Neighbor Discovery Mechanism for Underwater Acoustic Communication Networks Based on Directional Transmission and Reception
-
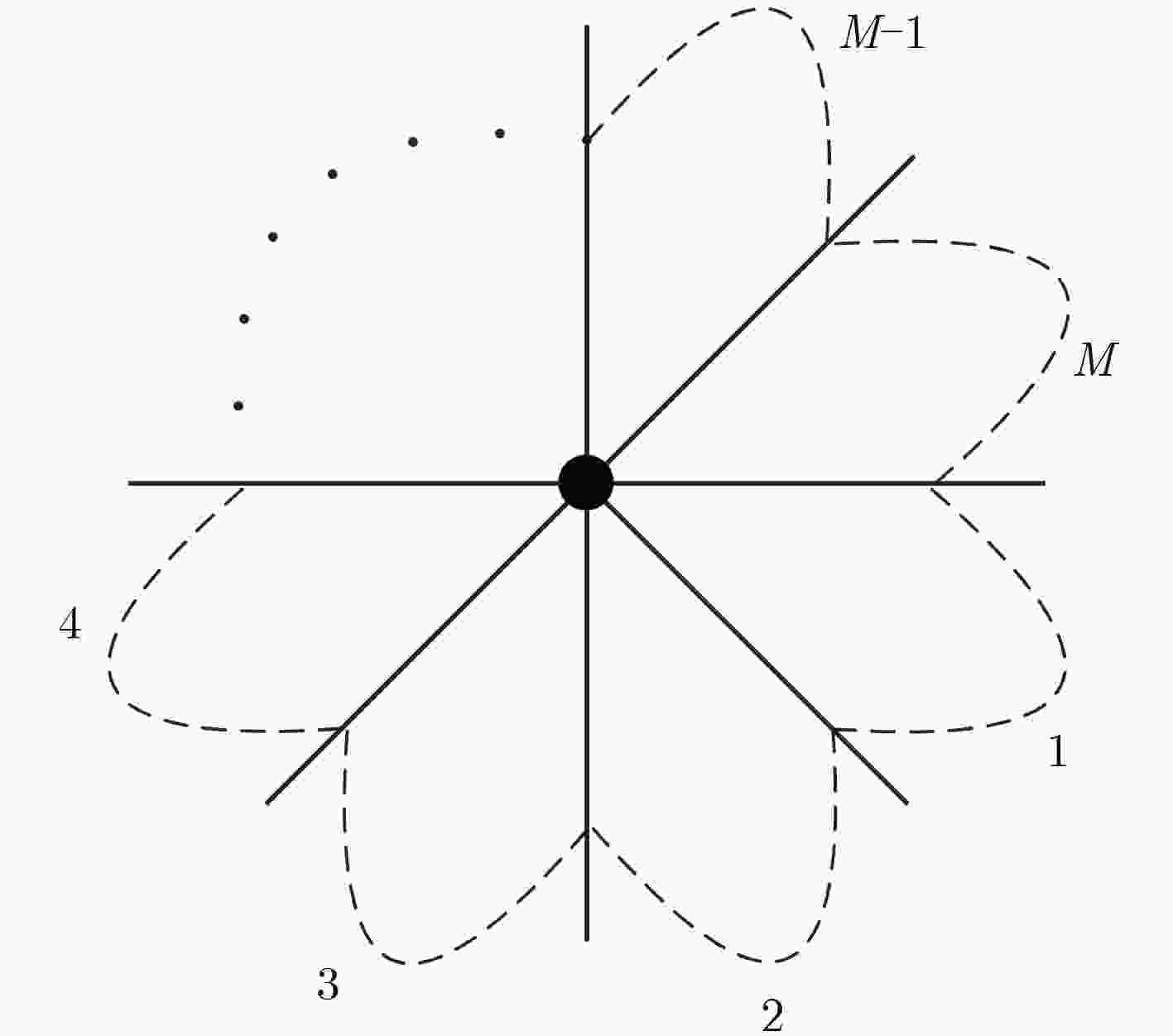
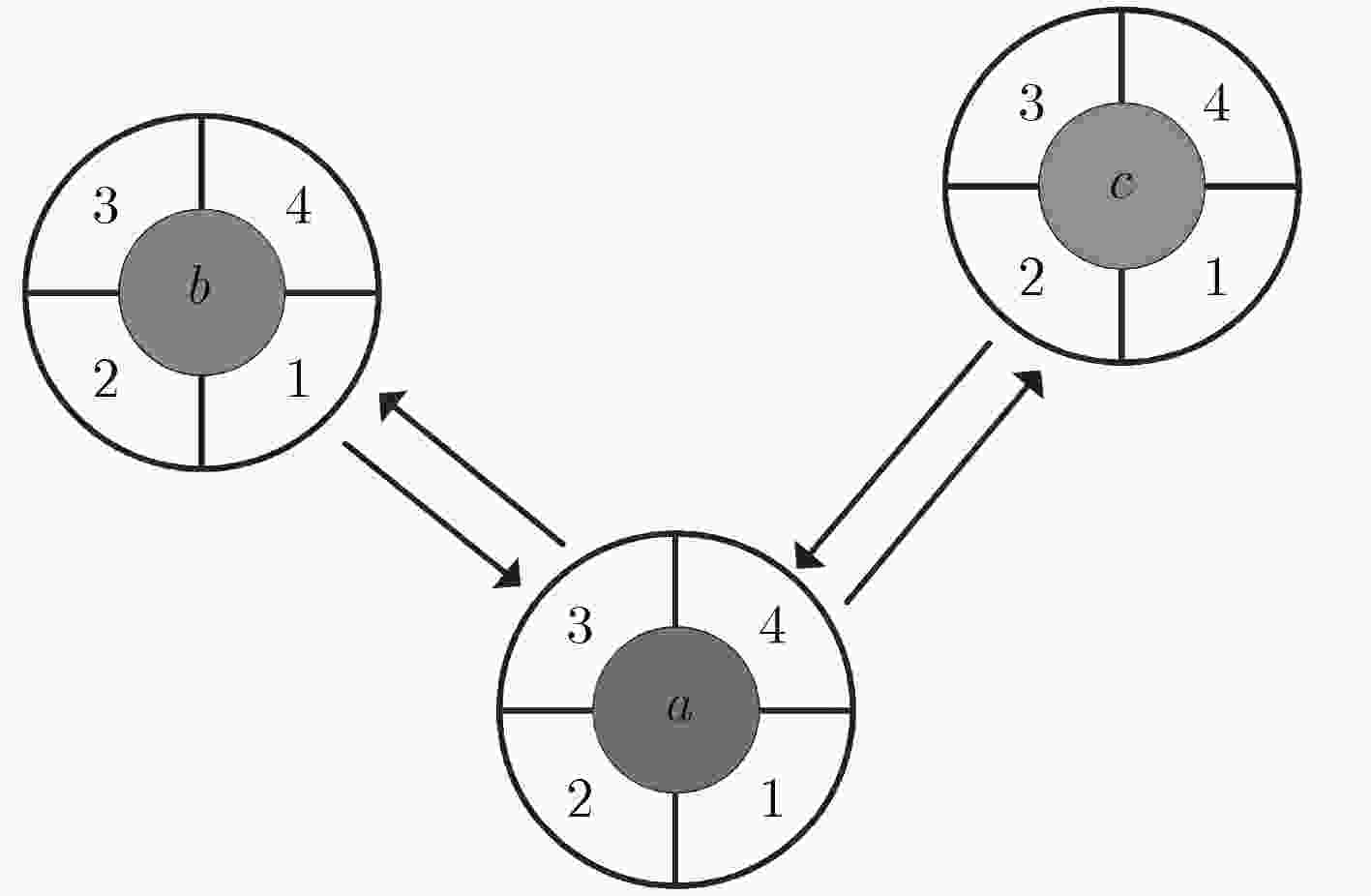
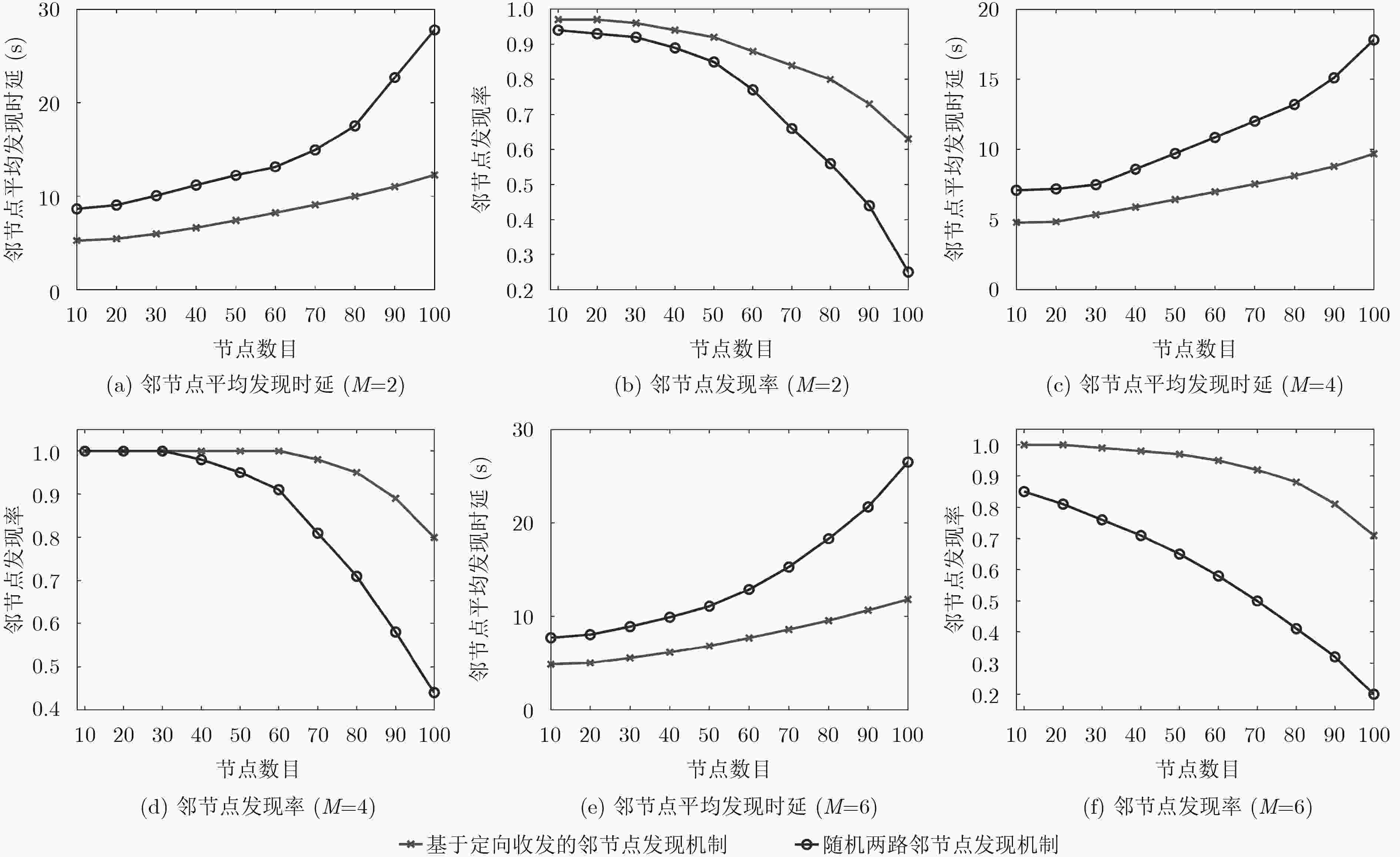
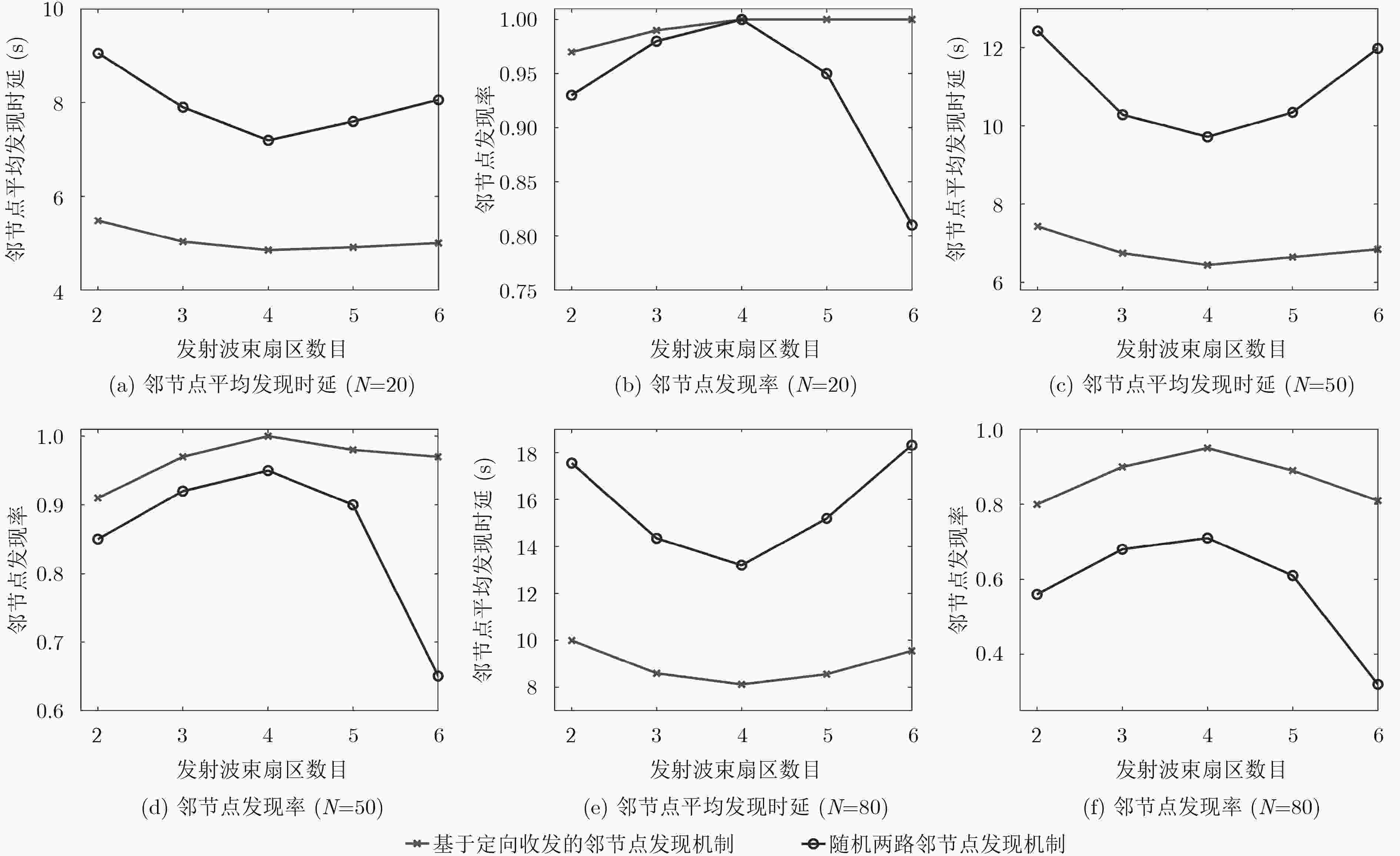
摘要: 针对水声通信网络邻节点发现困难的问题,该文提出一种基于定向收发的邻节点发现机制。该机制中节点只采用定向方式发送和接收信号,能够避免增益不对称引起的隐藏终端问题,增加网络覆盖范围;时间被划分为邻节点发现时隙和侦听回复时隙,发现时隙中节点发送HELLO信号,然后接收邻节点回复的REPLY信号,侦听回复时隙中节点侦听源节点发送的HELLO信号,然后回复REPLY信号,节点通过基于竞争的HELLO/REPLY两路握手以直接发现和间接发现两种方式完成邻节点发现,能够克服“聋”节点问题,提升邻节点发现效率。仿真结果表明,在不同的网络节点密度与发射天线波束扇区数目条件下,该邻节点发现机制相比随机两路邻节点发现机制,邻节点平均发现时延更短,邻节点发现率更高。Abstract: Considering the difficulty of neighbor discovery in underwater acoustic communication networks, a neighbor discovery mechanism is presented based on directional transmission and reception. In this mechanism, the nodes only send and receive signals directionally, which can avoid the hidden terminal problem caused by asymmetric gain and increase the network coverage. Time is divided into neighbor discovery time slot and listening & reply time slot. In neighbor discovery time slot, the node sends the HELLO signal, and then waits to receive the REPLY signal sent by its neighbor node. In listening & reply time slot, the node listens the channel for the HELLO signal sent by the source node, then replies REPLY signal to the source node. The node can discover its neighbor through HELLO/REPLY two-way handshake based on competition and direct & indirect discovery, which can overcome the " deaf” nodes problem and improve the efficiency of neighbor discovery. Compared with the randomized two-way neighbor discovery mechanism, simulation tests show that the proposed mechanism has the shorter average discovery latency and the higher average discovery ratio in various network density and number of antenna sectors.
-
表 1 仿真参数
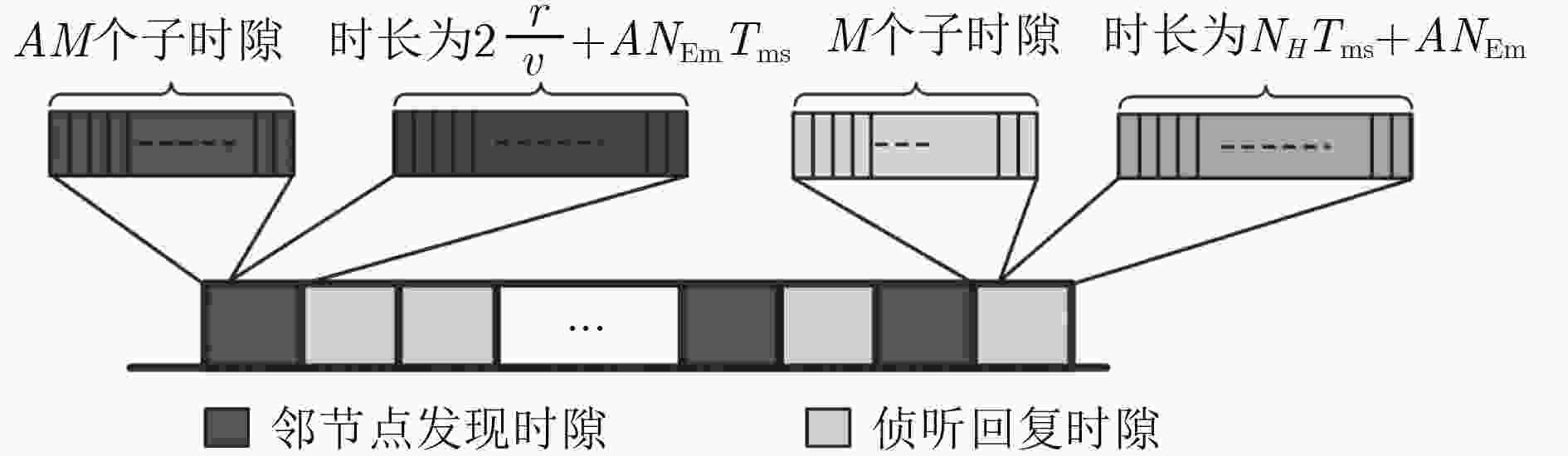
参数 取值 网络部署区域(km2) 5 $ \times $5 节点分布方式 均匀随机分布 节点数目 $N$ 10~100 天线发射波束扇区数目 $M$ 2~6 节点通信距离半径 $r$(km) 1 子时隙时长 $\tau $(ms) 200 仿真时长(s) 1000 水中声信号传播速度(m/s) 1500 -
许肖梅. 水声通信与水声网络的发展与应用[J]. 声学技术, 2009, 28(6): 811–816 doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2009.06.026XU Xiaomei. Development and applications of underwater acoustic communication and networks[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2009, 28(6): 811–816 doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2009.06.026 吴学智, 靳煜, 何如龙. 水声网络及其军事应用研究[J]. 电声技术, 2012, 36(8): 50–53 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8684.2012.08.012WU Xuezhi, JIN Yu, and HE Rulong. Research on underwater acoustic networks and military applications[J]. Audio Engineering, 2012, 36(8): 50–53 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8684.2012.08.012 HEIDEMANN J, STOJANOVIC M, and ZORZI M. Underwater sensor networks: Applications, advances and challenges[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A—Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2012, 370(1958): 158–175 doi: 10.1098/rsta.2011.0214 FELEMBAN E, SHAIKH F K, QURESHI U M, et al. Underwater sensor network applications: A comprehensive survey[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015(11): 1–14 doi: 10.1155/2015/896832 钟永信, 黄建国, 韩晶. 一种用于格型拓扑的水声传感器网络TDMA协议[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(7): 1774–1778 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00980ZHONG Yongxin, HUANG Jianguo, and HAN Jing. A TDMA protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks with grid topology[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2010, 32(7): 1774–1778 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00980 庞菲菲, 张群飞, 史文涛, 等. 基于Parzen窗的水下无线传感器网络目标定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(1): 45–50 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160246PANG Feifei, ZHANG Qunfei, SHI Wentao, et al. Target localization method based on parzen window in underwater wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(1): 45–50 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160246 钟永信, 黄建国, 韩晶. 基于空间唤醒的水声传感器网络节能路由协议[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(6): 1326–1331 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01090ZHONG Yongxin, HUANG Jianguo, and HAN Jing. Energy-efficient routing protocol based on spatial wakeup for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2011, 33(6): 1326–1331 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01090 GHAFOOR H, NOH Y, and KOO I. OFDM-based spectrum-aware routing in underwater cognitive acoustic networks[J]. IET Communications, 2017, 11(17): 2613–2620 doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2017.0244 LI Chao, XU Yongjun, XU Chaonong, et al. DTMAC: A delay tolerant MAC protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(11): 4137–4146 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2462740 ZHANG Senlin, QIAN Liangfang, LIU Meiqin, et al. A slotted-FAMA based MAC protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks with data train[J]. Journal of Signal Processing Systems for Signal Image and Video Technology, 2017, 89(1): 3–12 doi: 10.1007/s11265-016-1138-1 SIVANANTHAM E and RAMAKRISHNAN M. Energy-efficient sustainable cluster based neighbor discovery technique for wireless networks with directional antennas[J]. Cluster Computing-the Journal of Networks Software Tools and Applications, 2017, 20(2): 1527–1534 doi: 10.1007/s10586-017-0862-z SUBRAMANIAN A P and DAS S R. Addressing deafness and hidden terminal problem in directional antenna based wireless multi-hop networks[J]. Wireless Networks, 2010, 16(6): 1557–1567 doi: 10.1007/s11276-008-0138-x ZHANG Zhensheng. DTRA: Directional transmission and reception algorithms in WLANs with directional antennas for QoS support[J]. IEEE Network the Magazine of Global Internetworking, 2005, 19(3): 27–32 doi: 10.1109/MNET.2005.1453396 TRAN T, AN M K, and HUYNH D T. Antenna orientation and range assignment algorithms in directional WSNs[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2017, 25(6): 3368–3381 doi: 10.1109/TNET.2017.2743008 CHEN Jienan, XIE Junfei, Gu Yixin, et al. Long-range and broadband aerial communication using directional antennas (ACDA): Design and implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(12): 10793–10805 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2723802 FONT J L, LNIGO P, DOMINGUEZ M, et al. Analysis of source code metrics from ns-2 and ns-3 network simulators[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2010, 19(5): 1330–1346 doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2011.01.009 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
