Improved No-reference Noisy Image Quality Assessment Based on Masking Effect and Gradient Information
-
摘要:
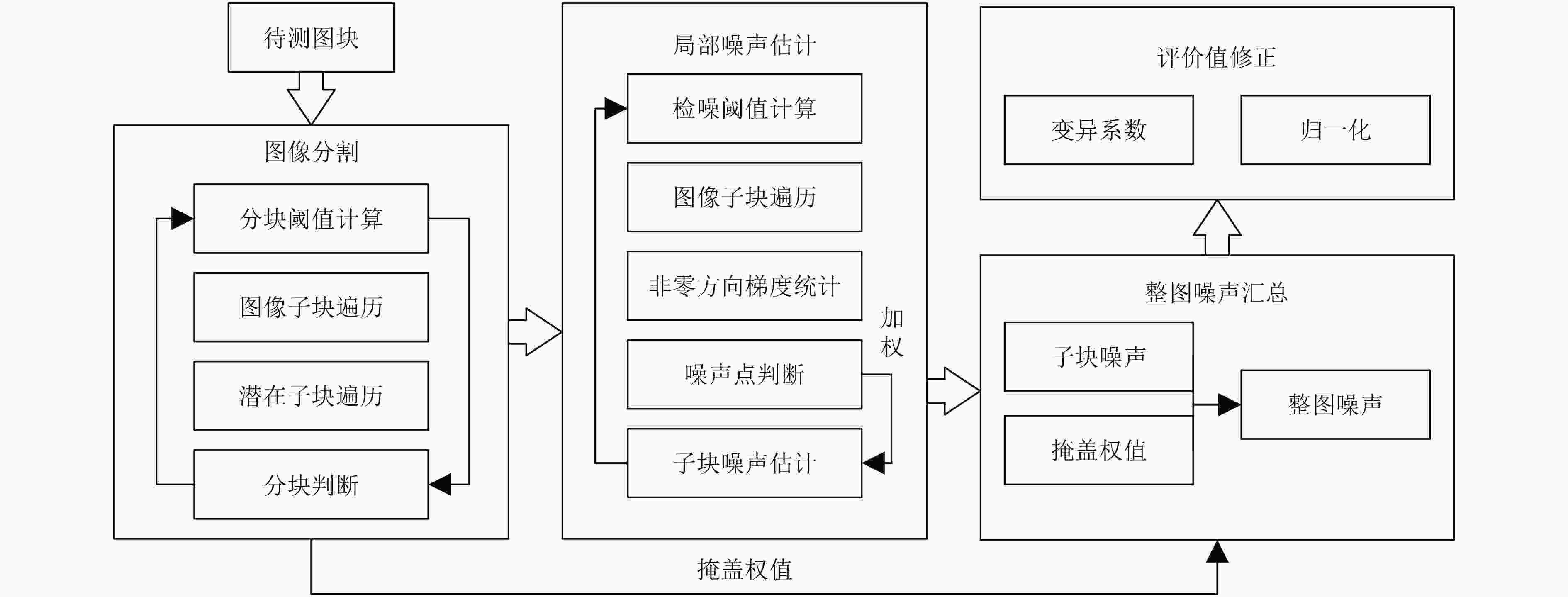
针对目前大多数噪声图像质量评价算法借助域变换或机器学习所带来的运算量大、训练过程繁复等弊端,以及依赖人工设置固定阈值存在普适性不佳的问题,该文改进了一种基于掩盖效应的空域噪声图像质量评价算法。首先依据Hosaka原理提出层递进的分块规则,将图像分成与其内容频率分布高低相符的不同尺寸的子块并赋予相应的掩盖权值;然后通过提取像素点梯度信息,经两步检噪实现子块噪点甄别;再使用掩盖权值对子块噪声污染指标加权得到初步质量评价结果;最终修正和归一化后为整图质量评价结果——改进的无参考峰值信噪比(MNRPSNR)。应用该算法在LIVE和TID2008图像质量评价数据库上对多种噪声类型图像进行实验,结果显示其较目前主流评价算法保有很强竞争力,对传统算法改进效果显著,与人眼主观感受一致性高,普适于多种噪声类型。
Abstract:Heavy computational burden, or complex training procedure and poor universality caused by the manual setting of the fixed thresholds are the main issues associated with most of the noise image quality evaluation algorithms using domain transformation or machine learning. As an attempt for solution, an improved spatial noisy image quality evaluation algorithm based on the masking effect is presented. Firstly, according to the layer-layer progressive rule based on Hosaka principle, an image is divided into sub-blocks with different sizes that match the frequency distribution of its content, and a masking weight is assigned to each sub-block correspondingly. Then the noise in the image is detected through the pixel gradient information extraction, via a two-step strategy. Following that, the preliminary evaluation value is obtained by using the masking weights to weight the noise pollution index of all the sub-blocks. Finally, the correction and normalization are carried out to generate the whole image quality evaluation parameter——i.e. Modified No-Reference Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (MNRPSNR). Such an algorithm is tested on LIVE and TID2008 image quality assessment database, covering a variety of noise types. The results indicate that compared with the current mainstream evaluation algorithms, it has strong competitiveness, and also has the significant effects in improving the traditional algorithm. Moreover, the high degree of consistency to the human subjective feelings and the applicability to multiple noise types are well demonstrated.
-
表 1 数据库信息及实验使用子集
数据库 国家/机构 参考图像数量 主观评价指标 所选失真类型 损伤层级 LIVE 美国/德克萨斯州立大学 29 DMOS 白噪声(WN) 6 TID2008 乌克兰/国家航空航天大学
意大利/罗马大学
芬兰/坦佩雷理工大学25 MOS 加性高斯噪声(AGN) 5 颜色通道加性噪声(ANCC) 空间相关噪声(SCN) 掩蔽噪声(MN) 高频噪声(HFN) 脉冲噪声(IMN) 表 2 改进算法与不同检噪阈值下传统NRPSNR算法对monarch图像组评价结果
DMOS NRPSNR MNRPSNR Nth=10 Nth=50 Nth=100 图2(a1) 0.000000 58.35138 69.74312 79.08684 90.0779 图2(a2) 23.94275 50.45518 69.31391 79.51719 77.9929 图2(a3) 28.44905 47.50428 69.01371 79.70202 76.7756 图2(a4) 41.16959 39.03095 49.28878 65.95135 68.3129 图2(a5) 49.08675 36.47912 43.03078 52.72840 65.3847 图2(a6) 65.73029 33.06348 36.52051 41.17893 60.7793 表 3 MNRPSNR与相关算法特征及在LIVE数据库测试性能指标
算法名称 是否有参考图像 是否需要训练 是否需要域变换 性能指标 PLCC SROCC RMSE PSNR 是 否 否 0.9050 0.9010 8.4500 SSIM 是 否 否 0.9700 0.9690 3.9540 BIQI 否 是 小波 0.9538 0.9510 8.4094 LBIQ 否 是 小波 0.9761 0.9700 7.9100 DIIVINE 否 是 小波 0.9880 0.9840 4.3100 BLIINDS 否 是 离散余弦 0.9140 0.8900 11.2700 BLIINDS-II 否 是 离散余弦 0.9799 0.9691 N/A NIQE 否 是 否 0.9773 0.9662 N/A BRISQUE 否 是 否 0.9851 0.9786 N/A NRPSNR 否 否 否 0.8681 0.8900 10.9133 MNRPSNR 否 否 否 0.9745 0.9813 4.9369 表 4 TID2008数据库测试PLCC指标比对
VSNR IFC NQM UQI NRPSNR MNRPSNR AGN 0.7513 0.6147 0.7397 0.5407 0.6467 0.7922 ANCC 0.7489 0.5628 0.6935 0.4930 0.0402 0.7291 SCN 0.7700 0.6567 0.7757 0.5589 0.1624 0.5808 MN 0.7799 0.7309 0.7575 0.7515 0.7903 0.5164 HFN 0.8861 0.7199 0.9134 0.7059 0.9283 0.9005 IMN 0.6244 0.4950 0.7492 0.4829 0.6403 0.8214 表 5 TID2008数据库测试SROCC指标比对
VSNR IFC NQM UQI NRPSNR MNRPSNR AGN 0.7745 0.6204 0.7592 0.5335 0.6276 0.7900 ANCC 0.7725 0.5921 0.7200 0.4798 0.0869 0.7115 SCN 0.7860 0.6403 0.7910 0.5472 0.0491 0.5786 MN 0.7555 0.7374 0.7624 0.7292 0.8018 0.5214 HFN 0.8870 0.7488 0.8952 0.6863 0.9039 0.8852 IMN 0.6460 0.5378 0.7666 0.4951 0.6495 0.8300 表 6 TID2008数据库测试RMSE指标比对
VSNR IFC NQM UQI NRPSNR MNRPSNR AGN 0.4005 0.4783 0.4131 0.5112 0.4682 0.3746 ANCC 0.3646 0.4448 0.3942 0.4844 0.5594 0.3832 SCN 0.3878 0.4655 0.3924 0.5055 0.6134 0.5060 MN 0.3745 0.3844 0.3890 0.3955 0.3673 0.5133 HFN 0.4259 0.6069 0.3691 0.6671 0.3563 0.4161 IMN 0.4022 0.4366 0.3402 0.4483 0.3933 0.2948 表 7 MNRPSNR与相关算法在LIVE数据库上运行时间(s)
算法名称 DIIVINE BLIINDS-II NRPSNR MNRPSNR 平均单幅耗时 149 70 3.45 10.10 -
HADIZADEH H and VAN BAJIC I. Full-reference objective quality assessment of tone-mapped images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(2): 392–404. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2740023 MA Jian, AN Ping, SHEN Liquan, et al. Reduced-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment using natural scene statistics and structural degradation[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 2768–2780. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2785282 FANG Yuming, YAN Jiebin, LI Leida, et al. No reference quality assessment for screen content images with both local and global feature representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(4): 1600–1610. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2781307 WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 YE Peng and DAVID D. No-reference image quality assessment based on visual codebook[C]. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium 2011: 11–14. WAN Wenfei, WU Jinjian, XIE Xuemei, et al. A novel just noticeable difference model via orientation regularity in DCT domain[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 22953–22964. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2699858 MA Lin, WANG Xu, LIU Qiong, et al. Reorganized DCT-based image representation for reduced reference stereoscopic image quality assessment[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 215: 21–31. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.06.116 SAAD M A, BOVIK A C, and CHARRIER C. A DCT statistics-based blind image quality index[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010, 17(6): 583–586. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2045550 SAAD M A, BOVIK A C, and CHARRIER C. Blind image quality assessment: A natural scene statistics approach in the DCT domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 22(8): 3339–3352. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2191563 CHANDLER D M and HEMAMI S S. VSNR: A wavelet-based visual signal-to-noise ratio for natural images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(9): 2284–2298. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901820 QIN Ming, LÜ Xiaoxin, CHEN Xiaohui, et al. Hybrid NSS features for no-reference image quality assessment[J]. IET Image Processing, 2017, 11(6): 443–449. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2016.0411 LI Leida, YAN Ya, LU Zhaolin, et al. No-reference quality assessment of deblurred images based on natural scene statistics[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 2163–2171. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2661858 YANG Guangyi, LIAO Yue, ZHANG Qingyi, et al. No-reference quality assessment of noise-distorted images based on frequency mapping[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 23146–23156. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2764126 ABDEL-HAMID L, EI-RAFEI A, and MICHELSON G. No-reference quality index for color retinal images[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2017, 90: 68–75. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.09.012 MA Kede, LIU Wentao, ZHANG Kai, et al. End-to-end blind image quality assessment using deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(3): 1202–1213. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2774045 LIU Tsungjung and LIU Kuanhsien. No-reference image quality assessment by wide-perceptual-domain scorer ensemble method[J]. IEEE Transaction on Image Processing, 2018, 27(3): 1138–1151. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2771422 MITTAL A, MOORTHY A K, and BOVIK A C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(12): 4659–4708. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2214050 MOORTHY A K and BOVIK A C. Blind image quality assessment: From natural scene statistics to perceptual quality[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(12): 3350–3364. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2147325 LIU Anmin and LIN Weisi. Image quality assessment based on gradient similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1500–1512. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2175935 王正友, 肖文. 基于掩盖效应的无参考数字图像质量评价[J]. 计算机应用, 2006, 26(12): 2838–2840.WANG Zhengyou and XIAO Wen. No-reference digital image quality evaluation based on perceptual masking[J]. Computer Applications, 2006, 26(12): 2838–2840. 徐海勇, 郁梅, 骆挺, 等. 基于非负矩阵分解的彩色图像质量评价方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(3): 578–585. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150610XU Haiyong, YU Mei, LUO Ting, et al. A color image quality assessment method based on non-negative matrix factorization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(3): 578–585. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150610 蒋平, 张建州. 基于局部最大梯度的无参考图像质量评价[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(11): 2587–2593. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141447JIANG Ping and ZHANG Jianzhou. No-reference image quality assessment based on local maximum gradient[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(11): 2587–2593. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141447 SHEIKH H R, WANG Zhou, and CORMACK L. LIVE image quality assessment database, release 2 [EB/OL]. http://live.ece.utexass.edu/research/quality, 2005. PONOMARENKO N. Tampere image database 2008 TID2008, version 1.0[EB/OL]. http://www.ponomarenko.info/index.html, 2009. Final Report from the Video Quality Experts Group on the Validation of Objective Models of Video Quality Assessment, Phase II VQEG [OL]. http://www.vqeg.org/, 2003. MOORTHY A K and BOVIK A C. A two-step framework for constructing blind image quality indices[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010, 17(5): 513–516. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2043888 TANG Huixuan, JOSHI N, and KAPOOR A. Learning a blind measure of perceptual image quality[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado, USA, 2011: 305–312. MITTAL A, SOUNDARARAJAN R, and BOVIK A C. Making a " completely blind” image quality analyzer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209–212. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726 SHEIKH H R, BOVIK A C, and DE VECIANA G. An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(12): 2117–2128. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.859389 DAMERA-VENKATA N, KITE T D, GEISLER W S, et al. Image quality assessment based on a degradation model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2000, 9(4): 636–650. doi: 10.1109/83.841940 WANG Zhou and BOVIK A C. A universal image quality index[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2002, 9(3): 81–84. doi: 10.1109/97.995823 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
