Noise Suppression Algorithm for Ocean Magnetic Anomaly Detection
-
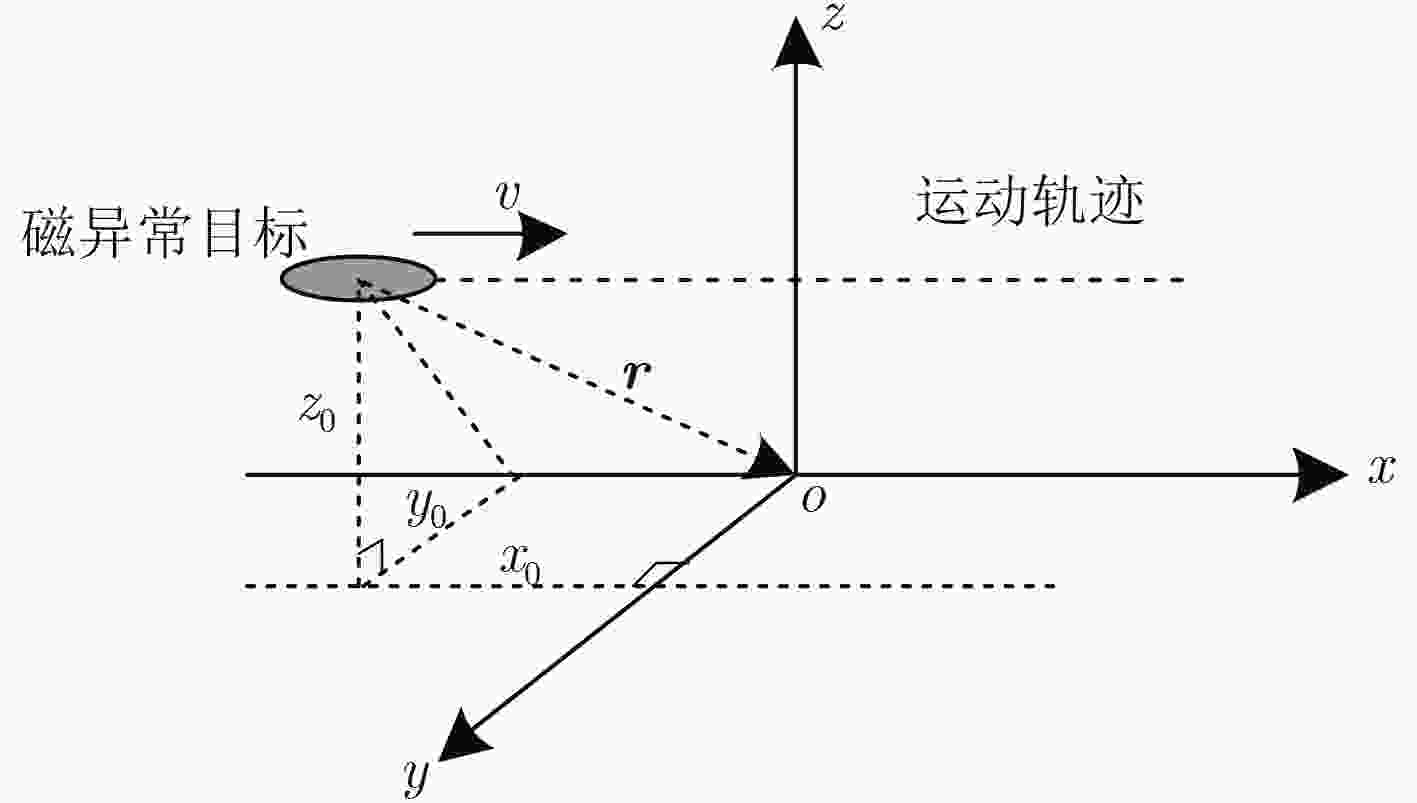
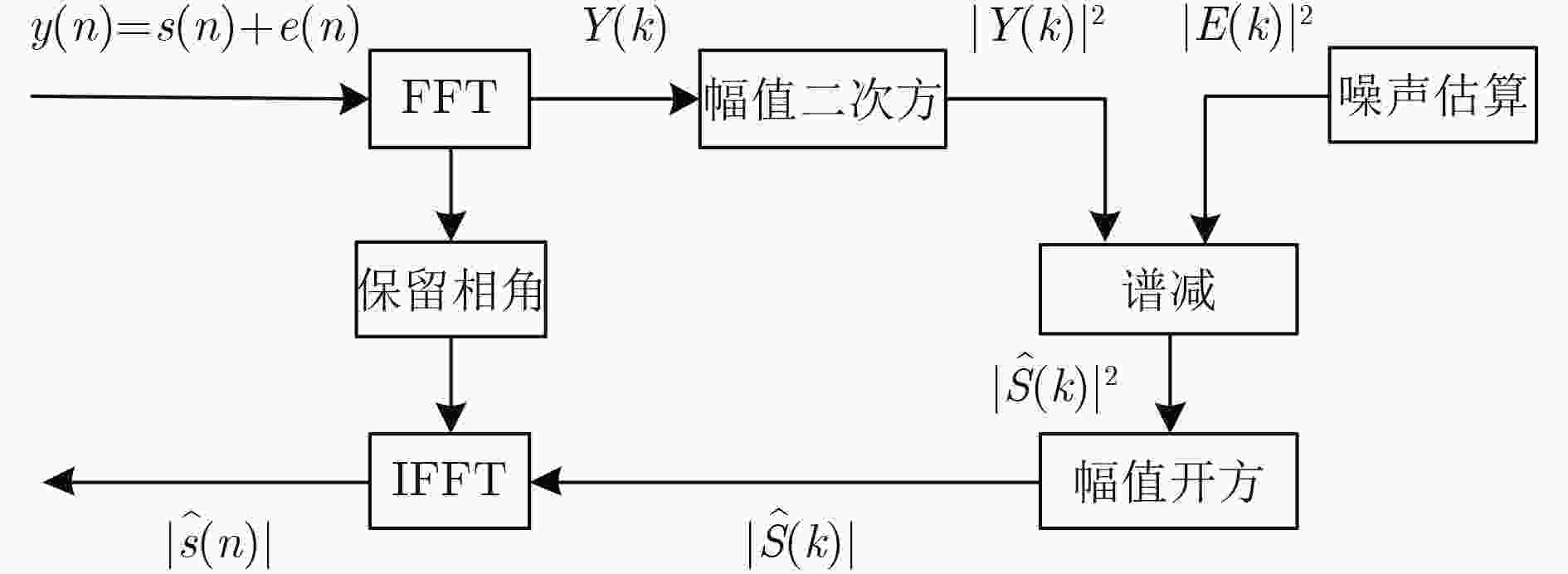
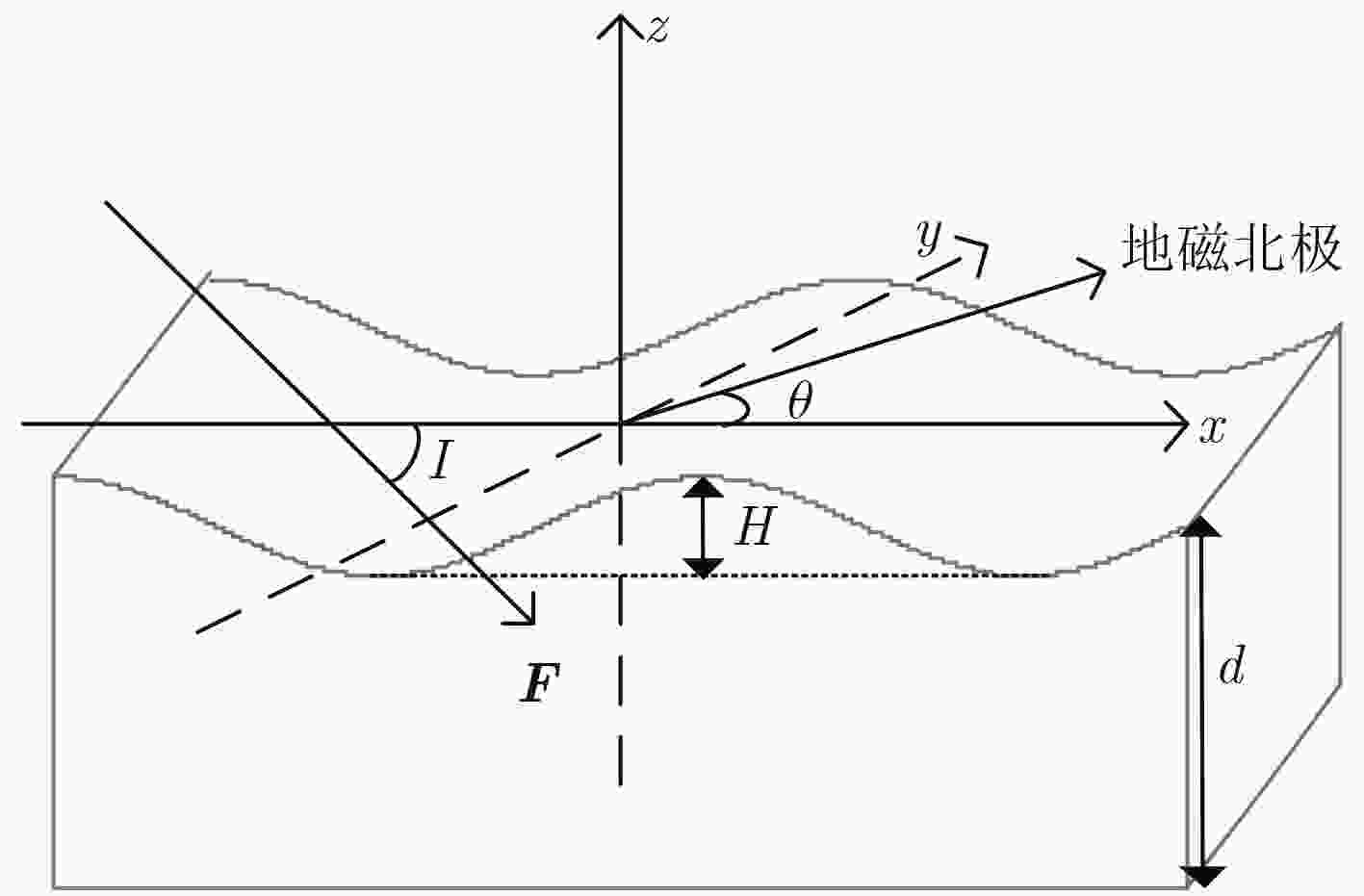
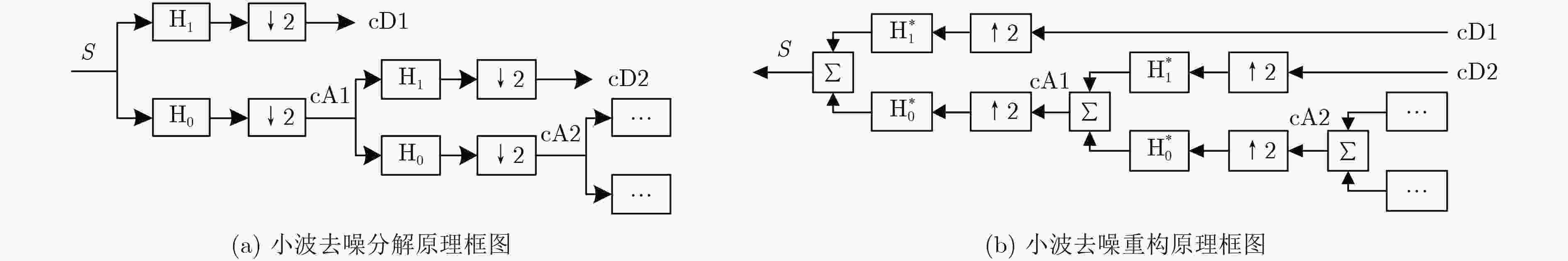
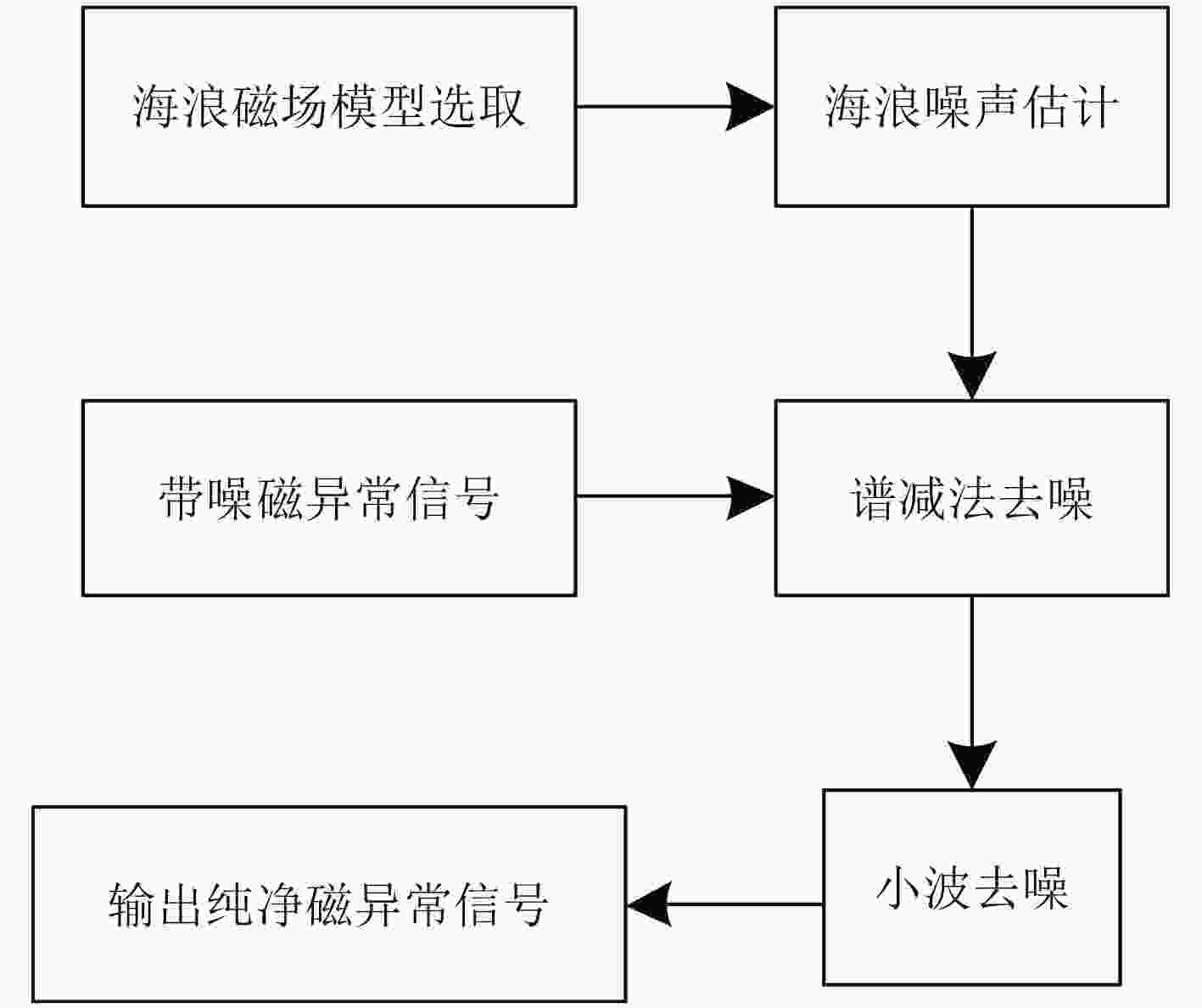
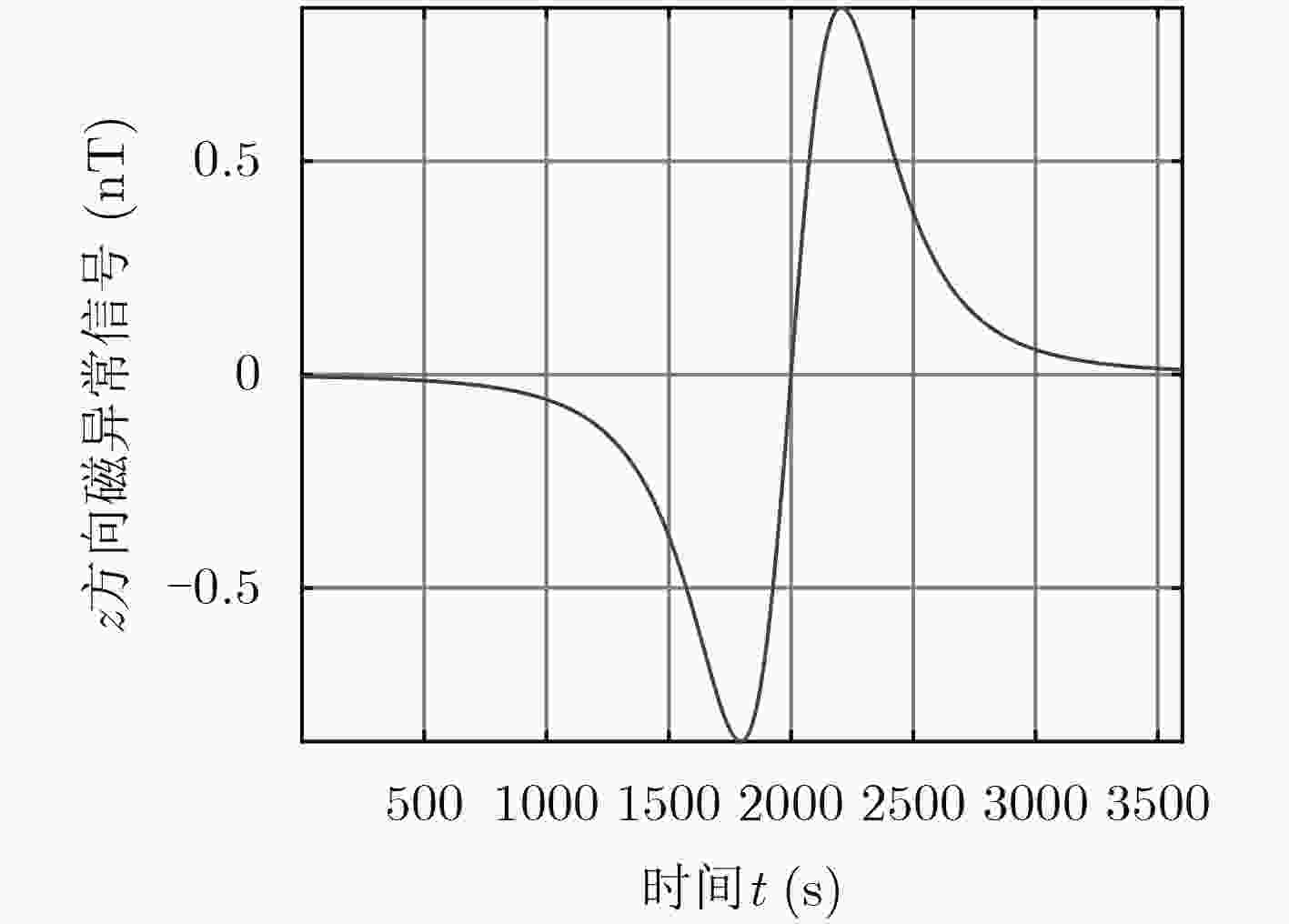
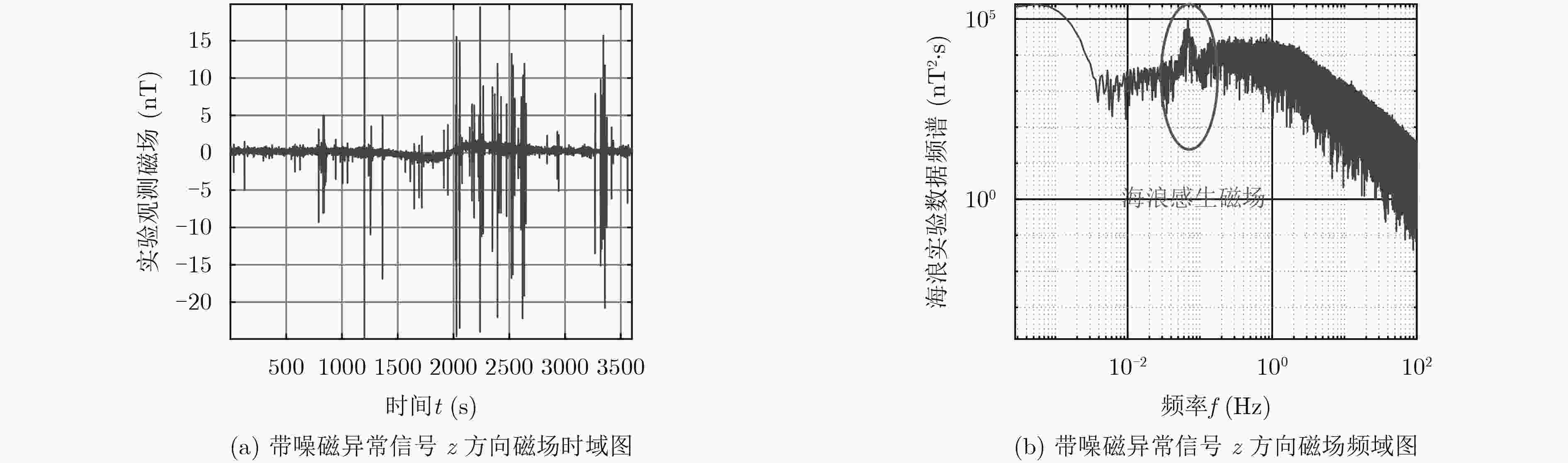
摘要: 海洋磁异常检测是海洋科学观测、海底资源勘探、国防安全等领域的重要手段之一,但复杂环境磁场噪声增加了目标磁探测的难度,研究各种磁场噪声机理及抑制方法对于测量精度的提升具有重要意义。该文提出一种磁异常检测噪声抑制算法,利用通用型和无限水深条件下的海浪磁场模型分别对海浪感生磁场噪声进行估算,通过谱减法和小波去噪相结合的方法对磁异常信号中的海浪和地磁场噪声进行滤除。该文利用2015年8月我国南海某海域的海洋磁场观测数据对该算法进行了验证。结果表明,该方法可以滤除大部分的海浪和地磁场噪声,在频段0.4~0.8 Hz范围内海浪的分布明显减少,较大幅度地改善了时域波形,突出了目标产生的磁异常信号,信噪比可提升近11 dB。该方法计算复杂度低,实时性强且易于实现,可为海洋磁异常检测的噪声抑制提供一种有效手段。Abstract: Marine magnetic anomaly detection is one of the basic means of marine scientific observation, exploration of undersea resources, national defense and security. However, the complexity of the magnetic field noise increases the difficulty of the magnetic detection. It is of great significance to study various magnetic field noise mechanisms and suppression methods for the improvement of measurement accuracy. In this paper, the wave magnetic field model under general and infinite depth conditions is used to estimate the noise induced by sea waves respectively. The wave and geomagnetic noise in the magnetic anomaly signal is filtered out by the combination of spectral subtraction and wavelet. In order to verify the validity of the algorithm, the ocean magnetic field in a sea area of South China Sea in August 2015 is observed. The results show that this method can filter out most of the wave and geomagnetic field noise. The wave distribution in the frequency range of 0.4~0.8 Hz is obviously reduced, the waveform in the time domain is greatly improved, the magnetic anomaly signal of the target is highlighted. Signal to noise ratio can be increased by nearly 11 dB. The proposed method has the advantages of low computational complexity, strong real-time performance and easy implementation, which can provide an effective measure for noise suppression of marine magnetic anomaly detection.
-
表 1 海浪基本参数信息
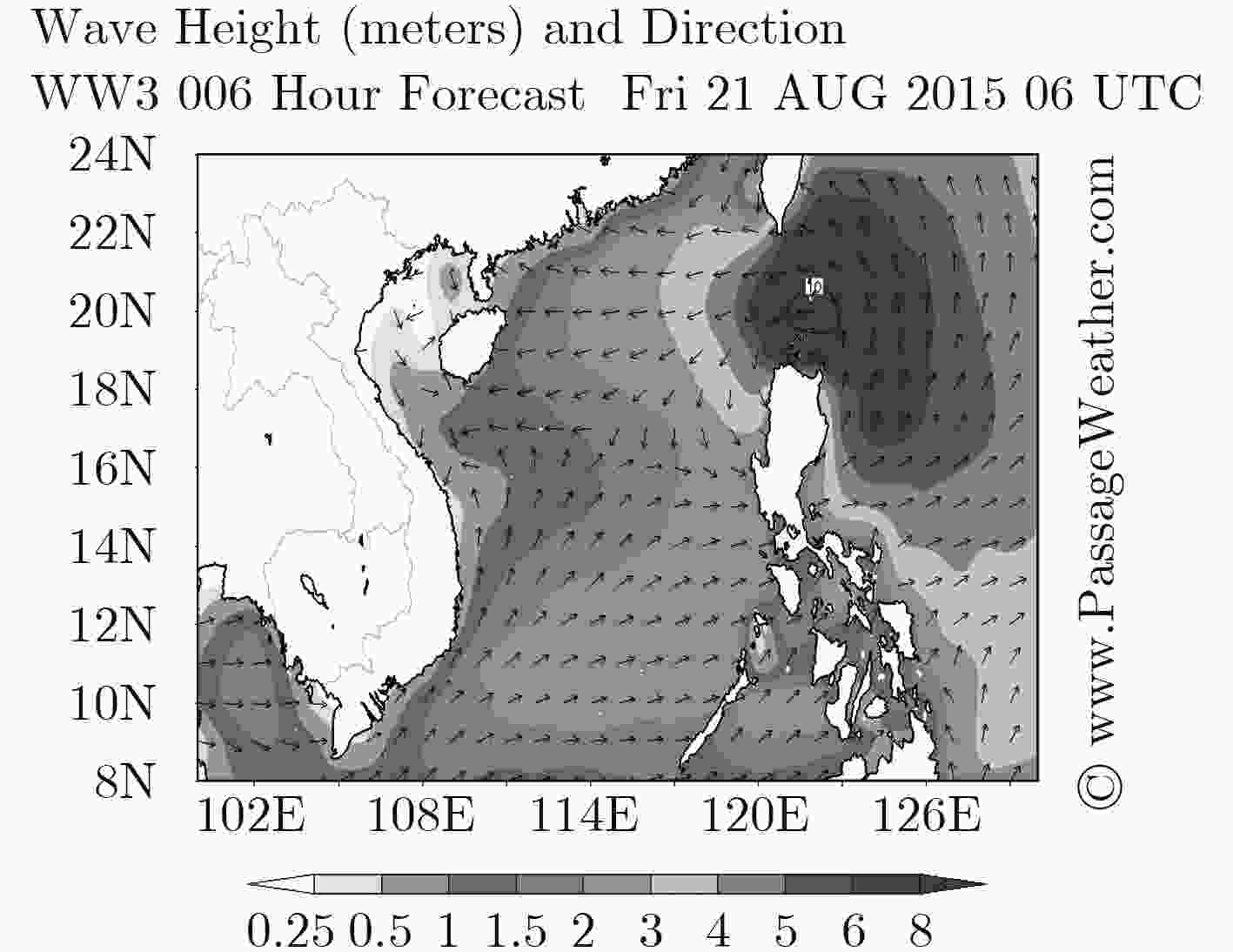
精确传感器测量时间 WW3海浪时间 波长(×108 m) 周期(s) 有效波高(m) 2015-8-21 08:00-09:00 08-21 006/06UTC 30~75 10~25 0.5~1.0 -
任来平, 张启国, 马刚. 水下铁磁体的海面磁场计算模型研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2004, 24(6): 16–19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2004.06.005REN Laiping, ZHANG Qiguo, and MA Gang. Research for calculating model of underwater ferromagnet magnetic field on sea surface[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2004, 24(6): 16–19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2004.06.005 NAIN H, ISA M C, MUHAMMAD M M, et al. Management of naval vessel’s electromagnetic signatures: A review of sources and countermeasures[J]. Defence S&T Technical Bulletin, 2013, 6(2): 93–110. TORRANCE B. Low signature impressed current cathodic protection-new development-future concepts[J]. Journal of Computing Science and Engineering, 2006, 9(17): 511–526. WATERMANN J and LAM J. Distributions of magnetic field variations, differences and residuals[R]. DTIC Document, 1999. SHEINKER A, GINZBURG B, SALOMONSKI N, et al. Magnetic anomaly detection using high-order crossing method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1095–1103 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164086 FRUMKIS L, GINZBURG B, SALOMONSKI N, et al. Optimization of scalar magnetic gradiometer signal processing[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2005, 121(1): 88–94 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2005.01.019 SHEINKER A, FRUMKIS L, GINZBURG B, et al. Magnetic anomaly detection using a three-axis magnetometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2009, 45(1): 160–167 doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2008.2006635 SHEINKER A, GINZBURG B, SALOMONSKI N, et al. Localization in 2D using beacons of low frequency magnetic field[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2013, 6(2): 1020–1030 doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2012.2213240 OTNES R. Static magnetic dipole detection using vector linear prediction, Anderson functions, and block-based adaptive processing[C]. Europe Oceans Conference, Aberdeen, Scotland, 2007: 1–6. LUCAS C and OTNES R. Noise removal using multi-channel coherence[R]. DTIC Document, 2010. 刘敦歌. 目标磁异常/轴频信号处理方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2016: 9–12.LIU Dunge. Research on processing of targets’ magnetic anomaly/shaft frequency signatures[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016: 9–12. FAGGIONI O, SOLDANI M, GABELLONE A, et al. Undersea harbour defence: A new choice in magnetic networks[J].Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2010, 72(1): 46–56 doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2010.07.001 WAHLSTRÖM N. Localization using magnetometers and light sensors[D]. [Master dissertation], Linköping University, 2013: 23–25. 费春娇, 吴佩霖, 张群英, 等. 一种改进型的基于Stokes一阶波的海浪磁场模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(8): 2007–2013 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161123FEI Chunjiao, WU Peiling, ZHANG Qunying, et al. Improved model of ocean wave induced magnetic field based on the first order Stokes Equtions[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(8): 2007–2013 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161123 BR Webworks, Status[OL]. http://passageweather.com/, 2006-2017. -





 下载:
下载:
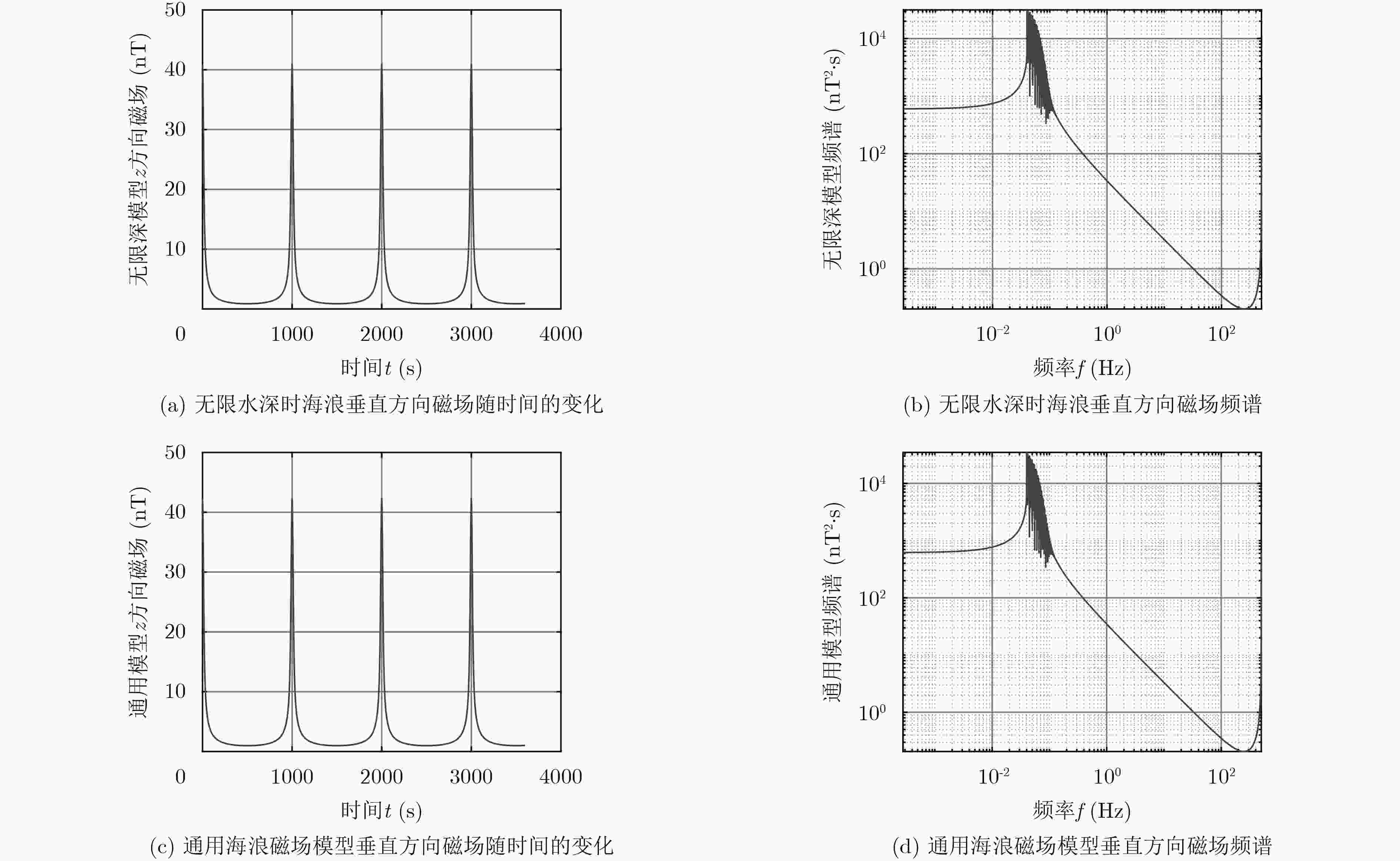
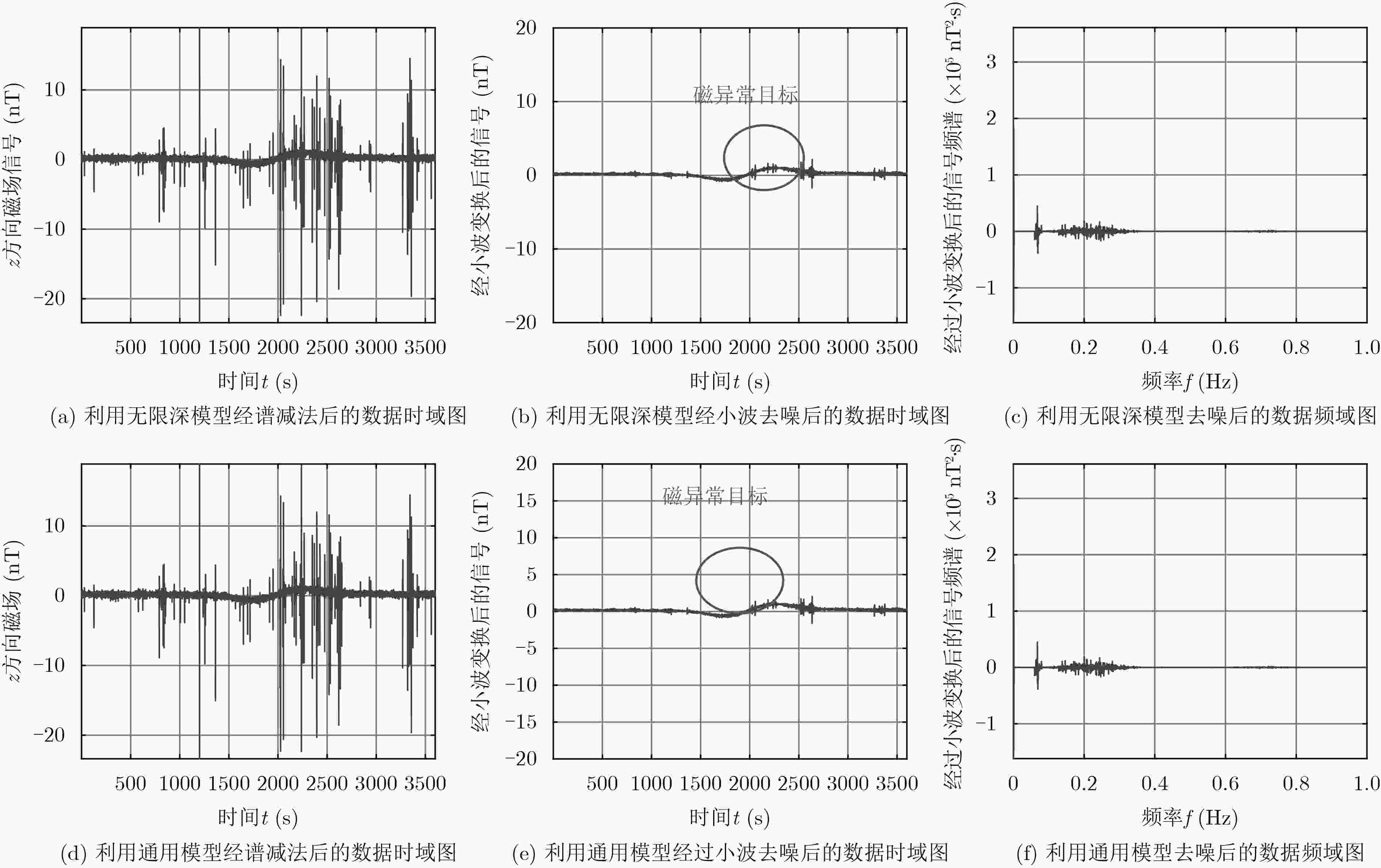


 下载:
下载:
