Airborne Bistatic Radar Clutter Suppression Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning
-
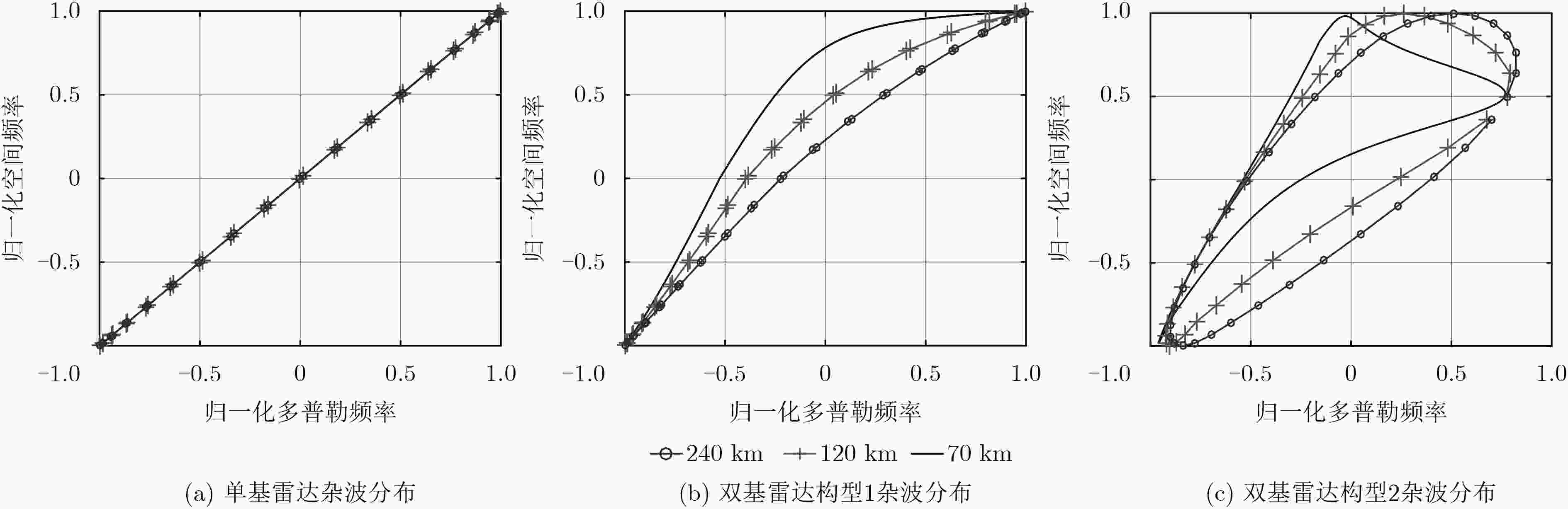
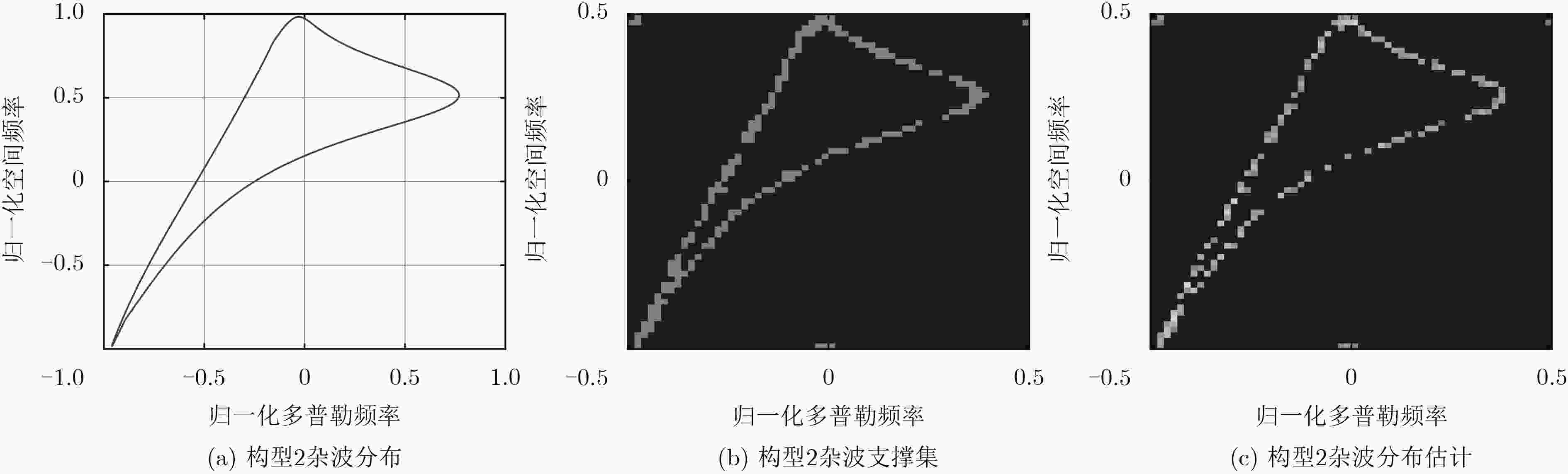
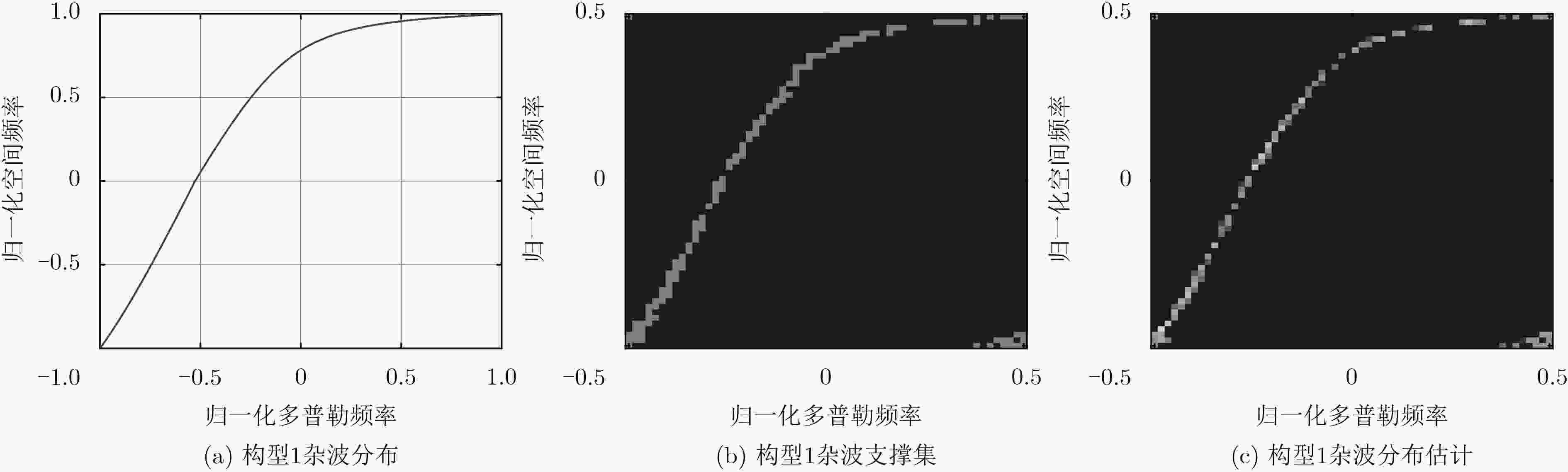
摘要: 机载双基雷达杂波与构型有关且具有严重的距离依赖性,因此杂波脊复杂多变,独立同分布(IID)的样本很少。传统的空时自适应处理(STAP)方法受独立同分布样本数的限制,对机载双基雷达杂波的抑制性能有限。基于机载雷达杂波在角度-多普勒域分布的稀疏特性和稀疏贝叶斯学习(SBL)在稀疏信号重建方面的优势,该文将SBL算法应用于较为复杂的机载双基雷达双动模式下杂波抑制,该方法可以用少量训练单元杂波估计待测距离单元的杂波协方差矩阵(CCM),然后进行空时自适应处理;同时,该算法不需要样本独立同分布,在双基双动模式下对杂波的抑制性能较好,仿真结果验证了算法的有效性。Abstract: Clutter of airborne bistatic radar is related to configuration and has serious range dependence characteristic, therefore the clutter ridge is complex and variable, and few Independent and Identically Distributed (IID) samples exist. As the result, the traditional Space-Time Adaptive Processing (STAP) has a degraded suppression performance for airborne bistatic radar clutter. Based on the sparsity of airborne radar clutter in the angle-Doppler domain and the advantages of Sparse Bayesian Learning (SBL) in sparse signal reconstruction, SBL algorithm is applied to the more complex airborne bistatic radar with both transmitter and receiver moving. The method can estimate the Clutter Covariance Matrix (CCM) of the unit under test with very few training samples, then perform space-time adaptive processing. Since the method does not need independent and identically distributed samples, it has better performance of clutter suppression in the airborne bistatic radar with both transmitter and receiver moving. Simulation results verify the effectiveness of the algorithm.
