Saliency Detection Using Wavelet Transform in Hypercomplex Domain
-
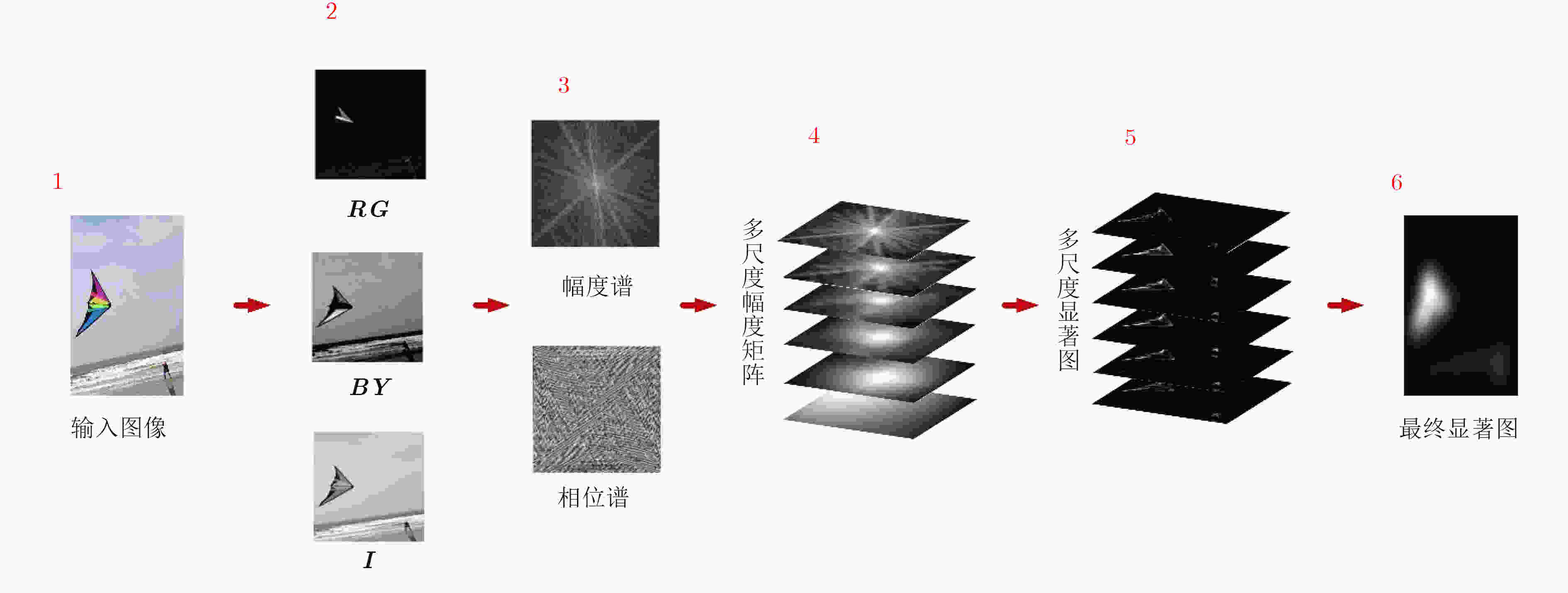
摘要: 针对现有频域显著性检测方法得到的显著区域不完整的问题,该文提出一种多尺度分析的频率域显著性检测方法。首先由输入图像特征通道信息构建4元超复数,然后通过小波变换对4元超复数域中幅度谱进行多尺度分解,计算生成多尺度下的视觉显著图,最后由评价函数选出效果较好显著图合成最终视觉显著图。实验结果表明,该文方法能够有效地抑制背景干扰,快速、精确地找到完整的显著目标,具有较高的检测精确度。Abstract: To solve the incompleteness of the salient region obtained by the existing saliency detection method in the frequency domain, a frequency saliency detection method of multi-scale analysis is proposed. Firstly, the quaternion hypercomplex is constructed by the input image feature channels. Then, the multi-scale decomposition of the quaternion amplitude spectrum is performed by wavelet transform, and the multi-scale visual saliency map is calculated. Finally, the better saliency map is fused based on the evaluation function, and central bias is used to generate the final visual saliency map. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively suppress the background interference, find significant target quickly and accurately, and have high detection accuracy.
-
表 1 注视点AUC得分
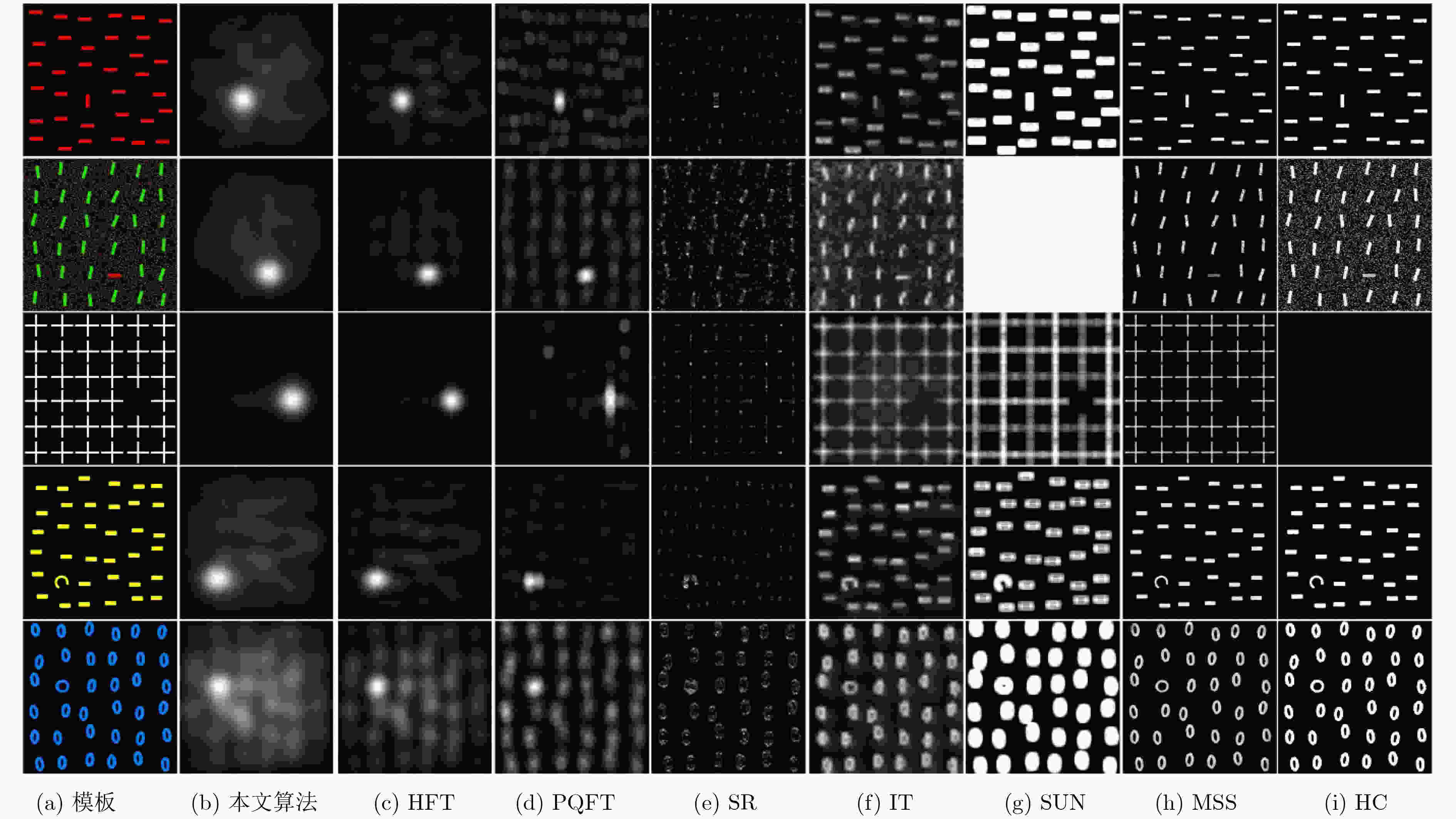
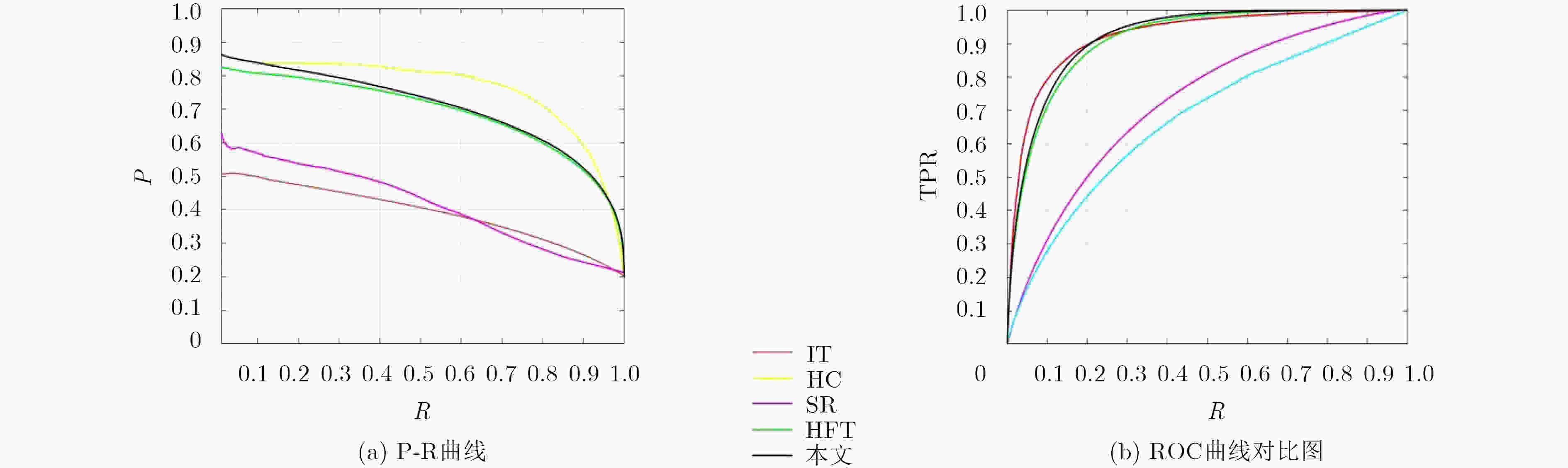
注视点 本文算法 HFT PQFT SR IT SUN MSS HC 全部 0.8328 0.8046 0.7570 0.6228 0.5365 0.6729 0.6558 0.5766 2个 0.8831 0.8402 0.7696 0.6274 0.5444 0.6746 0.6698 0.5853 表 2 自然图像AUC得分
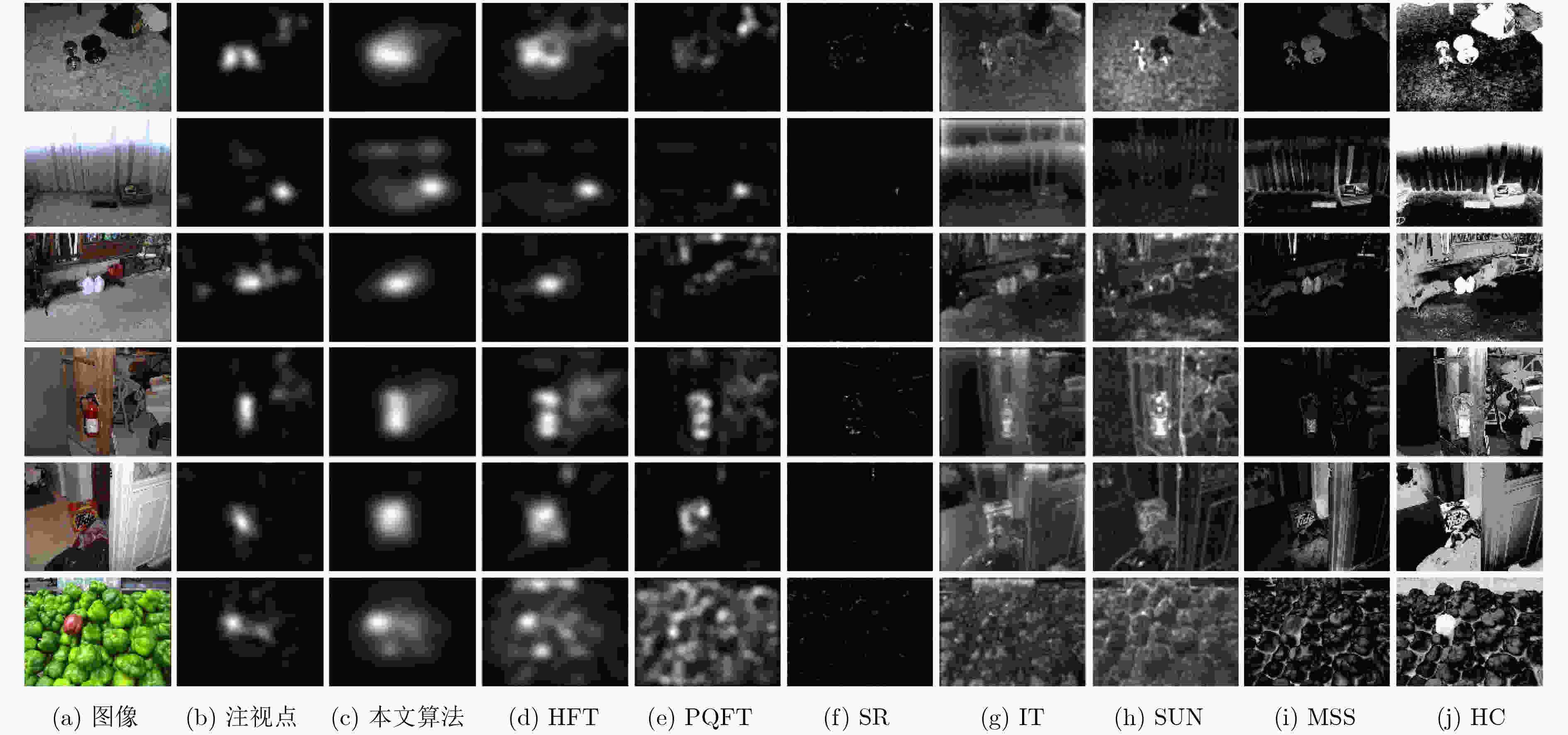
方法 本文算法 HFT SR IT HC AUC 0.9202 0.9118 0.6736 0.7252 0.9212 表 3 算法计算速度(s)
方法 本文算法 HFT PQFT SR IT SUN MSS HC 时间 0.0832 0.0936 0.0198 0.0081 0.2697 1.6185 0.0767 0.6585 -
YAO Haishan and LI Chaoyi. Clustered organization of neurons with similar extra-receptive field properties in the primary visual cortex[J]. Neuron, 2002, 35(3): 547–553. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00782-1 ITTI L, KOCH C, and NIEBUR E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254–1259. doi: 10.1109/34.730558 ITTI L and KOCH C. Computational modelling of visual attention[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2001, 2(3): 194–203. doi: 10.1038/35058500 ZHANG Lingyun, TONG M H, MARKS T K, et al. SUN: A Bayesian framework for saliency using natural statistics[J]. Journal of Vision, 2008, 8(7): 32, 1–20. doi: 10.1167/8.7.32 ACHANTA R and SÜSSTRUNK S. Saliency detection using maximum symmetric surround[C]. 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 2010: 2653–2656. CHENG Mingming, ZHANG Guoxin, MITRA N J, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[C]. CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, USA, 2011: 409–416. CHENG Mingming, MITRA N J, HUANG Xiaolei, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 569–582. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401 ZHANG Lihe, YANG Chuan, and LU Huchuan. Ranking saliency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(9): 1892–1904. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2609426 AZAZA A and DOUIK A. Saliency detection based object proposal[C]. The 14th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices, Marrakech, Morocco, 2017: 597–600. WANG Wenguan and SHEN Jianbing. Deep visual attention prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(5): 2368–2378. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2787612 CAO Feilong, LIU Yuehua, and WANG Dianhui. Efficient saliency detection using convolutional neural networks with feature selection[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 456: 34–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.05.006 吴泽民, 王军, 胡磊, 等. 基于卷积神经网络与全局优化的协同显著性检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(12): 2896–2904. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180241WU Zemin, WANG Jun, HU Lei, et al. Co-saliency detection based on convolutional neural network and global optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(12): 2896–2904. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180241 HOU Xiaodi and ZHANG Liqing. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach[C]. 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA, 2007: 1–8. GUO Chenlei, MA Qi, and ZHANG Liming. Spatio-temporal saliency detection using phase spectrum of quaternion Fourier transform[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–8. LI Jian, LEVINE M D, AN Xiangjing, et al. Visual saliency based on scale-space analysis in the frequency domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(4): 996–1010. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.147 SANGWINE S J. Fourier transforms of colour images using quaternion or hypercomplex, numbers[J]. Electronics Letters, 1996, 32(21): 1979–1980. doi: 10.1049/el:19961331 ELL T A and SANGWINE S J. Hypercomplex Fourier transforms of color images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(1): 22–35. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.884955 ANTONINI M, BARLAUD M, MATHIEU P, et al. Image coding using wavelet transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1992, 1(2): 205–220. doi: 10.1109/83.136597 BIAN Peng and ZHANG Liming. Visual saliency: A biologically plausible contourlet-like frequency domain approach[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2010, 4(3): 189–198. doi: 10.1007/s11571-010-9122-0 GOFERMAN S, ZELNIK-MANOR L, and TAL A. Context-aware saliency detection[C]. Processing of 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2376–2383. GOFERMAN S, ZELNIK-MANOR L, and TAL A. Context-aware saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(10): 1915–1926. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.272 DAVIS J and GOADRICH M. The relationship between precision-recall and ROC curves[C]. Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, USA, 2006: 233–240. BRUCE N D B and TSOTSOS J K. Saliency, attention, and visual search: An information theoretic approach[J]. Journal of Vision, 2009, 9(3): 5, 1–24. doi: 10.1167/9.3.5. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
