Independent Vector Analysis Convolutive Blind Separation Algorithm Based on Step-size Adaptive
-
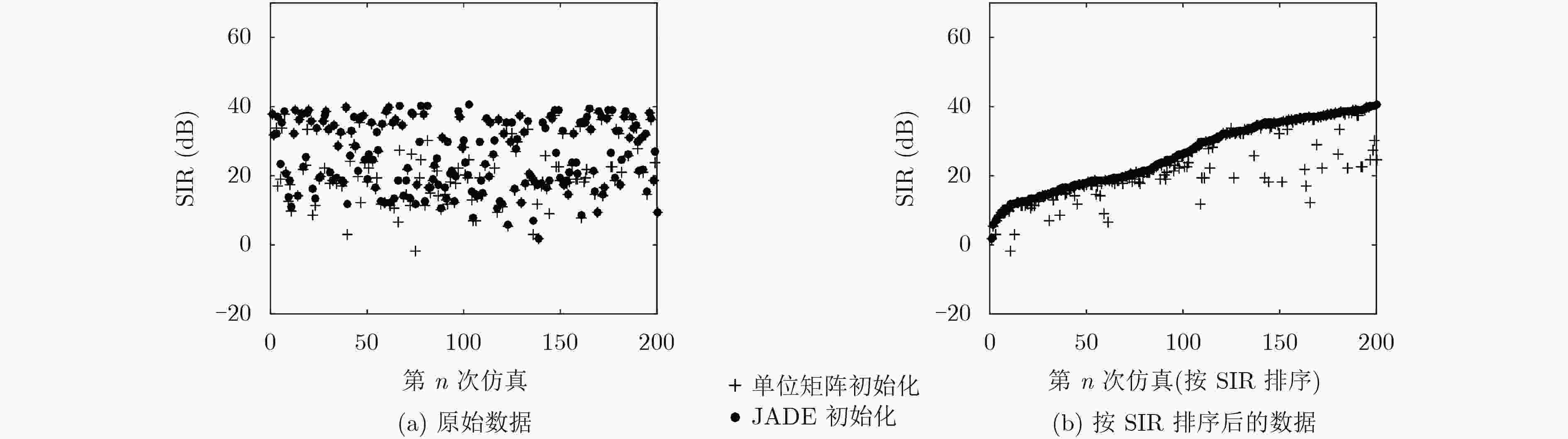
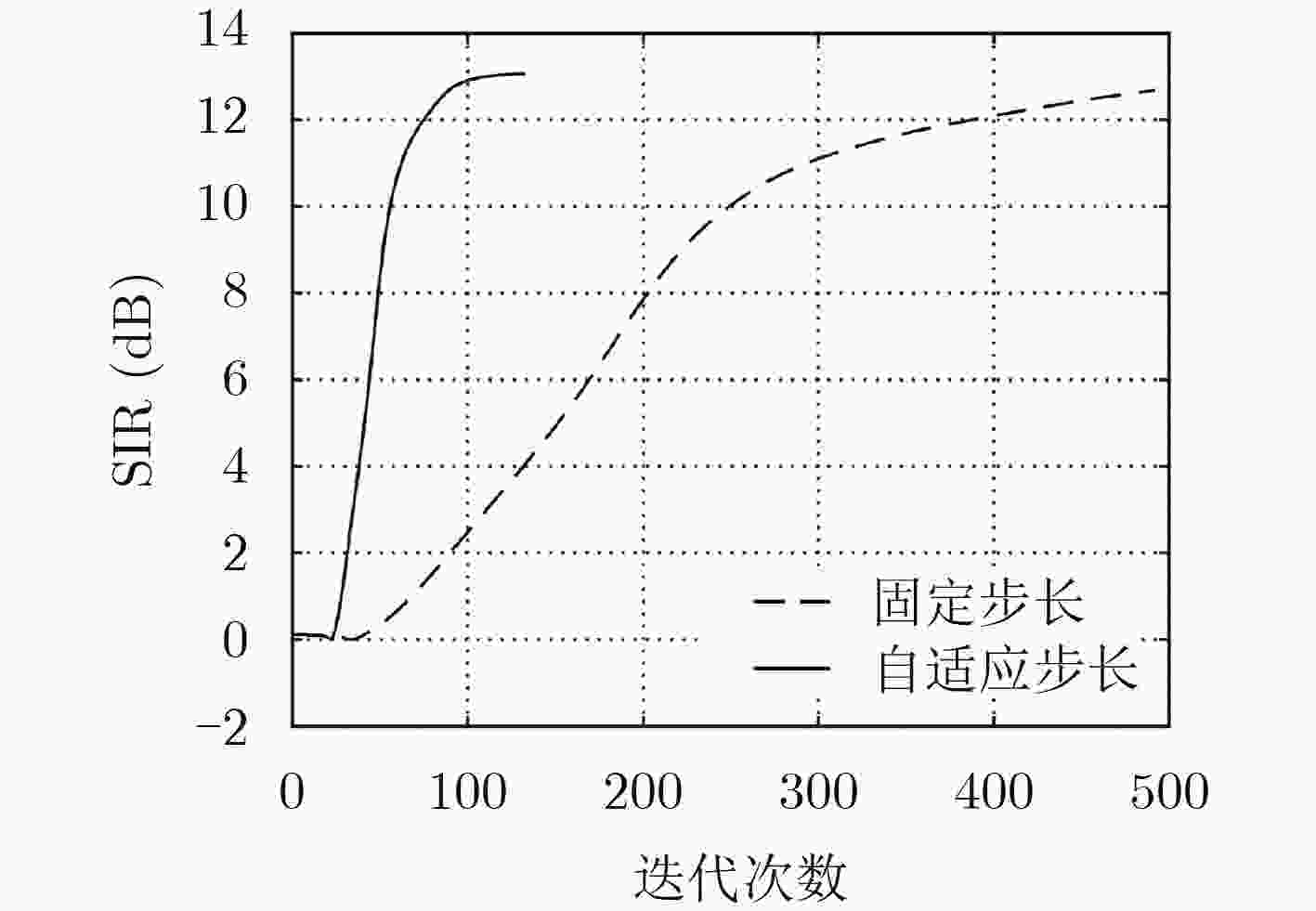
摘要: 独立向量分析(IVA)是解决频域卷积盲分离排序模糊性最好的方法之一,但存在迭代次数较多、运算时间较长、分离效果易受分离矩阵初值影响的局限性。该文提出一种基于步长自适应的IVA卷积盲分离算法,该算法使用特征矩阵联合近似对角化(JADE)算法对分离矩阵进行初始化,并对步长参数进行了自适应优化。JADE初始化能够使分离矩阵具有合理的初值,避免局部收敛的情况;步长的自适应优化能够显著提升算法的收敛速度。仿真结果表明,该算法进一步提升了分离性能,并显著缩短了运算时间。
-
关键词:
- 盲源分离 /
- 卷积混合 /
- 独立向量分析 /
- 特征矩阵联合近似对角化 /
- 步长自适应
Abstract: Independent Vector Analysis (IVA) is one of the best methods to solve the sort ambiguity of convolutive blind separation in frequency domain. However, it needs more iterations and computing time, and the separation effect is susceptible to the initial value of the separation matrix. This paper proposes an IVA convolutive blind separation algorithm based on step-size adaptive, which uses Joint Approximative Diagonalization of Eigenmatrices (JADE) algorithm to initialize the separation matrix and optimizes adaptively the step step-size parameters. JADE initialization can make the separation matrix have an appropriate initial value, thus avoiding the situation of local convergence; step-size adaptive optimization can significantly improve the convergence speed of the algorithm. Simulation results show that this algorithm improves the separation performance and shortens the operation time significantly. -
表 1 基于步长自适应的IVA卷积盲分离算法
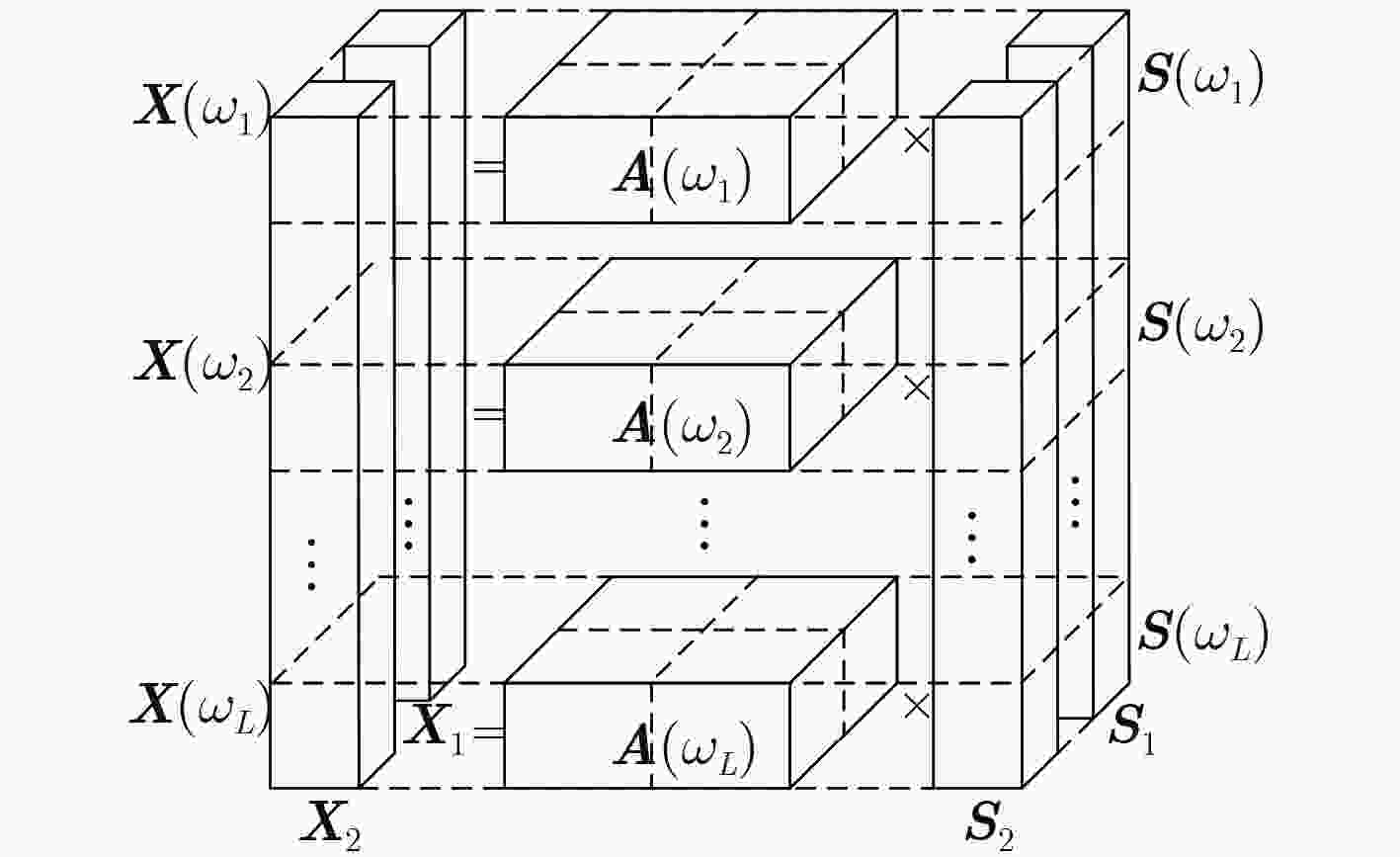
步骤1 将时域卷积混合信号经STFT 转换为各个频率点的线性
瞬时混合复值信号;步骤2 对各频率点的混合信号进行中心化和白化预处理; 步骤3 使用JADE算法初始化各频点的分离矩阵 ${{{W}}_0}\left( \omega \right)$,并初
始化迭代步长 ${\eta _0}$;步骤4 根据 ${{Y}}\left( \omega \right){{ = W}}\left( \omega \right){{X}}\left( \omega \right)$来估计各频点的源信号; 步骤5 根据估计出的源信号来计算目标函数和非线性函数,并
判断分离矩阵是否收敛。若收敛,执行步骤9;步骤6 根据式(14)来更新各频点分离矩阵; 步骤7 根据式(25)来更新迭代步长; 步骤8 若达到最大迭代次数,输出最终各频点分离信号,否则
返回步骤4;步骤9 将各频点分离信号经ISTFT恢复成时域分离信号,即
源信号估计。表 2 仿真运行时间
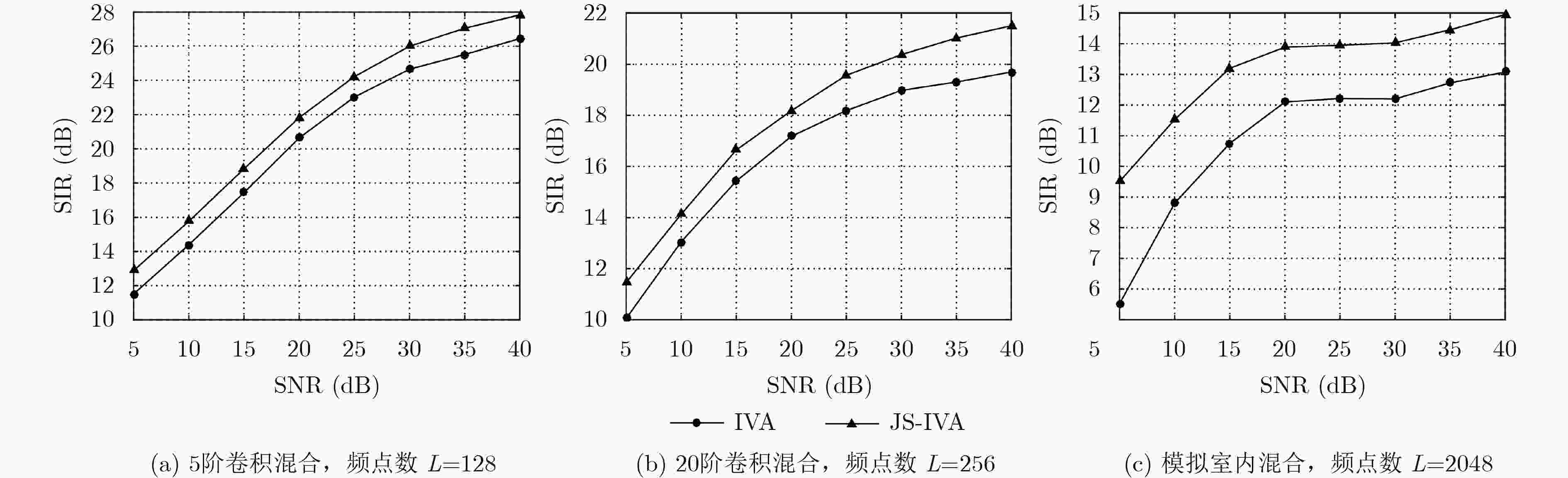
算法 运行次数 运行总时间(s) IVA 1840 23803.8 JS-IVA 1840 12283.4 表 3 算法单次迭代时间对比(ms)
算法 5阶混合 20阶混合 模拟室内混合 IVA 27.81 34.73 51.18 JS-IVA 28.70 38.31 63.10 表 4 算法迭代次数和运行时间对比(次数/s)
算法 5阶混合 20阶混合 模拟室内混合 IVA 114/3.17 167/5.80 658/33.68 JS-IVA 62/1.78 89/3.41 174/10.98 -
BELAID S, HATTAY J, NAANAA W, et al. A new multi-scale framework for convolutive blind source separation[J]. Signal Image&Video Processing, 2016, 10(7): 1–8 doi: 10.1007/s11760-016-0877-6 ZOULIKHA M and DJENDI M. A new regularized forward blind source separation algorithm for automatic speech quality enhancement[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 112: 192–200 doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.05.012 NEGRO F, MUCELI S, CASTRONOVO A M, et al. Multi-channel intramuscular and surface EMG decomposition by convolutive blind source separation[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2016, 13(2): 026027 doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/13/2/026027 HAILE M A and DYKAS B. Blind source separation for vibration-based diagnostics of rotorcraft bearings[J]. Journal of Vibration&Control, 2016, 22(18): 3807–3820 doi: 10.1177/1077546314566041 CHERRAK O, GHENNIOUI H, THIRION-MOREAU N, et al. Preconditioned optimization algorithms solving the problem of the non unitary joint block diagonalization: Application to blind separation of convolutive mixtures[J]. Multidimensional Systems&Signal Processing, 2017(1): 1–24 doi: 10.1007/s11045-017-0506-8 贾志成, 韩大伟, 陈雷, 等. 基于复Givens矩阵与蝙蝠优化的卷积盲分离算法[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(7): 107–117 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016138JIA Zhicheng, HAN Dawei, CHEN Lei, et al. Convolutive blind separation algorithm based on complex Givens matrix and bat optimization[J]. Journal of Communications, 2016, 37(7): 107–117 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016138 BINGHAM E and HYVARINEN A. A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis of complex valued signals[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2000, 10(1): 1–8 doi: 10.1142/S0129065700000028 CARDOSO J F. Equivariant adaptive source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(12): 3017–3029 doi: 10.1109/78.553476 CARDOSO J F. High order contrast for independent component analysis[J]. Neural Computation, 1999, 11(1): 157–193 doi: 10.1162/089976699300016863 KIM T, ATTIAS H T, LEE S Y, et al. Blind source separation exploiting higher-order frequency dependencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio Speech&Language Processing, 2006, 15(1): 70–79. 杨福生, 洪波. 独立分量分析的原理与应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006: 20–23.YANG Fusheng and HONG Bo. The Principle and Application of Independent Component Analysis[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2006: 20–23. 孙守宇, 郑君里, 吴德伟. 基于自然梯度算法的盲信源分离研究[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 4(3): 50–54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2003.03.013SUN Shouyu, ZHENG Junli, and WU Dewei. Research on blind source separation based on natural gradient algorithm[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University(Natural Science Edition) , 2003, 4(3): 50–54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2003.03.013 ERIKSSON J and KOIVUNEN V. Complex random vectors and ICA models: Identifiability, uniqueness, and separability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(3): 1017–1029 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.864440 MATSUOKA K. Minimal distortion principle for blind source separation[C]. Proceedings of the 41th SICE Annual Conference, Kitakyushu, Japan, 2002, 4: 2138–2143. doi: 10.1109/SICE.2002.1195729. 付卫红, 杨小牛, 刘乃安, 等. 基于步长最优化的EASI盲源分离算法[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2008, 40(1): 118–121 doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.2008.01.023FU Weihong, YANG Xiaoniu, LIU Naian, et al. Step-size optimization based EASI algorithm for blind source separation[J]. Journal of Sichuan University(Engineering Science) , 2008, 40(1): 118–121 doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.2008.01.023 VINCENT E, GRIBONVAL R, and FEVOTTE C. Performance measurement in blind audio source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2006, 14(4): 1462–1469 doi: 10.1109/TSA.2005.858005 PHAM D T, SERVIERE C, and BOUMARAF H. Blind separation of speech mixtures based on nonstationarity[C]. International Symposium on Signal Processing and ITS Applications, Grenoble Cedex, France, 2003, 2: 73–76. doi: 10.1109/ISSPA.2003.1224818. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
