Pre-decoding Based Maximum-likelihood Simplified Successive-cancellation Decoding of Polar Codes
-
摘要:
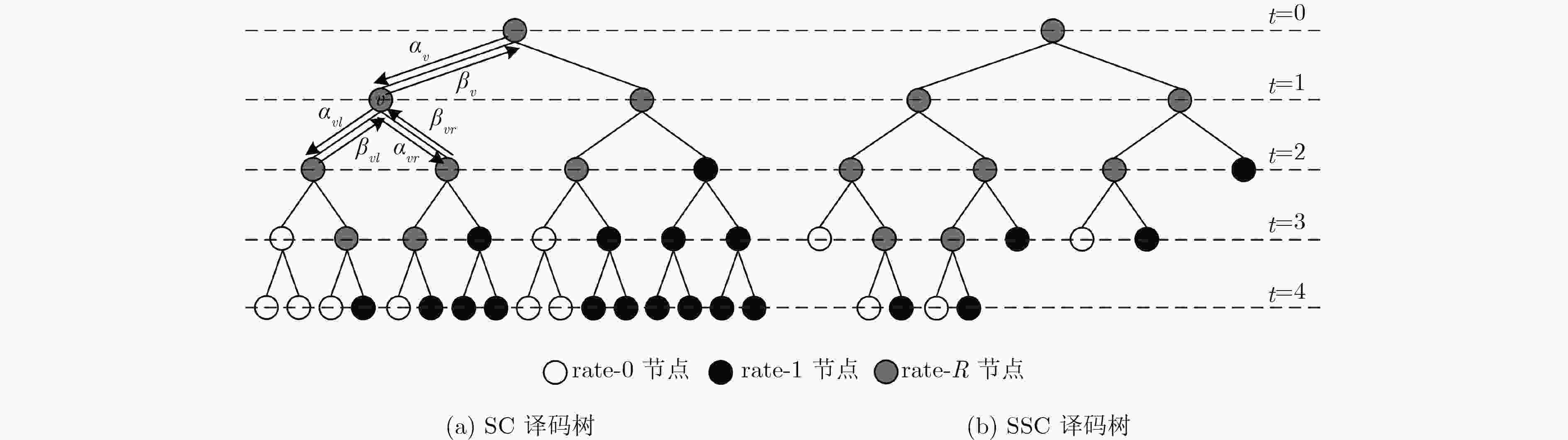
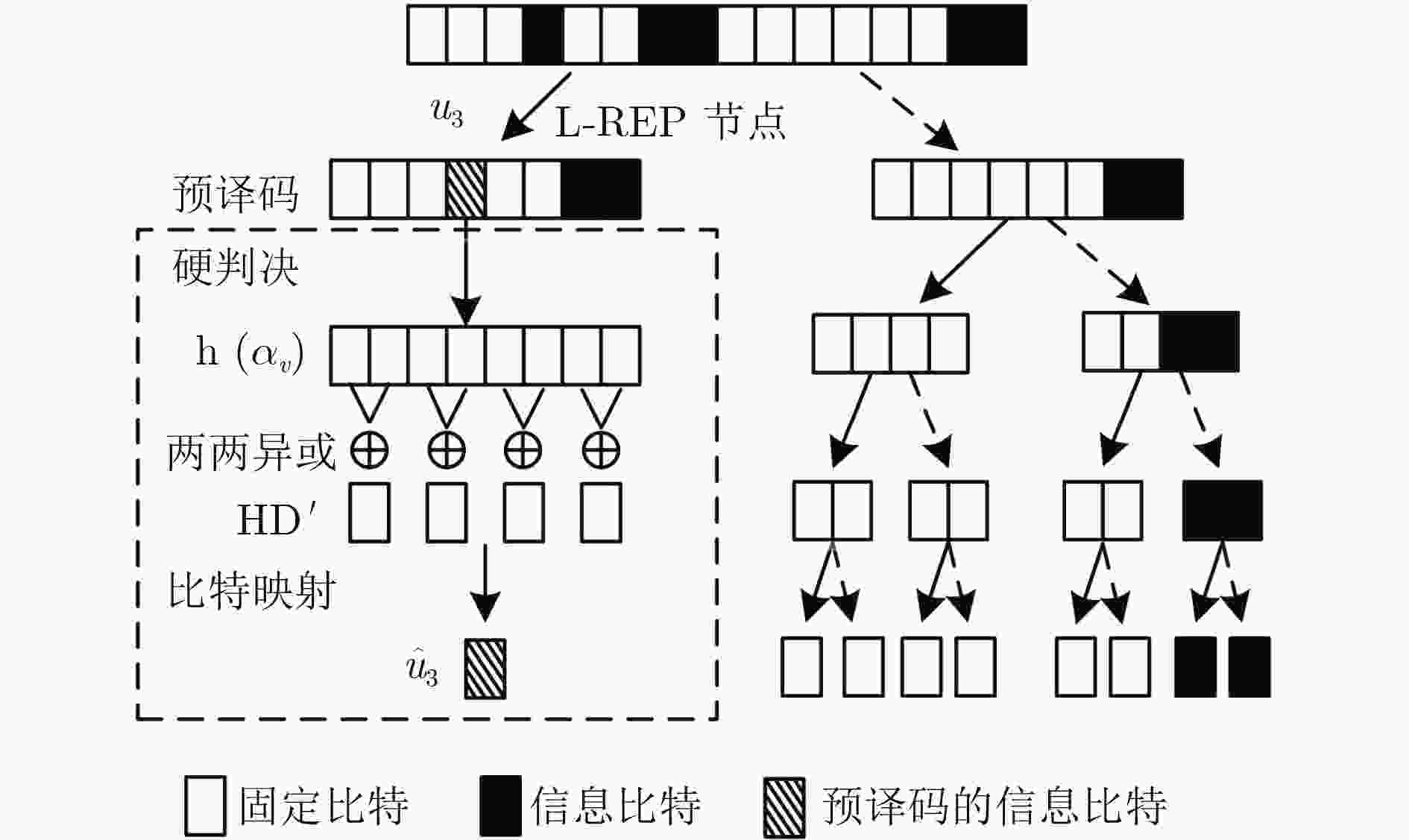
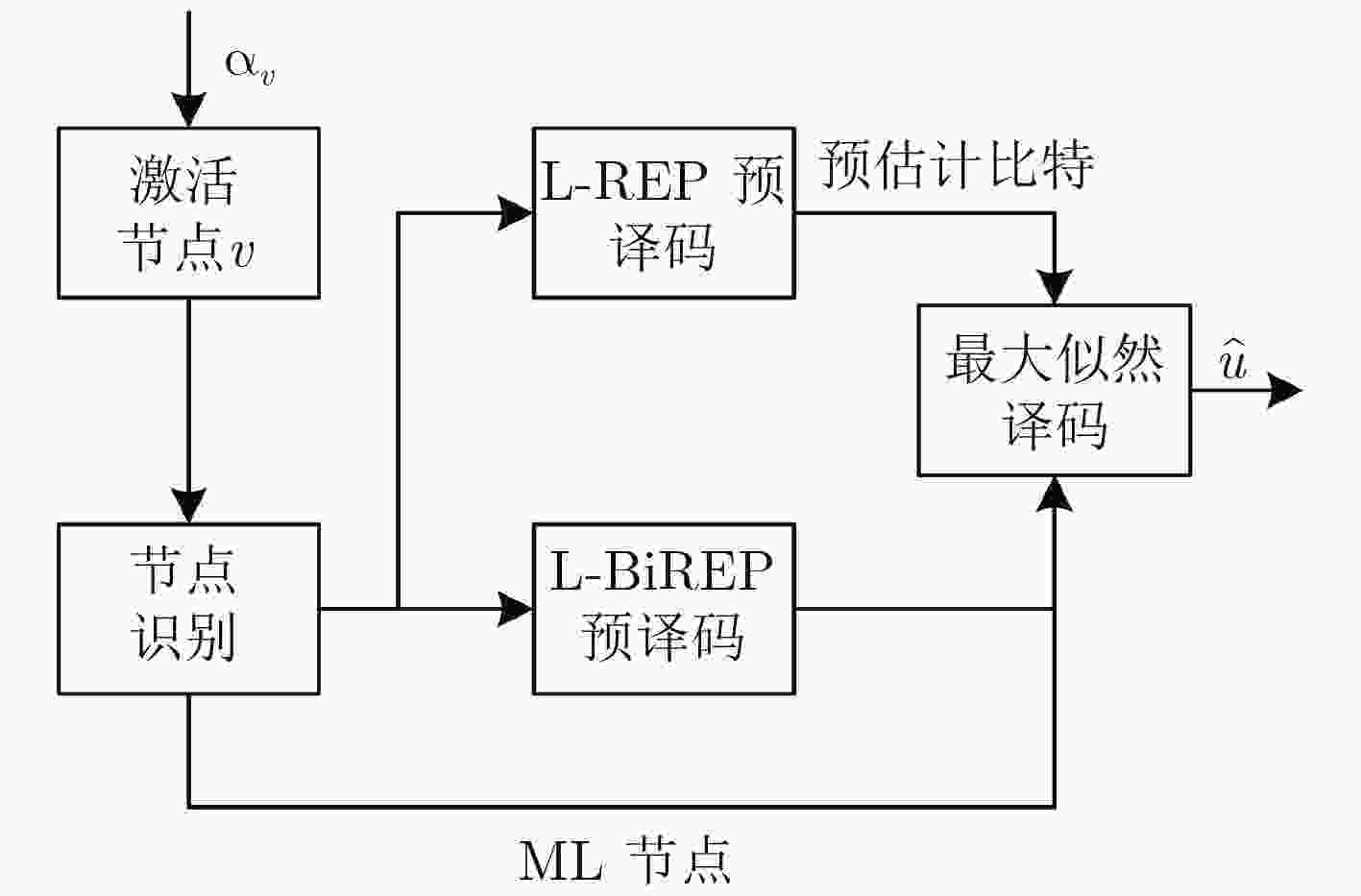
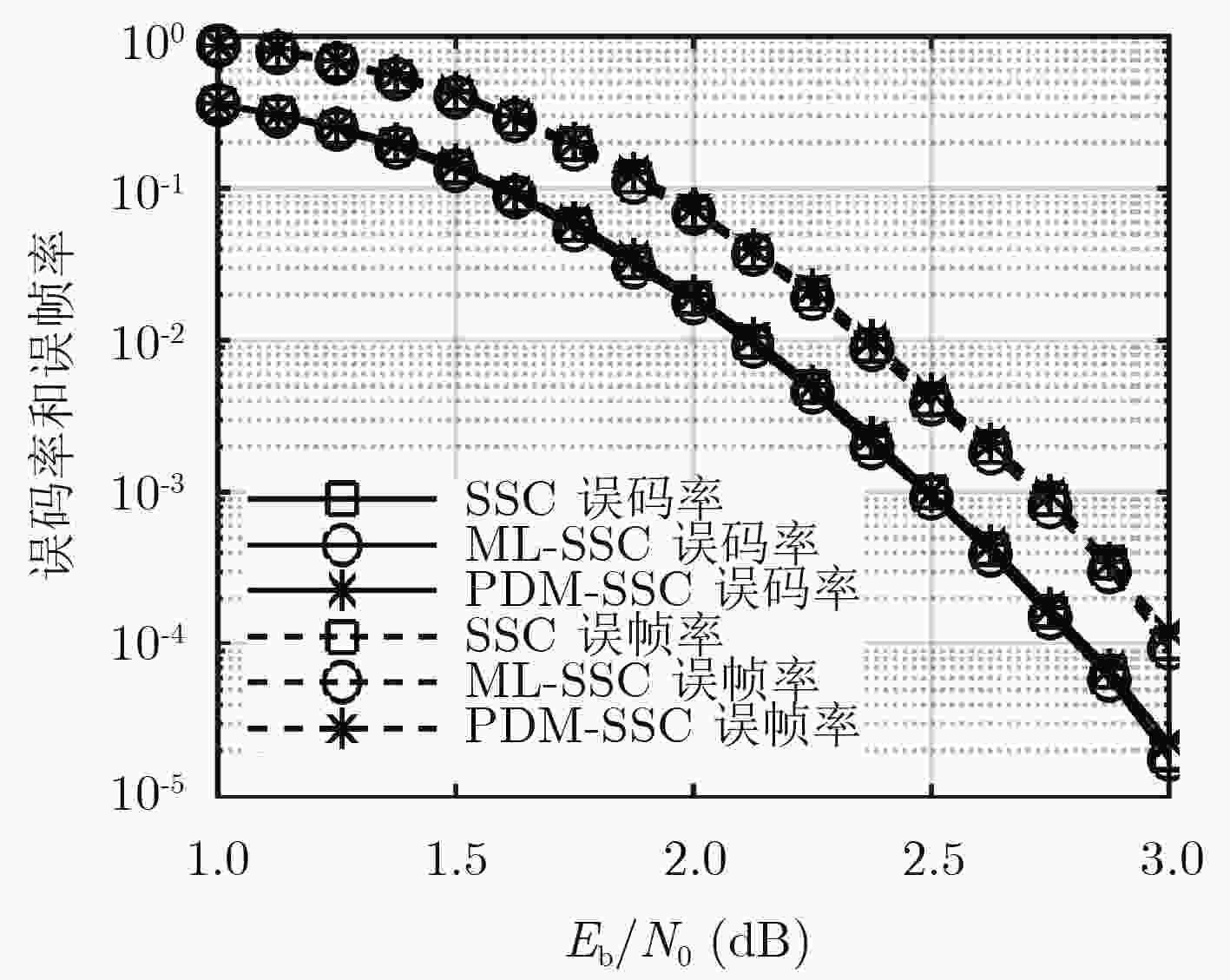
针对极化码译码串行输出造成较大译码时延的问题,该文提出一种基于预译码的最大似然简化连续消除译码算法。首先对译码树节点存储的似然值进行符号提取并分组处理,得到符号向量组;然后比较符号向量组与该节点的某些信息位的取值情况,发现向量组中储存的正负符号分布规律与该节点的中间信息位的取值具有一一对应的关系;在此基础上对组合码中间的1~2 bit进行预译码;最后结合最大似然译码方法估计组合码中的剩余信息位,从而得到最终的译码结果。仿真结果表明:在不影响误码性能的情况下,所提算法与已有的算法相比可有效降低译码时延。
-
关键词:
- 极化码 /
- 简化连续删除译码算法 /
- 最大似然译码 /
- 预译码
Abstract:To solve the long decoding latency caused by the serial nature of the decoding of polar codes, a pre-decoding based maximum-likelihood simplified successive-cancellation decoding algorithm is proposed. First, the signs of the likelihood values stored in the decoding tree nodes are extracted and grouped to obtain symbol vectors. Then comparing the symbol vectors and the values of some information bits, the distribution rules are found that positive and negative values stored in the vectors are one-to-one corresponding to the value of middle information bits of the node. Based on the above analysis, one or two bits in the middle of the constituent code are pre-decoded. Finally, the maximum likelihood decoding method is used to estimate the remaining information bits in the constituent code, and the final decoding results are obtained. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively reduce the decoding delay compared with the existing algorithms without affecting the error performance.
-
表 1
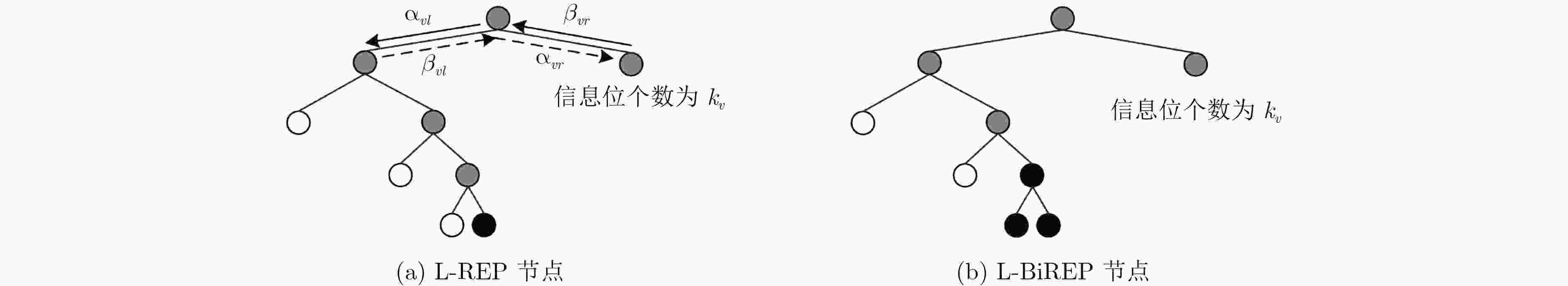
${u_{{\rm{mid}}1}}$ 和${u_{{\rm{mid}}0}}$ 对应${{x}}_{vi}^0$ 和${{x}}_{vi}^1$ 的取值情况${u_{{\rm{mid}}1}}$ ${u_{{\rm{mid}}0}}$ ${{x}}_{vi}^0$ ${{x}}_{vi}^1$ 0 0 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0 \end{array}} \right]$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0 \end{array}} \right]$ 0 1 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0 \end{array}} \right]$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0 \end{array}} \right]$ 1 0 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0 \end{array}} \right]$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0 \end{array}} \right]$ 1 1 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0 \end{array}} \right]$ $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&1 \end{array}} \right]$/$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0 \end{array}} \right]$ 表 2 P个计算单元下L-REP节点和L-BiREP节点的译码时延
算法 L-REP节点的译码时延 L-BiREP节点的译码时延 SSC $ \ge {\log _2}{N_v} + {\tau _r} + 2$ $ \ge {\log _2}{N_v} + {\tau _r} + 1$ ML-SSC $\left( {{2^{{k_v} + 1}} + 1} \right)\left( {{N_v} - 1} \right)/P$ $\left( {{2^{{k_v} + 2}} + 1} \right)\left( {{N_v} - 1} \right)/P$ PDM-SSC $\left( {\left( {{2^{{k_v}}} + 1} \right)\left( {{N_v} - 1} \right) + 1} \right)/P$ $\left( {\left( {{2^{{k_v}}} + 1} \right)\left( {{N_v} - 1} \right) + 1} \right)/P$ 表 3 P=256, R=0.5时,本文算法与SSC算法时延情况对比
算法 码长 时延(时间周期) 时延增益(%) SSC 2048 817 – 32768 6973 – PDM-SSC 2048 606 25.8 32768 5731 17.8 表 4 P=256, N=32768时,本文算法与ML-SSC算法时延情况对比
算法 码率 译码节点个数 时延(时间周期) 时延增益(%) ML-SSC 0.5 69 6679 – 0.9 60 3470 – PDM-SSC 0.5 148 5731 14.2 0.9 114 2822 18.7 -
ARIKAN E. Channel polarization: A method for constructing capacity-achieving codes for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(7): 3051–3073 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2021379 İŞCAN O, BÖHNKE R, and XU Wen. Shaped polar codes for higher order modulation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(2): 252–255 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2766621 郭锐, 王美洁, 王杰. 基于缩短极化码的MLC NAND Flash差错控制技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(7): 1658–1665 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160864GUO Rui, WANG Meijie, and WANG Jie. Research on the MLC NAND Flash error control technology based on polar codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(7): 1658–1665 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160864 GULCU T C and BARG A. Achieving secrecy capacity of the wiretap channel and broadcast channel with a confidential component[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2017, 63(2): 1311–1324 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2631223 朱鸿斌, 戴胜辰, 康凯, 等. 改进型极化码混合自动请求重传法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1136–1141 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160736ZHU Hongbin, DAI Shengchen, KANG Kai, et al. An improved HARQ scheme with polar codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1136–1141 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160736 LEROUX C, RAYMOND A J, SARKIS G, et al. A semi-parallel successive-cancellation decoder for polar codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(2): 289–299 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2223693 HUSMANN C, NIKOLAOU P C, and NIKITOPOULOS K. Reduced latency ML polar decoding via multiple sphere-decoding tree searches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1835–1839 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2761262 HASHEMI S A, CONDO C, and GROSS W J. A fast polar code list decoder architecture based on sphere decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2016, 63(12): 2368–2380 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2619324 ALAMDA-YAZDI A and KSCHISCHANG F R. A simplified successive-cancellation decoder for polar codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2011, 15(12): 1378–1380 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2011.101811.111480 SARKIS G, GIARD P, VARDY A, et al. Fast polar decoders: algorithm and implementation[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32(5): 946–957 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.140514 HANIF M and ARDAKANI M. Fast successive-cancellation decoding of polar codes: identification and decoding of new nodes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(11): 2360–2363 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2740305 HUANG Zhiliang, DIAO Chunjuan, DAI Jianxin, et al. An improvement of modified successive-cancellation decoder for polar codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2013, 17(12): 2360–2363 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2013.110413.132136 CHOI J and PARK I C. Improved successive-cancellation decoding of polar codes based on recursive syndrome decomposition[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(11): 2344–2347 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2730860 YOO H and PARK I C. Efficient pruning for successive-cancellation decoding of polar codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(12): 2362–2365 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2607167 SARKIS G and GROSS W J. Increasing the throughput of polar decoders[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2013, 17(4): 725–728 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2013.021213.121633 CHASE D. Class of algorithms for decoding block codes with channel measurement information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1972, 18(1): 170–182 doi: 10.1109/TIT.1972.1054746 -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
