IBeacon/INS Data Fusion Location Algorithm Based on Unscented Kalman Filter
-
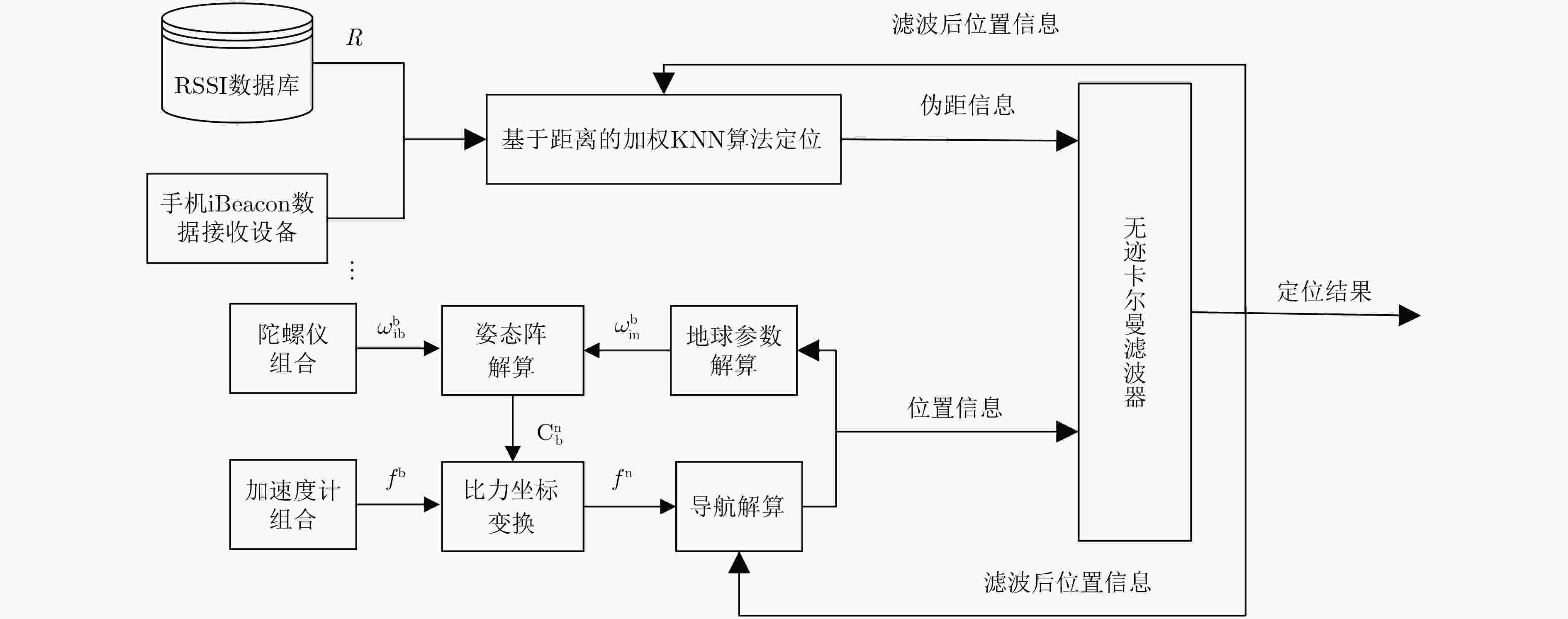
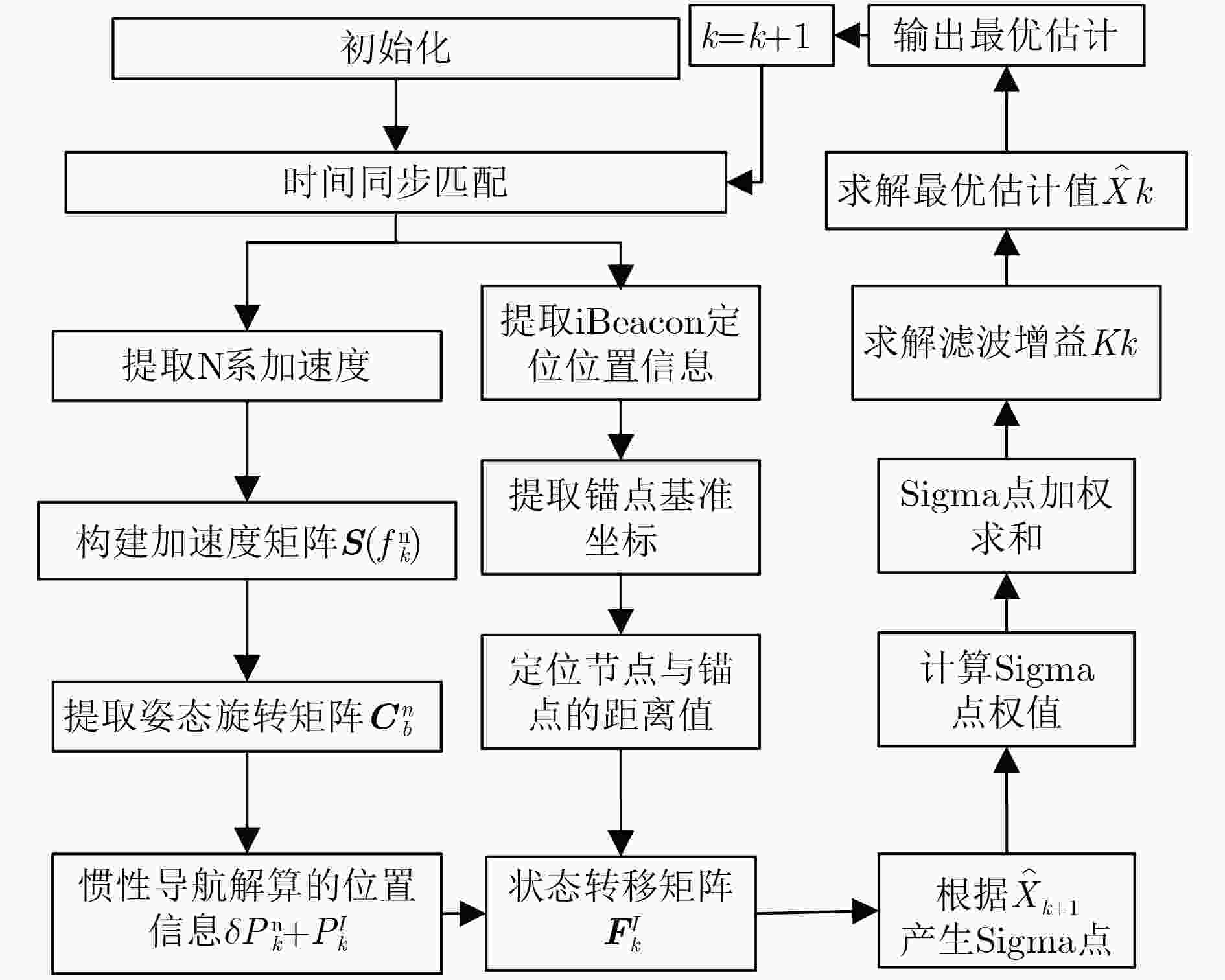
摘要: 针对微机电惯性导航系统(MEMS-INS)定位解算存在积累误差及低功耗蓝牙技术iBeacon指纹定位存在跳变误差等问题,该文提出一种基于无迹卡尔曼滤波器(UKF)的iBeacon/MEMS-INS数据融合定位算法。该算法对iBeacon锚点与定位目标的距离进行解算,利用加速度计和陀螺仪的数据实现姿态阵和位置解算。将蓝牙锚点位置向量、载体速度误差信息等组成状态量,将惯性导航定位信息和蓝牙定位距离信息等组成观测量,设计无迹卡尔曼滤波器,实现iBeacon/MEMS-INS数据融合定位。实验测试结果表明,该算法有效解决MEMS-INS存在较大积累误差及iBeacon指纹定位存在跳变误差的问题,可以实现1.5 m内的定位精度。Abstract: In order to overcome the accumulation error in Micro-Electro-Mechanical System-Inertial Navigation System (MEMS-INS) and the jump error in iBeacon fingerprint positioning, an iBencon/MEMS-INS data fusion location algorithm based on Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) is proposed. The new algorithm solves the distance between the iBeacon anchor and the locating target. The solution of attitude matrix and position are obtained respectively by using accelerometer and gyroscope data. Bluetooth anchor position vector, the carrier speed error and other information constitute state variables. Inertial navigation location and bluetooth system distance information constitute measure variables. Based on state variables and measure variables, the UKF is designed to realize iBencon/MEMS-INS data fusion indoor positioning. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively solve the problem of the large accumulation error of INS and the jump error of iBeacon fingerprint positioning, and this algorithm can realize 1.5 m positioning accuracy.
-
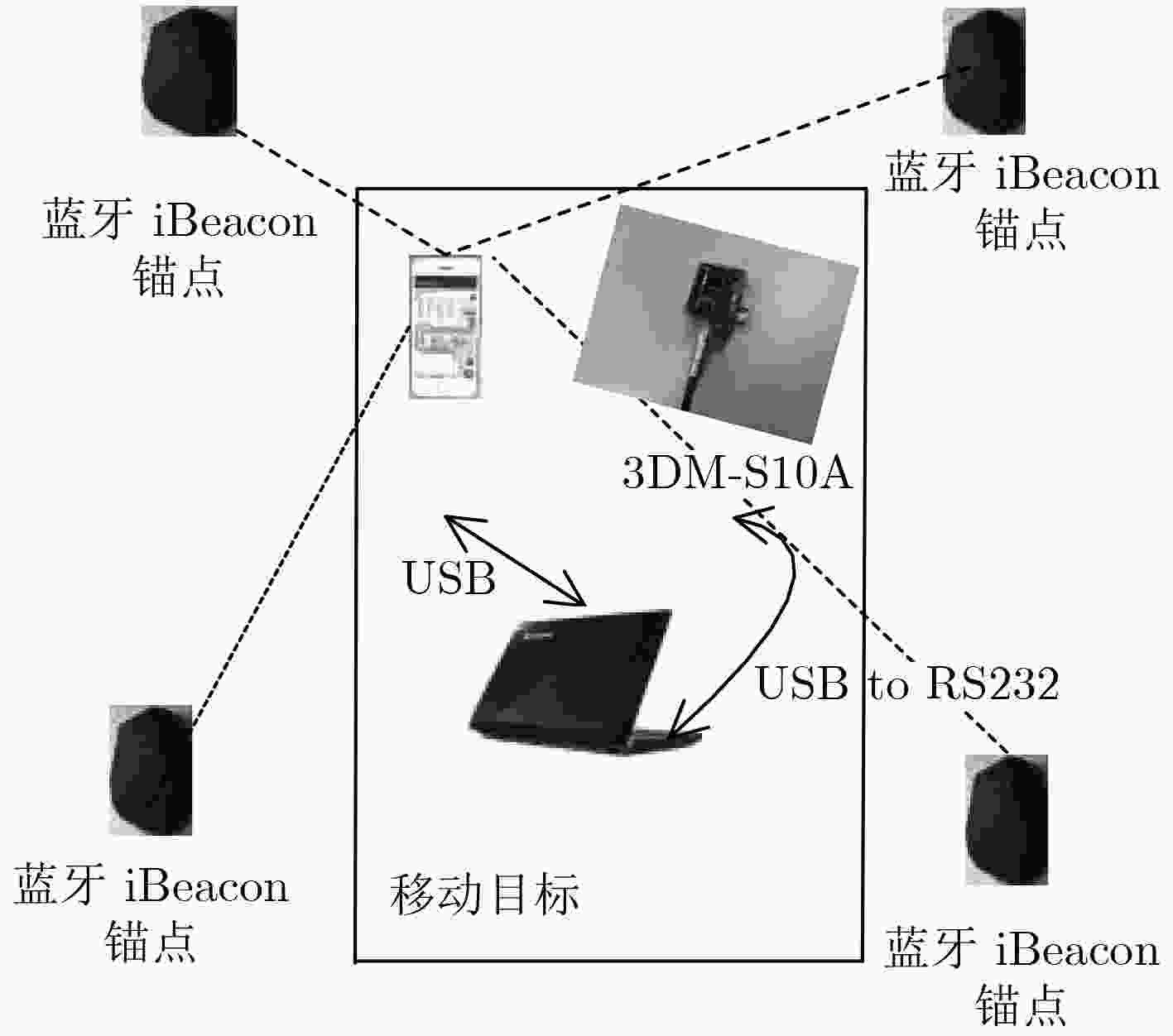
表 1 3DM模块各项指标
加速度计 陀螺仪 磁力计 轴数 3 3 3 量程 ±8 g ±1.700 °/s ±1/104 特斯拉(T) 数据更新频率 100 Hz 100 Hz 100 Hz 表 2 多种方法的性能比较
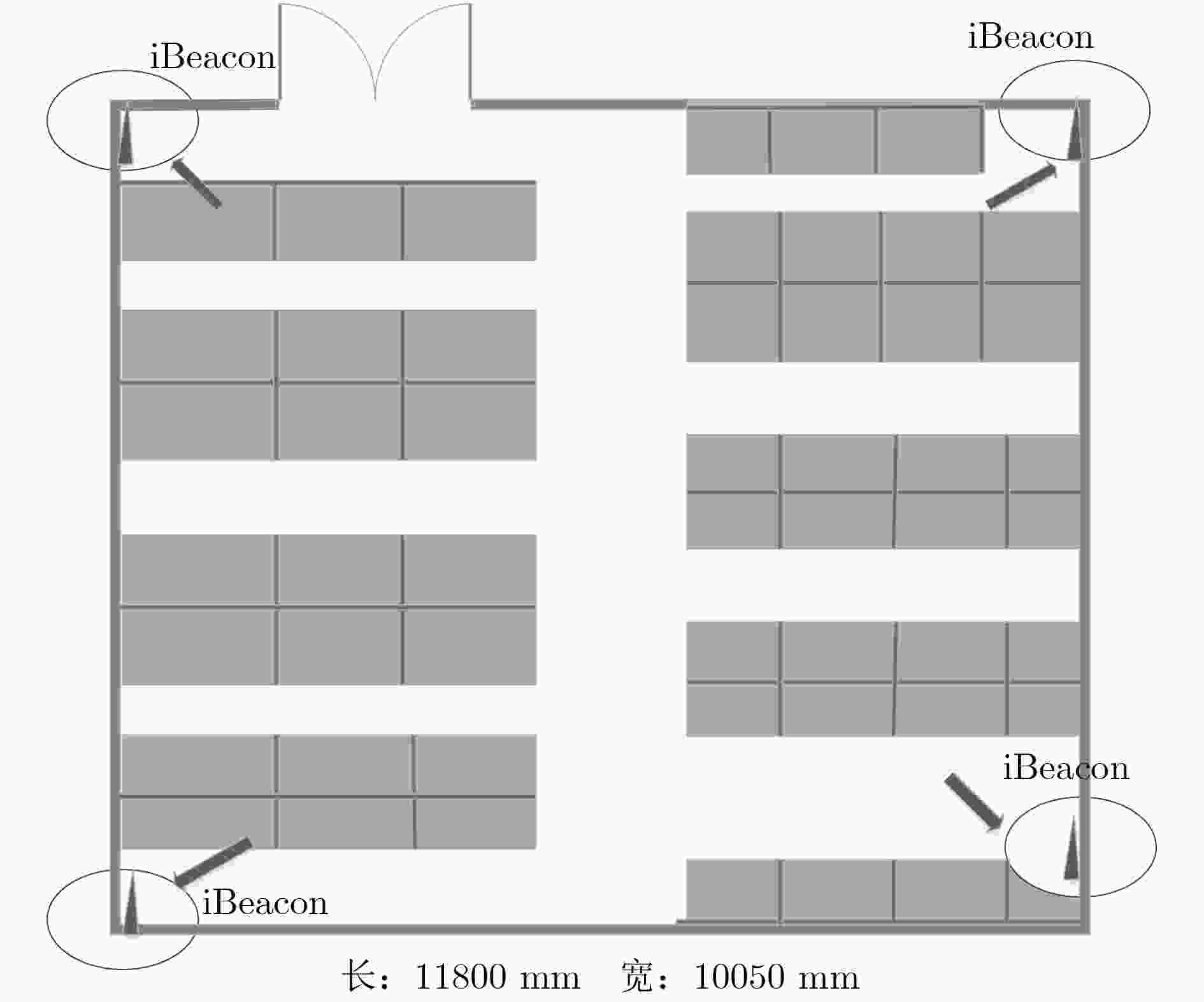
方法 平均绝对位置误差(m) 运行时间(ms) MEMS-INS 6.758 0.054 iBeacon 3.523 0.023 BLE/MEMS跨楼层 1.545 0.407 iBeacon/MEMS-INS 1.315 0.468 -
XU Yuan, CHEN Xiyuan, and LI Qinghua. Autonomous integrated navigation for indoor robots utilizing on-line iterated extended Rauch-Tung-striebel smoothing[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(12): 15937–15953. doi: 10.3390/s131215937 WIN M Z, DARDARI D, MOLISCH A F, et al. History and applications of UWB[scanning the issue][J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2009, 97(2): 198–204. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2008.2008762 CHAN E C L, BACIU G, and MAK S C. Using Wi-Fi signal strength to localize in wireless sensor networks[C]. Proceedings of 2009 WRI International Conference on Communications and Mobile Computing, Yunnan, China, 2009: 538–542. CASTILLO-CARA M, LOVON-MELGAREJO J, BRAVO-ROCCA G, et al. An empirical study of the transmission power setting for Bluetooth-based indoor localization mechanisms[J]. Sensors (Basel) , 2017, 17(6): 1318–1340. doi: 10.3390/s17061318 CHENG Jiantong, YANG Ling, LI Yong, et al. Seamless outdoor/indoor navigation with WIFI/GPS aided low cost Inertial Navigation System[J]. Physical Communication, 2014, 13: 31–43. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2013.12.003 ZHUANG Yuan and EL-SHEIMY N. Tightly-coupled integration of WiFi and MEMS sensors on handheld devices for indoor pedestrian navigation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(1): 224–234. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2477444 LIAO J K, CHIANG K W, and ZHOU Zhiming. The performance analysis of smartphone-based pedestrian dead reckoning and wireless locating technology for indoor navigation application[J]. Inventions, 2016, 1(4): 25–44. doi: 10.3390/inventions1040025 WALTER C S, SEIFFERT S, VINCENT F, et al. Indoor navigation assistant for visually impaired by pedestrian dead reckoning and position estimative of correction for patterns pecognition[J]. IFAC PapersOnLine, 2016, 49(30): 167–170. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.11.149 宋丽君, 秦永元. MEMS加速度计的六位置测试法[J]. 测控技术, 2009, 28(7): 11–13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2009.07.004SONG Lijun and QIN Yongyuan. Six-position testing of MEMS accelerometer[J]. Measurement &Control Technology, 2009, 28(7): 11–13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2009.07.004 CORREA A, DIAZ E M, AHMED D B, et al. Advanced pedestrian positioning system to smartphones and smartwatches[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(11): 1903–1921. doi: 10.3390/s16111903 NETO P, MENDES N, and MOREIRA A P. Kalman filter-based yaw angle estimation by fusing inertial and magnetic sensing: A case study using low cost sensors[J]. Sensor Review, 2015, 35(3): 244–250. doi: 10.1108/SR-10-2014-0723 杨东勇, 顾东袁, 傅晓婕. 一种基于RSSI相似度的室内定位算法[J]. 传感技术学报, 2009, 22(2): 264–268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2009.02.025YANG Dongyong, GU Dongyuan, and FU Xiaojie. An indoor location algorithm base on RSSI-similarity degree[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2009, 22(2): 264–268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2009.02.025 PEI Ling, CHEN Ruizhi, LIU Jingbin, et al. Using inquiry-based Bluetooth RSSI probability distributions for indoor positioning[J]. Journal of Global Positioning Systems, 2010, 9(2): 122–130. 李荣冰, 刘建业, 孙永荣. MEMS-IMU构型设计及惯性器件安装误差标定方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2007, 15(5): 526–529, 563. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6734.2007.05.005LI Rongbing, LIU Jianye, and SUN Yongrong. MEMS-IMU configuration and its inertial sensors’ calibration for installation errors[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2007, 15(5): 526–529, 563. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6734.2007.05.005 周牧, 王斌, 田增山, 等. 室内BLE/MEMS跨楼层融合定位算法[J]. 通信学报, 2017, 38(5): 1–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.05.001ZHOU Mu, WANG Bin, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Indoor BLE and MEMS based multi-floor fusion positioning algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(5): 1–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.05.001 -





 下载:
下载:
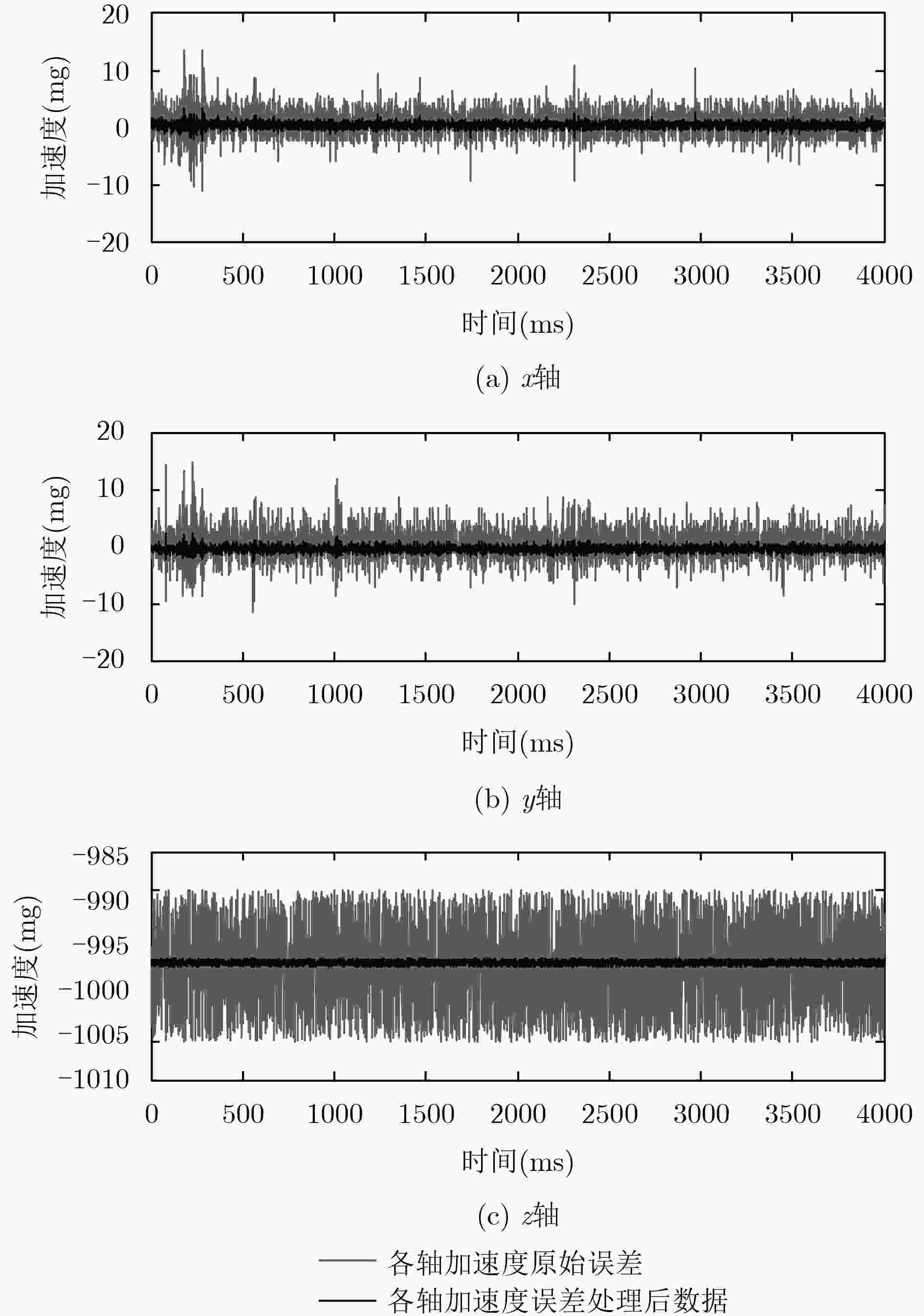
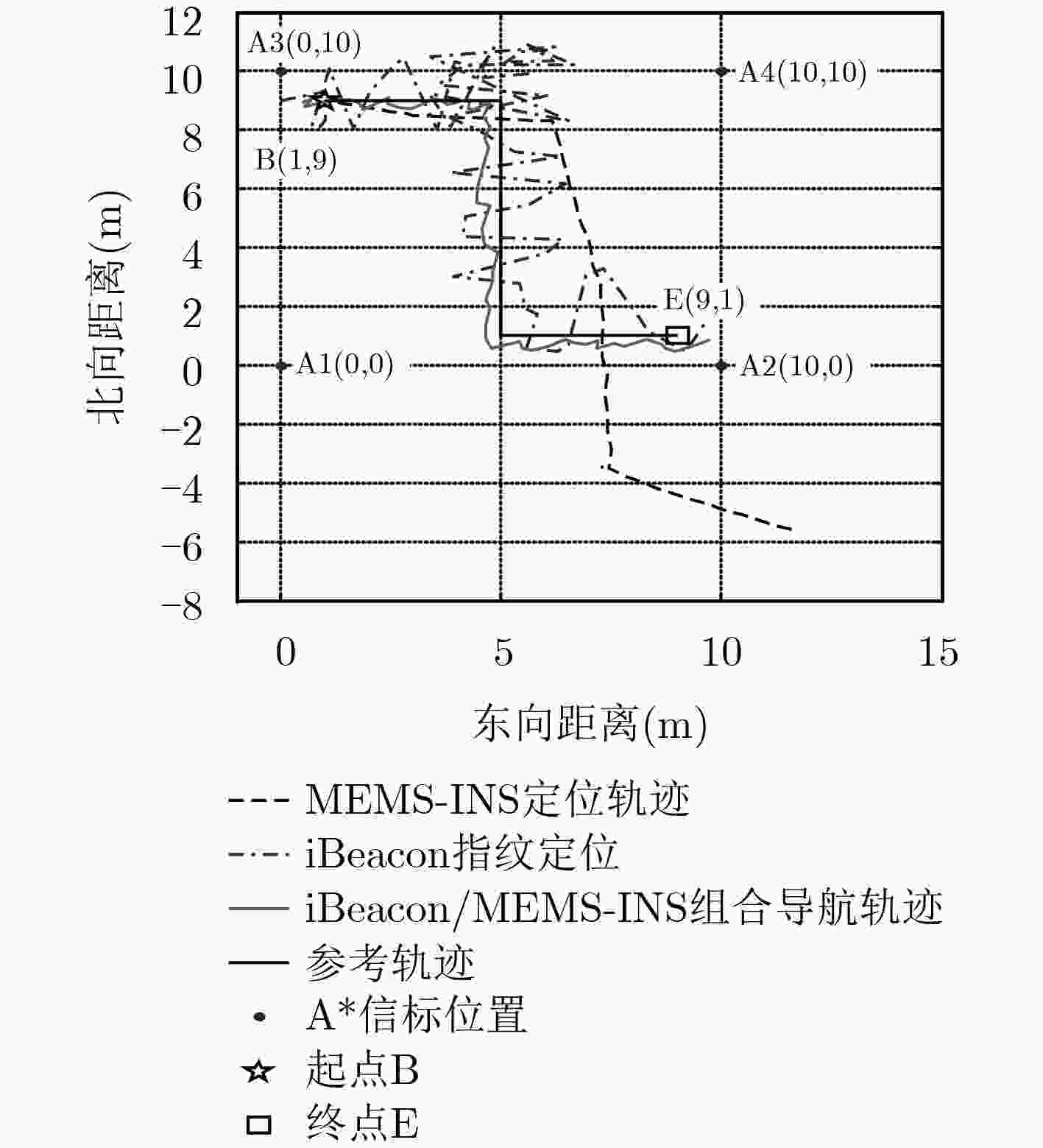
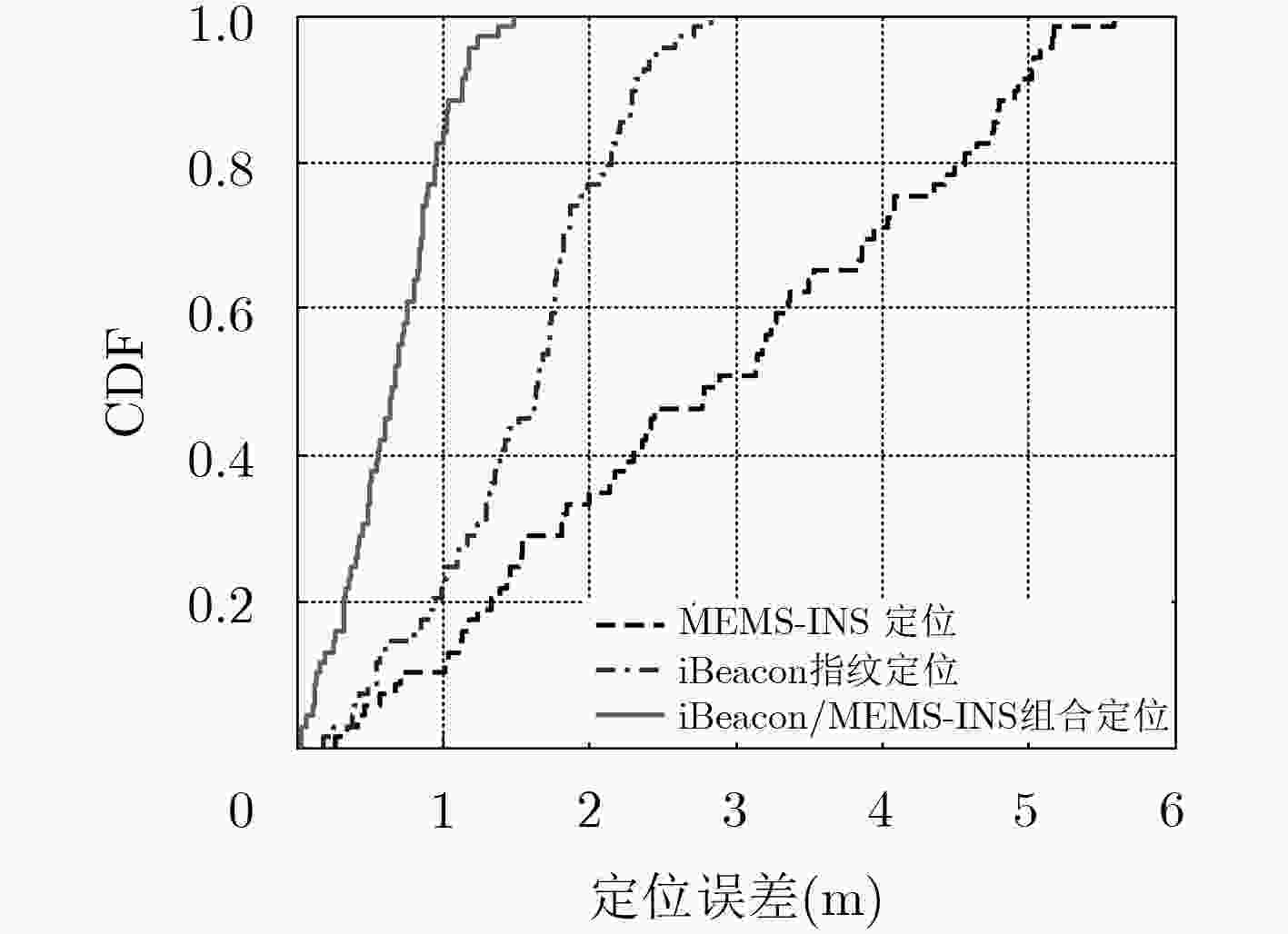


 下载:
下载:
