Random Chirp Frequency-stepped Signal ISAR Imaging Algorithm Based on Joint Block-sparse Model
-
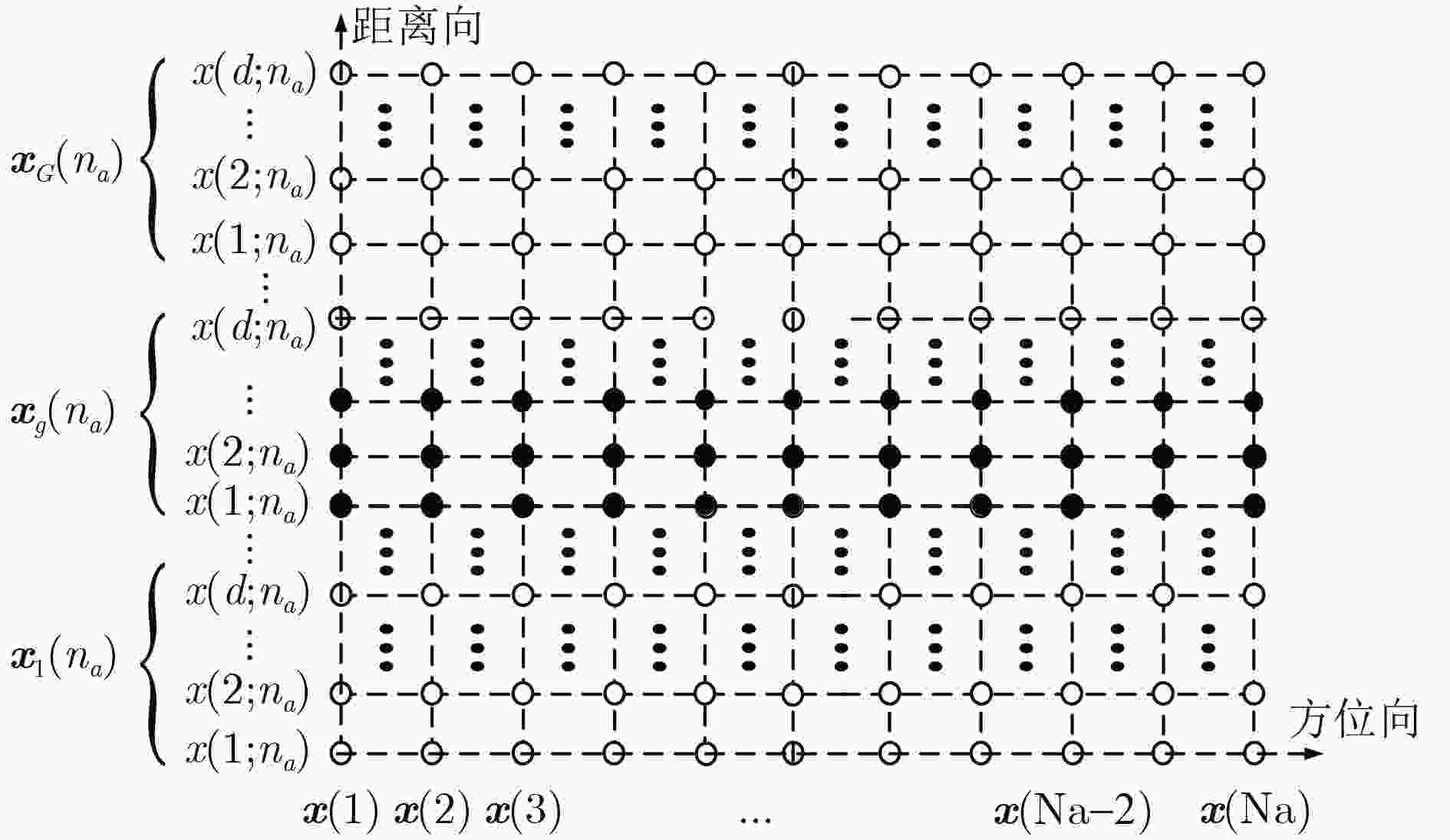
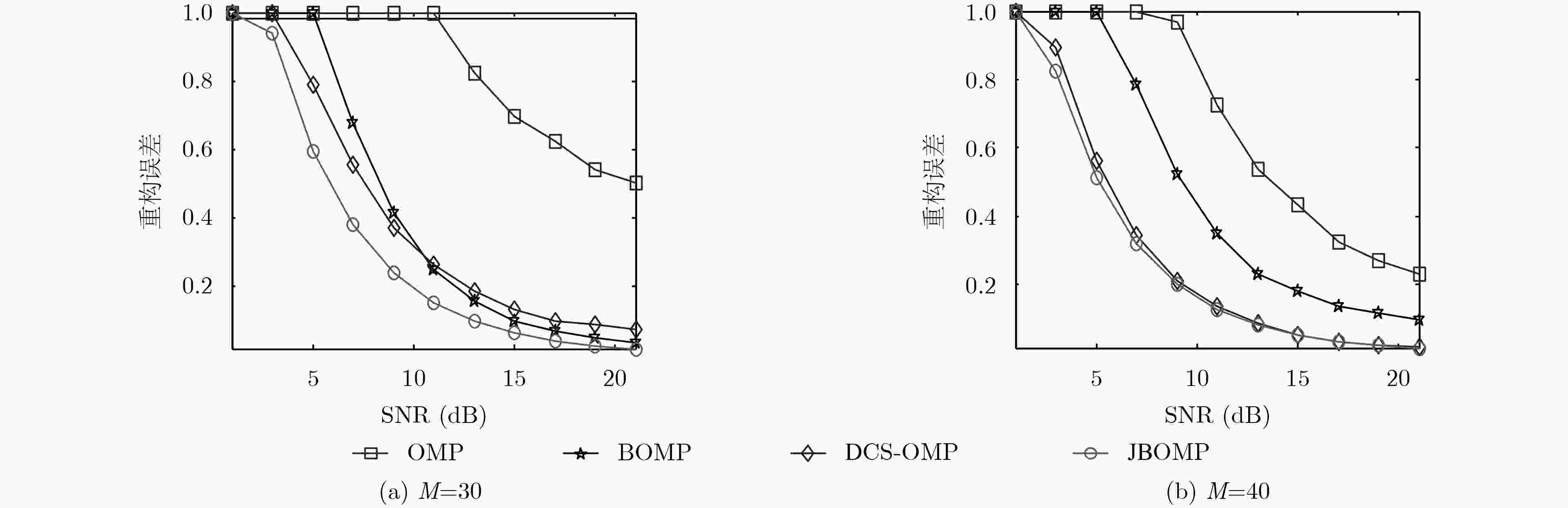
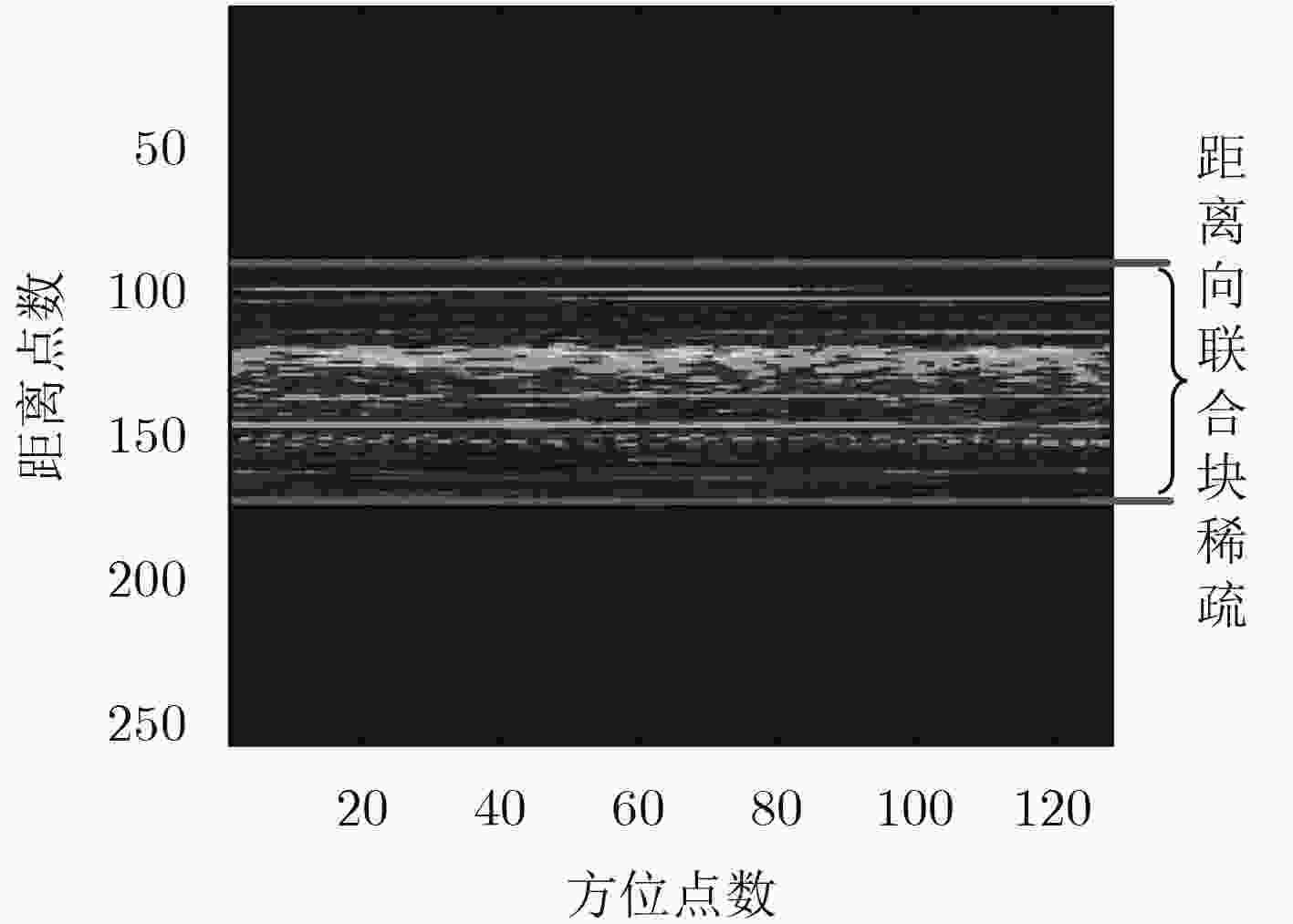
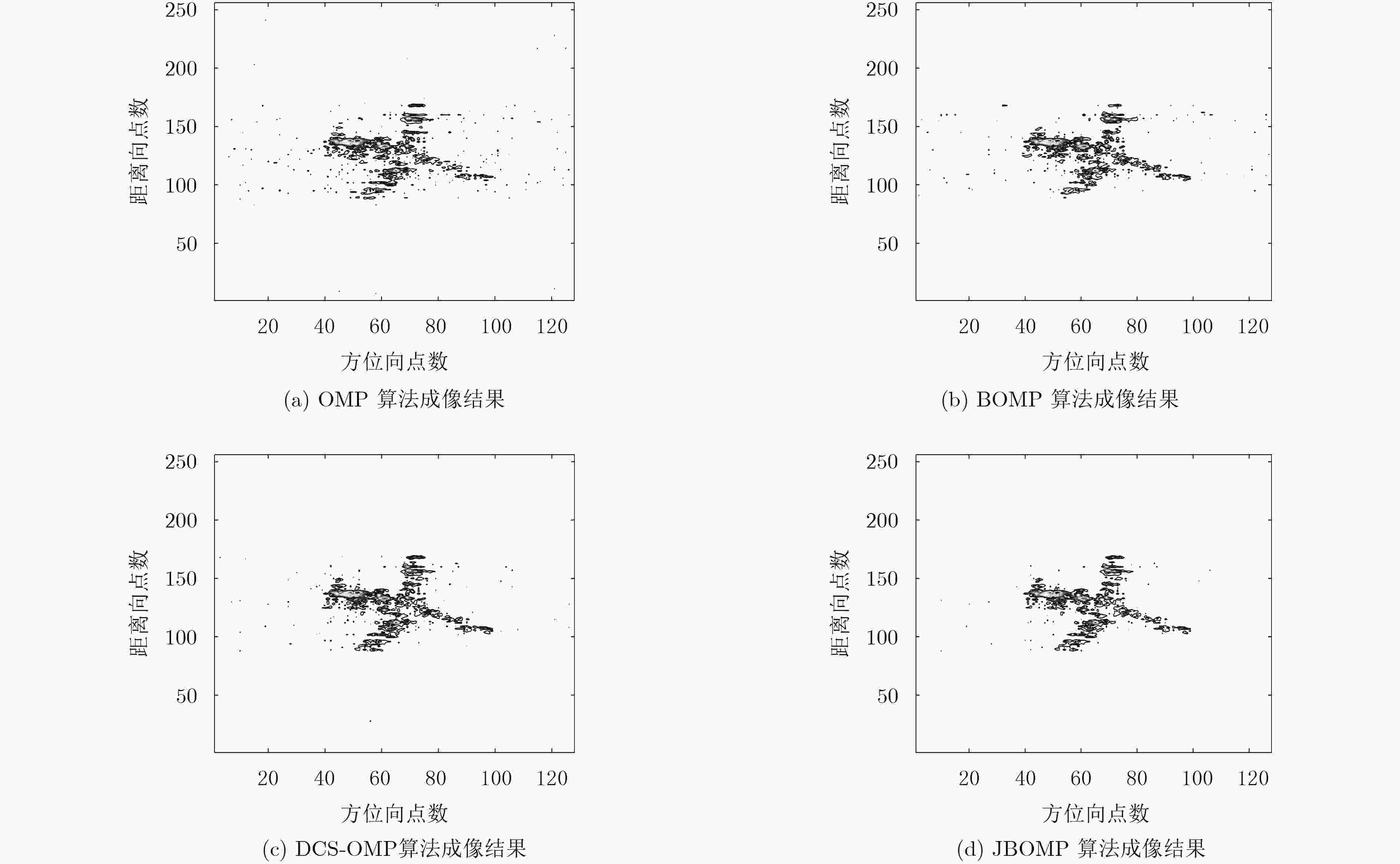
摘要: 在回波数据稀疏、低信噪比等不利条件下,利用随机调频步进信号进行ISAR成像时,成像性能将会严重下降。针对上述问题,该文在充分分析随机调频步进信号回波特性的基础上,提出利用目标距离向具有的联合块稀疏特征来获得高质量ISAR图像的新方法。首先,推导了在随机调频步进信号发射波形条件下目标回波信号的联合块稀疏成像模型并分析了该模型特征;其次,提出了联合块稀疏正交匹配追踪稀疏重构算法(JBOMP)实现对模型的求解。该算法利用ISAR回波信号具有的块稀疏以及联合稀疏等先验信息,因此在低量测值、低信噪比条件下的ISAR成像性能得到了增强。所提算法还可以实现对多维信号的联合处理,且具有较快的运算速度。理论分析与仿真实验均验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Under the condition of lack of echo data and low SNR, the ISAR imaging performance is greatly reduced by using Random Chirp Frequency-Stepped (RCFS) signal. To solve the above problems, based on fully analyzing the echo characteristics of the random chirp frequency-stepped signal, a new method of obtaining high quality ISAR images is proposed using the joint sparse feature of the target range dimension. First, a joint block sparse imaging model of the target echo signal under the condition of random chirp frequency-stepped signal is derived and the characteristics of the model are analyzed. Secondly, a Joint Block sparse Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (JBOMP) algorithm is proposed for solving the model. The algorithm utilizes the sparse information and the joint sparse information of the ISAR echo. Therefore, the ISAR imaging performance is enhanced under the condition of low measurement and low SNR. The proposed algorithm also can achieve joint processing of multidimensional signals and has a faster operation speed. Both theoretical analysis and simulation experiments verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 JBOMP算法
输入:量测数据 ${{S}}$、感知矩阵 ${{Θ}} ({n_a})$、信号个数Na、块稀疏度 $k$、迭代次数n=1 初始化:初始残差 ${{R}}_g^{\left( 0 \right)}({n_a}) = {{s}}({n_a})$,重构结果 ${\hat {{x}}_{{n_a}}} = 0$,支撑集 ${{{T}}^0} = \varnothing $。 第1步 子块选择:通过式(8)计算每个子块的平均内积值 ${{{u}}_g}$,并根据式(9)索引出内积最大的子块对应的位置 ${\lambda _g}$并更新子块支撑集:
${{{T}}^n} = {{{T}}^{n - 1}} \cup {\lambda _g}$;第2步 子块重构:采用最小二乘法重构 ${\rm Na}$个子块信号: ${{\hat{{x}}}_g}({n_a}) = {\left( {{{Θ}}({n_a})_{{{{T}}^n}}^*{{Θ}}{{({n_a})}_{{{{T}}^n}}}} \right)^{ - 1}}{{Θ}}({n_a})_{{{{T}}^n}}^*{{s}}({n_a})$; 第3步 残差更新:对 ${\rm Na}$个信号的残差值进行更新: ${{R}}_g^{\left( n \right)}({n_a}) = {{s}}({n_a}) - {{Θ}}{({n_a})_{{{T}^n}}}{{\hat{{x}}}_g}({n_a})$; 第4步 迭代终止条件:若 $n < K$,则返回执行第1步至第3步的循环操作;若 $n \ge K$,则停止迭代,执行第5步; 第5步 输出重构信号 $\hat {{x}}({n_a})$:将每个子块的稀疏重构信号 ${\hat {{x}}_g}({n_a})$进行组合即可得到最终的 ${\rm Na}$个重构信号 $\hat {{x}}({n_a})$,其中 $\hat {{x}}{({n_a})_{{{{T}}^c}}} = 0$。 ${{{T}}^c}$为 ${{T}}$的
补集, ${{T}}$表示信号的支撑集。 -
DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 HASHEMPOUR H R, MASNADI-SHIRAZI M A, and ARAND B A. Compressive Sensing ISAR imaging with LFM signal[C]. Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, Tehran, Iran, 2017: 1869–1873. ZHU Feng, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. A novel cognitive ISAR imaging method with random stepped frequency chirp signal[J]. Science China Information Science, 2012, 55(8): 1910–1924 doi: 10.1007/s11432-012-4629-0 GAO Xunzhang, LIU Zhen, CHEN Haowen, et al. Fourier-sparsity integrated method for complex target ISAR imagery[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(2): 2723–2736 doi: 10.3390/s150202723 ZHAO Guanghui, SHEN Fangfang, LIN Jie, et al. Fast ISAR imaging based on enhanced sparse representation model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas&Propagation, 2017, 65(10): 5453–5461 doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2734165 FANG Jun , ZHANG Lizao, and LI Hongbin. Two-dimensional pattern-coupled sparse bayesian learning via generalized approximate message passing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(6): 2920–2930 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2556582 ELDAR Y C, PATRICK K, and HELMUT B. Block-sparse signals: Uncertainty relations and efficient recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(6): 3042–3054 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2044837 吕明久, 李少东, 杨军, 等. 基于随机调频步进信号的高分辨ISAR成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3129–3136 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160177LÜ Mingjiu, LI Shaodong, YANG Jun, et al. High resolution ISAR imaging method based on random chirp frequency stepped signal[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3129–3136 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160177 JUSTIN Z and PHILIP S. Efficient high-dimensional inference in the multiple measurement vector problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 61(2): 340–354 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2222382 MOSHE M and ELDAR Y C. The Continuous joint sparsity prior for sparse representations: Theory and applications[C]. 2nd IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, St. Thomas, USA, 2008: 125–128. DUARTE M F, SARVOTHAM S, BARON D, et al. Distributed compressed sensing of jointly sparse signals[C]. Signals, Systems & Computers, Asilomar, USA, 2005: 1537–1541. -






 下载:
下载:

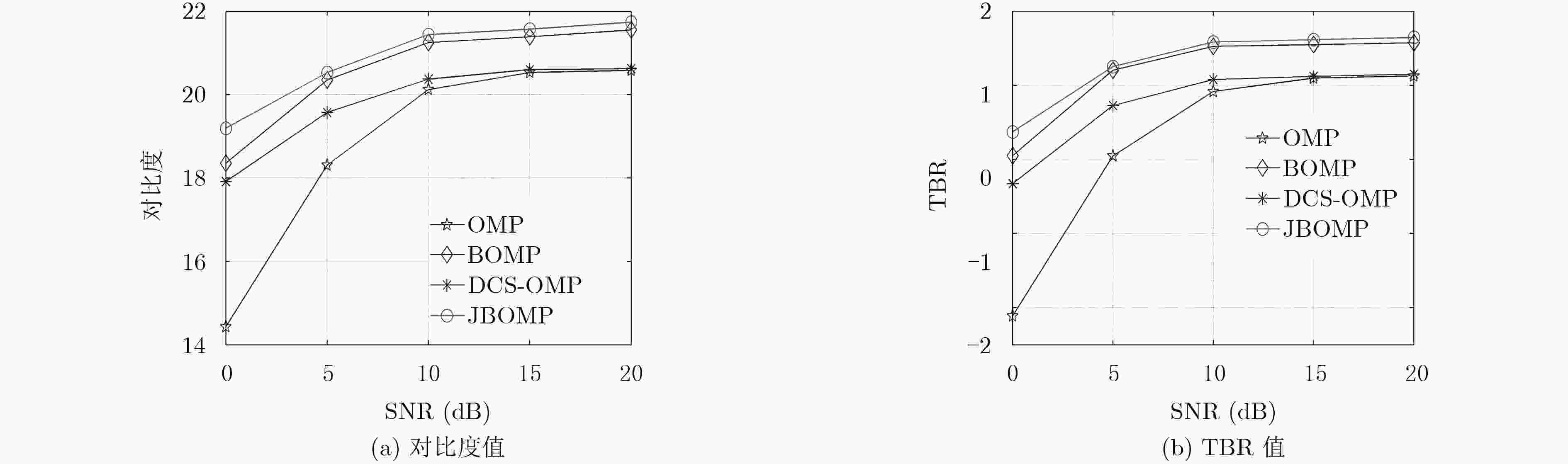


 下载:
下载:
