Dynamic Object Localization Based on Radio Frequency Identification and Laser Information
-
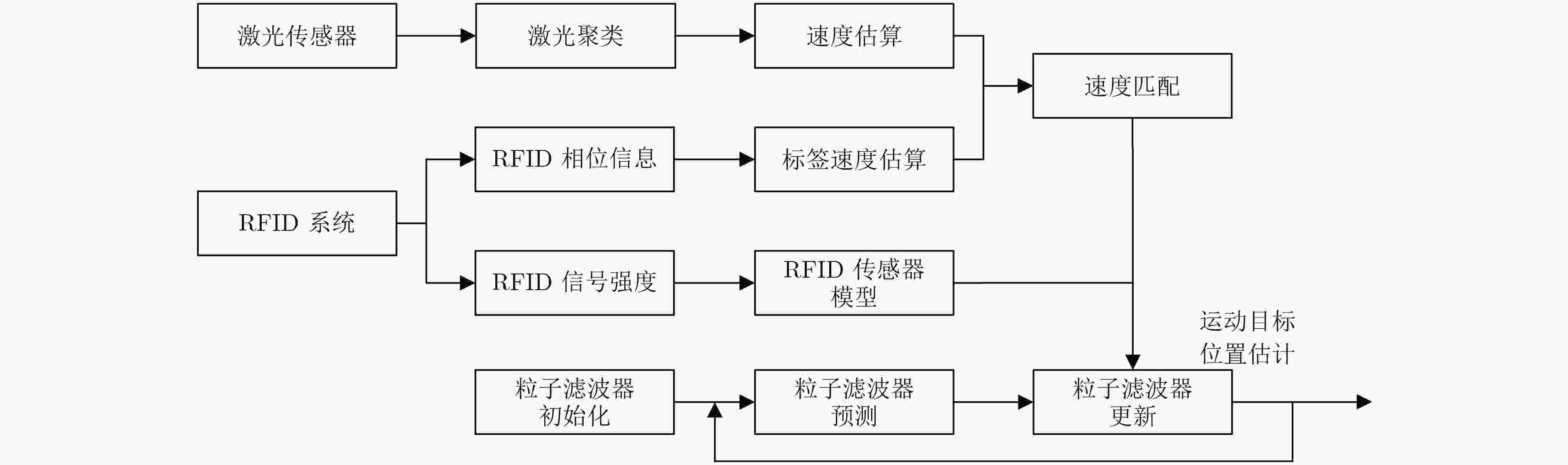
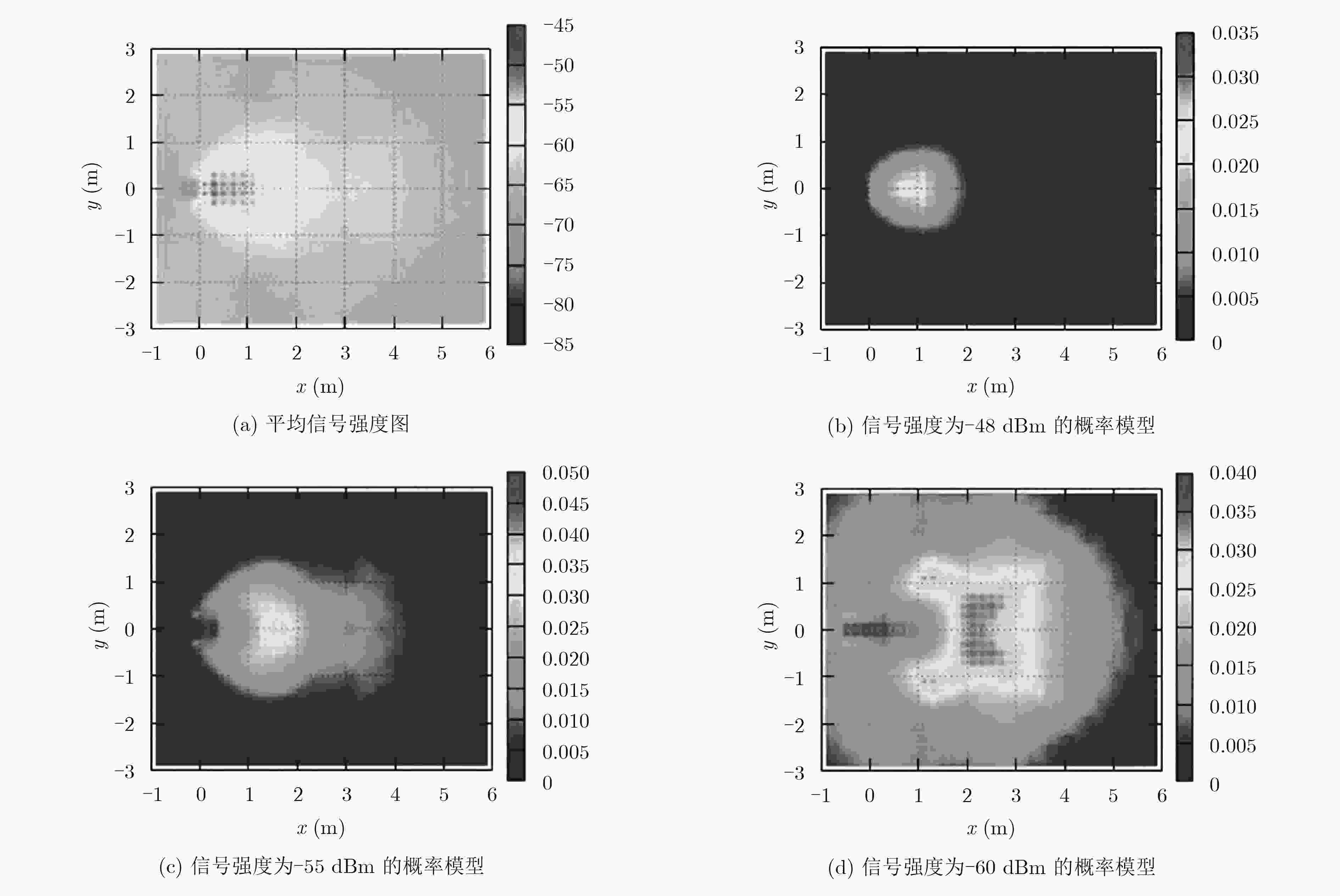
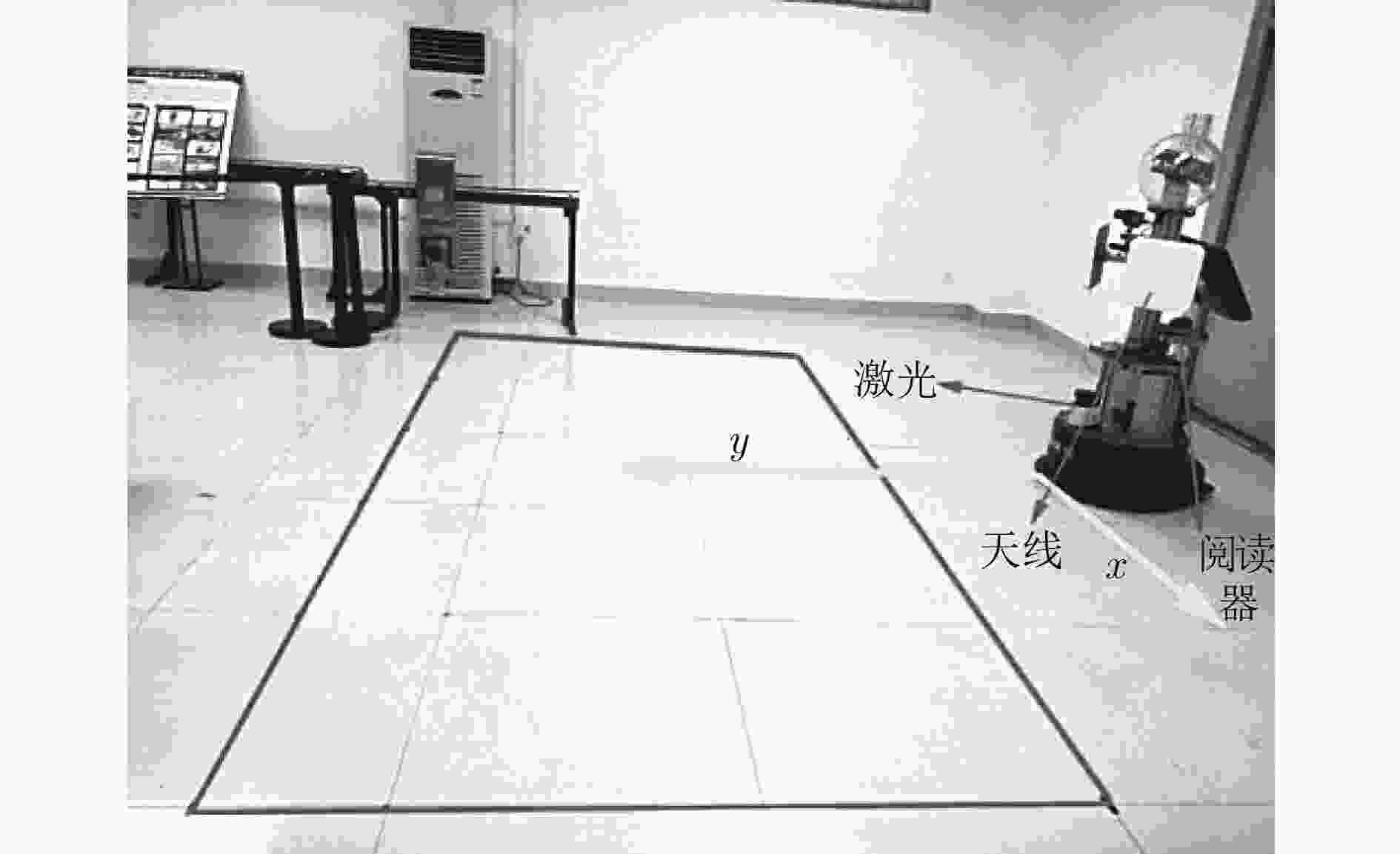
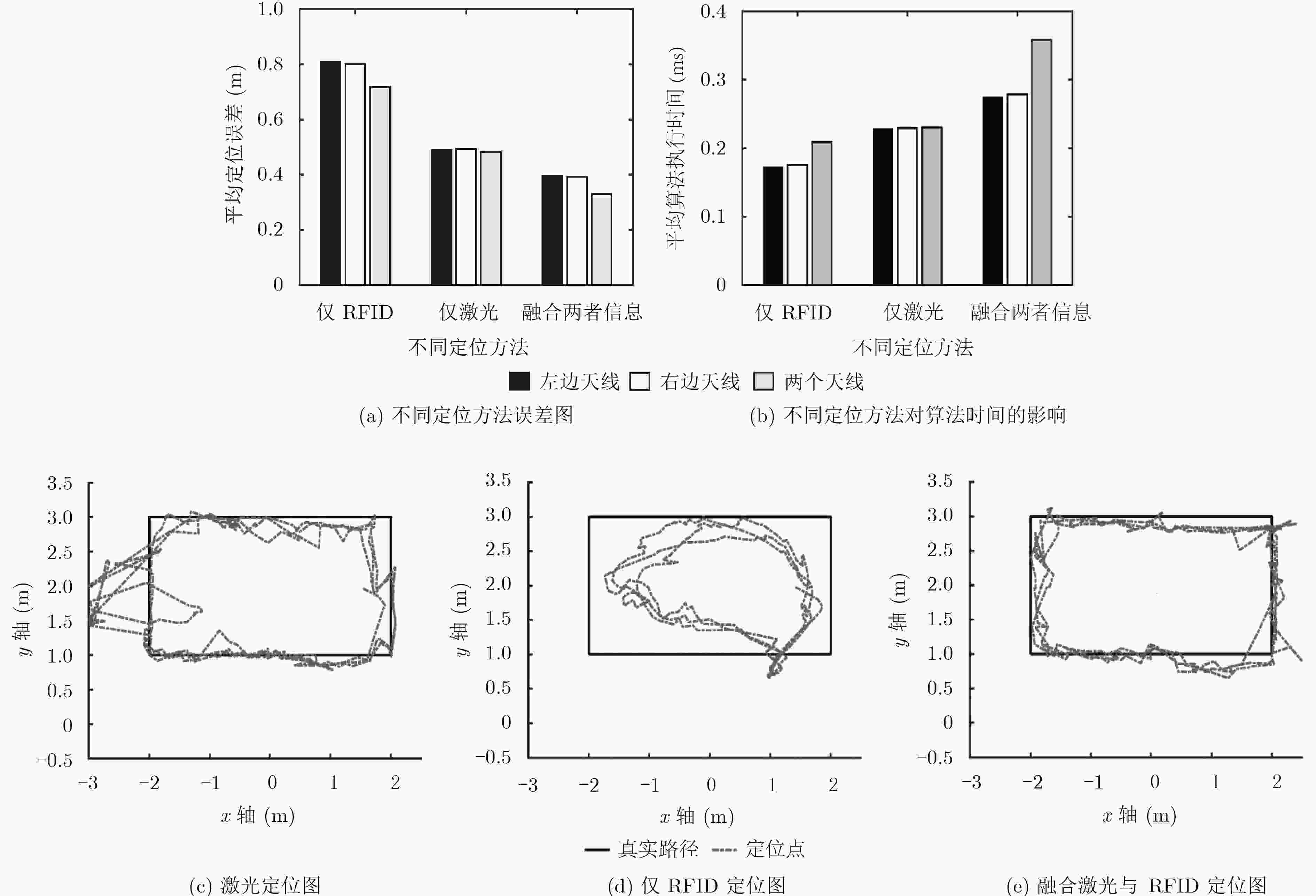
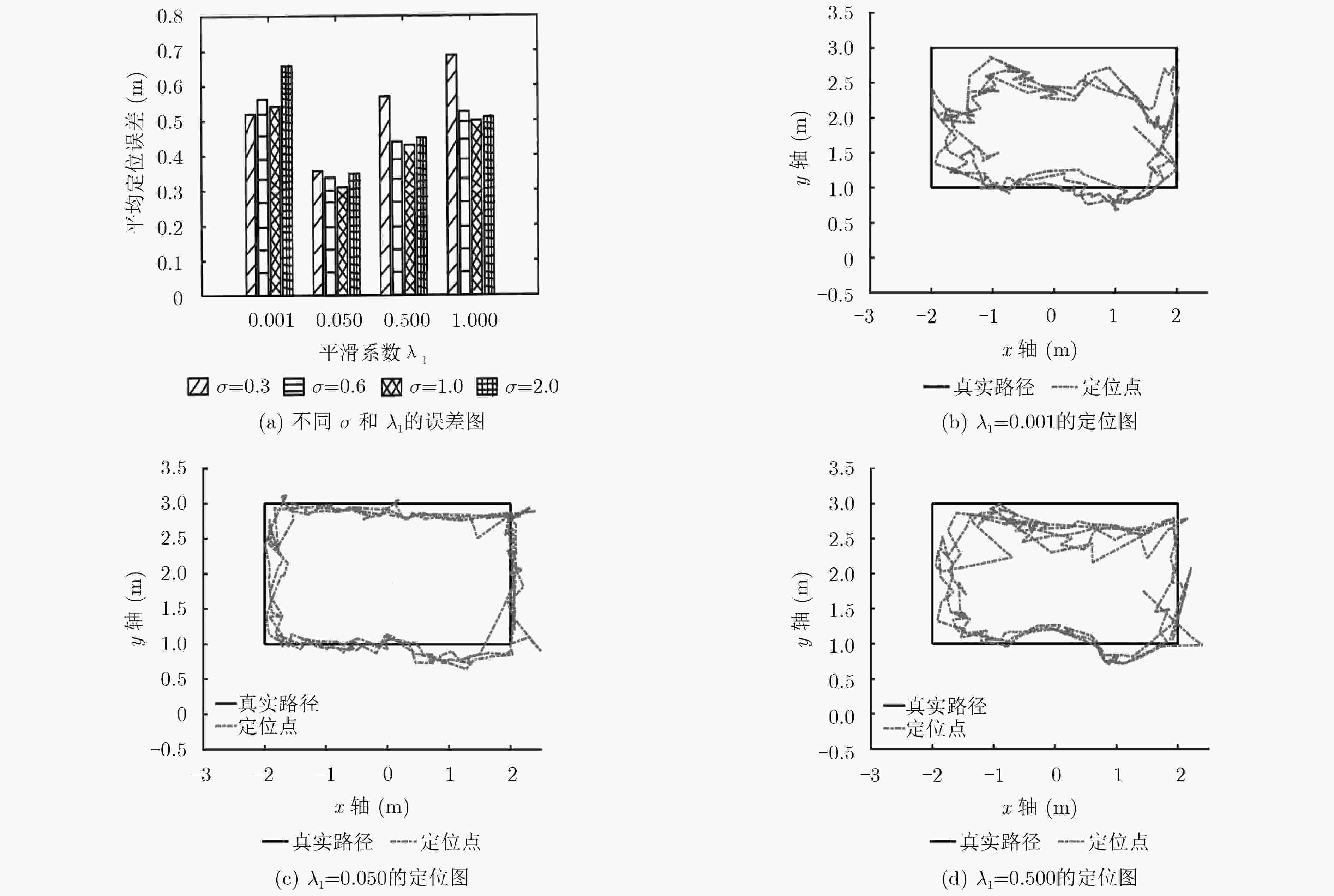
摘要: 低成本、可靠的动态目标定位方法成为目前研究的热点。传统的激光定位或视觉定位方法需要解决识别奇异性和环境遮挡等问题,射频识别(RFID)通过无线射频信号对特定目标进行识别,因此被广泛用于动态目标的定位。该文提出一种融合激光信息与RFID信息对动态目标快速定位的方法。该方法利用粒子滤波器融合RFID信号强度、相位信息和激光数据。首先使用预先训练的信号强度模型将信号强度融入粒子滤波器;然后利用激光聚类后的数据估算运动目标的速度,与RFID相位差估算出的运动目标速度进行匹配;最后利用匹配成功的激光数据对粒子进一步约束。在SCITOS服务机器人上验证了算法的可行性,结果表明,与激光和信号强度的定位方法相比,该方法的定位精度得到了明显提高。
-
关键词:
- RSSI信号强度模型 /
- 射频识别相位 /
- 激光聚类 /
- 速度匹配 /
- 粒子滤波
Abstract: Recent researches show great interests in localizing dynamic objects through cost-effective technologies. Laser or visual-based approaches have to solve the singularity and occlusion problem from the environment. Radio Frequency IDentification (RFID) is used as a preferred technology to address these issues, due to the unique identification and the communication without line of sight. In this paper, an innovative method is proposed to localize precisely a dynamic object equipped with an RFID tag by fusing laser information RFID information. A particle filter is used to fuse RFID signal strength, phase information, and laser ranging data. Particularly, a pre-trained signal strength-based model is used to incorporate the signal strength information. Then, the laser ranging data is divided into different clusters and the velocities of these clusters are compared with the RFID phase velocity. Matching results of both velocities are used to confine the locations of the particles during the update stage of the particle filtering. The proposed approach is verified by several experiments on a SCITOS service robot and results show that the proposed approach provides better localization accuracy when compared with laser-based approach and the signal strength-based approach. -
表 2 不同N与K对实验误差的影响 (m)
N K 1 5 8 12 100 20 0.399 0.379 0.365 0.365 0.367 50 0.363 0.342 0.336 0.336 0.338 100 0.349 0.337 0.322 0.324 0.323 500 0.342 0.335 0.320 0.325 0.326 表 1 不同粒子数N对算法执行时间和定位精度的影响
粒子个数(N) 算法执行时间(ms) 平均定位误差(m) 20 0.145 0.365 50 0.284 0.336 100 0.352 0.322 500 0.856 0.320 表 3 不同dg与ds对定位精度的影响(m)
${d_g}$ ${d_s}$ 0.05 0.20 1.00 2.00 0.05 0.580 0.598 0.634 0.363 0.20 0.364 0.320 0.371 0.431 1.00 0.578 0.556 0.582 0.622 2.00 0.732 0.695 0.714 0.744 表 4 不同dp与Rmax对定位精度的影响(m)
${R_{\max }}$ ${d_p}$ 0.05 0.10 0.20 0.50 0.20 0.613 0.601 0.648 0.884 0.60 0.323 0.320 0.361 0.661 1.00 0.369 0.366 0.422 0.702 2.00 0.409 0.402 0.444 0.744 -
WANT R. An introduction to RFID technology[J]. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 2006, 5(1): 25–33 doi: 10.1109/MPRV.2006.2 YANG Zhixin, ZHANG Pengbo, and CHEN Lei. RFID-enabled indoor positioning method for a real-time manufacturing execution system using OS-ELM[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 174(PA): 121–133. PRINSLOO J and MALEKIAN R. Accurate vehicle location system using RFID, an Internet of Things approach[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(6): 1–24 doi: 10.3390/s16060825 HAHNEL D, BURGARD W, FOX D, et al. Mapping and localization with RFID technology[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, Australia, 2004: 1015–1020. VORST P and ZELL A. Semi-autonomous learning of an RFID sensor model for mobile robot self-localization[C]. European Robotics Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 2008: 273–282. JOHO D, PlLAGEMANN C, and BURGARD W. Modeling RFID signal strength and tag detection for localization and mapping[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 2009: 3160–3165. LIONEL M N, LIU Y H, YIU C L, et al. LANDMARC: Indoor location sensing using active RFID[J]. ACM Wireless Networks, 2004, 10(6): 701–710 doi: 10.1023/B:WINE.0000044029.06344 YANG Lei, GUO Yi, LIU Tianci, et al. Perceiving the slightest tag motion beyond localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2015, 14(11): 2363–2375 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2393859 YANG Lei, CHEN Yekui, LI Xiangyang, et al. Tagoram: Real-time tracking of mobile RFID tags to high precision using COTS devices[C]. Mobile Computing and Networking, New York, USA, 2014: 237–248. LIU Ran, HUSKIC G, and ZELL A. Dynamic objects tracking with a mobile robot using passive UHF RFID tags[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, USA, 2014: 4247–4252. LIU Ran, HUSKIC G, and ZELL A. On tracking dynamic objects with long range passive UHF RFID using a mobile robot[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015, 2015(P1): 1–12 doi: 10.1155/2015/781380 LIU Ran, YUEN C, DO T N, et al. Indoor positioning using similarity-based sequence and dead reckoning without training[C]. IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, Sapporo, Japan, 2017: 1–5. 李军怀, 贾金朋, 王怀军, 等. 基于信号强度差的RFID室内定位[J]. 计算机科学, 2015, 42(11): 154–157 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2015.11.032LI Junhuai, JIA Jinpeng, WANG Huaijun, et al. Indoor positioning of RFID based on signal strength difference[J]. Computer Science, 2015, 42(11): 154–157 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2015.11.032 黄保虎, 刘冉, 张华, 等. 基于不同重采样算法的RFID指纹定位[J]. 计算机应用, 2013, 33(2): 595–599 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1087.2013.00595HUANG Baohu, LIU Ran, ZHANG Hua, et al. RFID fingerprinting based on different resampling algorithms[J].Computer Application, 2013, 33(2): 595–599 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1087.2013.00595 李珣, 刘丽, 洪良, 等. 移动机器人室内无源RFID定位方法及实现[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2017, 53(16): 230–236 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1608-0434LI Xun, LIU Li, HONG Liang, et al. Indoor passive RFID location method for mobile robot and its implementation[J]. Computer Engineering and Application, 2017, 53(16): 230–236 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1608-0434 黄如林, 梁华为, 陈佳佳, 等. 基于激光雷达的无人驾驶汽车动态障碍物检测、跟踪与识别方法[J]. 机器人, 2016, 38(4): 437–443 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.2016.0437HUANG Rulin, LIANG Huawei, CHEN Jiajia, et al. Method of tracking and recognition of laser radar unmanned vehicle dynamic obstacle detection[J]. Robot, 2016, 38(4): 437–443 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.2016.0437 李昀泽. 基于激光雷达的室内机器人SLAM研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华南理工大学, 2016.LI Yunze. Research on indoor robot SLAM based on laser radar[D]. [Master dissereation], South China University of Technology, 2016. PRZYBYLA M. Detection and tracking of 2D geometric obstacles from LRF data[C]. IEEE International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control, Bukowy Dworek, Poland, 2017: 135–141. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