-
表 1 MSBL算法流程
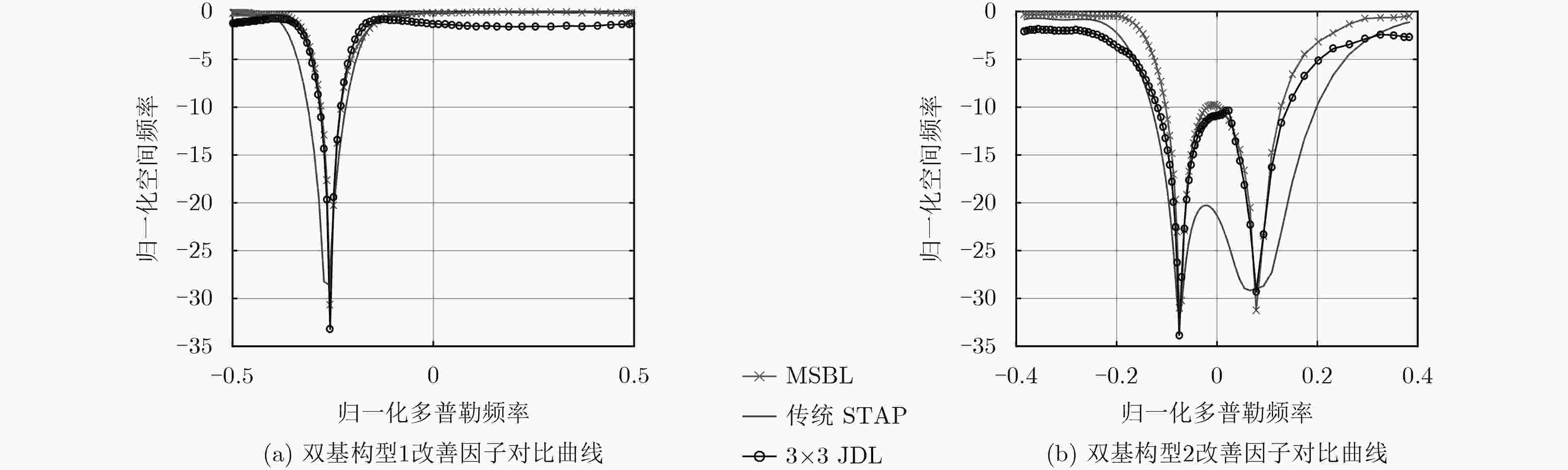
(1)初始化 $\beta $的合理值; (2)初始化一个基向量 ${{φ}_1}$,由 ${{C}} \;=\; {{Φ}} \,{{{Λ}} ^{ - 1}}{{{Φ}} ^{\rm{H}}} \,+\, \beta\, {{{I}}_{MN}}$计算 ${{{C}}_{ - 1}} = \beta {{{I}}_M}$,由 ${a_i} = {φ} _i^{\rm{H}}{{C}}_{ - i}^{ - 1}{{φ}_i}$, ${b_i} = {φ} _i^{\rm{H}}{{C}}_{ - i}^{ - 1}{{x}}$计算 ${a_1}$, ${b_1}$, 根据式(19)计算 ${\hat \alpha _1}$,得到更新后的 ${{Λ}} $; (3)计算均值 ${{μ}} $和方差 ${{Σ}}$,及所有基向量对应的 ${a_i}$, ${b_i}$; (4)如果 $b_i^2 \,>\, {a_i}$且 ${\hat \alpha _i} \,<\, \infty $,则按式(19)更新 ${\hat \alpha _i}$;如果 $b_i^2 \,>\, {a_i}$且 ${\hat \alpha _i} = \infty $,在模型中增加基向量[16,17]${{φ} _i}$,并按式(19)更新 ${\hat \alpha _i}$;如 果 $b_i^2 < {a_i}$且 ${\hat \alpha _i} < \infty $,在模型中删除原子向量 ${{φ} _i}$,并更新 ${\hat \alpha _i} = \infty $,更新 ${{Λ}}$; (5)由 ${{μ}} $, ${{Σ}}$更新 $\beta $; (6)由 ${\beta _0}$, ${{Λ}} $计算均值 ${{μ}} $和方差 ${{Σ}}$及所有基向量对应的 ${a_i}$, ${b_i}$; (7)判断是否收敛,收敛则算法结束,否则转到步骤(4)继续迭代。 表 2 系统仿真参数
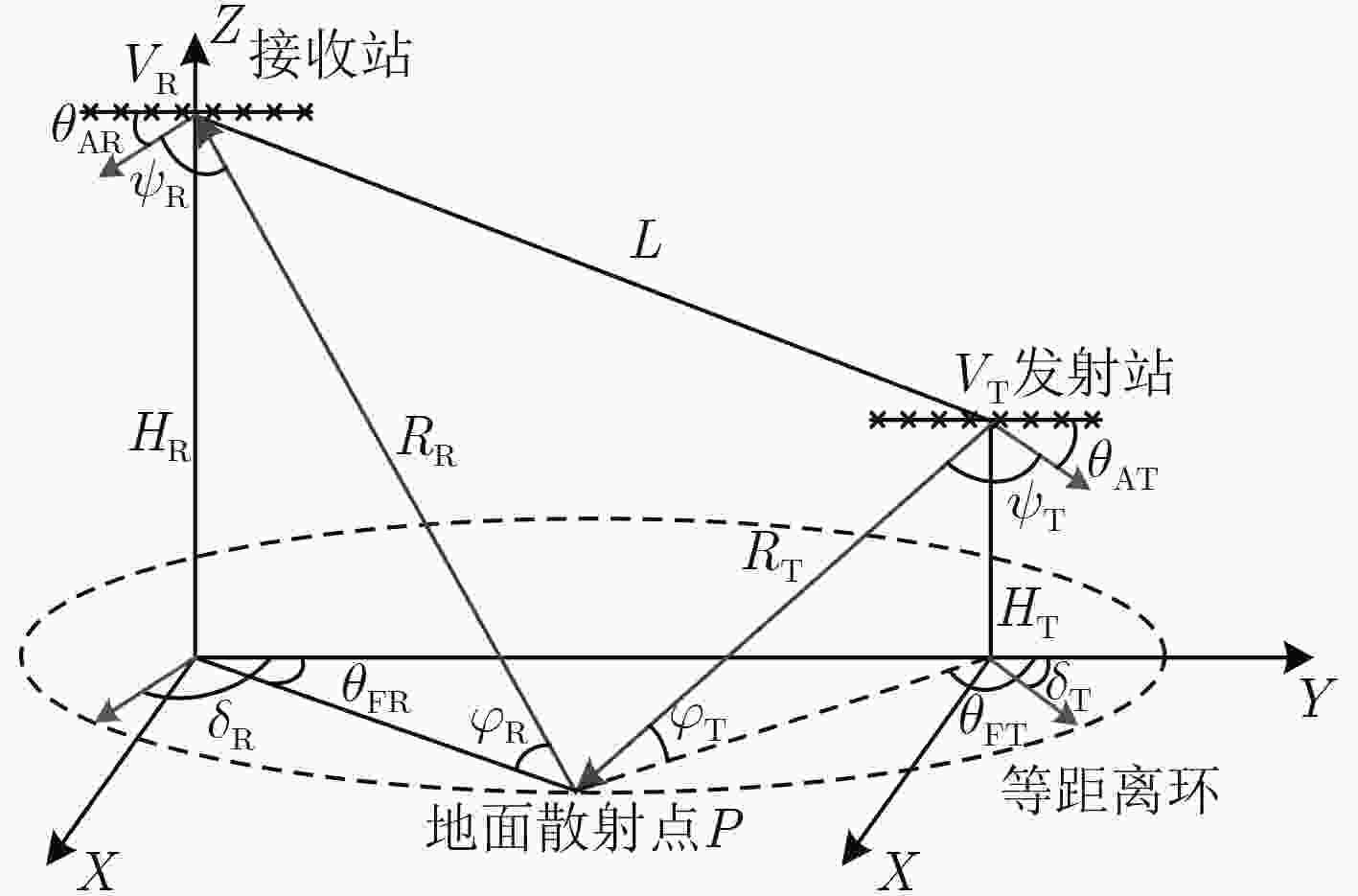
符号 参数名 参数值 ${f_{\rm{c}}}$ 载频 1 GHz ${f_{{\rm{prf}}}}$ 脉冲重复频率 1200 Hz $d$ 天线阵元间隔 0.15 m $N$ 天线阵元数 16 $M$ 相干积累脉冲数 10 $L$ 基线长度 50 km ${R_{{\rm{st}}}}$ 目标单元双基距离和 70 km ${H_{\rm{T}}}$ 发射载机平台高度 2 km ${H_{\rm{R}}}$ 接收载机平台高度 5 km ${V_{\rm{T}}}$ 发射载机平台速度 100 m/s ${V_{\rm{R}}}$ 接收载机平台速度 80 m/s CNR 杂噪比 30 dB -
WILLIS N J and GRIFFITHS H D. Advances in bistatic radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2008, 23(7): 46–46 doi: 10.1109/MAES.2008.4579292 段锐. 机载双基地雷达杂波仿真与抑制技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2009.DUAN Rui. The study on airborne bistatic radar clutter simulation and cancellation techniques[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2009. WARD J. Space-time adaptive processing for airborne radar[C]. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Detroit, MI, USA, 1995: 2809–2812. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1995.479429. KLEMM R. Principles of space-time adaptive processing[J]. Electronics&Communication Engineering Journal, 2002, 14(6): 295–296. WICKS M C, RANGASWAMY M, ADVE R, et al. Space-time adaptive processing: A knowledge-based perspective for airborne radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 51–65 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1593337 KLEMM R. Space-time adaptive processing: principles and applications[J]. Electronics&Communications Engineering Journal, 1999, 11(4): 172–172. KREYENKAMP O and KLEMM R. Doppler compensation in forward-looking STAP radar[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar,Sonar and Navigation, 2001, 148(5): 253–258 doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20010557 HIMED B, ZHANG Yinmin, and HAJJARI A. STAP with angle-doppler compensation for bistatic airborne radars[C]. Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Radar Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2002: 311–317. doi: 10.1109/NRC.2002.999737. HAYWARD S D. Adaptive beamforming for rapidly moving arrays[C]. Proceedings of International Radar Conference, Beijing, China, 1996: 480–483. doi: 10.1109/ICR.1996.574504. REED I S, MALLETT J D, and BRENNAN L E. Rapid convergence rate in adaptive arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1974, AES-10(6): 853–863 doi: 10.1109/TAES.1974.307893 WANG H and CAI L. On adaptive spatial-temporal processing for airborne surveillance radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 660–670 doi: 10.1109/7.303737 孙英. 机载雷达空时自适应处理技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2013.SUN Ying. Study on space-time adaptive pprocessing technology for airborne radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2013. 张永顺, 冯为可, 赵杰, 等. 时变加权的机载双基雷达降维空时自适应处理[J]. 电波科学学报, 2015, 30(1): 194–200 doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2014040701ZHANG Yongshun, FENG Kewei, ZHAO Jie, et al. A dimensional-reduced STAP for airborne bistatic radar based on time-varying weighting techniques[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2015, 30(1): 194–200 doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2014040701 WU Q, ZHANG Y D, AMIN M G, et al. Complex multitask bayesian compressive sensing[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 2014: 3375–3379. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854226. POLI L, OLIVERI G, VIANI F, et al. MT-BCS-based microwave imaging approach through minimum-norm current expansion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(9): 4722–4732 doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2265254 ZHANG Yimin and HIMED B. Space-time adaptive processing in bistatic passive radar exploiting complex bayesian learning[C]. 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, 2014: 0923–0926. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.6875723. WU Qisong, ZHANG Yimin, AMIN M G, et al. Space-time adaptive processing in bistatic passive radar exploiting group sparsity[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, UAS, 2015: 0886–0890. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131120. CARLIN M, ROCCA P, OLIVERI G, et al. Directions-of-arrival estimation through bayesian compressive sensing strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(7): 3828–3838 doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2256093 OLIVERI G, ROCCA P, and MASSA A. A bayesian-compressive-sampling-based inversion for imaging sparse scatterers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3993–4006 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2128329 OLIVERI G, CARLIN M, and MASSA A. Complex-weight sparse linear array synthesis by bayesian compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(5): 2309–2326 doi: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2189742 YANG Pengcheng, LÜ Xiaode, CHAI Zhihai, et al. Clutter cancellation along the clutter ridge for airborne passive radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(6): 951–955 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2689076 SUN Ke, ZHANG Hao, LI Gang, et al. A novel STAP algorithm using sparse recovery technique[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: 336–339. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417664. WANG Lei, LIU Yimin, MA Zeqiang, et al. A novel STAP method based on structured sparse recovery of clutter spectrum[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 2015: 0561–0565. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131061. MACKAY D J C. Bayesian Interpolation[J]. Neural Computation, 1992, 4(3): 415–447 doi: 10.1162/neco.1992.4.3.415 赵军, 田斌, 朱岱寅. 基于PAST处理的机载双基雷达自适应角度-多普勒补偿算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 594–601 doi: 10.12000/JR17053ZHAO Jun, TIAN Bin, and ZHU Daiyin. Adaptive angle-Doppler compensation method for airborne bistatic radar based on PAST[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 594–601 doi: 10.12000/JR17053 WU Qisong, ZHANG Yimin, AMIN M G, et al. Space-time adaptive processing and motion parameter estimation in multistatic passive radar using sparse bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 944–957 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2470518 谢文冲, 段克清, 王永良. 机载雷达空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 575–586 doi: 10.12000/JR17073XIE Wenchong, DUAN Keqing, and WANG Yongliang. Space-time adaptive processing technique for airborne radar:an overview of its development and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 575–586 doi: 10.12000/JR17073 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
