Shift-variant Similarity Learning for Person Re-identification
-
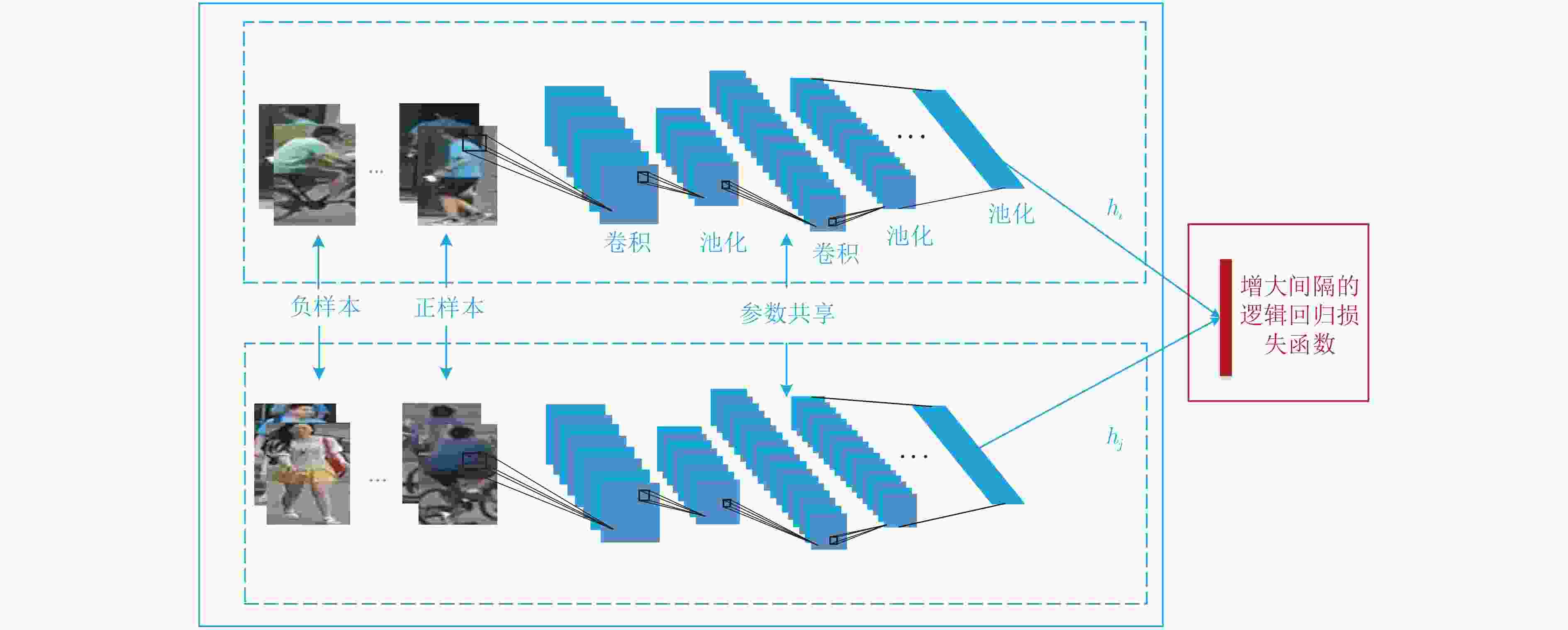
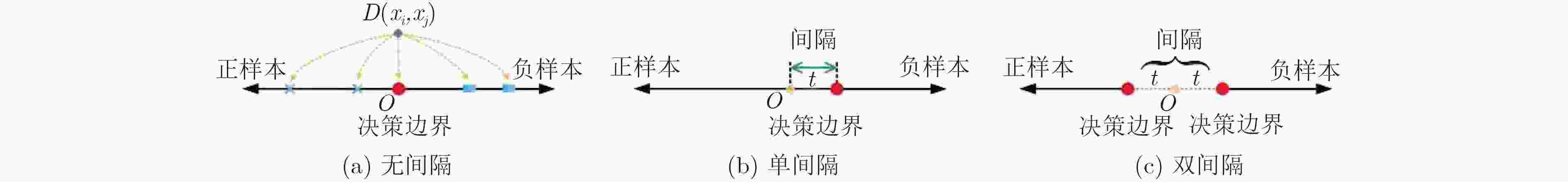
摘要: 行人重识别的精确度主要取决于相似性度量方法和特征学习模型。现有的度量方法存在平移不变性的特点,会增加网络参数训练的难度。现有的几种特征学习模型只强调样本之间的绝对距离而忽略了正样本对和负样本对之间的相对距离,造成网络学习到的特征判别性不强。针对现有度量方法的缺点该文提出一种平移变化的距离度量方法,能够简化网络的优化并能高效度量图像之间的相似性。针对特征学习模型的不足,提出一种增大间隔的逻辑回归模型,模型通过增大正负样本对之间的相对距离,使得网络得到的特征判别性更强。实验中,在Market1501和CUHK03数据库上对所提度量方式和特征学习模型的有效性进行验证,实验结果表明,所提度量方式性能更好,其平均精确率超出马氏距离度量6.59%,且所提特征学习模型也取得了很好的性能,算法的平均精确率较现有的先进算法有显著提高。Abstract: The accuracy of pedestrian re-recognition mainly depends on the similarity measure and the feature learning model. The existing measurement methods have the characteristics of translation invariance, which make the training of network parameters difficult. Several existing feature learning models only emphasize the absolute distance between sample pairs, but ignore the relative distance between positive sample pairs and negative sample pairs, resulting in a weak discriminant feature in network learning. In view of the shortcomings of existing measurement methods, a distance measurement method of translation change is presented, which can effectively measure the similarity between images. To overcome the shortcomings of the feature learning model, based on the proposed translation distance metric, a new logistic regression model with enlarged intervals is proposed. By increasing the relative distance between the positive and negative sample pairs, the network can get more discriminant features. In the experiment, the validity of the proposed measurement and the feature