An Adaptive Directional MAC Protocol for Terahertz Wireless Personal Networks
-
摘要:
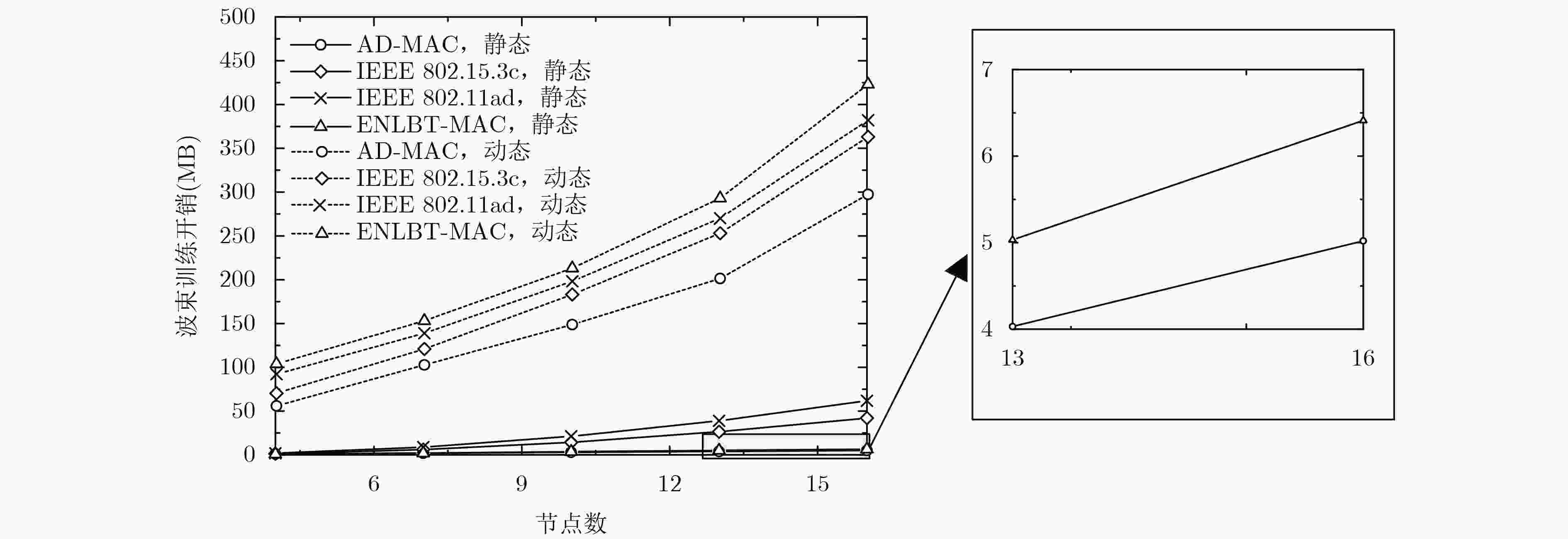
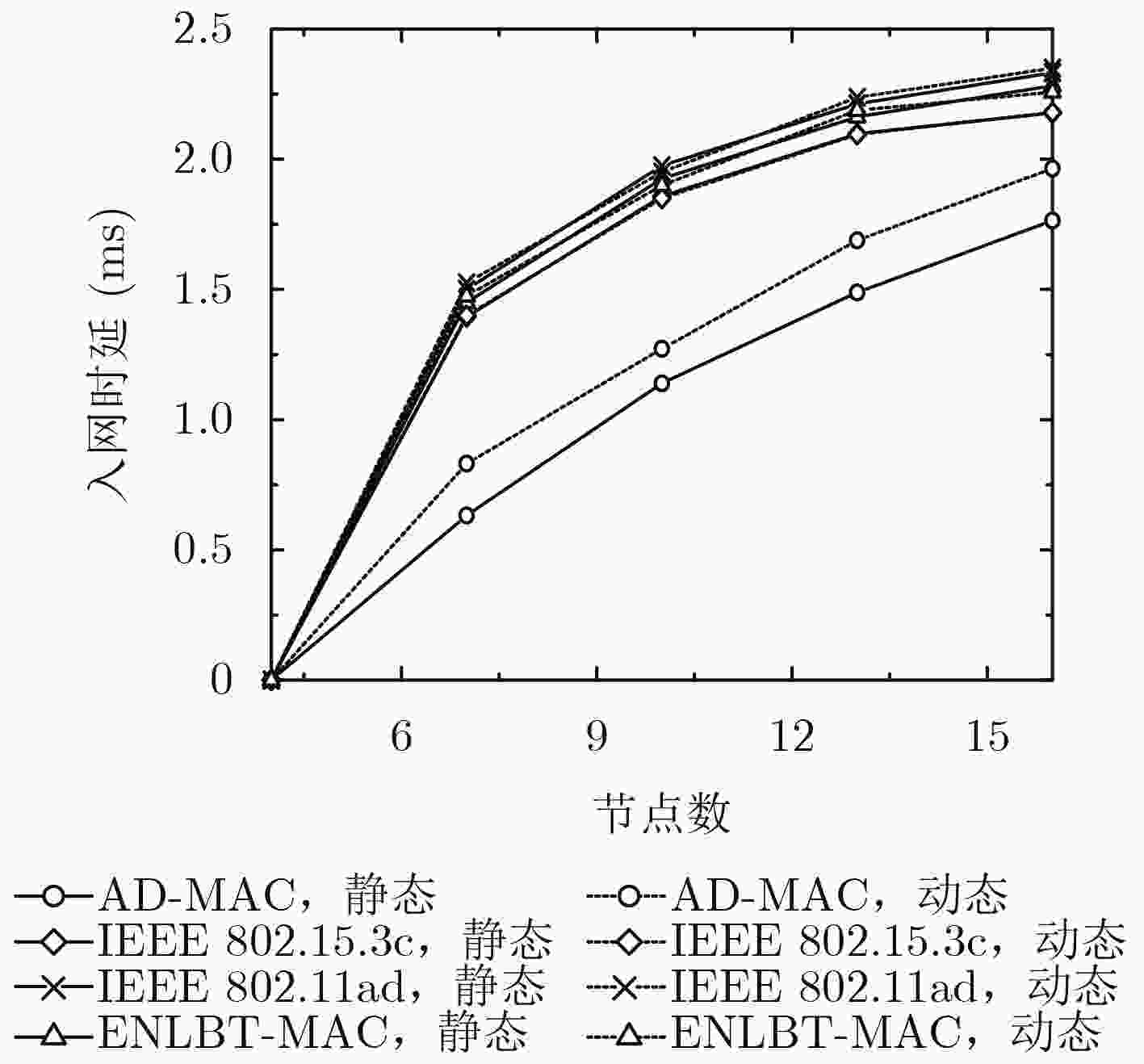
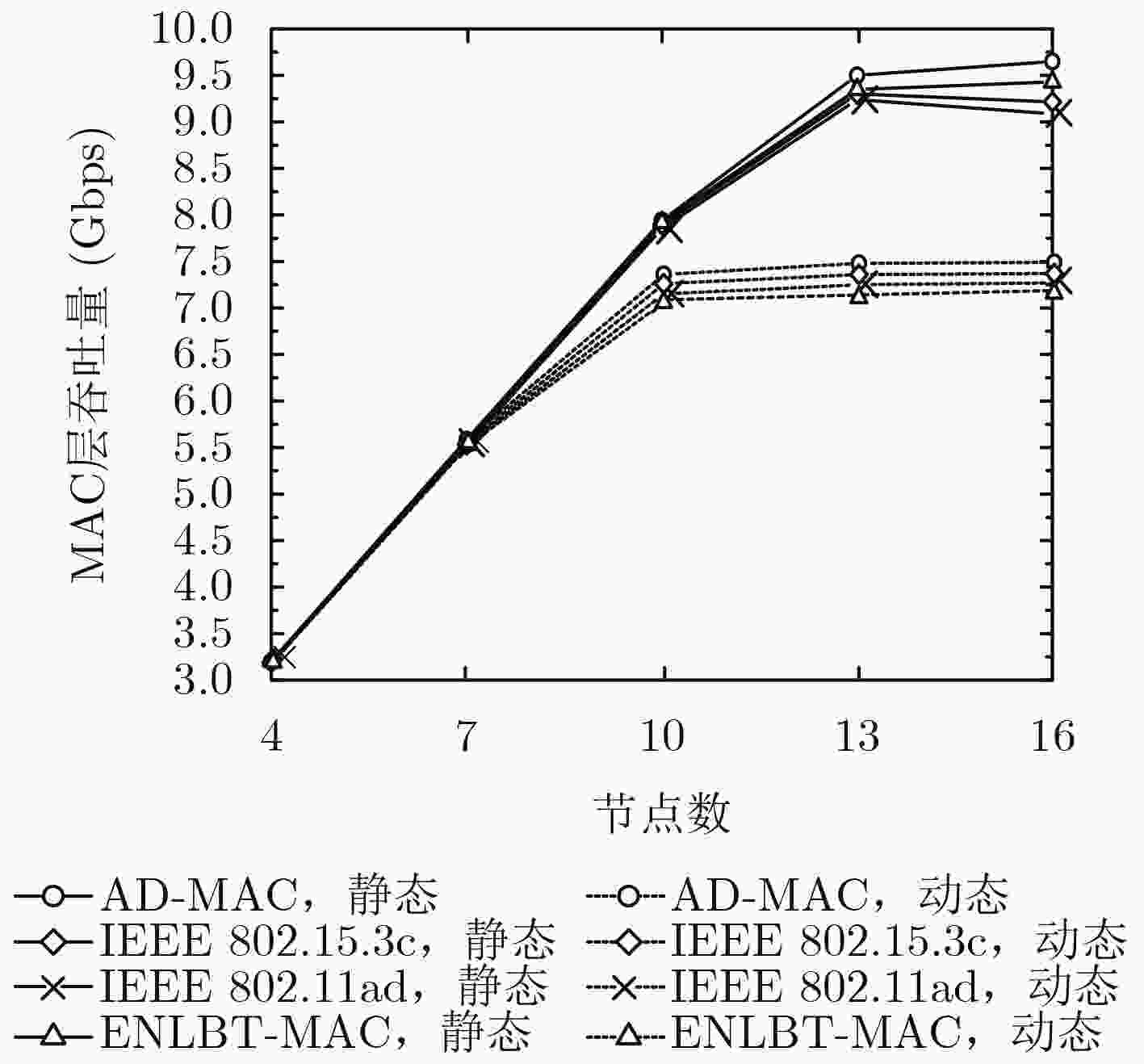
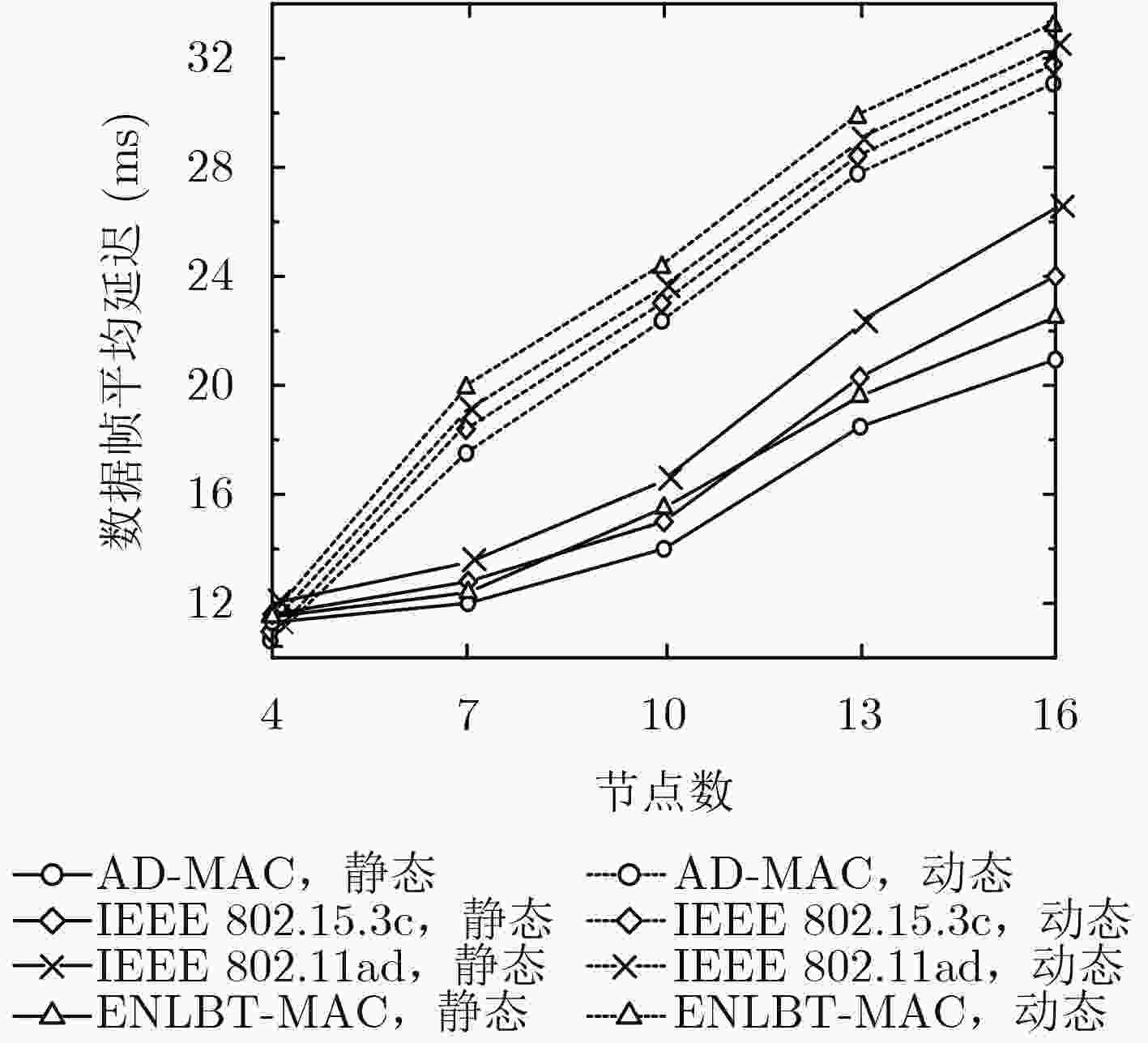
针对现有太赫兹无线个域网定向MAC协议存在的波束训练开销和入网时延偏大以及Beacon, S-CAP时段时隙利用不足问题,该文提出一种自适应的定向MAC协议——AD-MAC,自适应地在静态场景下采用全网协同波束训练,在动态场景下节点基于历史信息快速回复波束训练帧,同时使用反向监听策略减小同扇区节点的帧碰撞概率,并且通过时隙复用在Beacon和S-CAP时段并行发送控制帧和数据帧。理论分析表明了AD-MAC协议的有效性,仿真结果显示:相较于ENLBT-MAC等典型协议,AD-MAC在静态场景下的波束训练开销和节点平均入网时延分别降低了约21.84%和22.70%,在动态场景下上述二指标则分别减小了约18.7%和13.07%。
Abstract:To reduce the beamforming training cost and network delay, make the best of Beacon and S-CAP sub-period in the existing Terahertz Wireless Personal Access Network (TWPAN) directional MAC protocols, an Adaptive Directional MAC (AD-MAC) protocol for TWPAN is proposed. AD-MAC adaptively uses the entire network cooperative beam training in a static scenario, and makes network nodes quickly respond to beam training frames based on historical information in a dynamic scenario. The reverse listening strategy is used to reduce the collision probability of same sector nodes. The control frame and data frame are transmitted simultaneously in the Beacon and S-CAP slot using time-slot reuse. Theoretical analysis verifies the effectiveness of AD-MAC. Also, simulation results show that, comparing with ENLBT-MAC, AD-MAC reduces about 21.84% of beamforming training cost and 22.70% of the average network delay in static scene, and reduces about 18.7% of beamforming training cost and 13.07% of the average network delay in dynamic scene.
-
Key words:
- Wireless personal access networks /
- Terahertz /
- MAC protocols /
- Orientation
-
表 1 公共仿真参数
参数(单位) 数值 节点数目(个) 4,7,10,13,16 波束宽度(°) 5 传输速率(Gbps) 10 收发端距离(m) 10 仿真时间(s) 10 超帧周期(ms) 10 节点缓存(Mb) 10 发包间隔(ms) 0.08 数据帧长(bit) 64000 -
GE Xiaohu, TU Song, MAO Guoqiang, et al. 5G ultra-dense cellular networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2016, 23(1): 72–79. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2016.7422408 张健, 邓贤进, 王成, 等. 太赫兹高速无线通信: 体制, 技术与验证系统[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2014, 12(1): 1–13. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201401.0013ZHANG Jian, DENG Xianjin, WANG Cheng, et al. Terahertz high speed wireless communications: Systems, techniques and demonstrations[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2014, 12(1): 1–13. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201401.0013 WANG Pu, JORNET J M, MALIK M G A, et al. Energy and spectrum-aware MAC protocol for perpetual wireless nanosensor networks in the terahertz band[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2013, 11(8): 2541–2555. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2013.07.002 MUMTAZ S, JORNET J M, AULIN J, et al. Terahertz communication for vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(7): 5617–5625. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2712878 YAO Xinwei and JORNET J M. TAB-MAC: Assisted beamforming MAC protocol for terahertz communication networks[J]. Nano Communication Networks, 2016, 9: 36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.nancom.2016.07.003 任智, 游磊, 吕昱辉, 等. 高时隙利用率太赫兹无线个域网公平接入协议[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(10): 2339–2345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.10.27REN Zhi, YOU Lei, LÜ Yuhui, et al. High-slot-utilization and fair access protocol for terahertz wireless personal area networks[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(10): 2339–2345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.10.27 CAO Jianling, WANG Min, CHEN Cong, et al. High-throughput low-delay MAC protocol for terahertz ultra-high data-rate wireless networks[J]. The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications, 2016, 23(4): 17–24. doi: 10.1016/S1005-8885(16)60041-9 SHAHRAM M, MICHELE C W, and SAJAL K D. DRIH-MAC: A distributed receiver-initiated harvesting-aware MAC for nanonetworks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological, and Multi-Scale Communications, 2015, 1(1): 97–110. doi: 10.1109/TMBMC.2015.2465519 KEN H, TORU T, MAKOTO Y, et al. Modifications to the draft TG3d ARD after the July 2014 meeting[OL]. https:mentor.ieee.org/802.15/dcn/14/15-14-0528-00-003d-modification-of-tg3d-ard-after-july-meeting.docx. 2014. BILE P, SEBASTIAN P, and THOMAS K. Fast beam searching concept for indoor terahertz communications[C]. The 8th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Hague, Netherlands, 2014: 639–643. doi: 10.1109/EuCAP.2014.6901840. WANG Junyi, ZHOU Lan, PYO C W, et al. Beam codebook based beamforming protocol for multi-Gbps millimeter-wave WPAN systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2009, 27(8): 1390–1399. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2009.091009 IEEE Standard802.15.3c-2009. Part 15.3: Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) specifications for high rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) amendment 2: Millimeter-wave-based alternative physical layer extension[S]. IEEE Computer Society, 2009. IEEE 802.11ad-2012. Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) specifications amendment 3: enhancements for very high throughput in the 60 GHz band[S]. IEEE Computer Society, 2012. AKHTAR A and ERGEN S C. Efficient network level beamforming training for IEEE 802.11 ad WLANs[C]. International Symposium Performance Evaluation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems, Chicago, USA, 2015: 1–6, doi: 10.1109/SPECTS.2015.7285289. CHONG Han, TONG Wenqian, and WU Xinyi. A memory-assisted MAC protocol with angular-division-multiplexing in terahertz networks[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks, Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
