y, et al. Geometric deep learning: Going beyond Euclidean data[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(4): 18–42. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2693418 LIPPMANN R, HAINES J W, FRIED D J, et al. The 1999 DARPA off-line intrusion detection evaluation[J]. Computer Networks, 2000, 34(4): 579–595. doi: 10.1016/S1389-1286(00)00139-0 SHIRAVI A, SHIRAVI H, TAVALLAEE M, et al. Toward developing a systematic approach to generate benchmark datasets for intrusion detection[J]. Computers& Security, 2012, 31(3): 357–374. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2011.12.012 KONIDARIS G, KAELBLING L P, and LOZANO-PEREZ T. From skills to symbols: Learning symbolic representations for abstract high-level planning[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2018, 61: 215–289. doi: 10.1613/jair.5575 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
