Depth Estimation of Monocular Road Images Based on Pyramid Scene Analysis Network
-
摘要: 针对从单目视觉图像中估计深度信息时存在的预测精度不够准确的问题,该文提出一种基于金字塔池化网络的道路场景深度估计方法。该方法利用4个残差网络块的组合提取道路场景图像特征,然后通过上采样将特征图逐渐恢复到原始图像尺寸,多个残差网络块的加入增加网络模型的深度;考虑到上采样过程中不同尺度信息的多样性,将提取特征过程中各种尺寸的特征图与上采样过程中相同尺寸的特征图进行融合,从而提高深度估计的精确度。此外,对4个残差网络块提取的高级特征采用金字塔池化网络块进行场景解析,最后将金字塔池化网络块输出的特征图恢复到原始图像尺寸并与上采样模块的输出一同输入预测层。通过在KITTI数据集上进行实验,结果表明该文所提的基于金字塔池化网络的道路场景深度估计方法优于现有的估计方法。Abstract: Considering the problem that the prediction accuracy is not accurate enough when the depth information is recovered from the monocular vision image, a method of depth estimation of road scenes based on pyramid pooling network is proposed. Firstly, using a combination of four residual network blocks, the road scene image features are extracted, and then through the sampling, the features are gradually restored to the original image size, and the depth of the residual block is increased. Considering the diversity of information in different scales, the features with same sizes extracted from the sampling process and the feature extraction process are merged. In addition, pyramid pooling network blocks are added to the advanced features extracted by four residual network blocks for scene analysis, and the feature graph output of pyramid pooling network blocks is finally restored to the original image size and input prediction layer together with the output of the upper sampling module. Through experiments on KITTI data set, the results show that the proposed method is superior to the existing method.
-
Key words:
- Monocular vision /
- Depth estimation /
- Neural network /
- Pyramid pooling network
-
表 1 深度图像的预测值与真实值之间的误差和相关性
RMSE Lg Lg_rms a1 a2 a3 Fine_coarse[17] 2.6440 0.272 0.167 0.488 0.948 0.972 ResNet50[18] 2.4618 0.243 0.126 0.674 0.943 0.972 ResNet_fcn50[19] 2.5284 0.247 0.134 0.636 0.950 0.979 D_U[20] 2.8246 0.305 0.127 0.634 0.916 0.945 UVD_fcn[21] 2.6507 0.264 0.145 0.566 0.945 0.970 本文方法 2.3504 0.230 0.120 0.684 0.949 0.975 表 2 不同恢复尺度方法的结果
RMSE Lg Lg_rms a1 a2 a3 使用反卷积层恢复尺度的方法 2.3716 0.237 0.125 0.673 0.946 0.973 使用卷积块恢复尺度的方法 2.4724 0.240 0.129 0.646 0.948 0.974 使用上采样层恢复尺度的方法 2.3504 0.230 0.120 0.684 0.949 0.975 -
LUO Yue, REN J, LIN Mude, et al. Single view stereo matching[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 155–163. SILBERMAN N, HOIEM D, KOHLI P, et al. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 746–760. REN Xiaofeng, BO Liefeng, and FOX D. RGB-(D) scene labeling: Features and algorithms[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2759–2766. SHOTTON J, SHARP T, KIPMAN A, et al. Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2013, 56(1): 116–124. doi: 10.1145/2398356 ALP GÜLER R, NEVEROVA N, and KOKKINOS I. Densepose: Dense human pose estimation in the wild[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7297–7306. LUO Wenjie, SCHWING A G, and URTASUN R. Efficient deep learning for stereo matching[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 5695–5703. FLINT A, MURRAY D, and REID I. Manhattan scene understanding using monocular, stereo, and 3D features[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2228–2235. KUNDU A, LI Yin, DELLAERT F, et al. Joint semantic segmentation and 3D reconstruction from monocular video[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 703–718. YAMAGUCHI K, MCALLESTER D, and URTASUN R. Efficient joint segmentation, occlusion labeling, stereo and flow estimation[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 756–771. BAIG M H and TORRESANI L. Coupled depth learning[C]. 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Lake Placid, USA, 2016: 1–10. EIGEN D and FERGUS R. Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 2650–2658. SCHARSTEIN D and SZELISKI R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 47(1/3): 7–42. doi: 10.1023/A:1014573219977 UPTON K. A modern approach[J]. Manufacturing Engineer, 1995, 74(3): 111–113. doi: 10.1049/me:19950308 FLYNN J, NEULANDER I, PHILBIN J, et al. Deep stereo: Learning to predict new views from the world's imagery[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 5515–5524. SAXENA A, CHUNG S H, and NG A Y. 3-D depth reconstruction from a single still image[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 76(1): 53–69. KARSCH K, LIU Ce, and KANG S B. Depth transfer: Depth extraction from video using non-parametric sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(11): 2144–2158. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2316835 EIGEN D, PUHRSCH C, and FERGUS R. Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2014: 2366–2374. LAINA I, RUPPRECHT C, BELAGIANNIS V, et al. Deeper depth prediction with fully convolutional residual networks[C]. The 4th International Conference on 3D Vision, Stanford, USA, 2016: 239–248. FU Huan, GONG Mingming, WANG Chaohui, et al. Deep ordinal regression network for monocular depth estimation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2002–2011. DIMITRIEVSKI M, GOOSSENS B, VEELAERT P, et al. High resolution depth reconstruction from monocular images and sparse point clouds using deep convolutional neural network[J]. SPIE, 2017, 10410: 104100H. MANCINI M, COSTANTE G, VALIGI P, et al. Toward domain independence for learning-based monocular depth estimation[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(3): 1778–1785. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2657002 GARG R, VIJAY KUMAR B G, CARNEIRO G, et al. Unsupervised CNN for single view depth estimation: Geometry to the rescue[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 740–756. KUZNIETSOV Y, STUCKLER J, and LEIBE B. Semi-supervised deep learning for monocular depth map prediction[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6647–6655. GODARD C, MAC AODHA O, and BROSTOW G J. Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6602–6611. ZORAN D, ISOLA P, KRISHNAN D, et al. Learning ordinal relationships for mid-level vision[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 388–396. CHEN Weifeng, FU Zhao, YANG Dawei, et al. Single-image depth perception in the wild supplementary Materia[C]. The 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 730–738. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, Ren Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Object detectors emerge in deep scene CNNs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6856, 2014. SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. UHRIG J, SCHNEIDER N, SCHNEIDER L, et al. Sparsity invariant CNNs[C]. 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision, Qingdao, China, 2017: 11–20. KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980, 2014. -





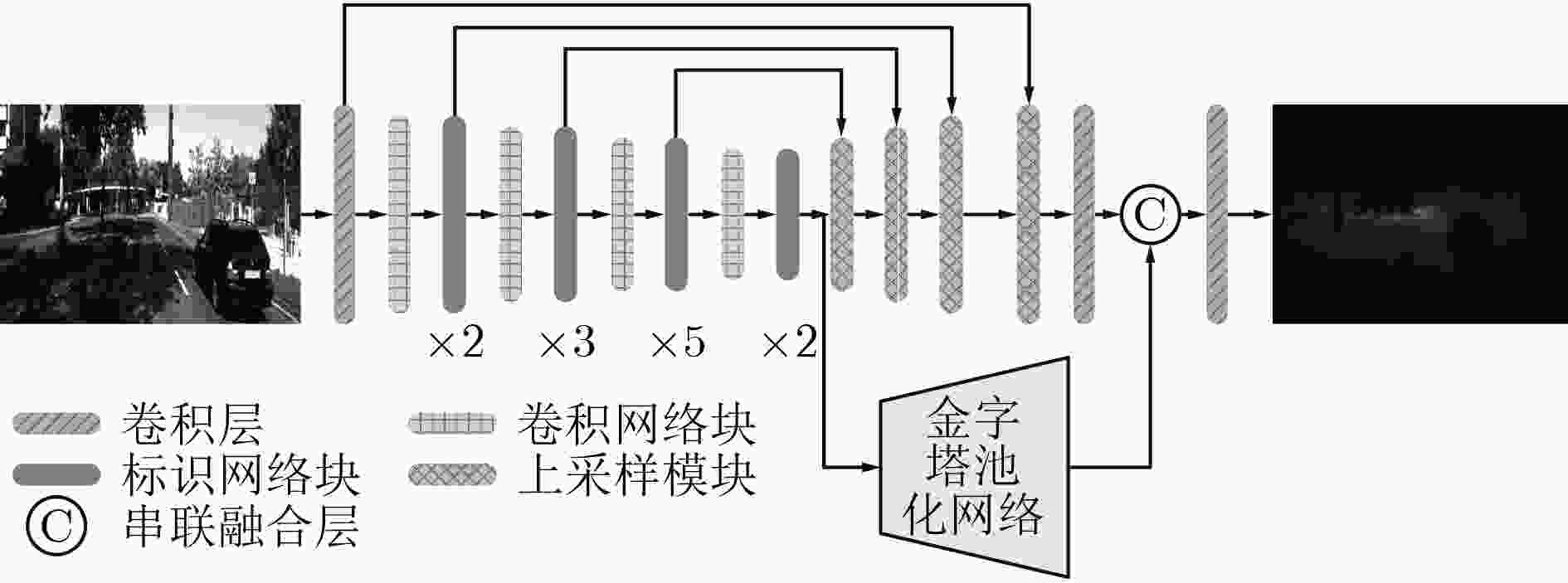
 下载:
下载:
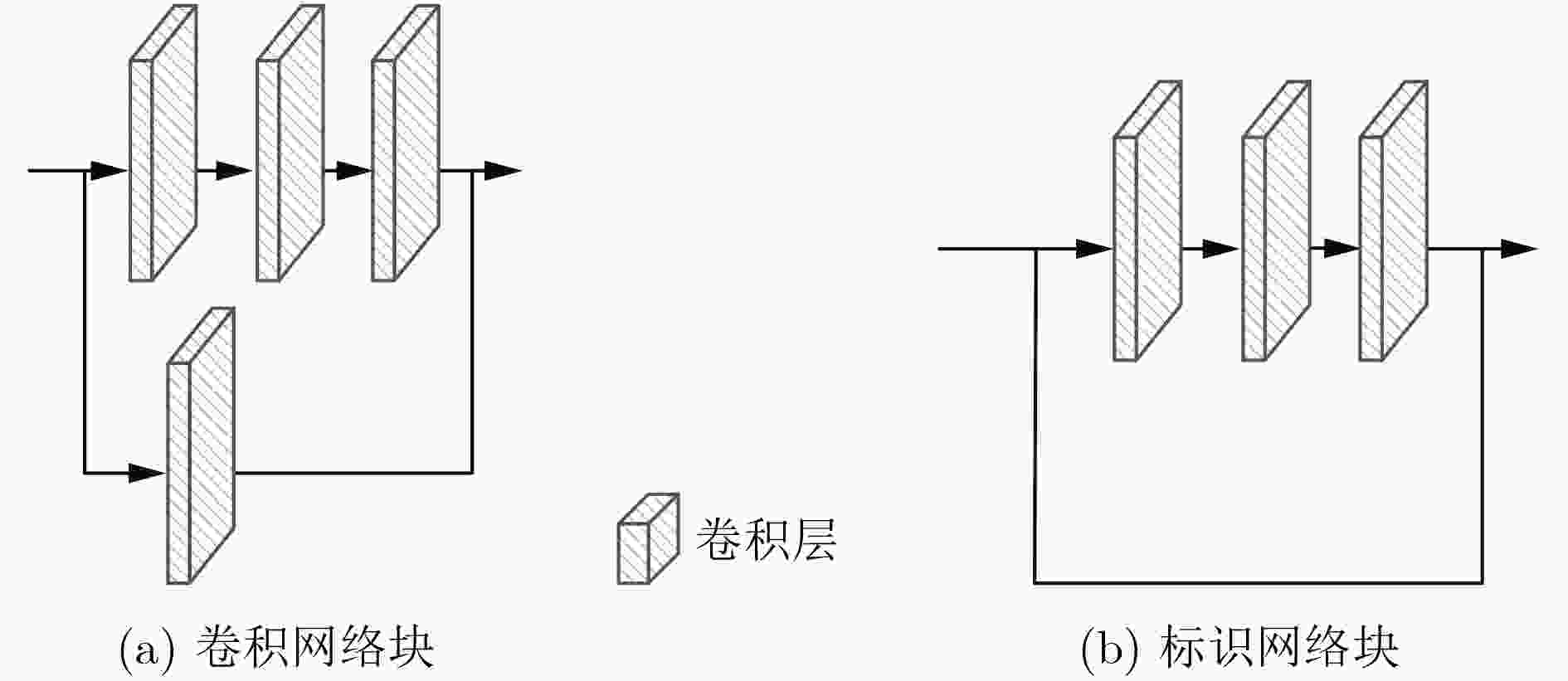
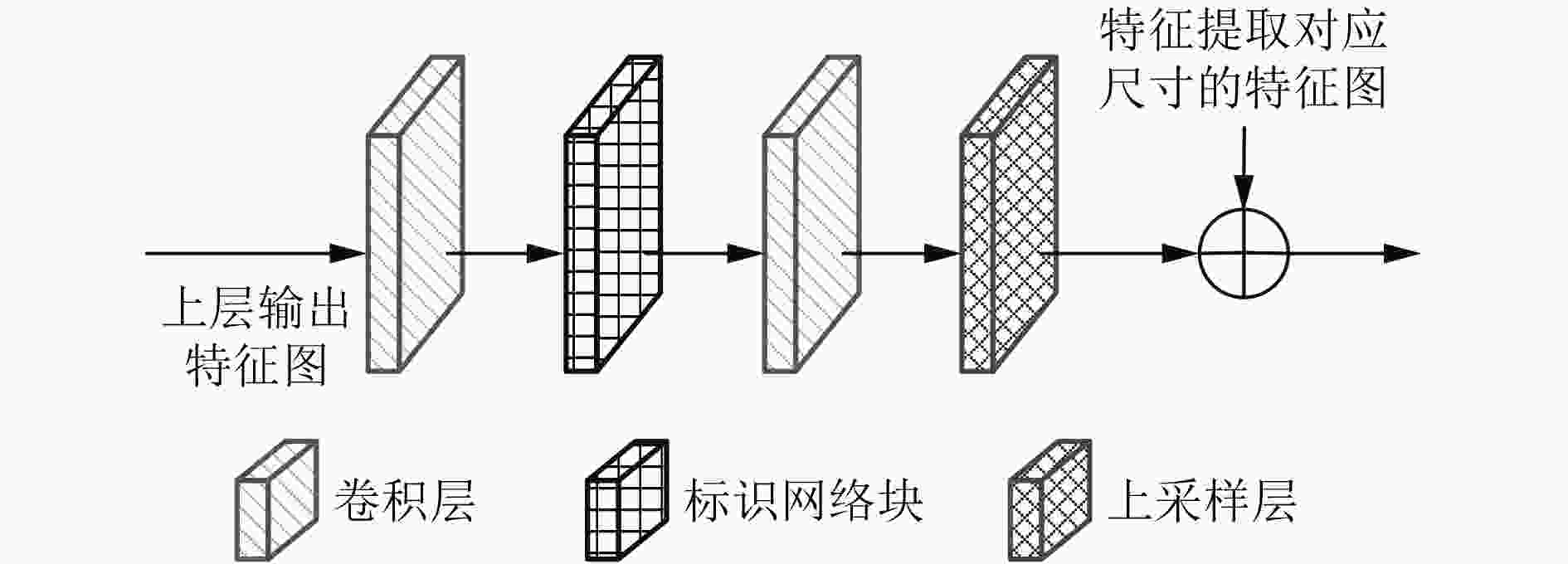
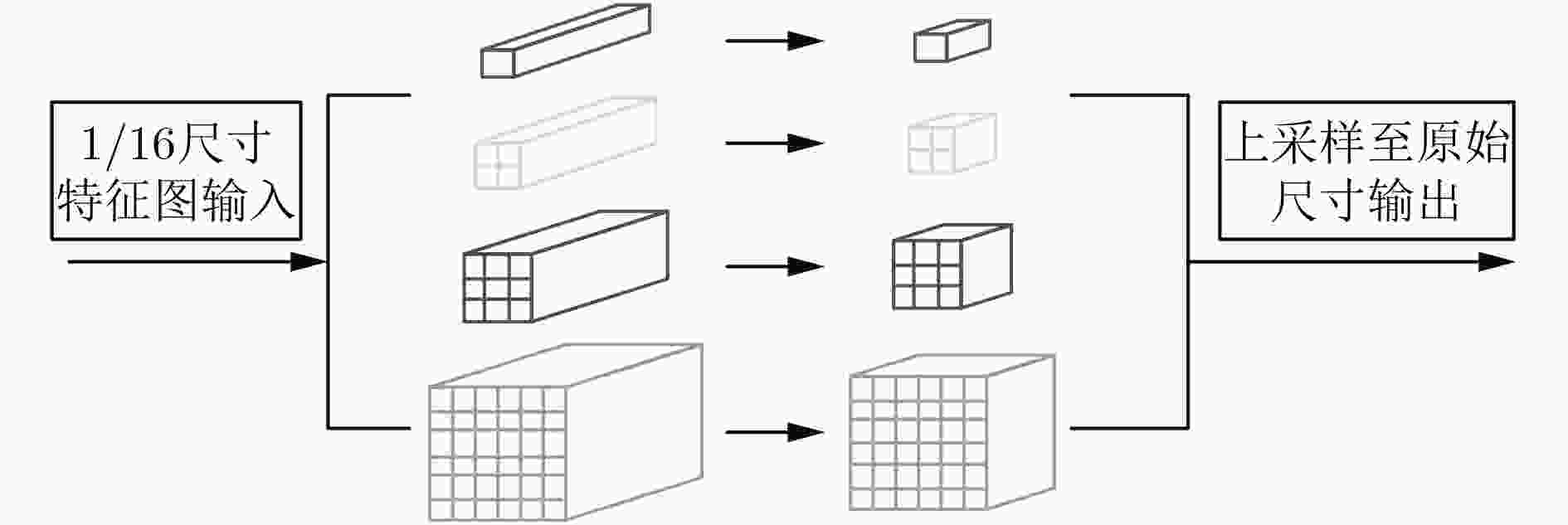


 下载:
下载:
