Training Multi-layer Perceptrons Using Chaos Grey Wolf Optimizer
-
摘要:
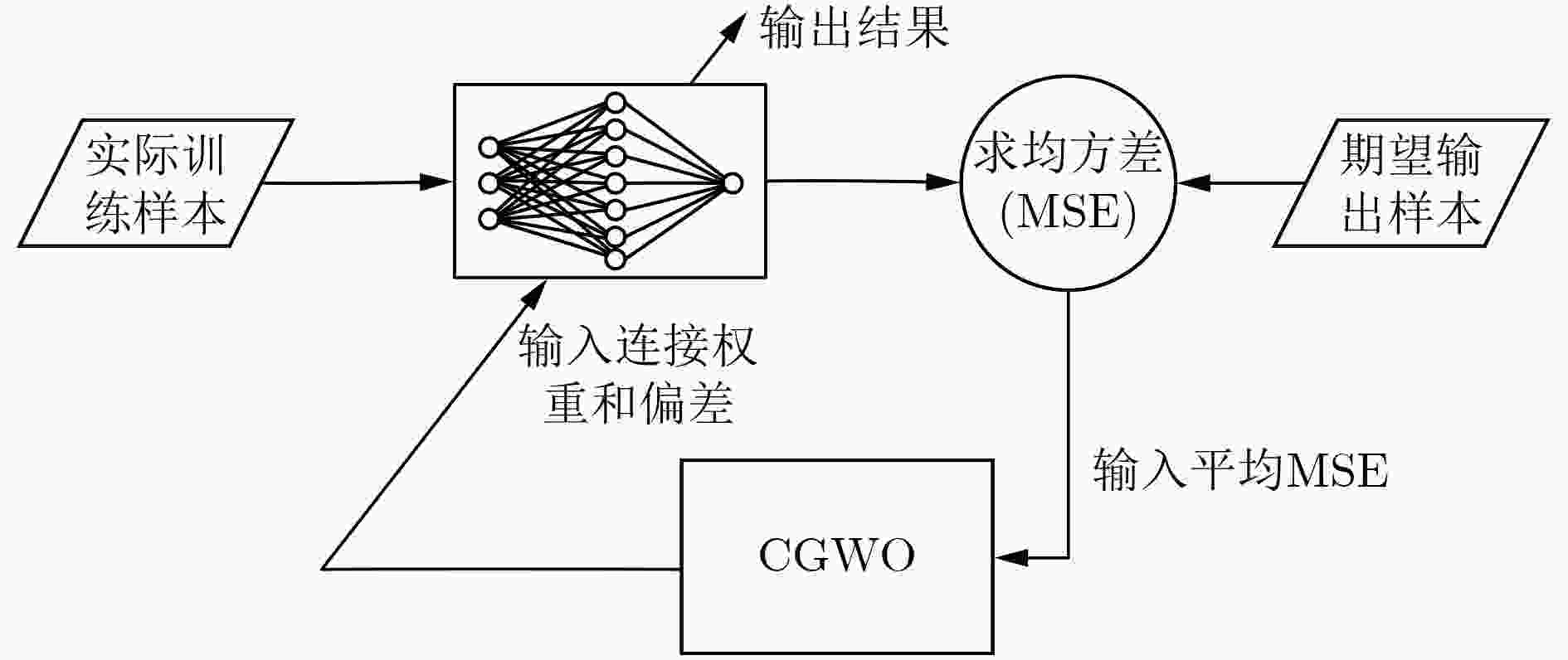
灰狼优化算法(GWO)是一种新的基于灰狼捕食行为的元启发式算法,被证明是一种具有高水平的探索和开发能力的算法。但是存在开发和探索不平衡的问题,以至于其优化性能并不理想。该文将混沌理论引入GWO中,用于平衡GWO的探索和开发,提出一种改进的混沌灰狼优化算法(CGWO),并应用于多层感知器(MLPs)的训练。首先,基于Cubic混沌理论对GWO的位置更新公式进行改进,以增加个体的多样性,增大跳出局部最优的概率和对解空间进行深入的搜索;其次,设计一种非线性收敛因子,用于协调和平衡CGWO算法在不同迭代进化时期的探索和开发能力;最后,将CGWO算法作为MLPs的训练器,用于对3个复杂分类问题进行分类实验。结果表明:CGWO在分类准确率,避免陷入局部最优,全局收敛速度和鲁棒性方面相较于其他对比算法均具有较好的性能。
Abstract:The Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) algorithm mimics the leadership hierarchy and hunting mechanism of grey wolves in nature, and it is an algorithm with high level of exploration and exploitation capability. This algorithm has good performance in searching for the global optimum, but it suffers from unbalance between exploitation and exploration. An improved Chaos Grey Wolf Optimizer called CGWO is proposed, for solving complex classification problem. In the proposed algorithm, Cubic chaos theory is used to modify the position equation of GWO, which strengthens the diversity of individuals in the iterative search process. A novel nonlinear convergence factor is designed to replace the linear convergence factor of GWO, so that it can coordinate the balance of exploration and exploitation in the CGWO algorithm. The CGWO algorithm is used as the trainer of the Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs), and 3 complex classification problems are classified. The statistical results prove the CGWO algorithm is able to provide very competitive results in terms of avoiding local minima, solution precision, converging speed and robustness.
-
表 1 3位奇偶校验问题(3 bit XOR)
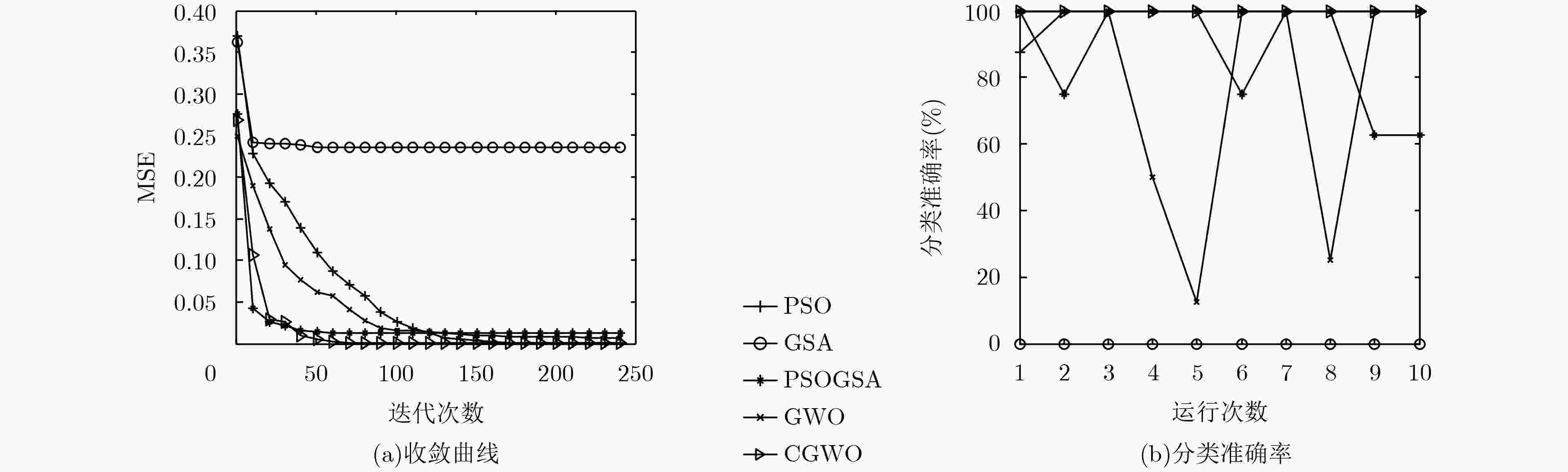
输入 输出 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 表 2 5种算法对3 bit XOR问题10次独立运行结果的比较
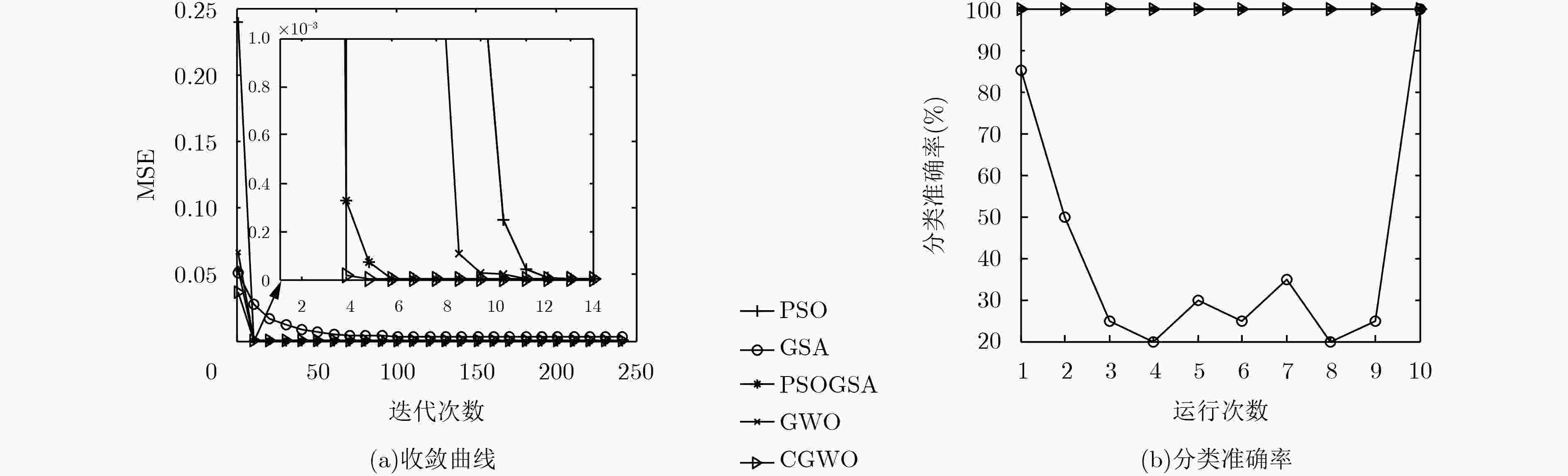
算法 平均值 中值 标准差 最好值 PSO-MLP 1.48e–04 1.65e–05 2.40e–04 7.67e–09 GSA-MLP 2.35e–01 2.38e–01 1.17e–02 2.10e–01 PSOGSA-MLP 1.27e–02 9.29e–06 2.57e–02 1.64e–09 GWO-MLP 7.00e–03 6.07e–03 1.89e–02 2.90e–05 CGWO-MLP 6.01e–06 1.21e–08 1.33e–05 2.69e–09 表 3 5种算法对气球分类问题10次独立运行结果的比较
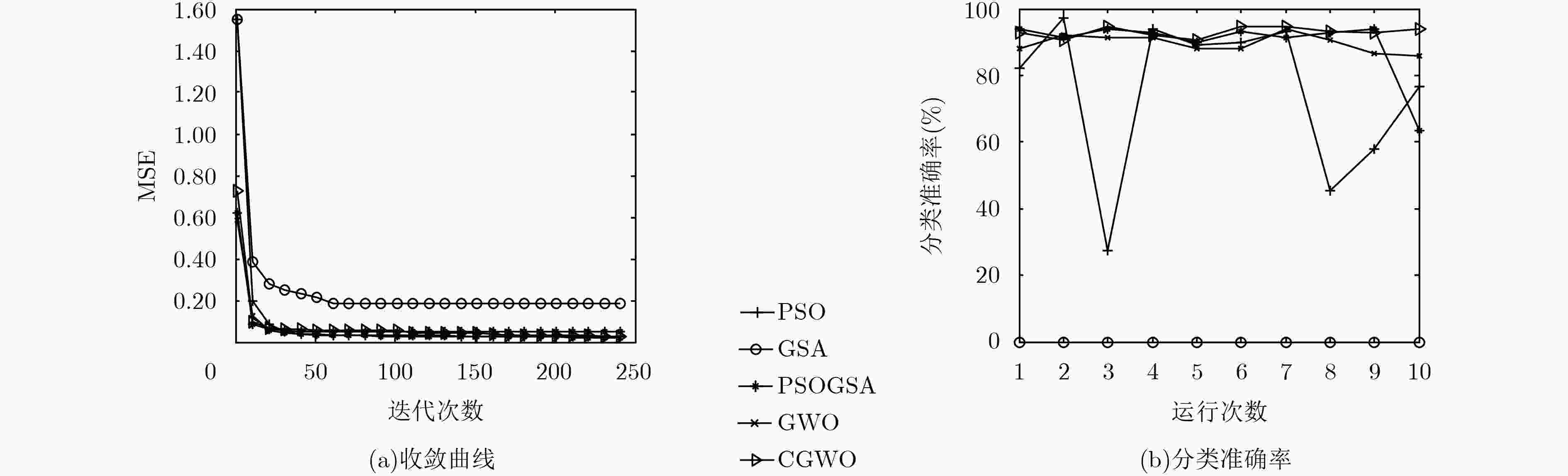
算法 平均值 中值 标准差 最好值 PSO-MLP 0 0 0 0 GSA-MLP 5.90e–03 4.10e–03 6.00e–03 4.69e–04 PSOGSA-MLP 9.85e–32 9.73e–40 2.94e–31 3.81e–61 GWO-MLP 1.12e–18 3.56e–20 2.38e–18 2.49e–26 CGWO-MLP 2.35e–15 2.07e–18 5.03e–15 1.00e–18 表 4 5种算法对虹膜分类问题10次独立运行结果的比较
算法 平均值 中值 标准差 最好值 PSO-MLP 2.70e–02 2.47e–02 1.76e–02 6.20e–03 GSA-MLP 1.83e–01 1.89e–01 2.30e–02 1.48e–01 PSOGSA-MLP 4.91e–02 1.84e–02 1.01e–01 1.16e–02 GWO-MLP 2.27e–02 2.19e–02 2.70e–03 1.71e–02 CGWO-MLP 1.90e–02 1.82e–02 4.10e–03 1.39e–02 -
MCCULLOCH W S and PITTS W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity[J]. The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 1943, 5(4): 115–133 doi: 10.1007/BF02478259 BEBIS G and GEORGIOPOULOS M. Feed-forward neural networks[J]. IEEE Potentials, 1994, 13(4): 27–31 doi: 10.1109/45.329294 KOHONEN T. The self-organizing map[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1990, 78(9): 1464–1480 doi: 10.1109/5.58325 JAFRASTEH B and FATHIANPOUR N. A hybrid simultaneous perturbation artificial bee colony and back-propagation algorithm for training a local linear radial basis neural network on ore grade estimation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 235: 217–227 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.016 CHICEA D. Using neural networks for dynamic light scattering time series processing[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2017, 28(5): 055206 doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aa61b4 MORRO A, CANALS V, OLIVER A, et al. A stochastic spiking neural network for virtual screening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(4): 1371–1375 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2657601 MIRJALILI S. How effective is the Grey Wolf Optimizer in training