learning model is verified on the Market1501, CUHK03 database. Experimental results show that the proposed metric performs better than the Mahalanobis distance metric 6.59%, and the proposed feature learning algorithm also achieves good performance. The average precision of the algorithm is improved significantly compared with the existing advanced algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Person Re-identification /
- Shift-variant /
- Similarity learning /
- Logistic regression
-
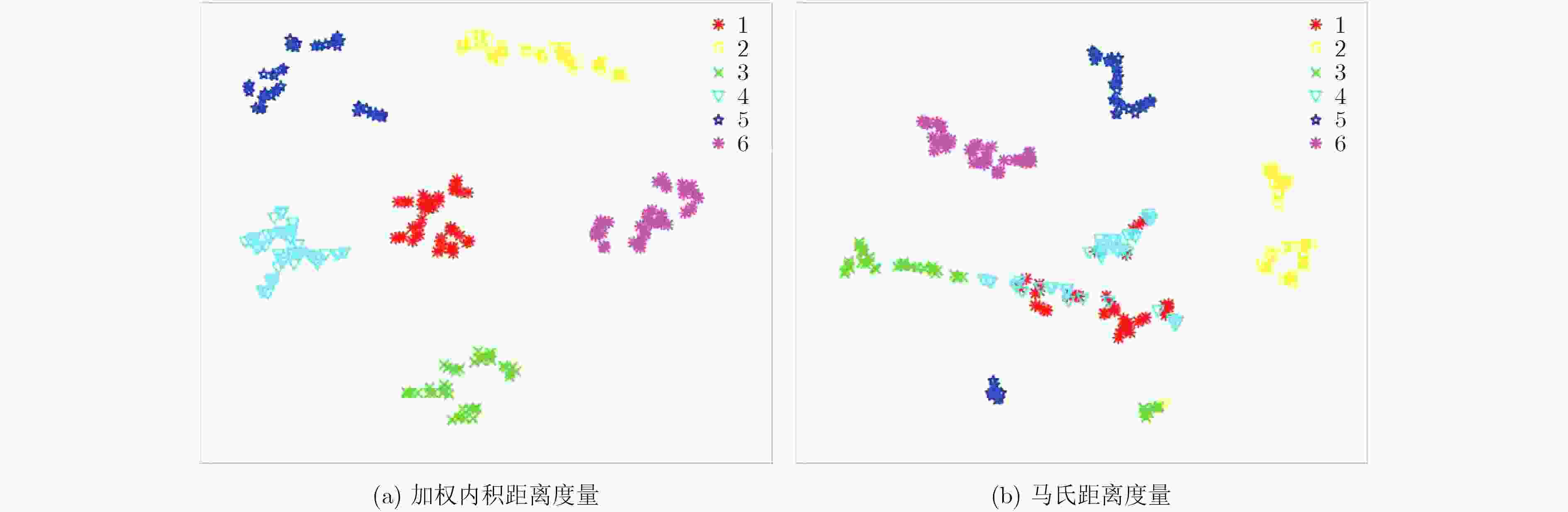
图 3 不同距离度量方式的t-SNE[21]图
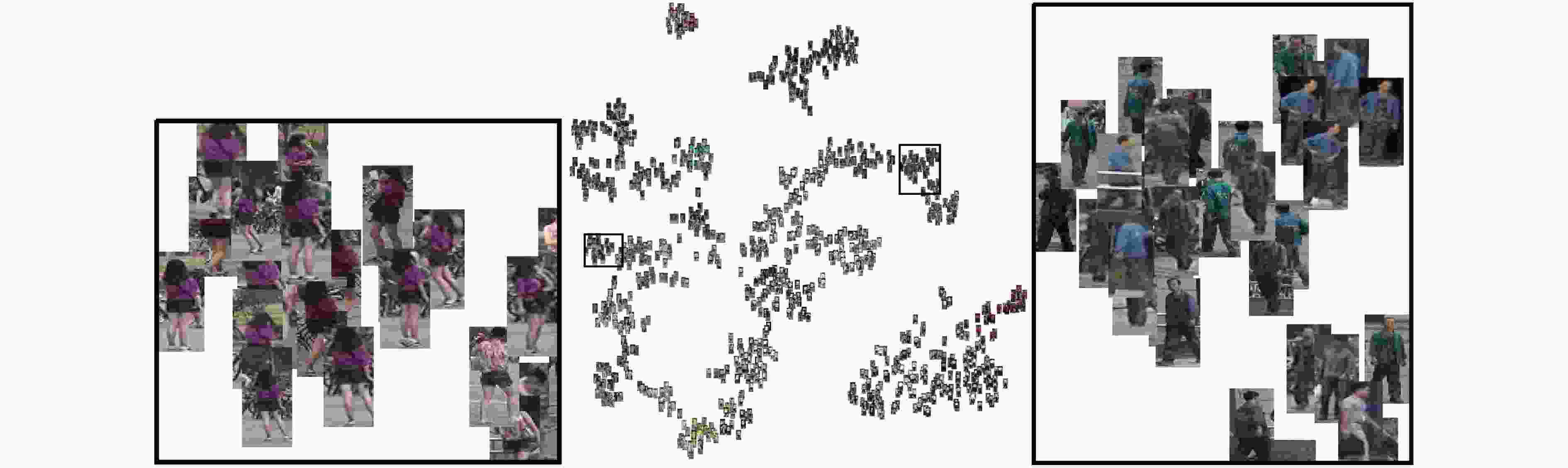
图 5 本文模型在Market1501测试数据集上的t-SNE[21]可视化图
表 1 与其他不同的距离度量方式相比
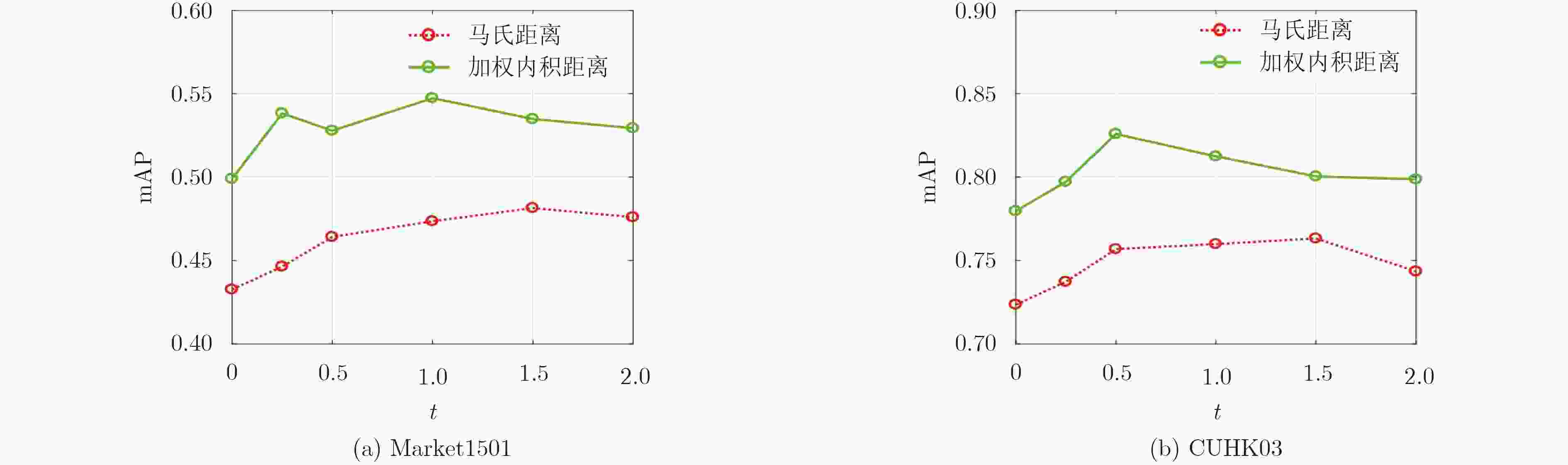
不同的度量方式 Market1501 rank-1 rank-5 rank-10 mAP 欧氏距离 55.08 75.03 82.63 37.53 马氏距离 65.68 83.82 88.93 48.14 加权内积距离(本文) 71.37 88.51 93.17 54.73 表 2 和先进算法在Market1501数据库上对比
方法 Market1501 rank-1 rank-5 rank-10 mAP Null Space[22] 55.43 – – 29.87 LSTM Siamese[19] 61.6 – – 35.3 Gated Siamese[18] 65.88 – – 39.55 DLCE (Pairwise)[6] 64.58 – – 44.94 DLSGLE(R)[23] 72.3 86.4 90.6 46.78 P2P[24] 61.31 – – 35.71 P2S[24] 70.72 – – 42.27 SOMAnet[25] 73.87 88.03 92.22 47.89 本文模型(t=0) 64.96 85.78 91.3 49.9 本文模型 71.37 88.51 93.17 54.73 表 3 和先进算法在CUHK03数据库上对比
方法 CUHK03 rank-1 rank-5 rank-10 mAP BoW+KISSME 24.33 – – – Deep ReID[8] 19.9 49.3 64.7 – Null Space[22] 62.55 90.05 94.8 29.87 LSTM Siamese[19] 57.3 80.1 88.3 46.3 Gated Siamese[18] 68.1 88.1 94.6 58.84 DLCE (Pairwise)[6] 64.58 – – 44.94 DLSGLE(R)[23] 73.2 93.7 97.2 – SIR&CIR[10] 52.17 – – – Triplet(Embedding)[26] 60.13 90.51 95.15 – Triplet(Learned Metric) 61.60 92.41 97.47 – SOMAnet[25] 68.9 91.1 95.6 – 本文模型(t=0) 73.07 95.71 98.54 77.96 本文模型 78.81 96.72 99.02 82.58 -
周全, 魏昕, 陈建新, 等. 一种基于稠密SIFT特征对齐的稀疏表达人脸识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(8): 1913–1919 doi: 10.11999/JEIT141194ZHOU Quan, WEI Xin, CHEN Jianxin, et al. Improved sparse representation algorithm for face recognition via dense SIFT feature alignment[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2015, 37(8): 1913–1919 doi: 10.11999/JEIT141194 张洁玉, 赵鸿萍, 陈曙. 自适应阈值及加权局部二值模式的人脸识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(6): 1327–1333 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01218ZHANG Jieyu, ZHAO Hongping, and CHEN Shu. Face recognition based on weighted local binary pattern with adaptive threshold[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2014, 36(6): 1327–1333 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01218 KOSTINGER M, HIRZER M, WOHLHART P, et al. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2288–2295. XIAO Tong, LI Hongsheng, OUYANG Wanli, et al. Learning deep feature representations with domain guided dropout for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1249–1258. DING Shengyong, LIN Liang, WANG Guangrun, et al. Deep feature learning with relative distance comparison for person re-identification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(10): 2993–3003 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.04.005 ZHENG Zhedong, ZHENG Liang, and YANG Yi. A discriminatively learned CNN embedding for person re-identification[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2017, 14(1): 13–28 doi: 10.1145/3159171 YI Dong, LEI Zhen, LIAO Shengcai, et al. Deep metric learning for person re-identification[C]. International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 2014: 24–28. LI Wei, ZHAO Rui, XIAO Tong, et al. Deep reid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 152–159. AHMED E, JONES M, and MARKS T K. An improved deep learning architecture for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3908–3916. WANG Faqiang, ZUO Wangmeng, LIN Liang, et al. Joint learning of single-image and cross-image representations for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, LasVegas, USA, 2016: 1288–1296. CHOPRA S, HADSELL R, and LECUN Y. Learning a similarity metric discriminatively, with application to face verification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 539–546. SONG H O, XIANG Y, JEGELKA S, et al. Deep metric learning via lifted structured feature embedding[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4004–4012. HIRZER M, ROTH P M, KOSTINGER M, et al. Relaxed pairwise learned metric for person re-identification[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 780–793. LIU Weiyang, WEN Yangdong, YU Zhiding, et al. Sphereface: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6738–6746. WANG Jian, ZHOU Feng, WEN Shilei, et al. Deep metric learning with angular loss[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2593–2601. PEDAGADI S, ORWELL J, VELASTIN S A, et al. Local fisher discriminant analysis for pedestrian re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3318–3325. XIONG Fei, GOU Mengran, CAMPS O, et al. Person re-identification using kernel-based metric learning methods[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 1–16. VARIOR R R, HALOI M, and WANG Gang. Gated siamese convolutional neural network architecture for human re-identification[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 791–808. VARIOR R R, SHUAI B, LU Jiwen, et al. A siamese long short-Term memory architecture for human re-identification[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 135–153. CHENG De, GONG Yihong, ZHOU Sanping, et al. Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1335–1344. VAN DER MAATENL J P and HINTON G E. Visualizing high dimensional data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(2): 2579–2605. ZHANG Li, XIANG Tao, and GONG Shaogang. Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1239–1248. CHENG De, GONG Yi, LI Zhe, et al. Deep feature learning via structured graph laplacian embedding for person re-Identification[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.07791, 2017. ZHOU Sanping, WANG Jinjun, WANG Jiayun, et al. Point to set similarity based deep feature learning for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5028–5037. BARBOSA I B, CRISTANI M, CAPUTO B, et al. Looking beyond appearances: Synthetic training data for deep CNNs in re-identification[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1701.03153, 2017. CHEN Weihua, CHEN Xiaotang, ZHANG Jianguo, et al. Beyond triplet loss: A deep quadruplet network for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1320–1329. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
