Secret Key Agreement Based on Secure Polar Code
-
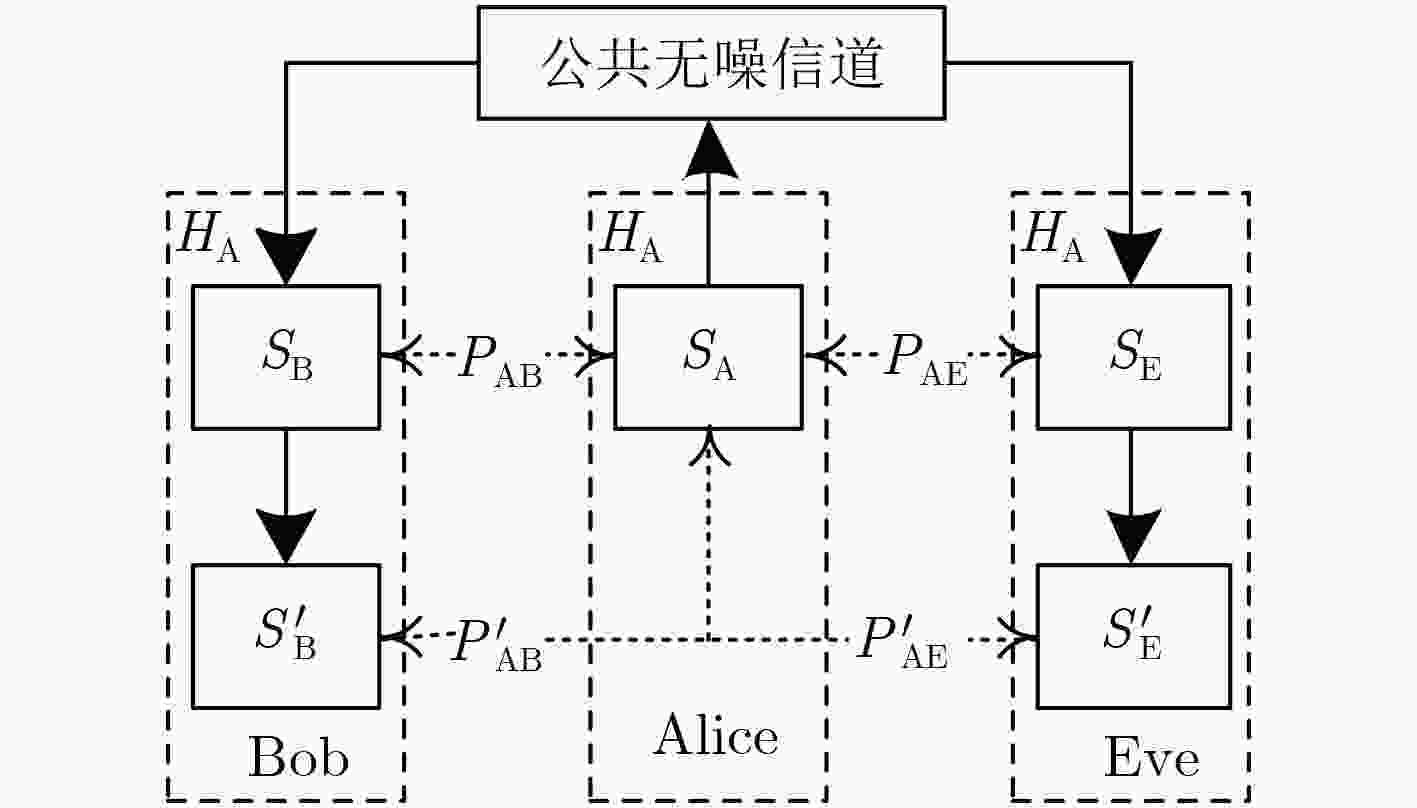
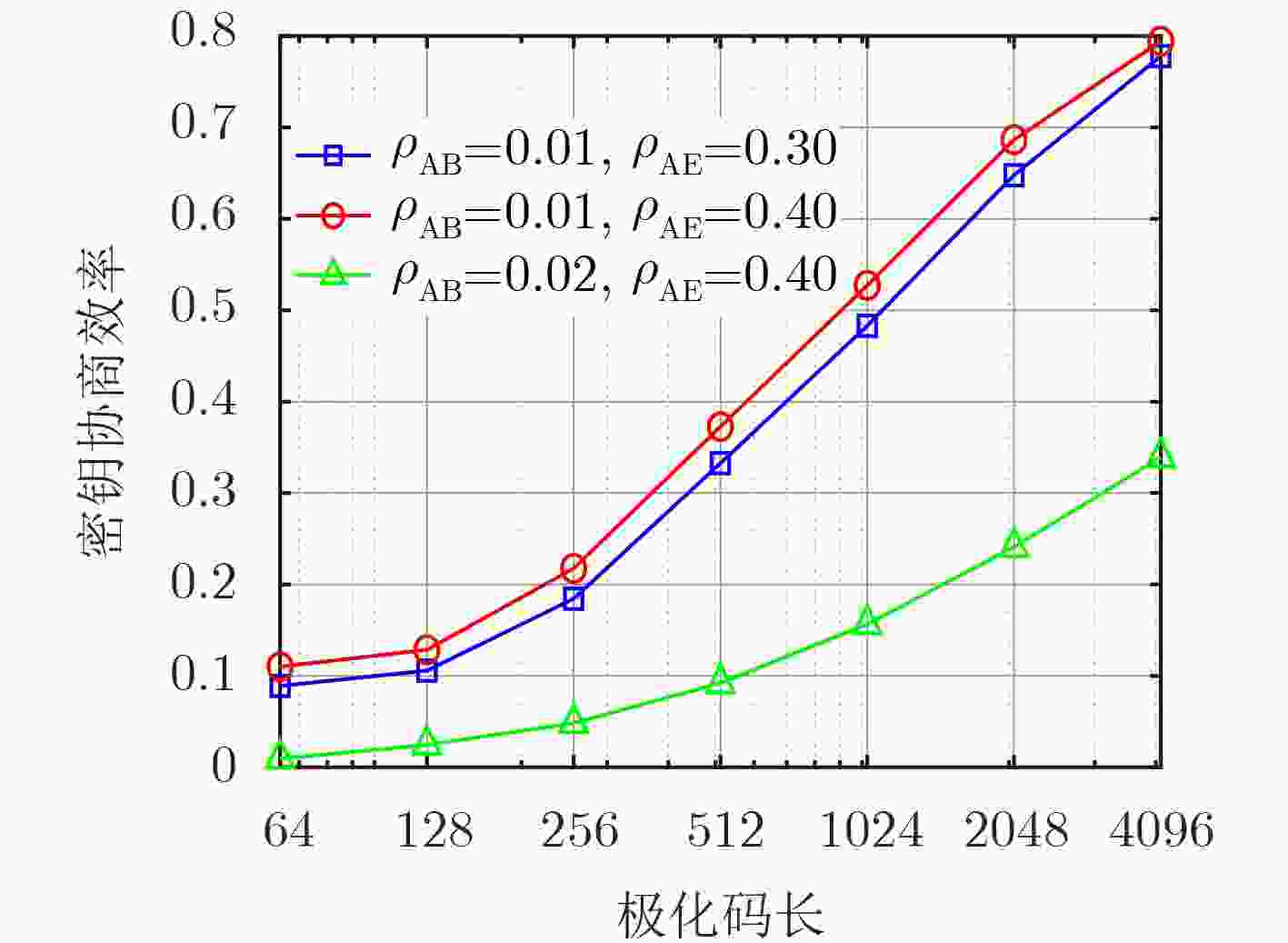
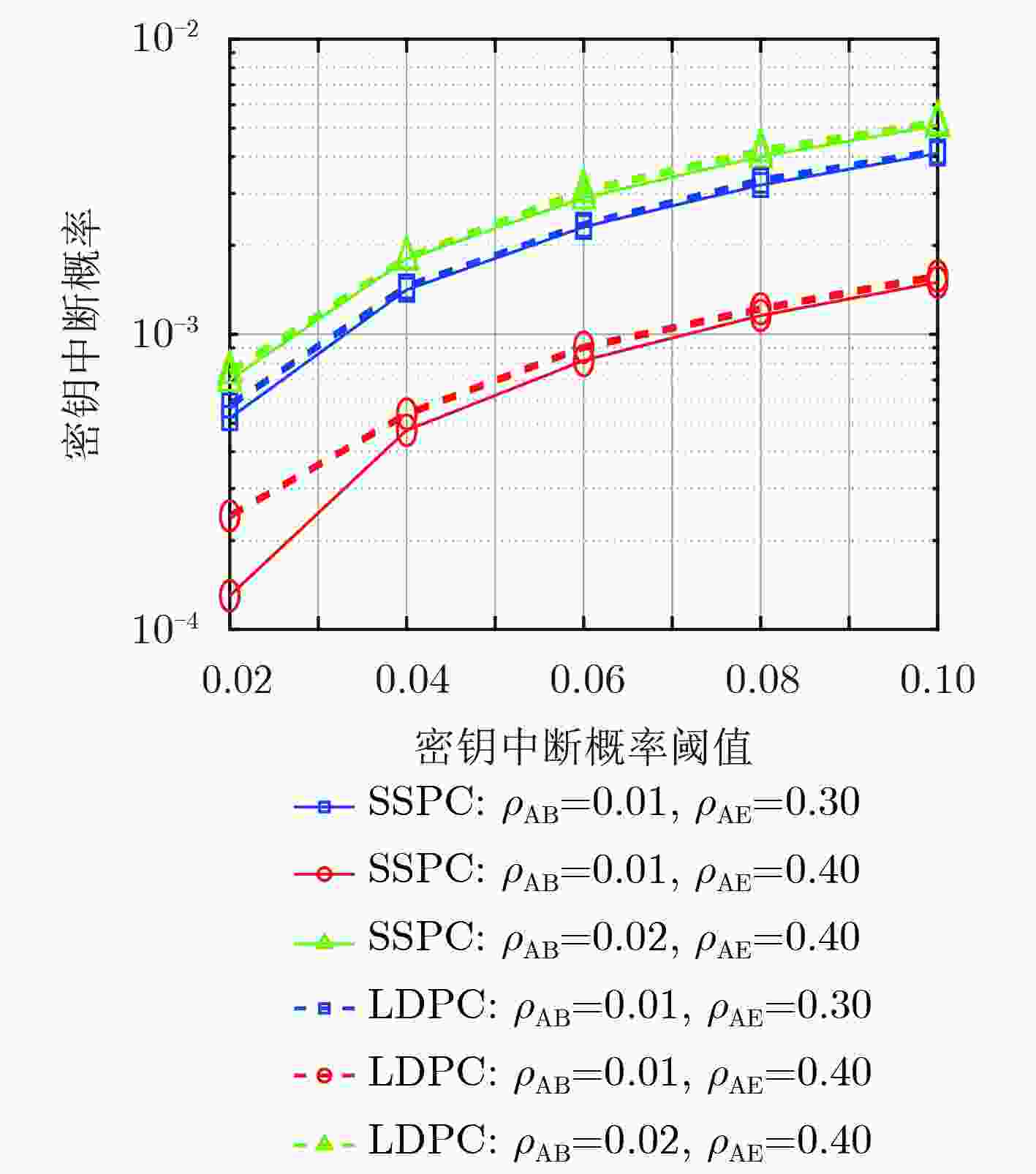
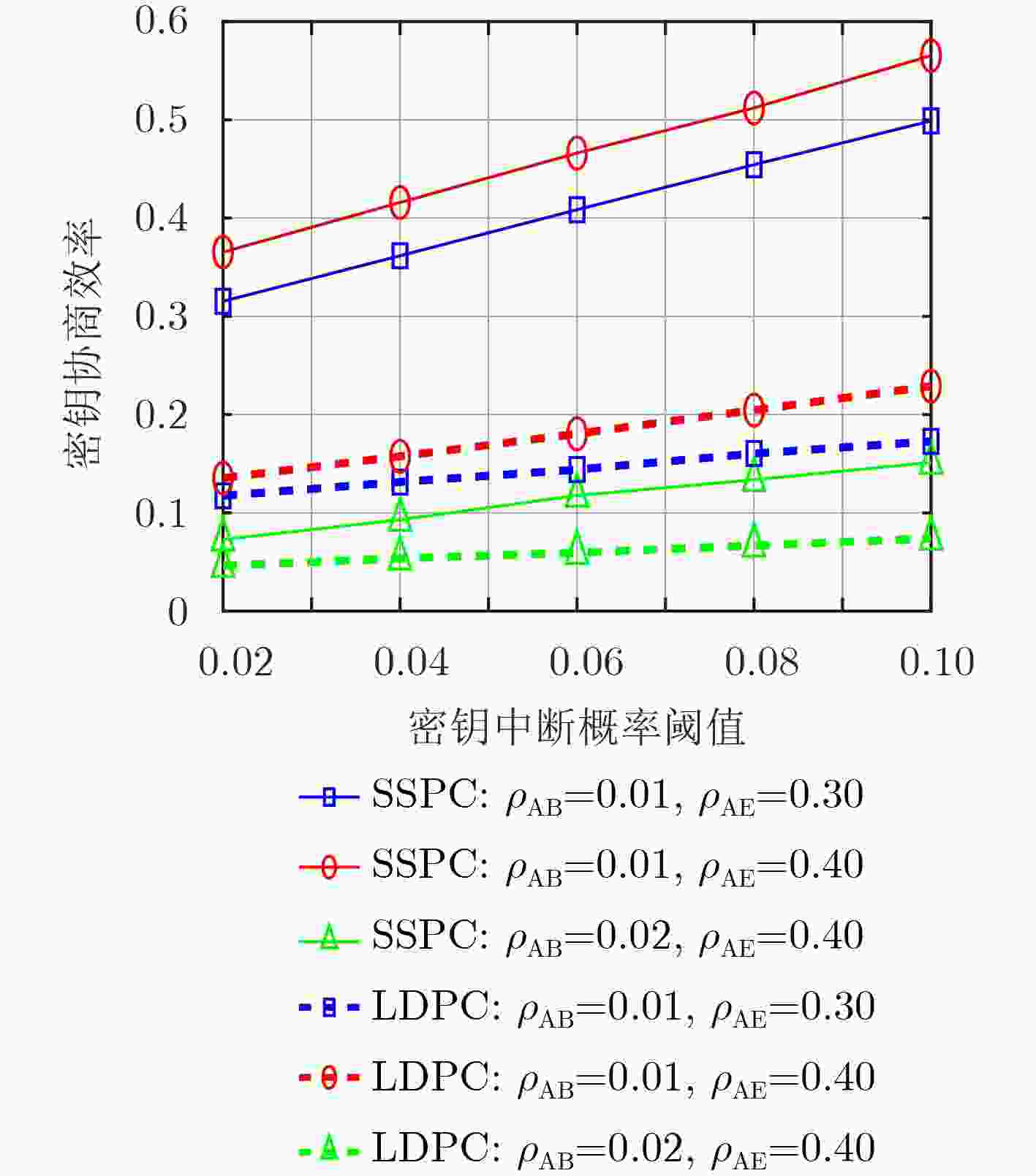
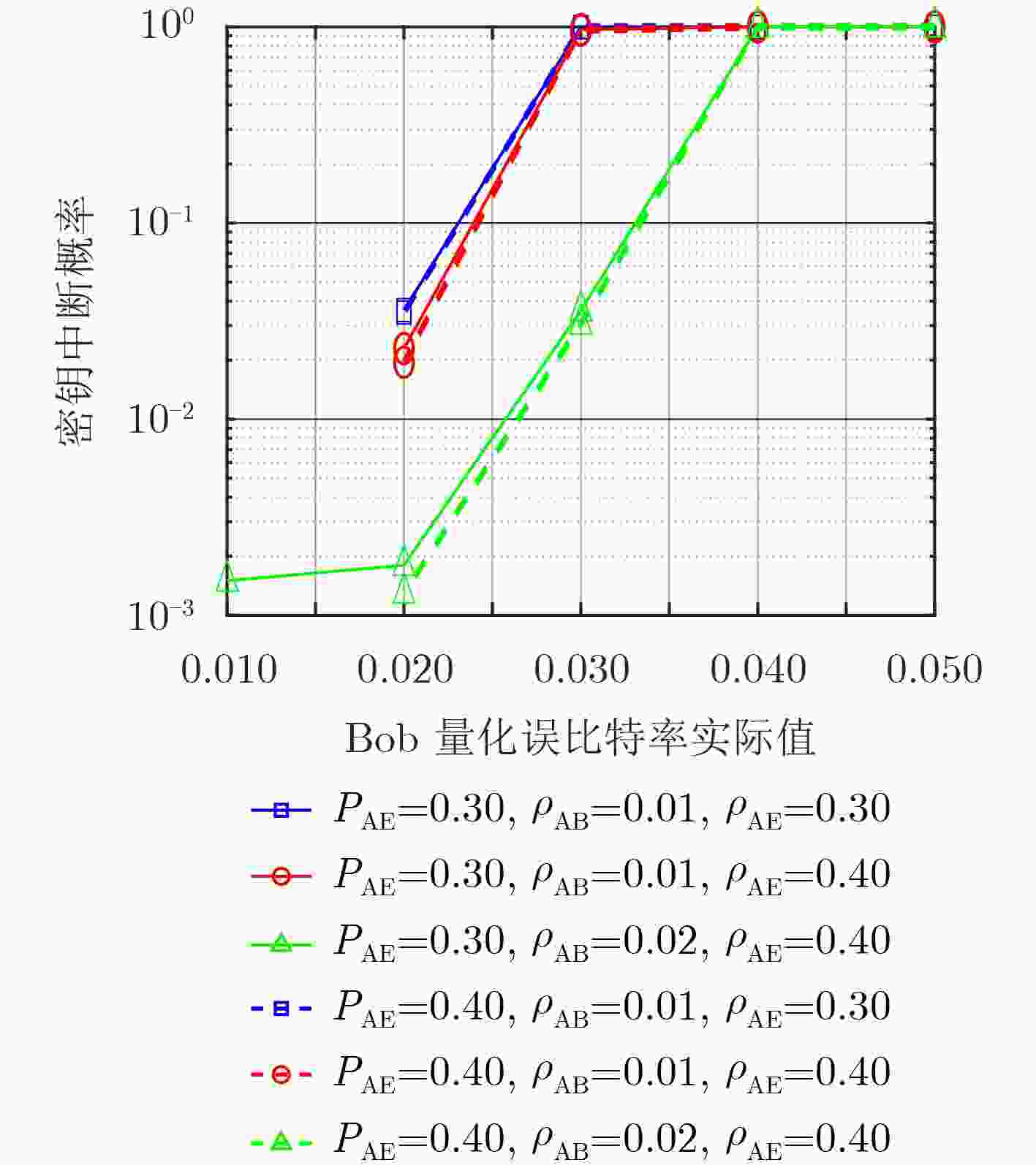
摘要: 针对密钥协商过程中的信息泄露问题,该文综合考虑信息协商和隐私放大提出了基于安全极化码(SPC)的密钥协商方法,打通了从量化误比特率(QBER)条件到密钥中断概率(SKOP)需求的桥梁。首先,将QBER建模为加性高斯白噪声(AWGN)信道的传输误比特率(TBER),进而将QBER优势转化为AWGN信道优势;然后,利用高斯近似计算出各极化子信道的传输错误概率,并进一步推导出安全极化码的译码误比特率上下界;最后,根据密钥中断概率阈值利用遗传算法构造出合适的安全极化码实现密钥协商。仿真结果表明,该文所提的密钥协商方法能够满足设计的密钥中断概率需求,且具有比低密度奇偶校验(LDPC)码更高的密钥协商效率。Abstract: Focusing on the problem of information leakage in secret key agreement, combining information reconciliation and privacy amplification, a method based on Secure Polar Code (SPC) is proposed, which builds the bridge from the condition of Quantized Bit Error Rate (QBER) to the requirement of Secret Key Outage Probability (SKOP). Firstly, QBER is modeled as the Transmitted Bit Error Rate (TBER) of Additional White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel, so the advantage of QBER is converted to the advantage of AWGN channel; Then, the TBER of each polarized sub-channel is calculated by Gaussian approximation, and the upper and lower bounds of decoded bit error rate are also derived. Finally, the SPC is constructed based on generic algorithm and SKOP threshold. Simulation results show that the proposed method satisfies the requirement of SKOP and achieves higher secret key agreement efficiency, compared with Low Density Parity Check (LDPC)-based method.
-
表 1 GA2SPCC算法
输入:$N,{\rho _{{\rm{AB}}}},\;{\rho _{{\rm{AE}}}},\;{L_{\rm{K}}},{\zeta _\tau },{G_{{m}}},{P_{{n}}},{P_{{c}}},{P_{{m}}}$ 输出:$({K_{\rm{M}}},{I_{\rm{M}}},{K_{\rm{R}}},{I_{\rm{R}}},{K_{\rm{F}}},{I_{\rm{F}}}),\eta ,{L_{\rm{I}}}$
(1) 利用高斯近似法和${\rho _{{\rm{AB}}}}$, ${\rho _{{\rm{AE}}}}$分别计算$P_e^{{\rm{AB}}}\!\!\left(\! {W_N^{(i)}} \!\right)$和$P_e^{{\rm{AE}}}\!\!\left(\! {W_N^{(i)}} \!\right)$;
(2) 对$P_e^{{\rm{AB}}}\left( {W_N^{(i)}} \right)$进行排序并根据式(17)式初步筛选极化子信道;(3) 按照相应参数利用遗传算法求解式(16); (4) 返回$({K_{\rm{M}}},{I_{\rm{M}}},{K_{\rm{R}}},{I_{\rm{R}}},{K_{\rm{F}}},{I_{\rm{F}}}),\eta ,{L_{\rm{I}}}$。 表 2 Alice侧密钥协商算法
输入:$({K_{\rm{M}}},{I_{\rm{M}}},{K_{\rm{R}}},{I_{\rm{R}}},{K_{\rm{F}}},{I_{\rm{F}}}),{L_{\rm{I}}},{S_{\rm{A}}}$ 输出:${H_{\rm{A}}},{K_{\rm{A}}}$ (1) 将${S_{\rm{A}}}$按照长度${K_{\rm{M}}}$分组; (2) 利用$({K_{\rm{M}}},{I_{\rm{M}}},{K_{\rm{R}}},{I_{\rm{R}}},{K_{\rm{F}}},{I_{\rm{F}}})$进行EncoderA系统编码; (3) 取出校验比特${H_{\rm{A}}}$并打包由“公共无噪信道”发送至
Bob(Eve);(4) 将${S_{\rm{A}}}$按照长度${L_{\rm{I}}}$分组,经过通用hash函数后生成密钥${K_{\rm{A}}}$。 表 3 Bob(Eve)侧密钥协商算法
输入:$\left( {N,{K_{\rm{M}}},{I_{\rm{M}}},{K_{\rm{R}}},{I_{\rm{R}}},{K_{\rm{F}}},{I_{\rm{F}}}} \right),{L_{\rm{I}}},{S_{\rm{B}}}({S_{\rm{E}}})$ 输出:${K_{\rm{B}}}({K_{\rm{E}}})$ (1) 将${S_{\rm{B}}}({S_{\rm{E}}})$按照长度${K_{\rm{M}}}$分组并与对应的${H_{\rm{A}}}$合并为新码字; (2) 利用$\left( {N,{K_{\rm{M}}},{I_{\rm{M}}},{K_{\rm{R}}},{I_{\rm{R}}},{K_{\rm{F}}},{I_{\rm{F}}}} \right)$进行系统译码得到${S'\!_{\rm{B}}}({S'\!_{\rm{E}}})$; (3) 将${S'\!_{\rm{B}}}({S'\!_{\rm{E}}})$按照长度${L_{\rm{I}}}$分组,经过通用hash函数后生成密钥
${K_{\rm{B}}}({K_{\rm{E}}})$。表 4 部分仿真参数
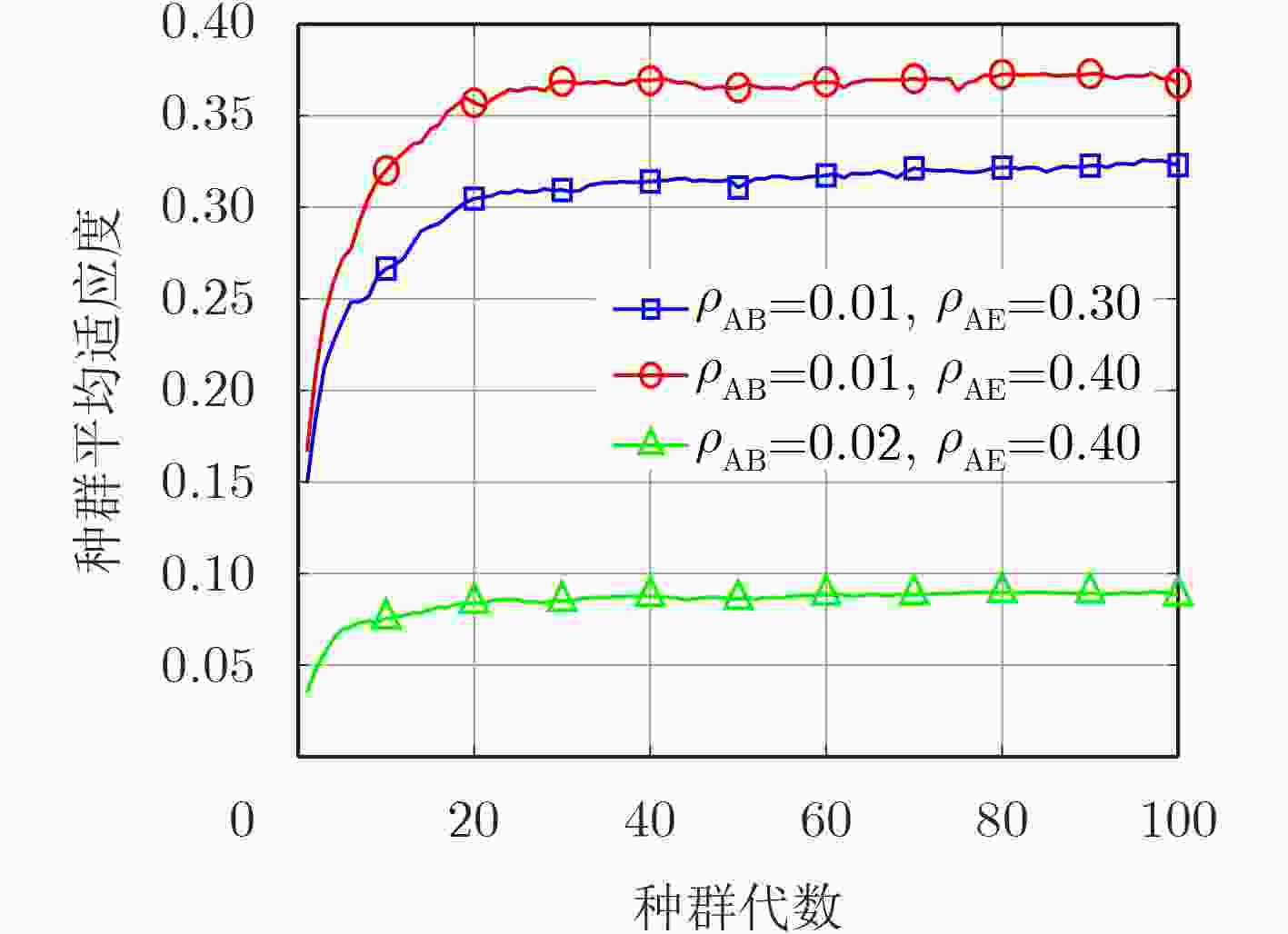
密钥长度 最大代数 种群个数 交叉概率 突变概率 ${L_{\rm{K}}} = 128$ ${G_{{m}}} = 100$ ${P_{{n}}} = 200$ ${P_{{c}}} = 0.6$ ${P_{{m}}} = 0.02$ -
ZOU Yulong, ZHU Jia, WANG Xianbin, et al. A survey on wireless security: Technical challenges, recent advances, and future trends[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(9): 1727–1765. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2558521 REZKI Z, ZORGUI M, ALOMAIR B, et al. Secret key agreement: Fundamental limits and practical challenges[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2017, 24(3): 72–79. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2017.1500365WC DIFFIE W and HELLMAN M. New directions in cryptography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1976, 22(6): 644–654. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1976.1055638 CASTELVECCHI D. Quantum computers ready to leap out of the lab in 2017[EB/OL]. http://www.nature.com/news/quantum-computers-ready-to-leap-out-of-the-lab-in-2017-1.21239, 2017. ZHANG Junqing, DUONG T Q, MARSHALL A, et al. Key generation from wireless channels: A review[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 614–626. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2521718 CSISZAR I and KORNER J. Broadcast channels with confidential messages[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1978, 24(3): 339–348. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1978.1055892 AHLSWEDE R and CSISZAR I. Common randomness in information theory and cryptography. I. Secret sharing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1993, 39(4): 1121–1132. doi: 10.1109/18.243431 MAURER U M. Secret key agreement by public discussion from common information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1993, 39(3): 733–742. doi: 10.1109/18.256484 MAURER U and WOLF S. Secret-key agreement over unauthenticated public channels. III. Privacy amplification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2003, 49(4): 839–851. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2003.809559 ETESAMI J and HENKEL W. LDPC code construction for wireless physical-layer key reconciliation[C]. Proceedings of the 1st IEEE International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Beijing, China, 2012: 208–213. doi: 10.1109/ICCChina.2012.6356879. PACHER C, GRABENWEGER P, MARTINEZ-MATEO J, et al. An information reconciliation protocol for secret-key agreement with small leakage[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Hongkong, China, 2015: 730–734. ARIKAN E. Channel polarization: A method for constructing capacity-achieving codes for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(7): 3051–3073. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2021379 ARIKAN E. Systematic polar coding[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2011, 15(8): 860–862. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2011.061611.110862 KOYLUOGLU O O and EL GAMAL H. Polar coding for secure transmission and key agreement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(5): 1472–1483. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2012.2207382 KIM Y S, KIM J H, and KIM S H. A secure information transmission scheme with a secret key based on polar coding[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(6): 937–940. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2318306 CHOU R A, BLOCH M R, and ABBE E. Polar coding for secret-key generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2015, 61(11): 6213–6237. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2015.2471179 CACHIN C and MAURER U M. Linking information reconciliation and privacy amplification[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 1997, 10(2): 97–110. doi: 10.1007/s001459900023 DAI Jincheng, NIU Kai, SI Zhongwei, et al. Does Gaussian approximation work well for the long-length polar code construction?[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 7950–7963. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2692241 SCHÜRCH C. A partial order for the synthesized channels of a polar code[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 220–224. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2016.7541293. VANGALA H, HONG Yi, and VITERBO E. Efficient algorithms for systematic polar encoding[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(1): 17–20. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2015.2497220 Final Report of 3GPP TSG RAN WG1 #88bis v1.0.0[R]. MCC Support, Spokane, USA, 2017. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