multi-layer perceptrons[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2015, 43(1): 150–161 doi: 10.1007/s10489-014-0645-7 ISA N A M and MAMAT W M F W. Clustered-hybrid multilayer perceptron network for pattern recognition application[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2011, 11(1): 1457–1466 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2010.04.017 韦岗, 李华, 徐秉铮. 关于前馈多层神经网络多维函数逼近能力的一个定理[J]. 电子科学学刊, 1997, 20(4): 433–438WEI Gang, LI Hua, and XU Bingzheng. A novel theorem on the multi-dimensional function approximation ability of feed forward multi-layer neural networks[J]. Journal of Electronics, 1997, 20(4): 433–438 LIBANO F, RECH P, TAMBARA L, et al. On the reliability of linear regression and pattern recognition feedforward artificial neural networks in FPGAs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2018, 65(1): 288–295 doi: 10.1109/TNS.2017.2784367 LI Feng, ZURADA J M, LIU Yan, et al. Input layer regularization of multilayer feedforward neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 10979–10985 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2713389 MIRJALILI S, MOHD H S, and MORADIAN S H. Training feedforward neural networks using hybrid particle swarm optimization and gravitational search algorithm[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2012, 218(22): 11125–11137 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2012.04.069 张长利, 房俊龙, 潘伟. 用遗传算法训练的多层前馈神经网络对番茄成熟度进行自动检测的研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2001, 17(3): 153–156 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2001.03.037ZHANG Changli, FANG Junlong, and PANG Wei. Automated identification of tomato maturation using multilayer feedforward neural network with genetic algorithms (GA)[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2001, 17(3): 153–156 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2001.03.037 ZHANG Ridong and TAO Jili. A nonlinear fuzzy neural network modeling approach using an improved genetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(7): 5882–5892 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2777415 海宇娇, 刘青昆. 基于差分进化的ELM加权集成分类[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2017, 53(8): 57–60 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1510-0051HAI Yujiao and LIU Qingkun. ELM weighting ensemble classification based on differential evolution[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2017, 53(8): 57–60 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1510-0051 LEEMAA N, NEHEMIAHA H K, and KANNANB A. Neural network classifier optimization using differential evolution with global information and back propagation algorithm for clinical datasets[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2016, 49: 834–844 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.08.001 MICHALIS M and YANG Shengxiang. Training neural networks with ant colony optimization algorithms for pattern classification[J]. Soft Computing, 2015, 19(6): 1511–1522 doi: 10.1007/s00500-014-1334-5 KRZYSZTOF S and CHRISTIAN B. An ant colony optimization algorithm for continuous optimization: application to feed-forward neural network training[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2007, 16(3): 235–247 doi: 10.1007/s00521-007-0084-z ROBERT C G, WANG Lingfeng, and MANSOOR A. Training neural networks using central force optimization and particle swarm optimization: Insights and comparisons[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(1): 555–563 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.07.046 ZHANG Jingru, ZHANG Jun, LOCK T M, et al. A hybrid particle swarm optimization–back-propagation algorithm for feedforward neural network training[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2007, 185(2): 1026–1037 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2006.07.025 CHEN Ke, ZHOU Fengyu, and LIU Aling. Chaotic dynamic weight particle swarm optimization for numerical function optimization[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 139: 23–40 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.10.011 LONG Wen, JIAO Jianjun, LIANG Ximing, et al. An exploration-enhanced grey wolf optimizer to solve high-dimensional numerical optimization[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 68: 63–80 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2017.10.024 MURO C, ESCOBEDO R, SPECTOR L, et al. Wolf-pack hunting strategies emerge from simple rules in computational simulations[J]. Behavioral Processes, 2011, 88(3): 192–197 doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2011.09.006 MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, and LEWIS A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46–61 doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007 UDWADIA F E and GUTTALU R S. Chaotic dynamics of a piecewise cubic map[J]. Physical Review A, 1989, 40(7): 4032–4044 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.40.4032 龙文, 蔡绍洪, 焦建军, 等. 求解大规模优化问题的改进鲸鱼优化算法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2017, 37(11): 2983–2994 doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2017)11-2983-12LONG Wen, CAI Shaohong, JIAO Jianjun, et al. Improved whale optimization algorithm for large scale optimization problems[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory &Practice, 2017, 37(11): 2983–2994 doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2017)11-2983-12 AlI M H, MOHAMMED B A D A, ISMAIL A, et al. A new intrusion detection system based on fast learning network and particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 20255–20261 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2820092 BLAKE C l and MERZ C J. UCI Repository of machine learning databases[OL]. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets.html, 1998. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
