Compressive Sensing Based Multi-target Device-free Passive Localization Algorithm Using Multidimensional Measurement Information
-
摘要:
无源被动定位是入侵者检测、环境监测以及智能交通等应用的关键问题之一。现有的无源被动定位方法可通过信道状态信息获取多个维度上的测量信息,但是现有方案未能充分挖掘多个信道上的频率分集以提高定位性能。该文提出一种基于多维测量信息的压缩感知多目标无源被动定位算法,在压缩感知框架下利用多维测量信息的频率分集提高定位精度和鲁棒性。根据鞍面模型建立无源字典,将多目标无源被动定位问题建模成多测量向量联合稀疏恢复问题,并利用多维稀疏贝叶斯学习算法估计目标位置向量。仿真结果表明,该算法能有效利用多维测量信息提高定位性能。
Abstract:Device-free passive localization is a key issue of the intruder detection, environmental monitoring, and intelligent transportation. The existing device-free passive localization method can obtain the multidimensional measurement information by channel state information, but the existing scheme can not fully exploit the frequency diversity on multiple channels to improve the localization performance. This paper proposes a Compressive Sensing (CS) based multi-target device-free passive localization algorithm using multidimensional measurement information. It takes advantage of the frequency diversity of multidimensional measurement information to improve the accuracy and robustness of localization results under the CS framework. The dictionary is built according to the saddle surface model, and the multi-target device-free passive localization problem is modeled as a joint sparse recovery problem based on multiple measurement vectors. The target location vector is estimated based on the multiple sparse Bayesian learning algorithm. Simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithm can make full use of the multidimensional measurement information to improve the localization performance.
-
表 1 联合稀疏恢复算法
(1) 令${\gamma _{{\rm{th}}}} = {10^{ - 3}}$, ${\tau _{\max }} = {10^3}$, ${\eta _{{\rm{th}}}} = - 10\ {\rm{dB}}$, $\gamma = \tau = 0$。 (2) while ($\gamma \ge {\gamma _{{\rm{th}}}}$或$\tau \le {\tau _{\max }}$) do (3) 根据式(16)和式(17),计算${{Σ}}$和${{Π}}$。 (4) 根据式(19)和式(20),更新参数${\alpha _n}$和${\sigma ^2}$。 (5) 令$\gamma \leftarrow \parallel{Y} - {{Φ}}{{Π}}\parallel $, $\tau \leftarrow \tau + 1$。 (6) end while (7) 选择使$\left\| {{{{y}}^f} - {{Φ}}{{{Π}} _{ \cdot f}}} \right\|$取得最小值的子信道$\hat f$。 (8) $\forall n \in \left\{ {1,2,·\!·\!·,N} \right\}$,若$20\lg ({{{Π}} _{nf}}/\mathop {\max }\limits_i |{{{Π}} _{i\hat f}}|) < {\eta _{{\rm{th}}}}$,则${{{Π}} _{n\hat f}} = 0$。 (9) 令恢复的位置向量$\hat {{θ}} = {{{Π}} _{ \cdot \hat f}}$,目标个数${\widehat K} = |\hat {{θ}}|$。 表 2 平均定位误差与定位均方根误差的比较
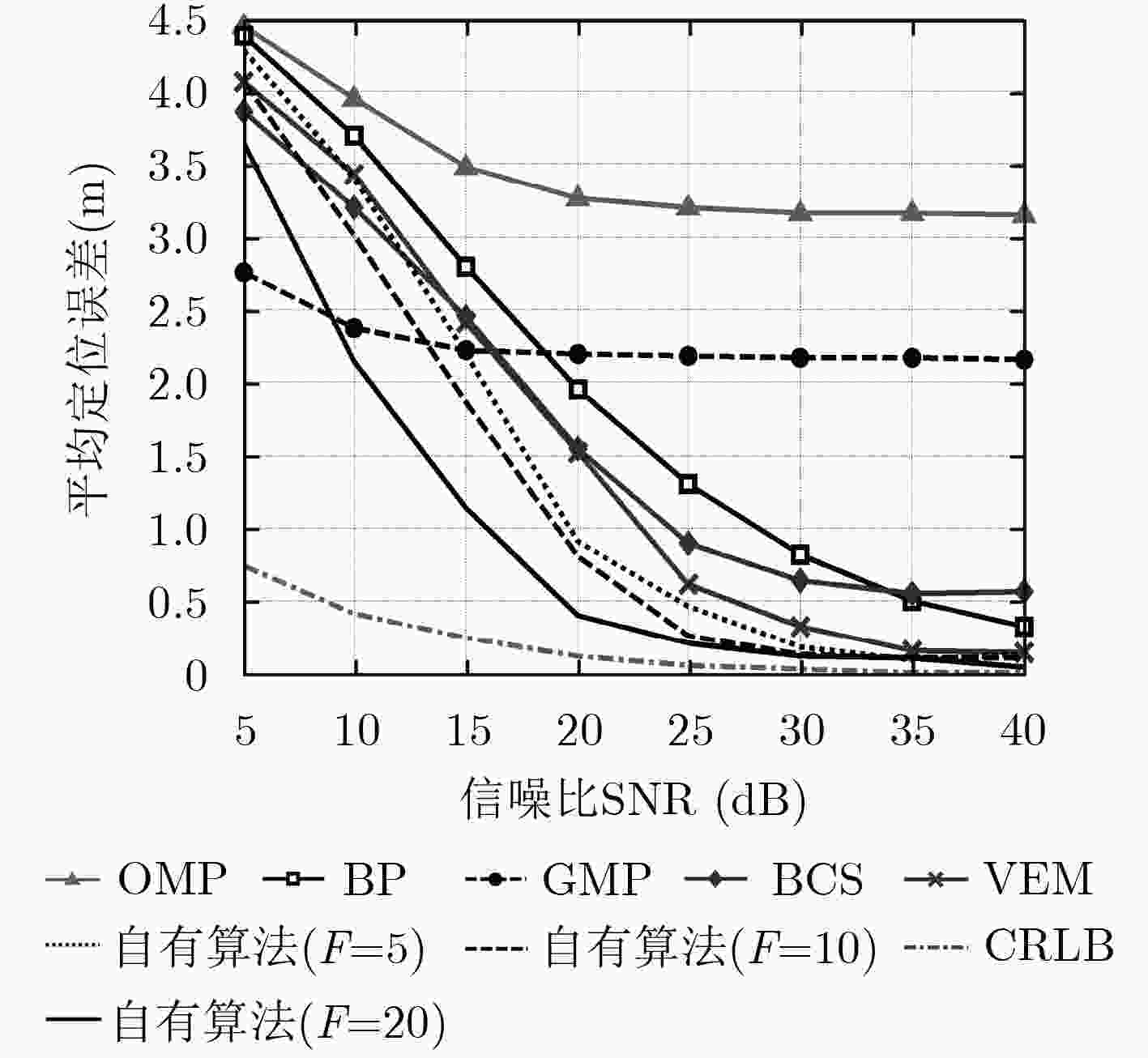
定位算法 OMP BP GMP BCS VEM 自有算法($F = 5$) 自有算法($F = 10$) 自有算法($F = 20$) 平均定位误差 3.2028 1.3028 2.1795 0.8955 0.6196 0.4631 0.2744 0.2584 定位均方根误差 3.3801 1.5735 2.4543 1.5838 1.0036 0.8392 0.6720 0.4738 -
LIU Dawei, SHENG Bin, HOU Fen, et al. From wireless positioning to mobile positioning: An overview of recent advances[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2014, 8(4): 1249–1259. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2013.2295136 冯奇, 曲长文, 周强. 多运动站异步观测条件下的直接定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(2): 417–422. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160314FENG Qi, QU Changwen, and ZHOU Qiang. Direct position determination using asynchronous observations of multiple moving sensors[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(2): 417–422. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160314 孙保明, 郭艳, 李宁, 等. 无线传感器网络中基于压缩感知的动态目标定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 1858–1864. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151203SUN Baoming, GUO Yan, LI Ning, et al. Mobile target localization algorithm using compressive sensing in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 1858–1864. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151203 YOUSSEF M, MAH M, and AGRAWALA A. Challenges: Device-free passive localization for wireless environments[C]. Proceedings of the ACM MobiCom’07, Montreal, 2007: 222–229. ZHANG Dian, MA Jian, CHEN Quanbin, et al. An RF-based system for tracking transceiver-free objects[C]. Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom’07), White Plains, 2007: 135–144. WANG Jie, GAO Qinhua, PAN Miao, et al. Device-free wireless sensing: Challenges, opportunities, and applications[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(2): 132–137. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2017.1700133 WANG Ju, FANG Dingyi, and YANG Zhe. E-HIPA: An energy-efficient framework for high-precision multi-target adaptive device-free localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(3): 716–729. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2567396 TALAMPAS M C R and LOW K S. A geometric filter algorithm for robust device-free localization in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(5): 1670–1678. doi: 10.1109/TII.2015.2433211 KHALAJMEHRABADI A, GATSIS N, and AKOPIAN D. Modern WLAN fingerprinting indoor positioning methods and deployment challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1974–2002. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2671454 WANG Qinghua, YIGITLER H, JANTTI R, et al. Localizing multiple objects using radio tomographic imaging technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(5): 3641–3656. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2432038 CANDES E J and WAKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21–30. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 WANG Ju, FANG Dingyi, CHEN Xiaojing, et al. LCS: Compressive sensing based device-free localization for multiple targets in sensor networks[C]. Proceeding of the IEEE INFOCOM 2013, Turin, 2013: 14–19. MAGER B, LUNDRIGAN P, and PATWARI N. Fingerprint-based device-free localization performance in changing environments[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 33(11): 2429–2438. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2430515 YU Dongping, GUO Yan, LI Ning, et al. Dictionary refinement for compressive sensing based device-free localization via the variational EM algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 9743–9757. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2649540 YANG Zheng, ZHOU Zimu, and LIU Yunhao. From RSSI to CSI: Indoor localization via channel response[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2013, 46(2): 1–32. doi: 10.1145/2543581.2543592 GAO Qinhua, WANG Jie, MA Xiaorui, et al. CSI-based device-free wireless localization and activity recognition using radio image features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(11): 10346–10356. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2737553 LEI Qian, ZHANG Haijian, SUN Hong, et al. Fingerprint-based device-free localization in changing environments using enhanced channel selection and logistic regression[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 2569–2577. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2784387 WANG Jie, GAO Qinhua, PAN Miao, et al. Towards accurate device-free wireless localization with a saddle surface model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(8): 6665–6677. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2476495 WIPF D P and RAO B D. An empirical Bayesian strategy for solving the simultaneous sparse approximation problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3704–3716. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894265 SAVAZZI S, NICOLI M, CARMINATI F, et al. A Bayesian approach to device-free localization: Modeling and experimental assessment[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(1): 16–29. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2286772 JI Shihao, XUE Ya, and CARIN L. Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(6): 2346–2356. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.914345 -





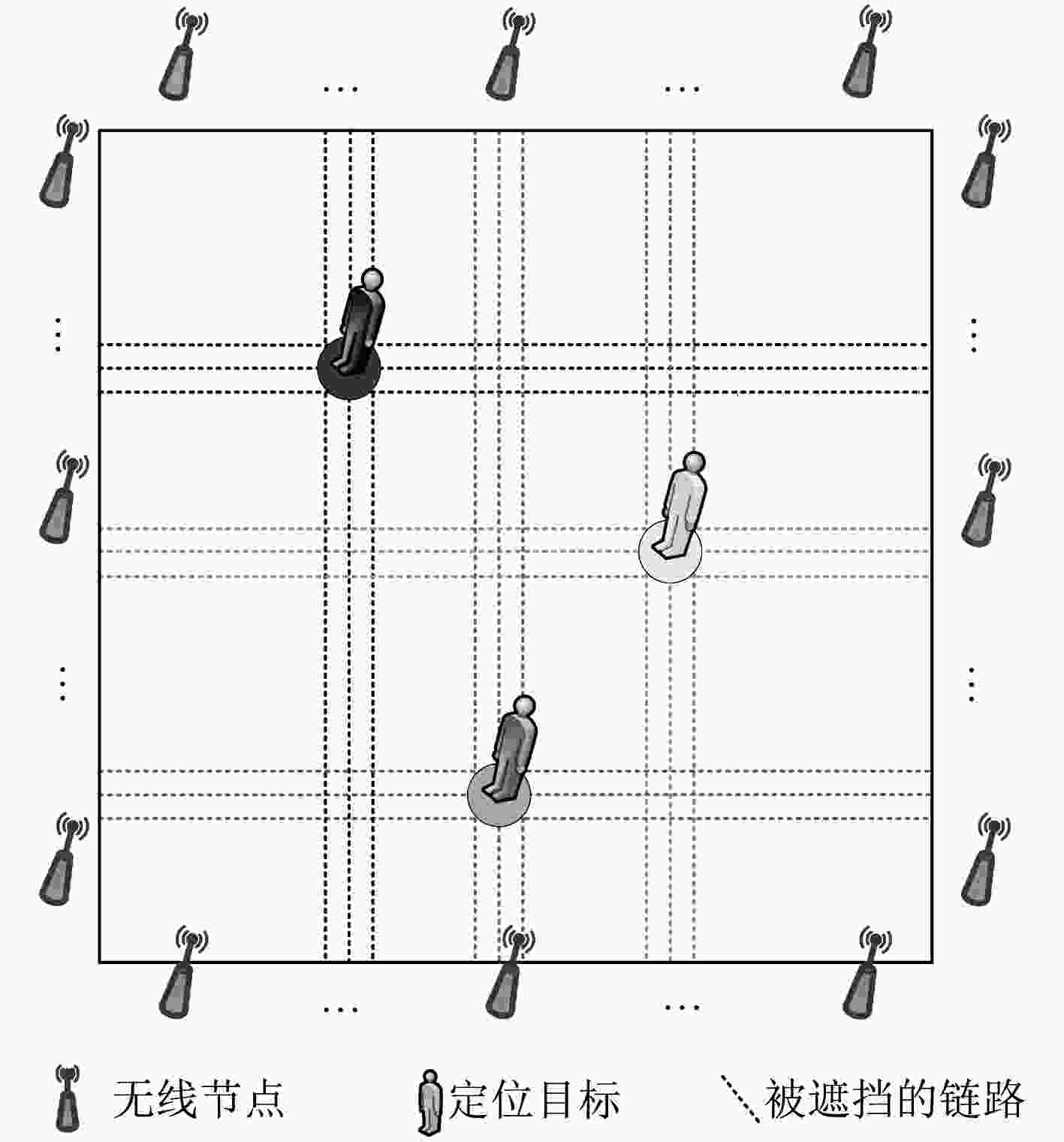
 下载:
下载:
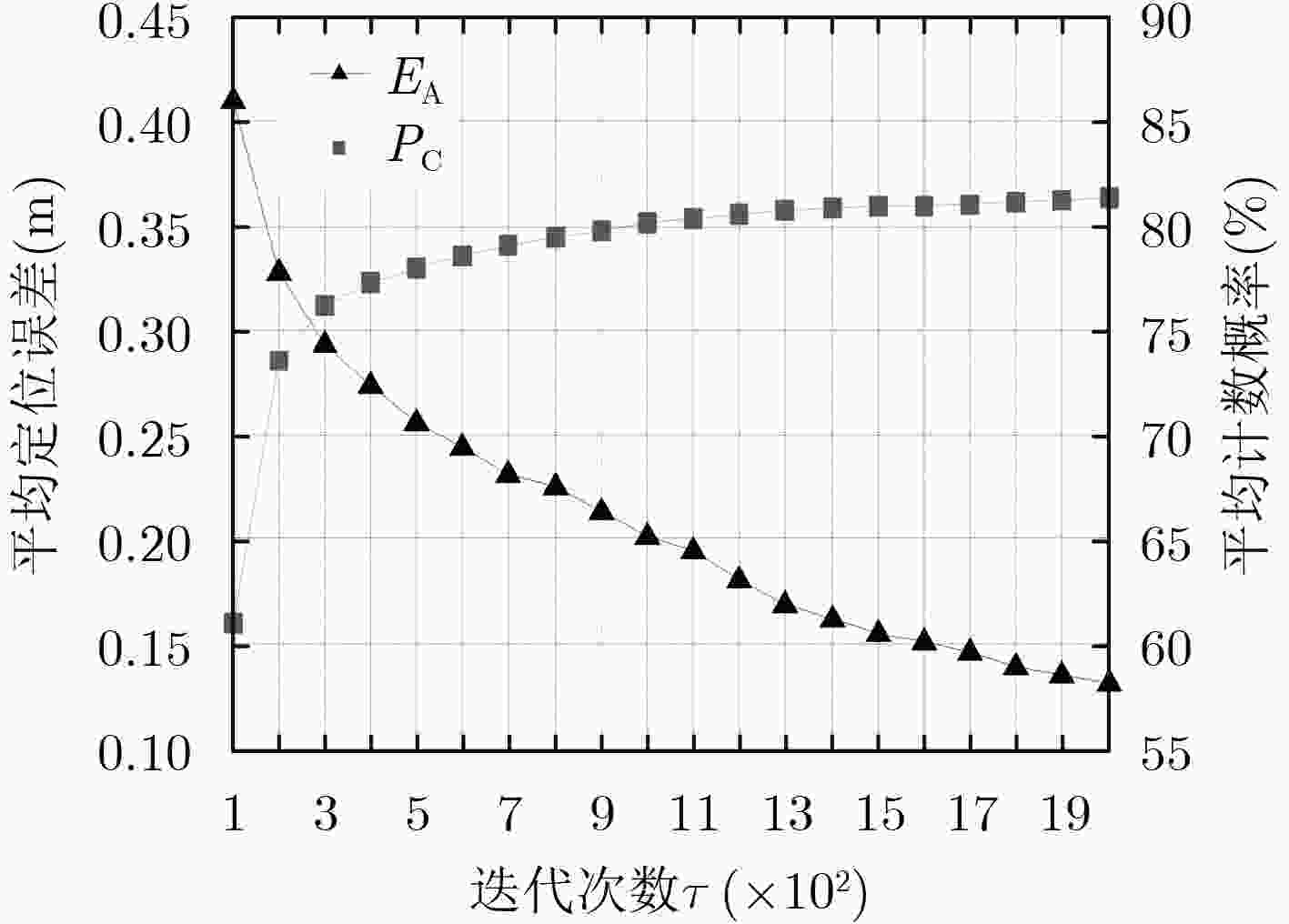
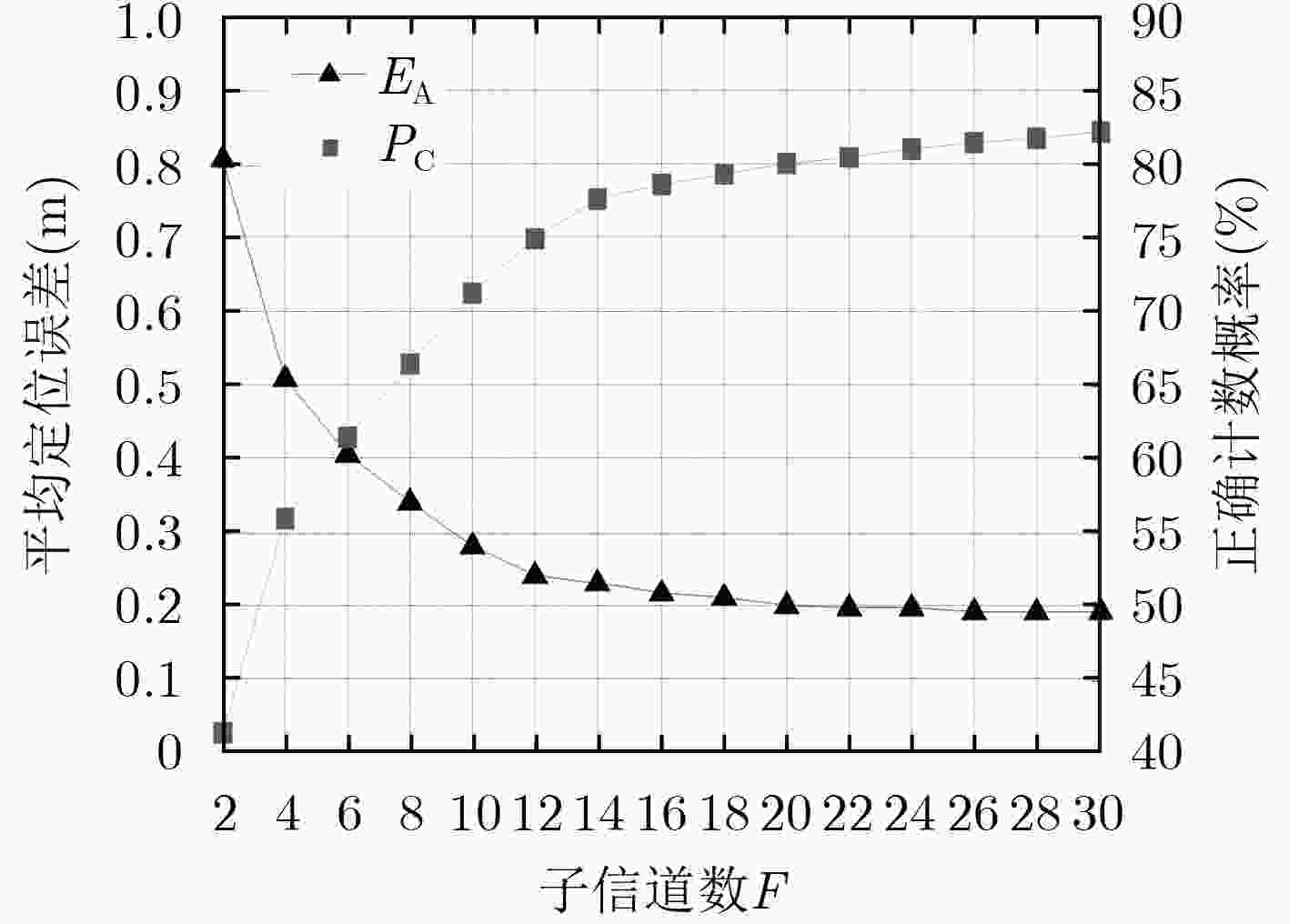
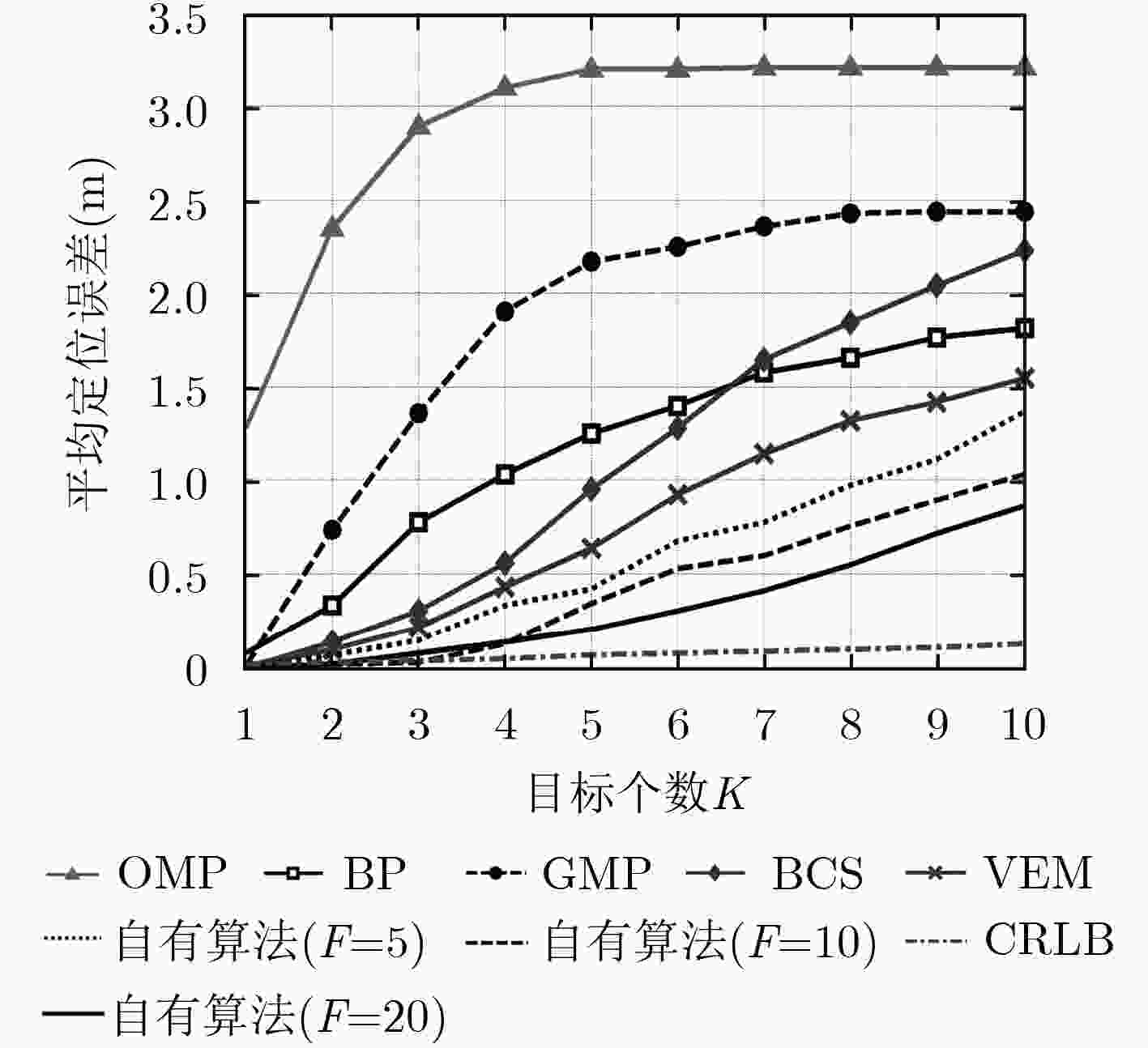


 下载:
下载:
