A Short Time 3D Geometry Reconstruction Method of Space Targets
-
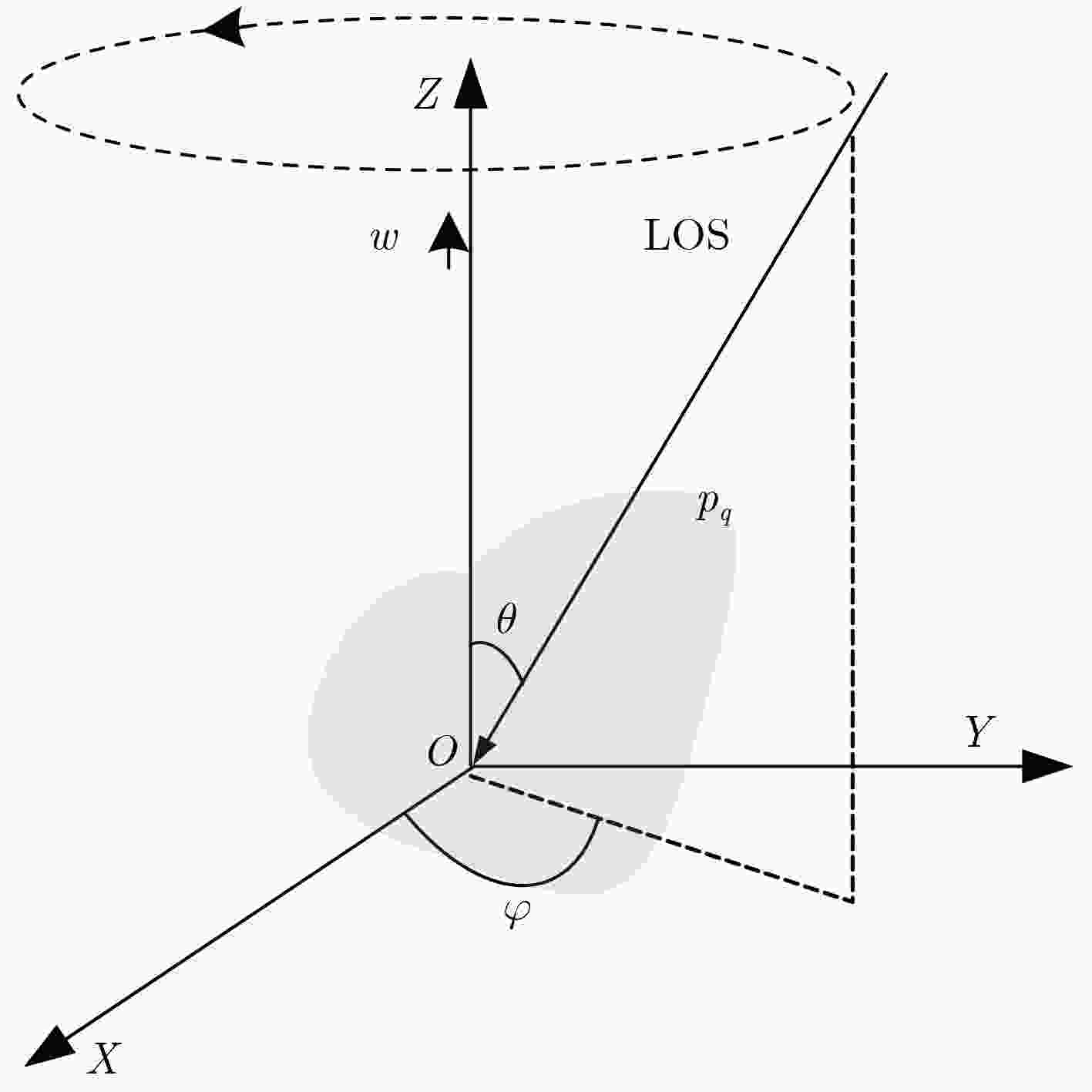
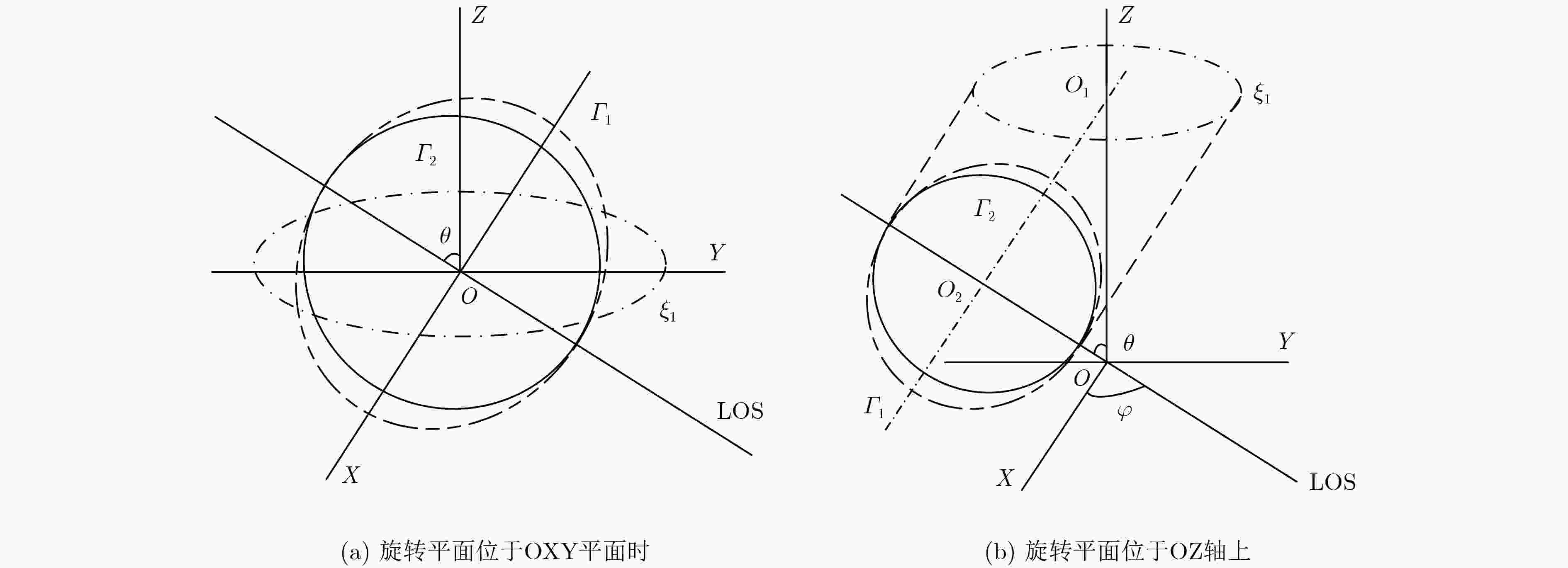
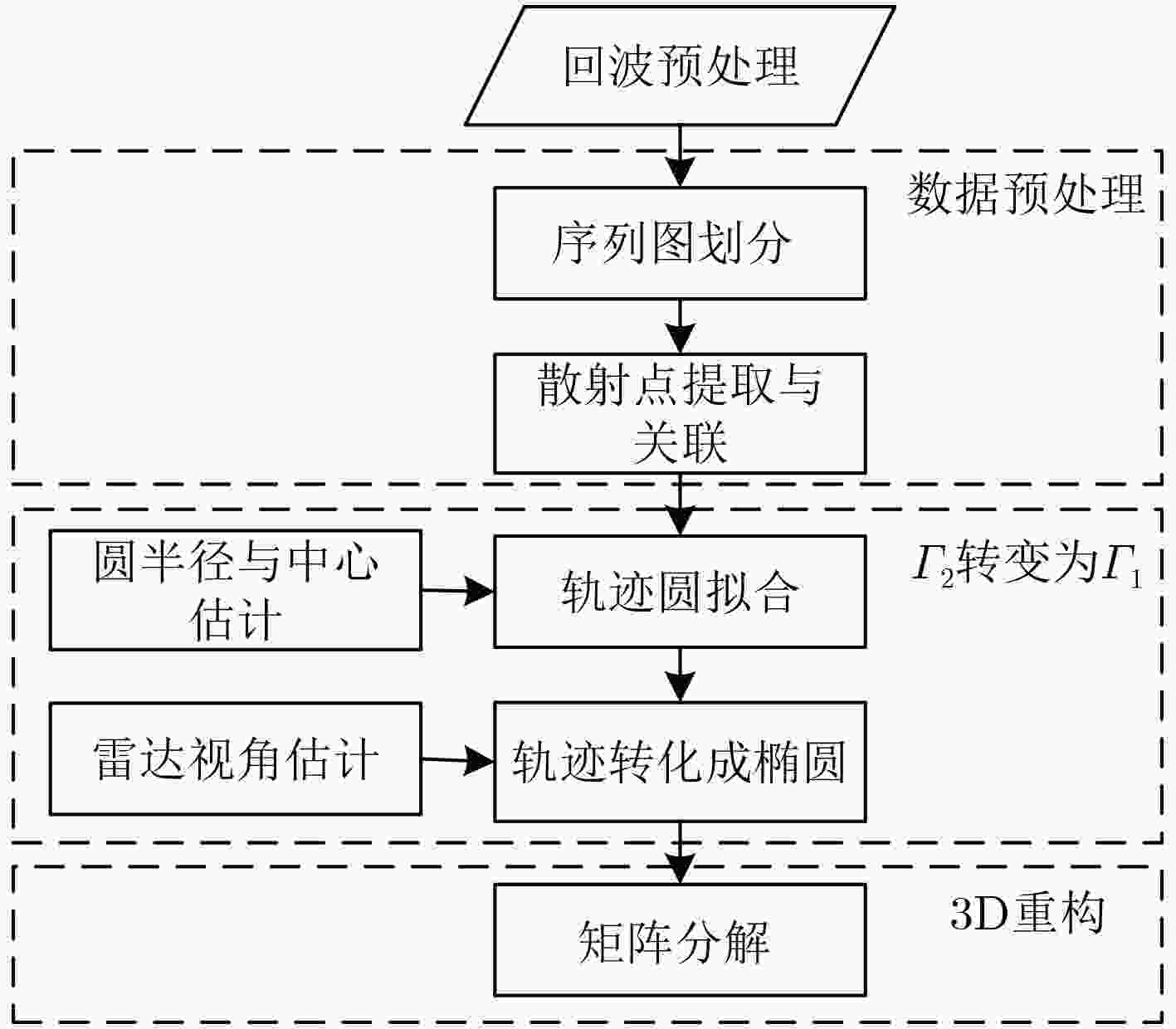
摘要: 通常空间自旋目标的3维(3D)重构都是通过对散射点轨迹进行矩阵分解的方法得到的,散射点轨迹是从雷达序列图提取并关联得到的。由于散射点提取与关联误差的存在,3D重构会出现精度下降,甚至失败的问题。另一方面,转台目标的散射点轨迹符合圆属性,这与几何投影理论认为散射点投影轨迹的椭圆属性相违背。为解决以上问题,该文提出了基于短时的空间目标3D重构算法。首先对提取的散射点轨迹进行2维圆属性拟合,使其轨迹光滑,更接近理论曲线。然后采用多视角的方法估计雷达视角(LOS),通过乘以雷达视角构成的系数,将圆属性轨迹曲线转变成椭圆属性轨迹曲线。通过对散射点椭圆属性轨迹进行矩阵分解的方法获得目标的3D结构。最后通过2个实验验证了该文所提算法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 雷达序列图 /
- 短时空间目标3D重构 /
- 圆属性拟合 /
- 矩阵分解
Abstract: Generally speaking, Three Dimension (3D) imaging of spinning space target is obtained by performing matrix factorization method on the scattering trajectories obtained from sequential radar images. Because of the errors of scattering center extraction and association, the 3D reconstruction accurate is reduced or even fail. In addition, the scattering center trajectory from turntable target consists with circle nature, which is inconsistent with the elliptic property of the scattering center trajectory obtained by optical geometry projection. To tackle these problems, this paper proposes a short time 3D reconstruction method of space target. Firstly, the retrieved trajectory is fitted with 2D circular nature to make the trajectory smooth and closer to the theoretical curve. Then the radar Line Of Sight (LOS) is estimated by multiple views and the circular curve is converted into elliptical curve by multiplying the coefficients calculated by the LOS. The 3D reconstruction can be obtained by performing matrix factorization method on elliptical curves. Finally, the simulations verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. -
表 1 实验参数
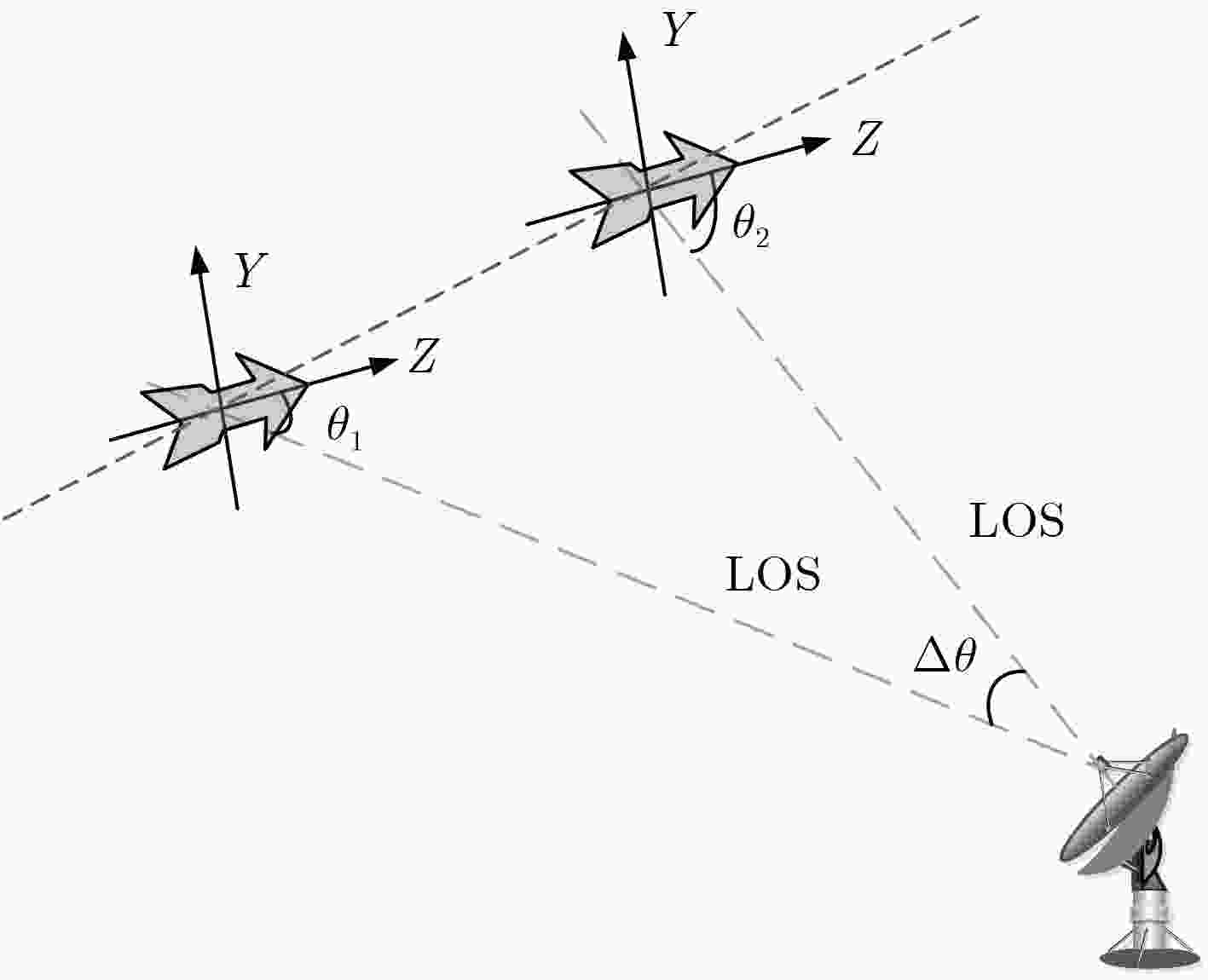
参数 数值 参数 数值 带宽(GHz) 2 相邻子孔径相差(°) 0.66 雷达视角(°) 45 目标转速(rad/s) 0.07 雷达重复频率(Hz) 600 子孔径大小(°) 4 信噪比(dB) 5 目标转轴 Z 轴 表 2 不同雷达视角差对应时长
情况 1 2 3 $\Delta \theta $(°) 5 3 2 耗时(s) 56.42 32.55 21.29 -
PATE-CORNELL E and SACHON M. Risks of particle hits during space walks in low earth orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(1): 134–146. doi: 10.1109/7.913673 SATO T. Shape estimation of space debris using single-range Doppler interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(2): 1000–1005. doi: 10.1109/36.752218 WANG Qi, XING Mengdao, LU Guangyue, et al. SRMF-CLEAN imaging algorithm for space debris[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(12): 3524–3533. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2007.910343 NING Yu, BAI Xueru, ZHOU Feng, et al. Method for inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of space debris using improved genetic algorithm[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(5): 812–821. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0048 XU Gang, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. 3D geometry and motion estimations of maneuvering targets for interferometric ISAR with sparse aperture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(5): 2005–2020. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2535362 WU Wenzhen, HU Pengjiang, XU Shiyou, et al. Image registration for InISAR based on joint translational motion compensation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(10): 1597–1603. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0140 MAYHAN J T, BURROWS M L, CUOMO K M, et al. High resolution 3D" snapshot”ISAR imaging and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(2): 630–642. doi: 10.1109/7.937474 MCFADDEN F E. Three-dimensional reconstruction from ISAR sequences[J]. SPIE, 2002, 4744: 58–67. LIU Lei, ZHOU Feng, BAI Xueru, et al. Joint cross-range scaling and 3D Geometry reconstruction of ISAR targets based on factorization method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1740–1750. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2526905 WANG Feng, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. Three-dimensional reconstruction from a multiview sequence of sparse ISAR imaging of a space target[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 611–620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2737988 LIU Lei, ZHOU Feng, and BAI Xueru. A modified EM algorithm for ISAR scatterer trajectory matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(7): 3953–3962. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2817650 段佳, 张磊, 邢孟道, 等. 合成孔径雷达目标特征提取新方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 41(4): 13–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2014.04.003DUAN Jia, ZHANG Lei, XING Mengdao, et al. Novel feature extraction method for synthetic aperture radar targets[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2014, 41(4): 13–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2014.04.003 DING Baiyuan, WEN Gongjian, HUANG Xiaohong, et al. Data augmentation by multilevel reconstruction using attributed scattering center for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(6): 979–983. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2692386 OH S, RUSSELL S, and SASTRY S. Markov chain Monte Carlo data association for multi-target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(3): 481–497. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2009.2012975 GRANSTRÖM K, SVENSSON L, REUTER S, et al. Likelihood-based data association for extended object tracking using sampling methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2018, 3(1): 30–45. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2017.2788184 -





 下载:
下载:
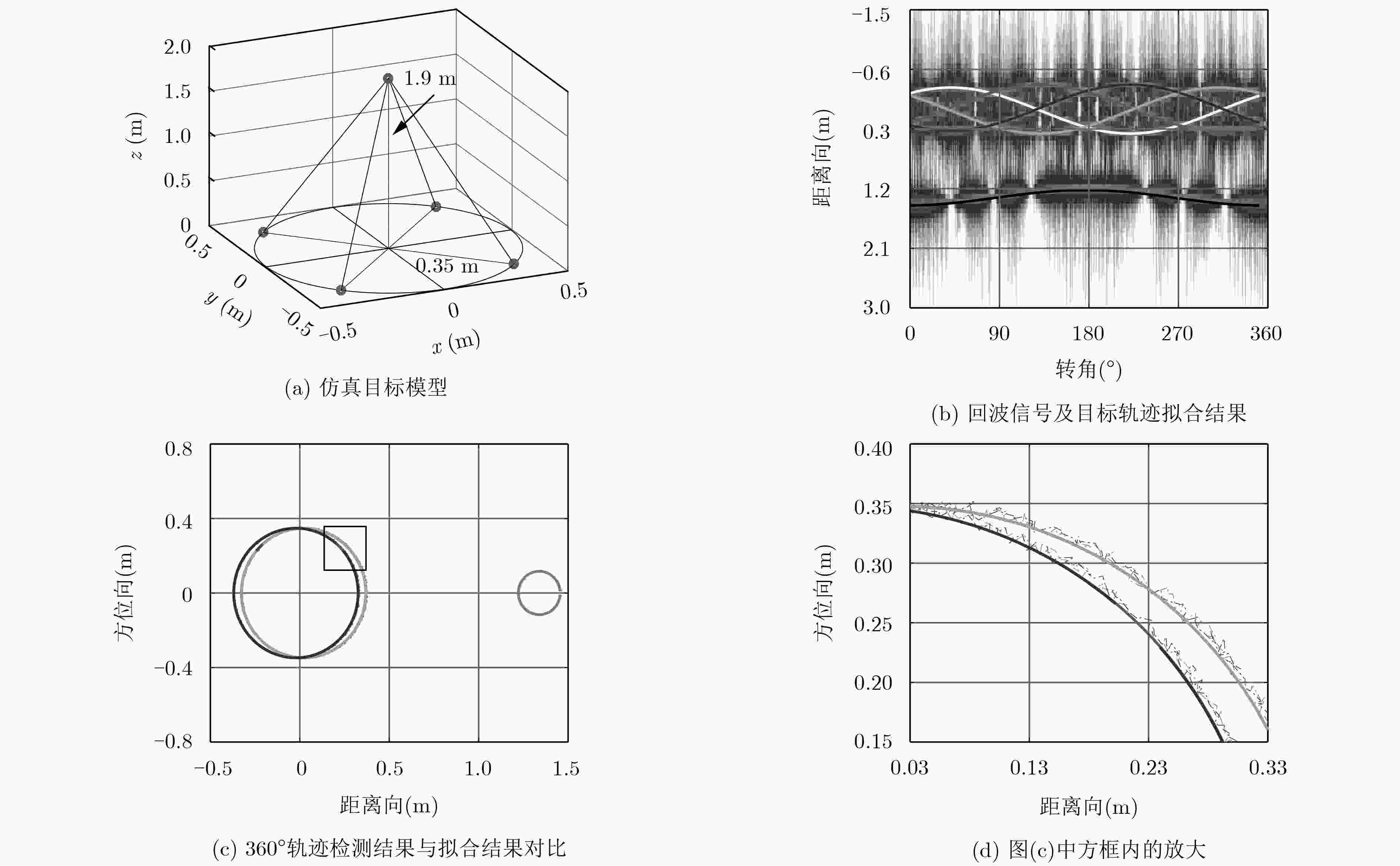
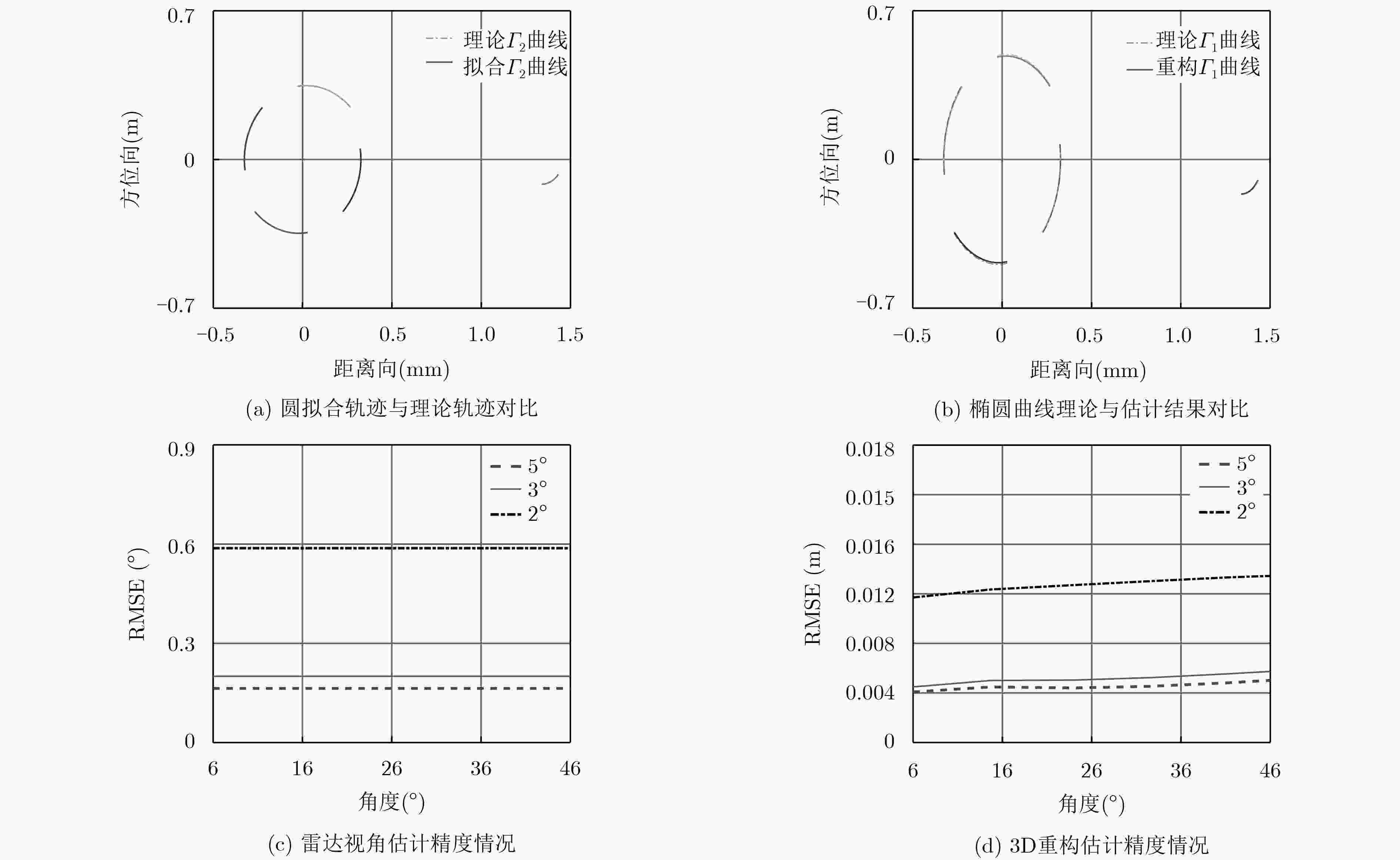
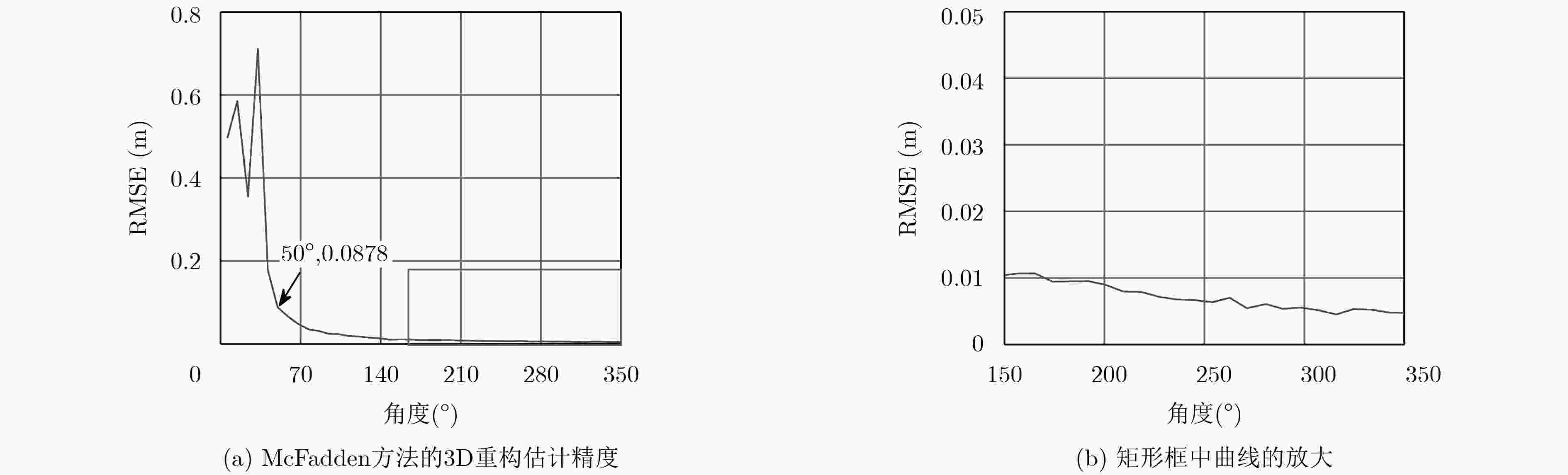
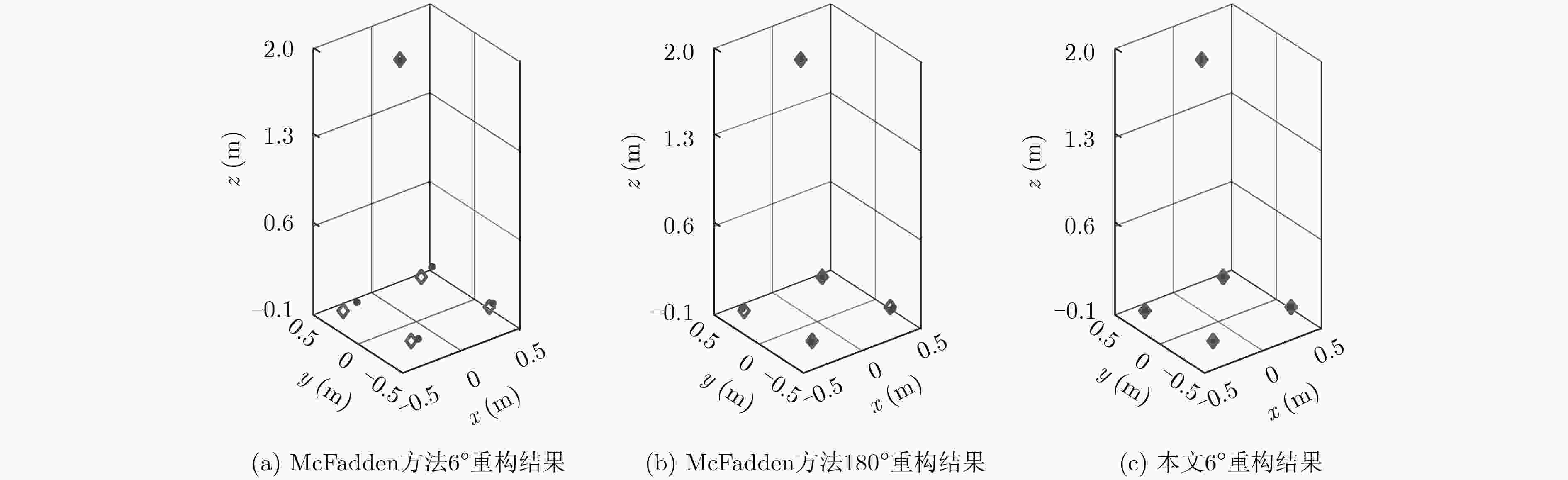


 下载:
下载:
