Estimation of Unknown Line Spectrum under Colored Noise via Sparse Reconstruction
-
摘要: 针对色噪声背景下的未知线谱信号估计问题,该文提出一种基于分子频带处理的稀疏重构类线谱估计方法。首先,利用多速率余弦调制滤波器组对观测信号进行子带分解,得到功率谱相对平坦的子带信号。之后,在每个子带信号上,利用基于迭代最小化的稀疏学习方法进行线谱估计,并将各子带上的线谱估计结果进行频域综合滤波以及门限判决等处理。最终得到色噪声背景下的线谱估计结果。理论推导及仿真实验表明所提方法在色噪声背景下具有较好的线谱估计性能。其能够有效地去除色噪声背景,同时保留稀疏重构类线谱估计方法所具有的高频率分辨力等优点。Abstract: To solve the problem of the line spectrum estimation under colored noise background, a subband line spectrum estimation method using sparse reconstruction is proposed. Firstly, the input signal is divided into several subbands by a multi-rate cosine modulated filter bank. The subband signal has the flatter power spectrum. The sparse learning via iterative minimization method is utilized on each subband to estimate the line spectrum signal. Then, the results of line spectrum estimation on each subband are processed by frequency domain synthesis filtering and threshold decision. Finally, the line spectrum signal under colored noise background is identified. Theoretical derivation and simulation experiments show that the proposed method has better line spectrum estimation performance under colored noise background. The colored noise background can be removed, and the advantage of high frequency resolution of sparse reconstruction method is retained.
-
表 1 SLIM算法计算步骤
初始化 $\hat s_k^{(0)}{\rm{ = }}\displaystyle\frac{{{{{a}}^{\rm{H}}}({\omega _k}){{X}}}}{{\left\| {{{a}}({\omega _k})} \right\|_2^2}}, (k = 0,1, ·\!·\!· ,K - 1), \ {\hat \eta ^{(0)}} = \frac{1}{{\gamma N}}\left\| {{{X}} - {{A}}{{{\hat{ S}}}^{(0)}}} \right\|_2^2, \ \gamma {为常数}$ (1)计算信号功率 ${{P}}$ ${{{P}}^{(i)}}{\rm{ = [}}p_0^{(i)}\;p_1^{(i)}\; ·\!·\!· \;p_{N - 1}^{(i)}{\rm{]}}, \ p_k^{(i)} = {\left| {s_k^{(i)}} \right|^{2 - q}}{\rm{,}}\;(k = 0{\rm{,}}\;1{\rm{,}}\; ·\!·\!·\! {\rm{,}}\ K - 1)$ (2)计算信号幅度 ${\hat{ S}}$ ${{\hat{ S}}^{(i + 1)}} = {\rm{diag}}\left({{{P}}^{(i)}}\right){{{A}}^{\rm{H}}}{\left( {{{A}}{\rm{diag}}\left({{{P}}^{(i)}}\right){{{A}}^{\rm{H}}} + {{\hat \eta }^{(i)}}{{I}}} \right)^{ - 1}}{{X}}$ (3)计算噪声功率 $\hat \eta $ $\;{\hat \eta ^{(i + 1)}} = \frac{1}{N}\left\| {{{X}} - {{A}}{{{\hat{ S}}}^{(i + 1)}}} \right\|_2^2$ 注:重复迭代步骤(1)—步骤(3)直至 ${\hat{ S}}$收敛或达到预定迭代次数(i表示迭代次数) -
WITTEKIND D K. A simple model for the underwater noise source level of ships[J]. Journal of Ship Production&Design, 2014, 30(1): 7–14 doi: 10.5957/JSPD.30.1.120052 JANSEN E and JONG C D. Experimental assessment of underwater acoustic source levels of different ship types[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2017, 42(2): 1–10 doi: 10.1109/JOE.2016.2644123 ROSENLICHT M. Introduction to Spectral Analysis[M]. New York: Dover Publications, 2005: 315–359. 吴国清, 李靖, 陈耀明, 等. 舰船噪声识别(Ⅰ)—总体框架、线谱分析和提取[J]. 声学学报, 1998, 23(5): 394–400 doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.1998.05.002WU Guoqing, LI Jing, CHEN Yaoming, et al. Ship radiated-noise recognition(I) the overall frameword, analysis and extraction of line-spectrum[J]. Acta Acustica, 1998, 23(5): 394–400 doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.1998.05.002 CHEN Zhaofu, LI Jian, TAN Xing, et al. On probing waveforms and adaptive receivers for active sonar[J]. OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE,Seattle USA, 2010: 1–10 doi: 10.1109/OCEANS.2010.5663834 STOICA P, BABU P, and LI Jian. New method of sparse parameter estimation in separable models and its use for spectral analysis of irregularly sampled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(1): 35–47 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2086452 TAN Xing, ROBERTS W, LI Jian, et al. Sparse learning via iterative minimization with application to MIMO radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(3): 1088–1101 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2096218 FLORESCU A and CIOCHINA S. Refining accuracy of the spectral lines estimation by a sparsity based approach[C]. Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Communications, Bucharest, 2012: 47–50. 沈志博, 董春曦, 黄龙, 等. 一种基于稀疏分解的窄带信号频率估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(4): 907–912 doi: 10.11999/JEIT140878SHEN Zhibo, DONG Chunxi, HUANG Long, et al. A frequency estimation algorithm of narrow-band signal based on sparse decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2015, 37(4): 907–912 doi: 10.11999/JEIT140878 YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. Enhancing sparsity and resolution via reweighted atomic norm minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(4): 995–1006 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2493987 TKACENKO A and VAIDYANATHAN P P. The role of filter banks in sinusoidal frequency estimation[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2001, 338(5): 517–547 doi: 10.1016/S0016-0032(01)00025-4 UDREA R M, VIZIREANU N, CIOCHINA S, et al. Nonlinear spectral subtraction method for colored noise reduction using multi-band bark scale[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 88(5): 1299–1303 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2007.11.023 GORDANA J D. Multirate Systems: Design and Applications[M]. Hershey, USA: Idea Group Inc., 2002: 3385–3388. LIU Hongying, YI Caixia, and YANG Zhiming. Design perfect reconstruction cosine-modulated filter banks via quadratically constrained quadratic programming and least squares optimization[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 141(3): 199–203 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.06.009 PREMA C S and DASGUPTA K S. An iterative design with variable step prototype filter for cosine modulated filter bank[J]. Radioengineering, 2016, 25(1): 156–160 doi: 10.13164/re.2016.0156 蒋俊正, 江庆, 欧阳缮. 一种设计近似完全重构非均匀余弦调制滤波器组的新算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(9): 2385–2390 doi: 10.11999/JEIT151260JIANG Junzheng, JIANG Qing, and OUYANG Shan. Novel method for designing near-perfect-reconstruction nonuniform cosine modulated filter banks[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(9): 2385–2390 doi: 10.11999/JEIT151260 李忠佳, 葛临东. 基于DCT-IV的余弦调制信道化技术[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2009, 10(4): 498–501 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2009.04.017LI Zhongjia and GE Lindong. Cosine modulated channelization based on DCT-IV[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2009, 10(4): 498–501 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2009.04.017 -





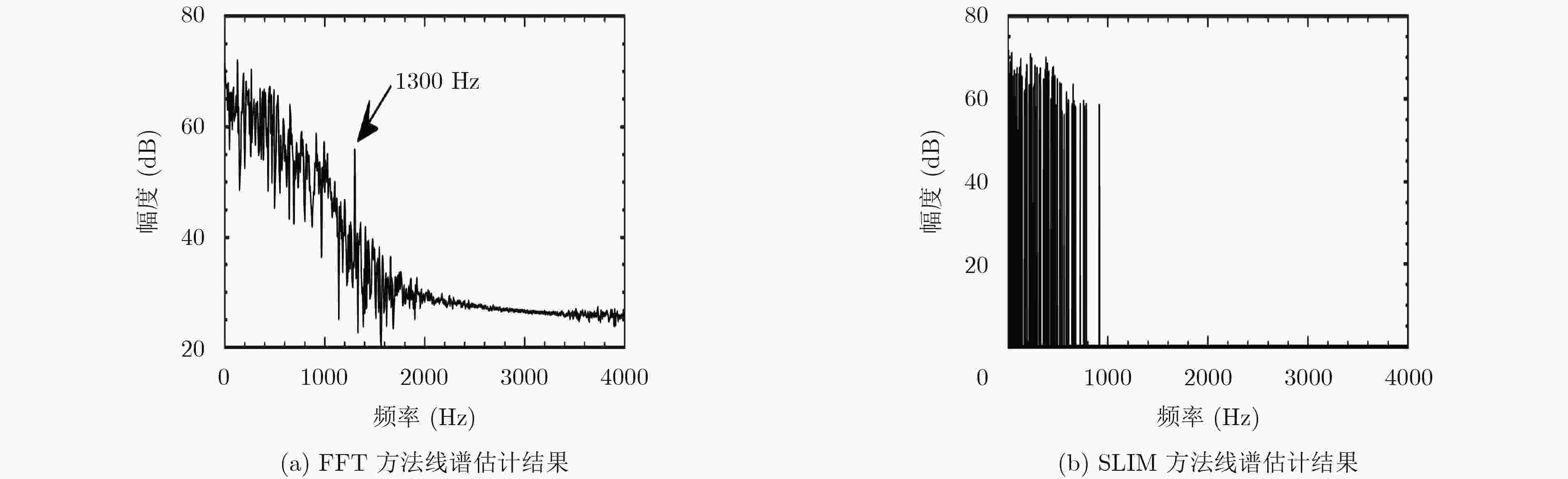
 下载:
下载:
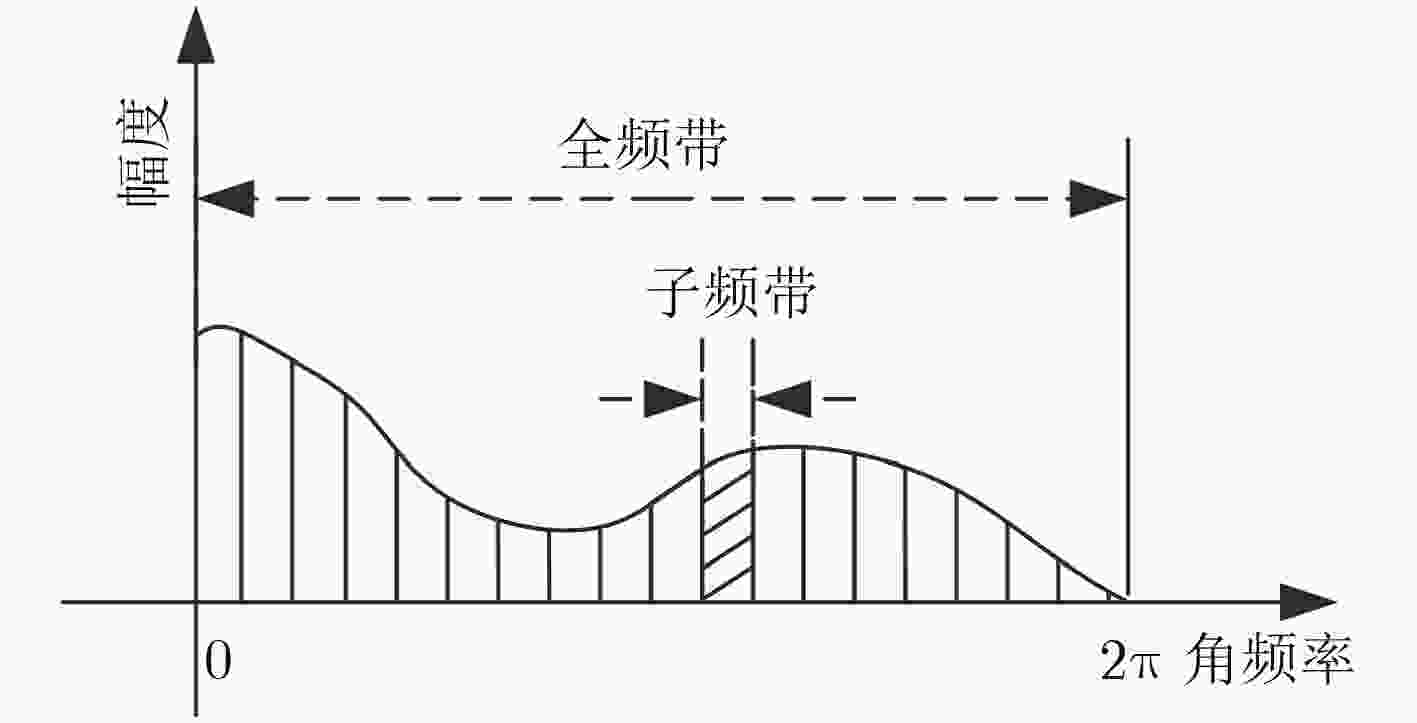
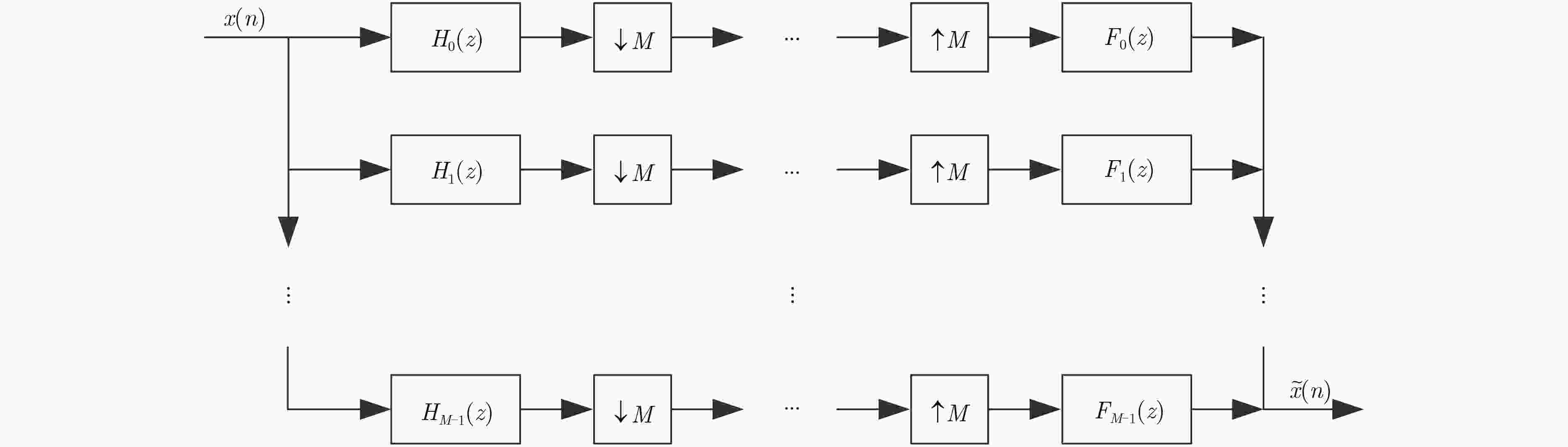
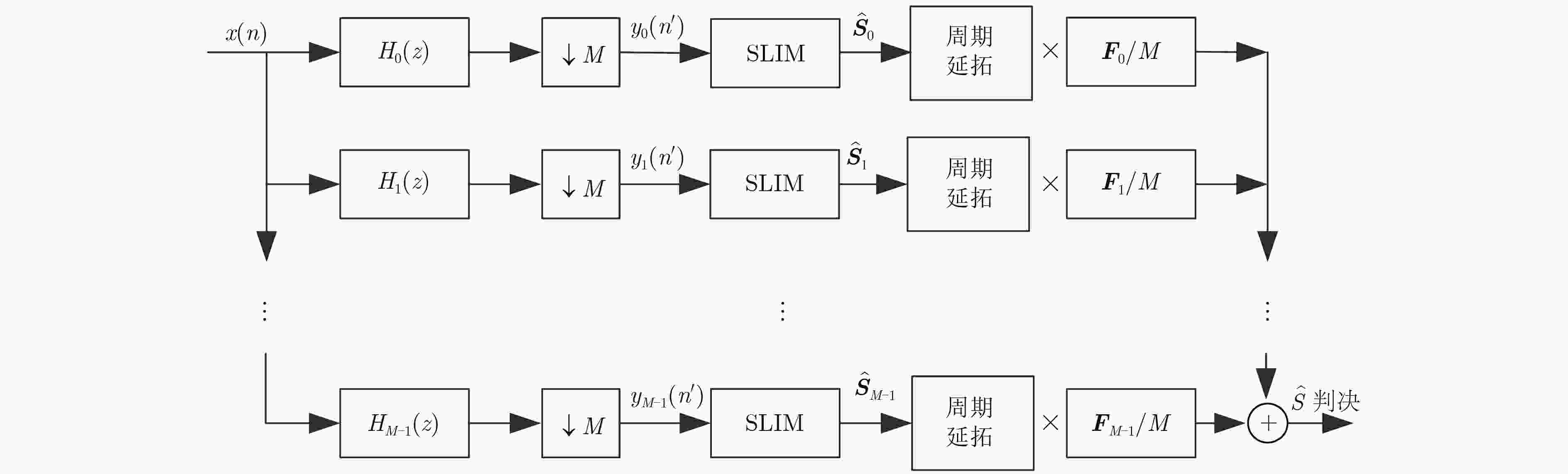
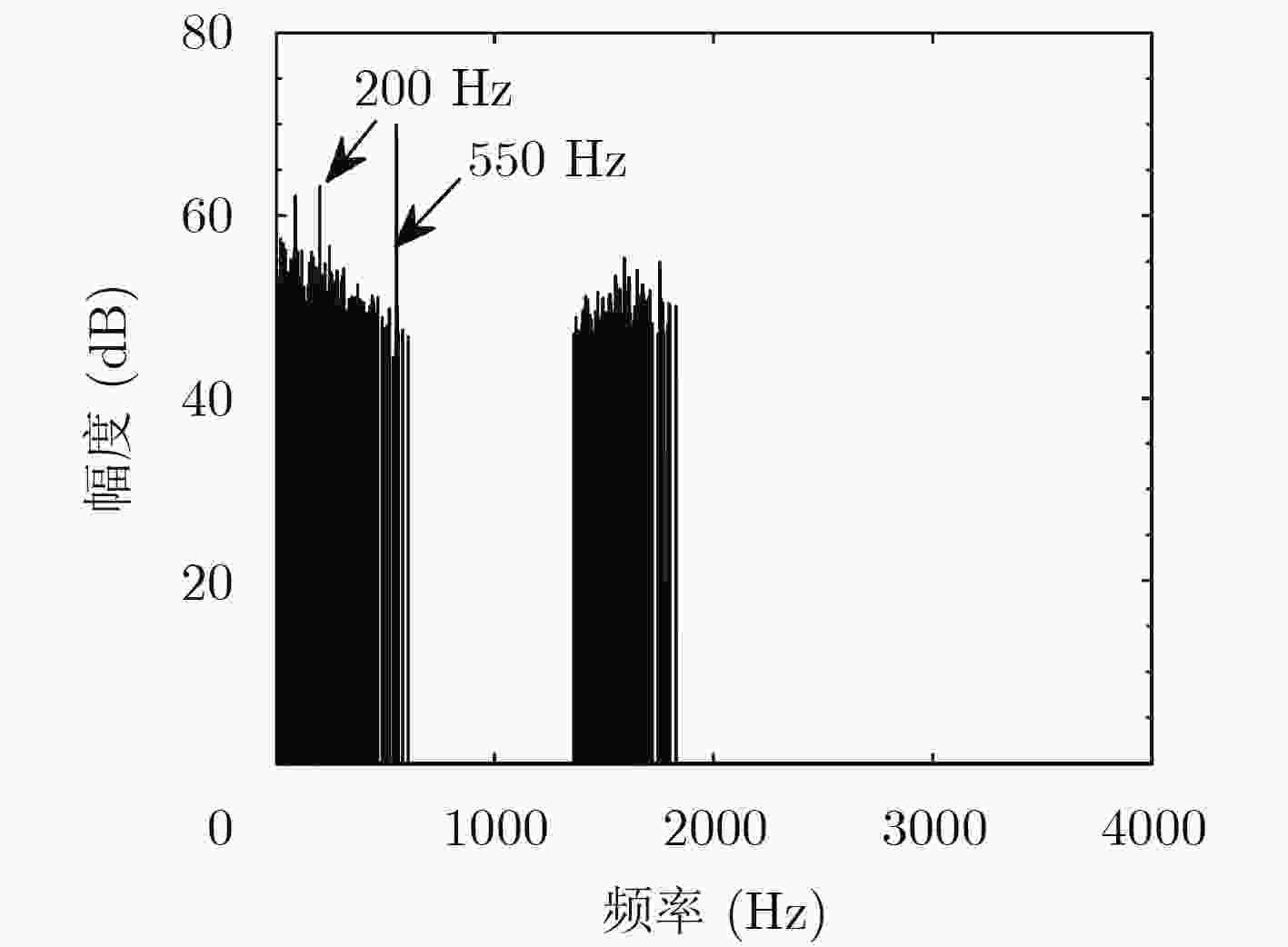
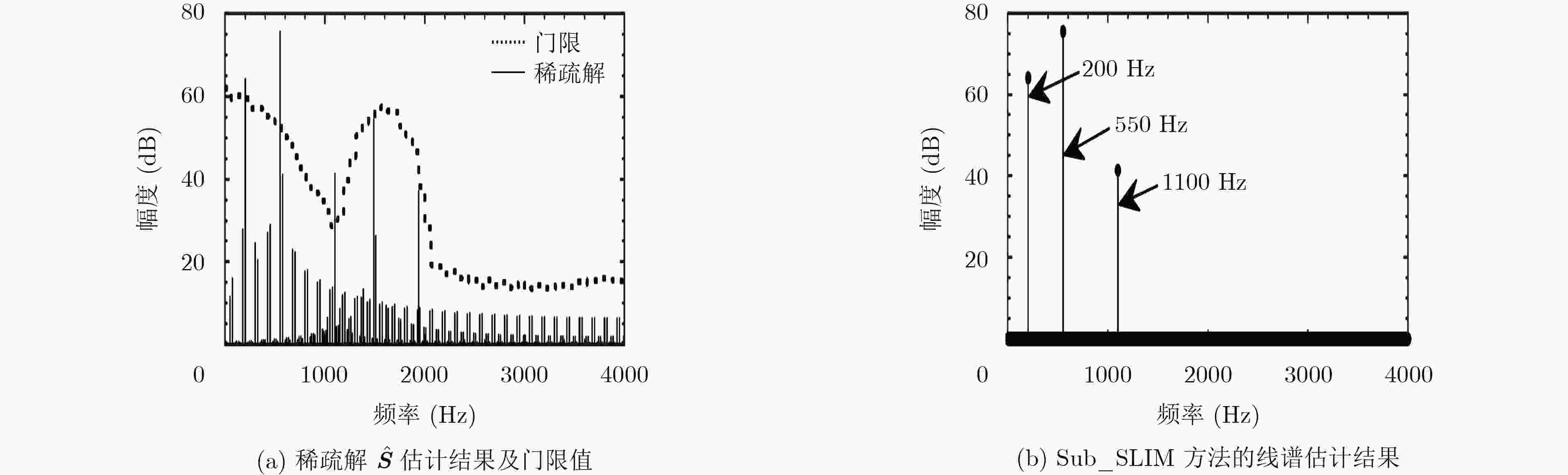
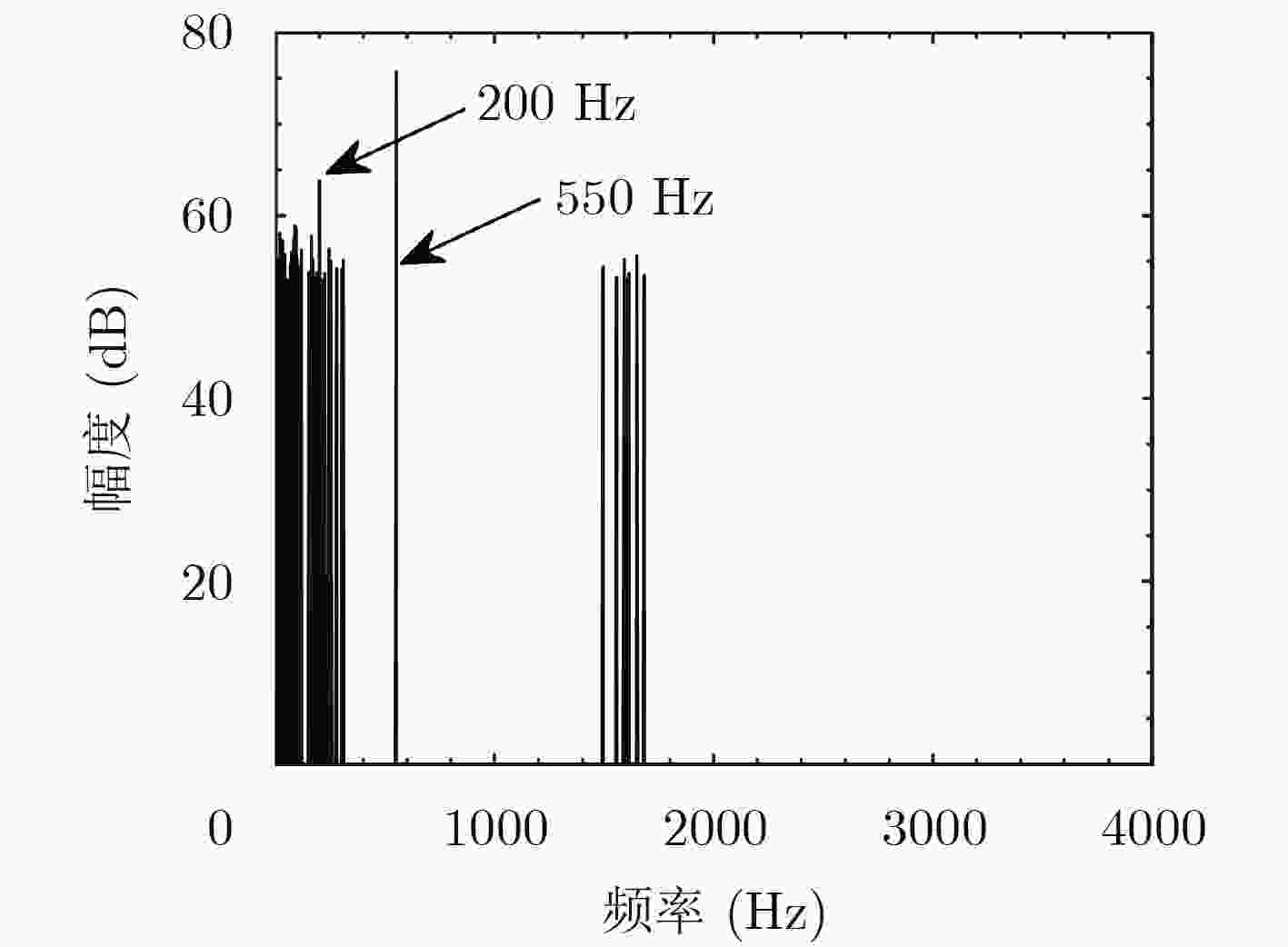
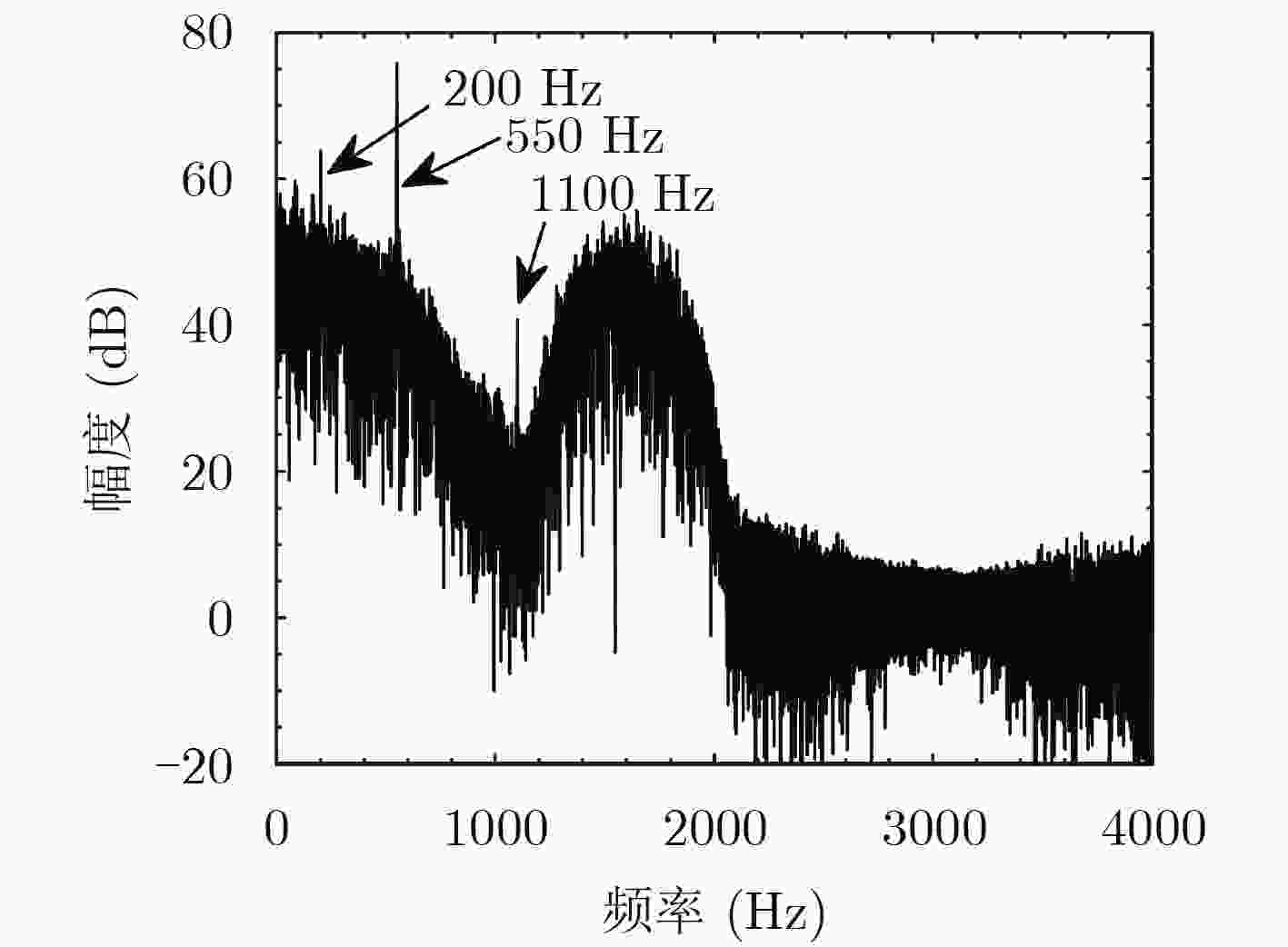
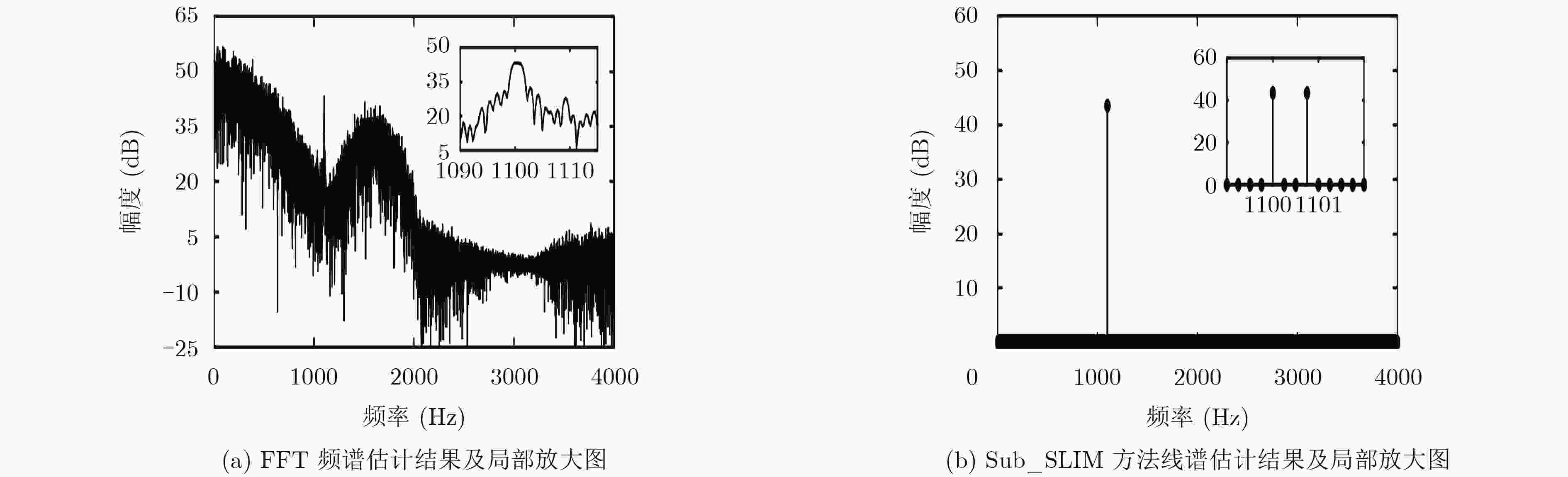
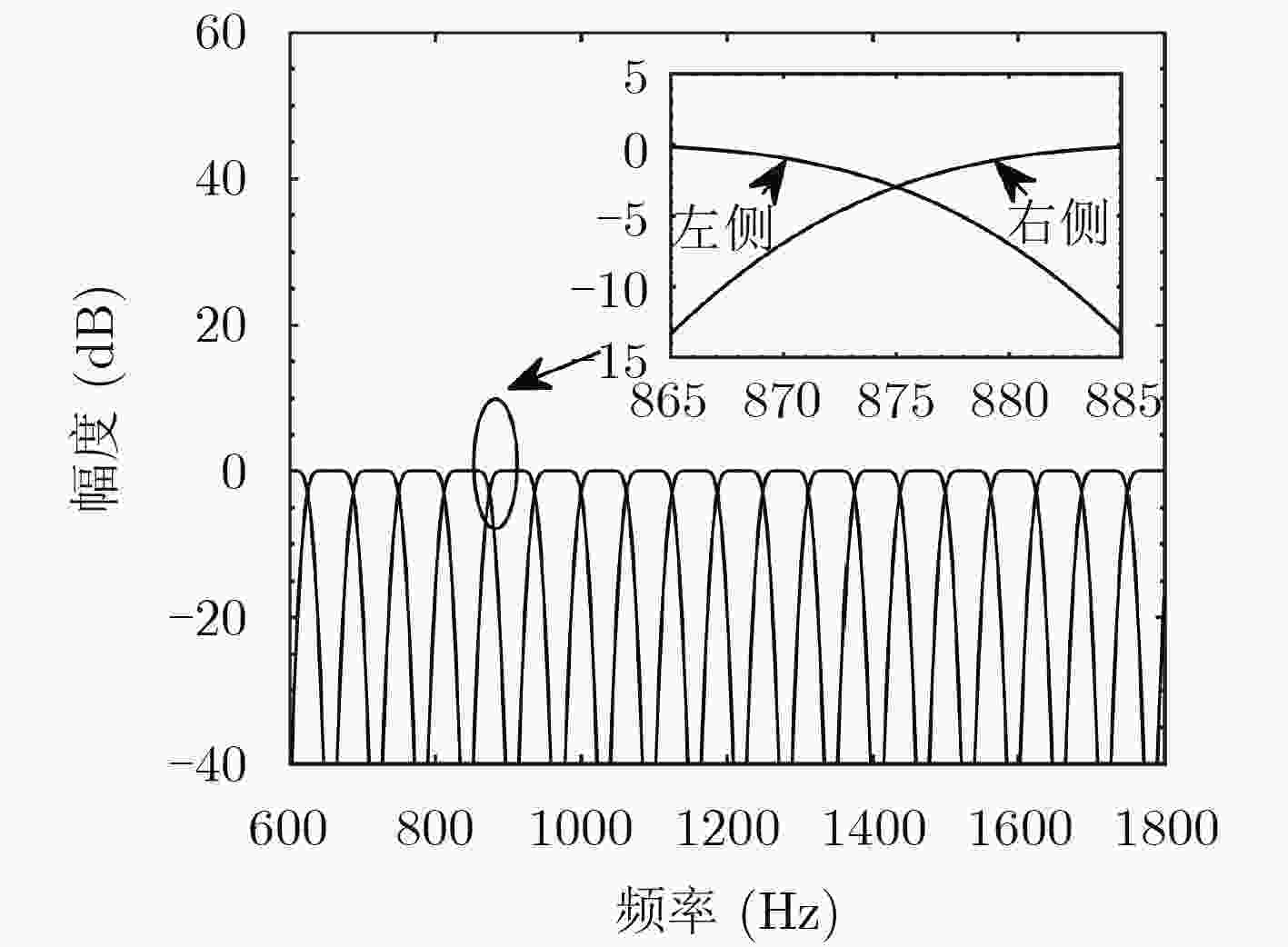
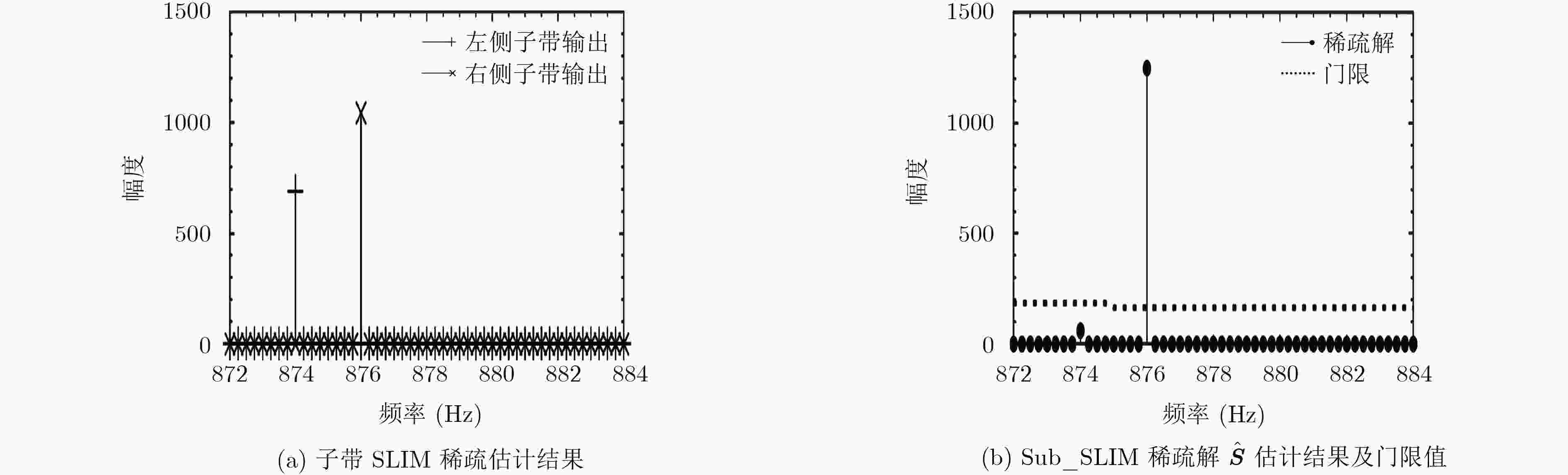


 下载:
下载:
