Driver Fatigue Detection Through Deep Transfer Learning in an Electroencephalogram-based System
-
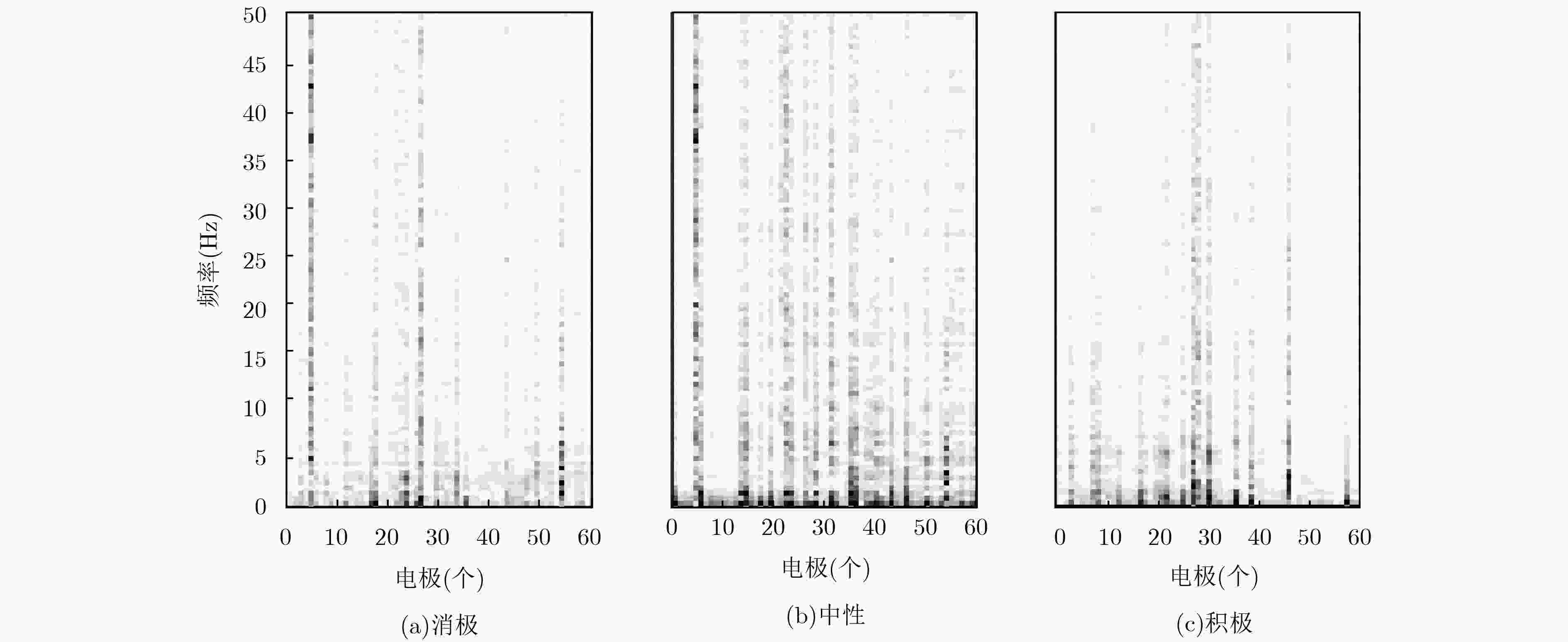
摘要: 脑电信号一直被誉为疲劳检测的“金标准”,驾驶者的精神状态可通过对脑电信号的分析得到。但由于脑电信号具有非线性、非平稳性和空间分辨率低等特点,传统的机器学习方法在运用脑电信号进行疲劳检测时还存在识别率低,特征提取操作繁琐等不足。为此,该文基于脑电信号的电极-频率分布图,提出运用深度迁移学习实现的驾驶疲劳检测方法,即搭建深度卷积神经网络,并利用SEED脑电情绪数据集对其进行预训练,然后通过迁移学习方法将其用于驾驶疲劳检测。实验结果表明,卷积神经网络模型能够很好地从电极-频率分布图中获得与疲劳状态相关的特征信息,达到较好的识别效果。此外,基于迁移学习策略可以将训练好的深度网络模型迁移到其他识别任务上,有助于推动脑电信号在驾驶疲劳检测系统中的应用。Abstract: ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) is regarded as a " gold standard” of fatigue detection and drivers’ vigilance states can be detected through the analysis of EEG signals. However, due to the characteristics of non-linear, non-stationary and low spatial resolution of EEG signals, traditional machine learning methods still have the disadvantages of low recognition rate and complicated feature extraction operations in EEG-based fatigue detection task. To tackle this problem, a fatigue detection method with transfer learning based on the Electrode-Frequency Distribution Maps (EFDMs) of EEG signals is proposed. A deep convolutional neural network is designed and pre-trained with SEED dataset, and then it is used for fatigue detection with transfer learning strategy. Experimental results show that the proposed convolutional neural network can automatically obtain vigilance related features from EFDMs, and achieve much better recognition results than traditional machine learning methods. Moreover, based on the transfer learning strategy, this model can also be used for other recognition tasks, which is helpful for promoting the application of EEG signals to the driver fatigue detection system.
-
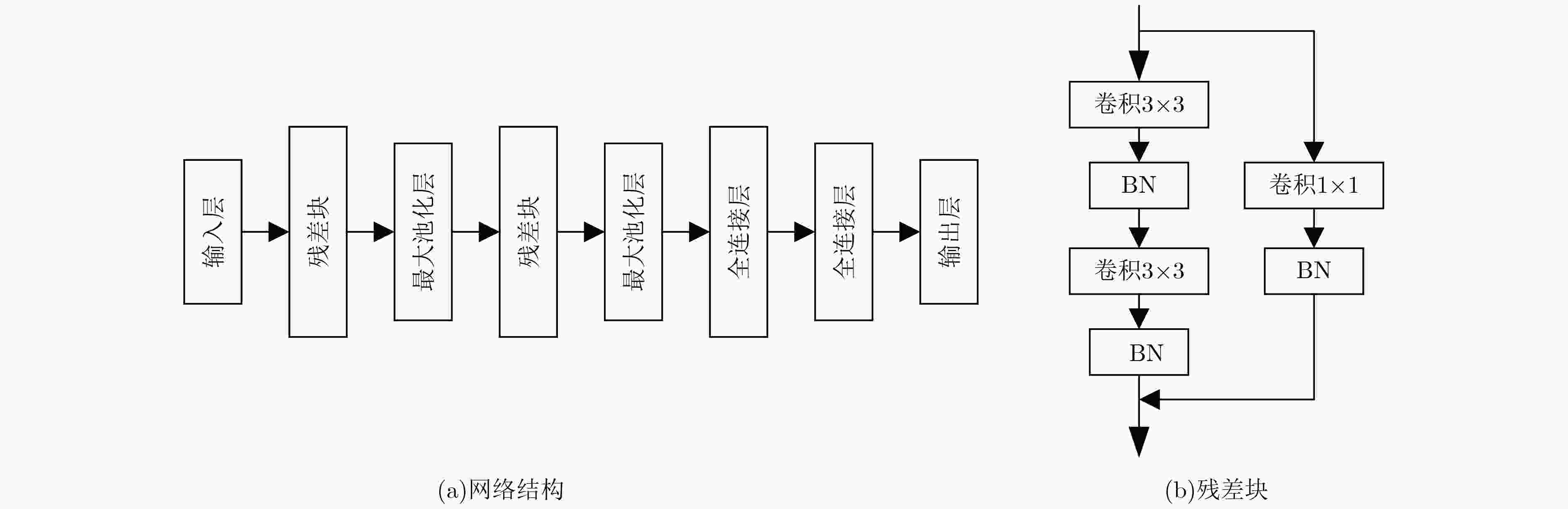
表 1 基于2层残差块的卷积神经网络模型的详细结构参数
网络层类型 特征层数 特征层尺寸 输入层 100×30 残差块1 卷积层Conv1_1(3×3)、批归一化(32) 32 100×30 卷积层Conv1_2(3×3)、批归一化(32) 32 100×30 卷积层Conv2(1×1)、批归一化(32) 32 100×30 池化层1 最大池化(2, 2) 32 50×15 残差块2 卷积层Conv1_1(3×3)、批归一化(64) 64 50×15 卷积层Conv1_2(3×3)、批归一化(64) 64 50×15 卷积层Conv2(1×1)、批归一化(64) 64 50×15 池化层2 最大池化(2, 2) 64 25×7 全连接层1 全连接 1024 全连接层2 全连接 3 输出层 Softmax 3 表 2 疲劳驾驶实验时间安排表
时间 事件 11:30~12:10 搭建实验平台,向被试说明实验要求和实验过程中的注意事项等; 12:10~12:20 被试者针对模拟驾驶环境进行适应性练习; 12:20~15:10 开始测试,被试者进行持续驾驶,实验组织人员记录实验相关数据; 15:10~ 整理实验设备,实验完成。 表 3 不同方法在SEED数据集上的识别结果
表 4 不同的模式识别方法对疲劳状态的识别结果
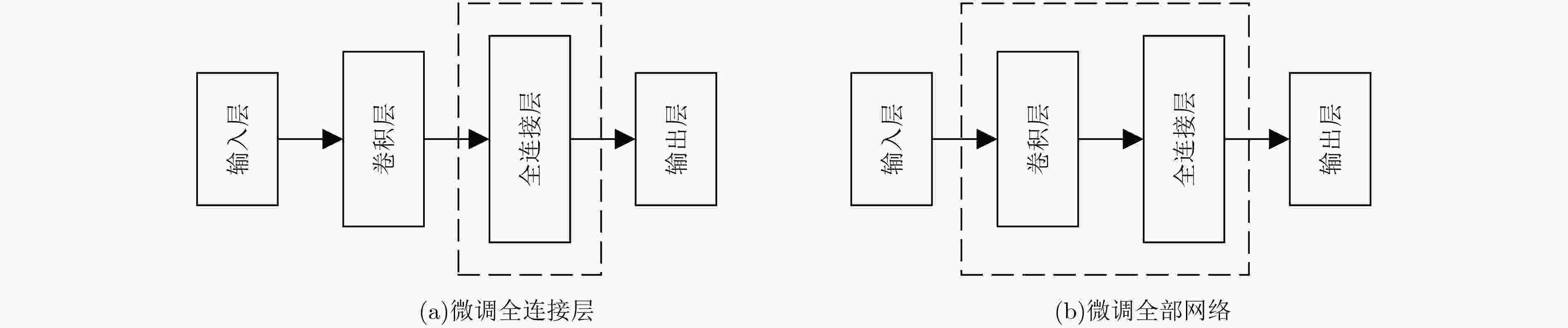
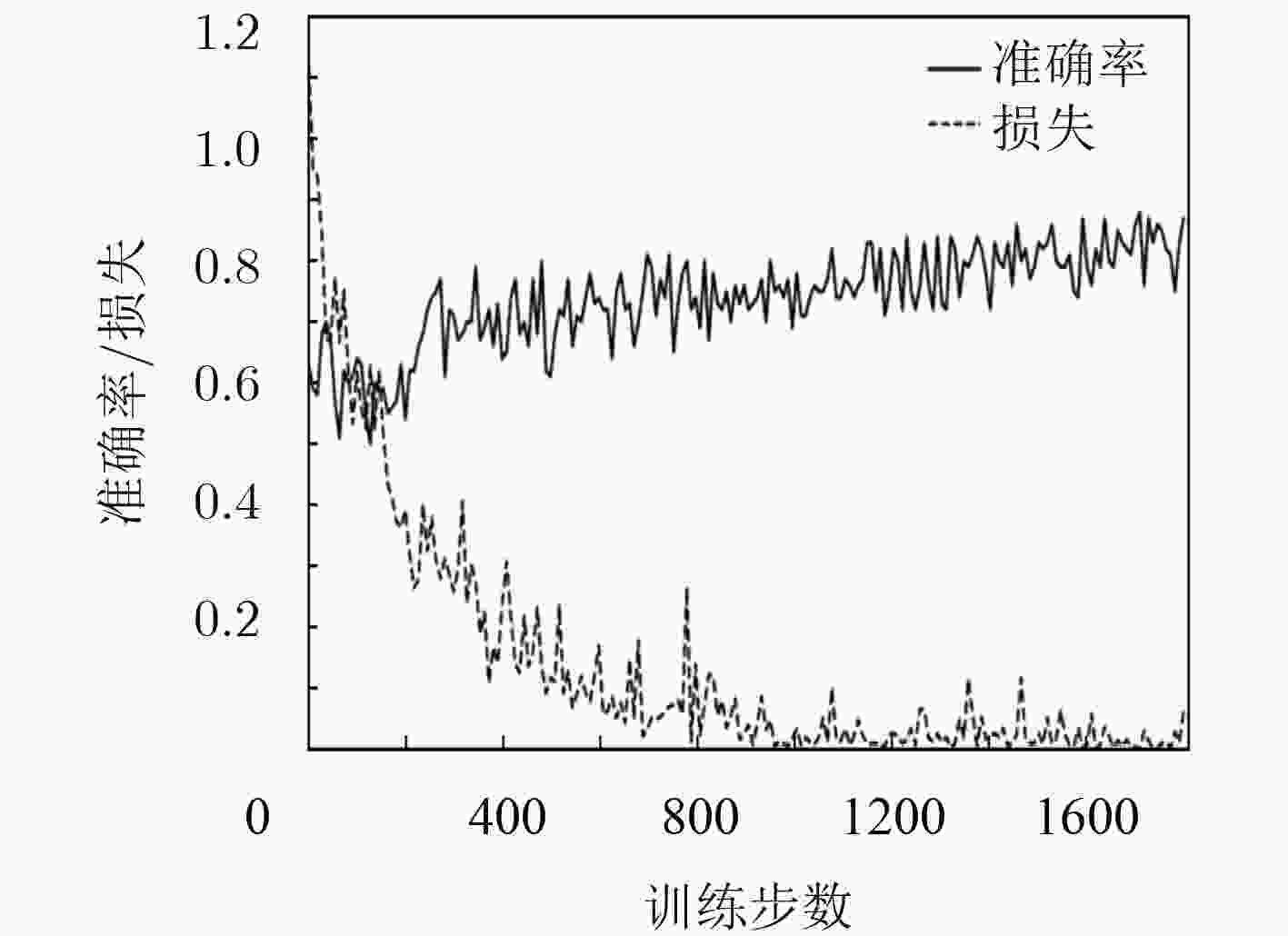
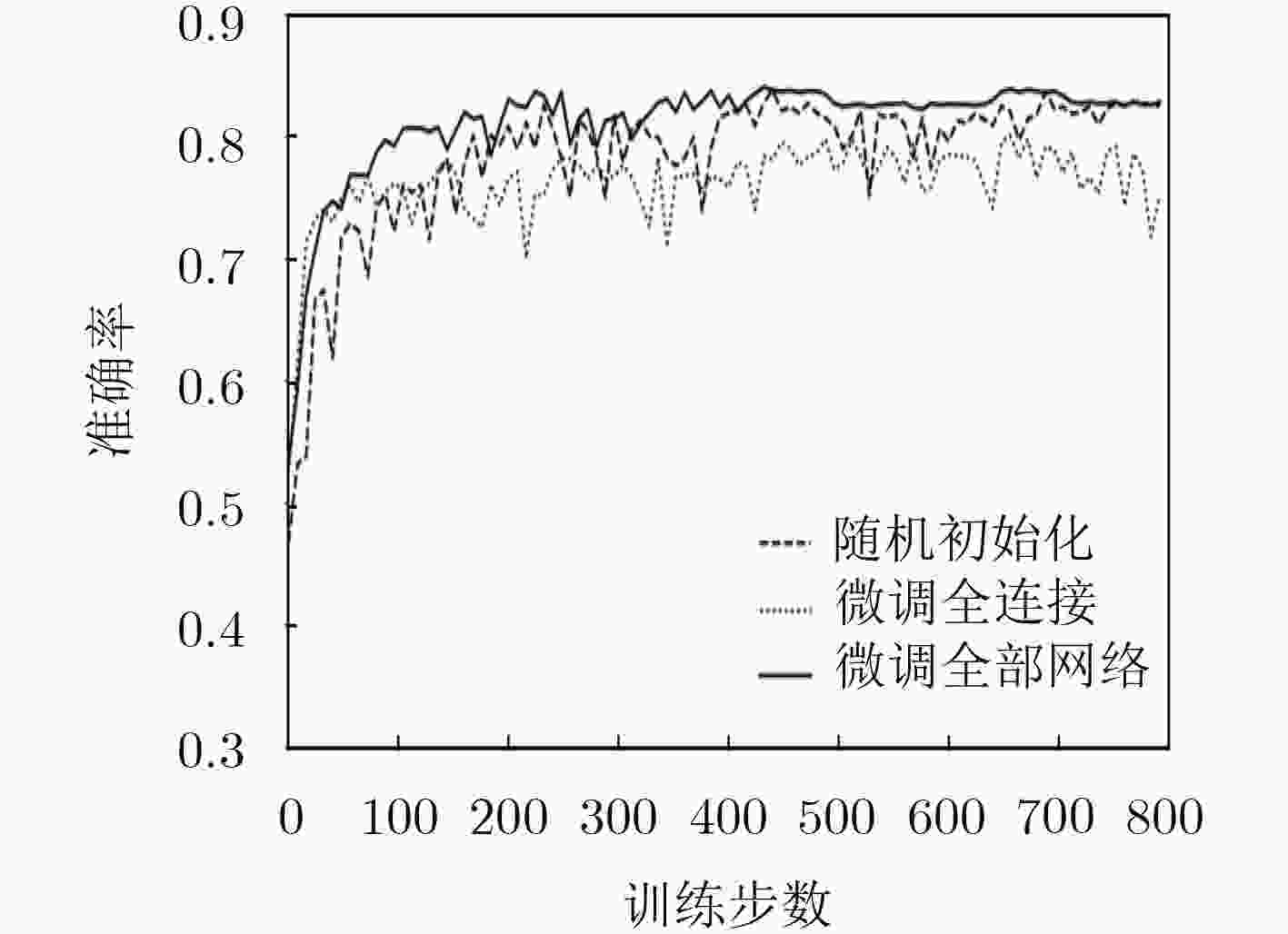
方法 平均准确率(%) EFDMs+随机初始化训练 82.60 EFDMs+微调全连接层 77.15 EFDMs+微调全部网络 83.90 PSD+SVM 75.53 SampEn+SVM 63.69 EEG+DBN 79.01 EFDMs+AlexNet 83.59 EFDMs+VGGNet 82.67 -
李刚. 基于脑功能网络的脑力疲劳检测技术及其形成机理研究[D]. [博士论文], 山东大学, 2017.LI Gang. Study on the mental fatigue detecting technology and its formation mechanism based on brain functional network[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Shandong University, 2017. BALANDONG R P, AHMAD R F, SAAD M N M, et al. A review on EEG-based automatic sleepiness detection systems for driver[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 22908–22919. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2811723 HU Jianfeng. Comparison of different features and classifiers for driver fatigue detection based on a single EEG channel[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2017: 5109530. doi: 10.1155/2017/5109530 XIONG Yijun, GAO Junfeng, YANG Yong, et al. Classifying driving fatigue based on combined entropy measure using EEG signals[J]. International Journal of Control and Automation, 2016, 9(3): 329–338. doi: 10.14257/ijca FU Rongrong, WANG Hong, and ZHAO Wenbo. Dynamic driver fatigue detection using hidden Markov model in real driving condition[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 63: 397–411. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.06.042 LI Zuojin, LI S M, LI Renjie, et al. Online detection of driver fatigue using steering wheel angles for real driving conditions[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 495–508. doi: 10.3390/s17030495 王斐, 王少楠, 王惜慧, 等. 基于脑电图识别结合操纵特征的驾驶疲劳检测[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2014, 35(2): 398–404.WANG Fei, WANG Shaonan, WANG Xihui, et al. Driving fatigue detection based on EEG recognition and vehicle handling characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(2): 398–404. LI Zuojin, CHEN Liukui, PENG Jun, et al. Automatic detection of driver fatigue using driving operation information for transportation safety[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(6): 1212–1222. doi: 10.3390/s17061212 ZHANG Qingchen, YANG L T, CHEN Zhikui, et al. A survey on deep learning for big data[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 42: 146–157. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.10.006 HATCHER W G and YU Wei. A survey of deep learning: Platforms, applications and emerging research trends[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 24411–24432. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2830661 DU Lihuan, LIU Wei, ZHENG Weilong, et al. Detecting driving fatigue with multimodal deep learning[C]. The 8th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Shanghai, China, 2017: 74–77. doi: 10.1109/NER.2017.8008295. MAO Zijing, YAO Wanxiang, and HUANG Yufei. EEG-based biometric identification with deep learning[C]. The 8th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Shanghai, China, 2017: 609–612. doi: 10.1109/NER.2017.8008425. WANG Haixian. Optimizing spatial filters for single-trial EEG classification via a discriminant extension to CSP: The Fisher criterion[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2011, 49(9): 997–1001. doi: 10.1007/s11517-1-0766-7 CHUANG C H, KO L W, LIN Yuanpin, et al. Independent component ensemble of EEG for brain-computer interface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2014, 22(2): 230–238. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2013.2293139 LI Mingyang, CHEN Wanzhong, and ZHANG Tao. Classification of epilepsy EEG signals using DWT-based envelope analysis and neural network ensemble[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2017, 31: 357–365. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2016.09.008 ZHENG Weilong and LU Baoliang. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 2015, 7(3): 162–175. doi: 10.1109/TAMD.2015.2431497 ZHANG Benyu, JIANG Huiping, and DONG Linshan. Classification of EEG signal by WT-CNN model in emotion recognition system[C]. The 2017 IEEE 16th International Conference on Cognitive Informatics & Cognitive Computing (ICCI*CC), Oxford, UK, 2017: 109–114. doi: 10.1109/ICCI-CC.2017.8109738. LEE H K and CHOI Y S. A convolution neural networks scheme for classification of motor imagery EEG based on wavelet time-frequecy image[C]. 2018 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2018: 906–909. doi: 10.1109/ICOIN.2018.8343254. PAN S J and YANG Qiang. A survey on transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345–1359. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 YOSINSKI J, CLUNE J, BENGIO Y, et al. How transferable are features in deep neural networks?[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, USA, 2014: 3320–3328. ZHENG Weilong, ZHU Jiayi, and LU Baoliang. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2017. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2712143 THEJASWINI S, RAVI KUMAR K M, RUPALI S, et al. EEG Based Emotion Recognition Using Wavelets and Neural Networks Classifier[M]. GURUMOORTHY S, RAO B N K, GAO Xiaozhi. Cognitive Science and Artificial Intelligence: Advances and Applications. Singapore: Springer, 2018: 101–112. TANG Hao, LIU Wei, ZHENG Weilong, et al.. Multimodal emotion recognition using deep neural networks[C]. The 24th International Conference on International Conference on International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Guangzhou, China, 2017: 811–819. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-70093-9_86. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
